Abstract
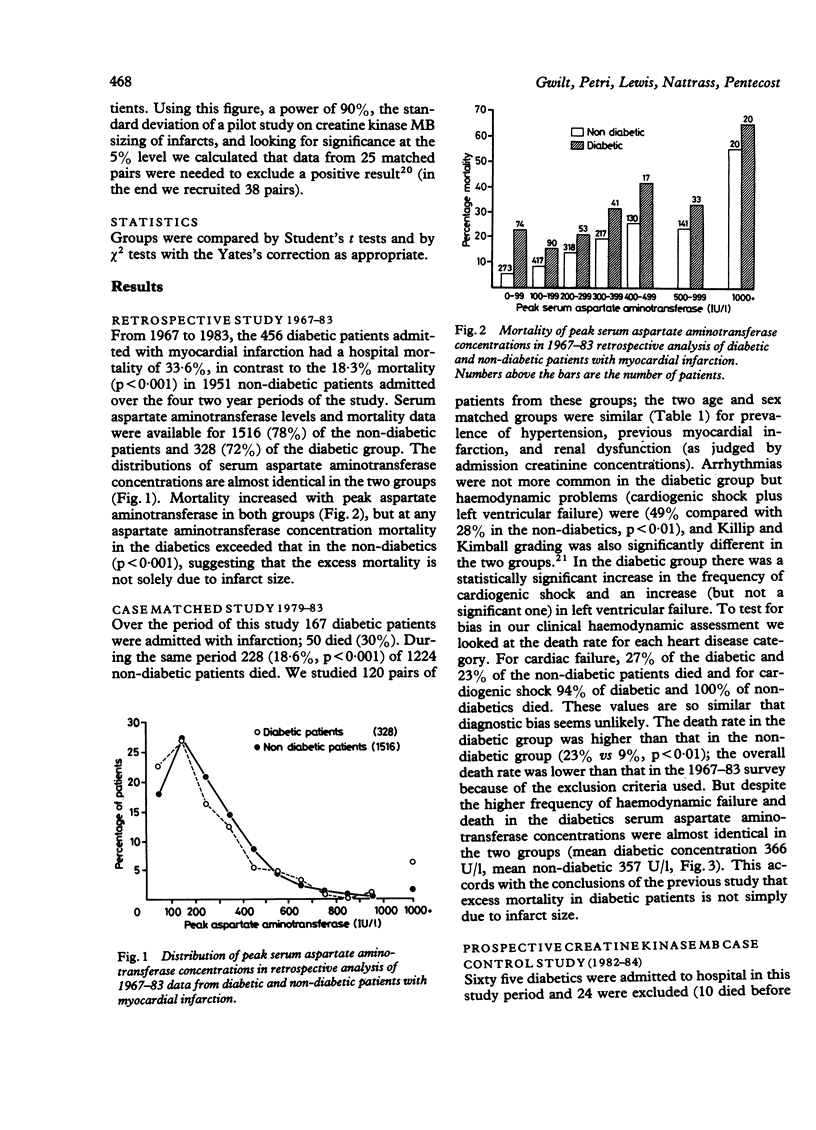
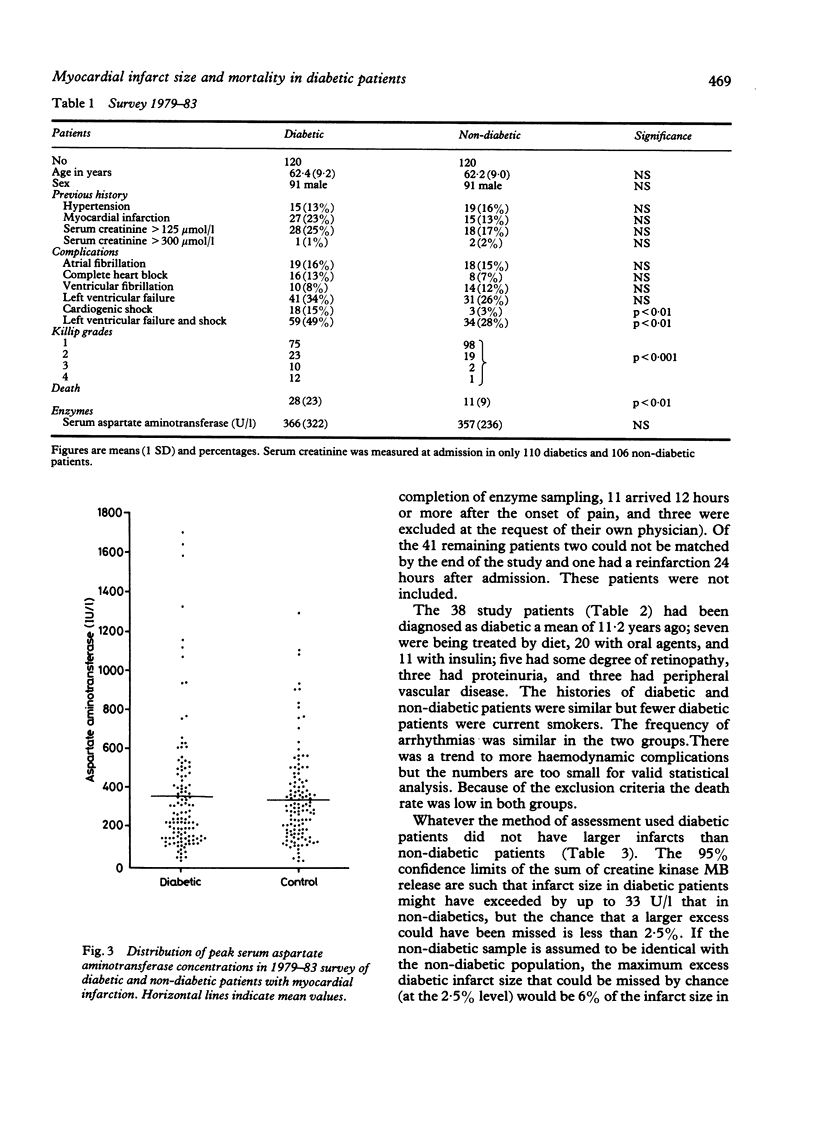
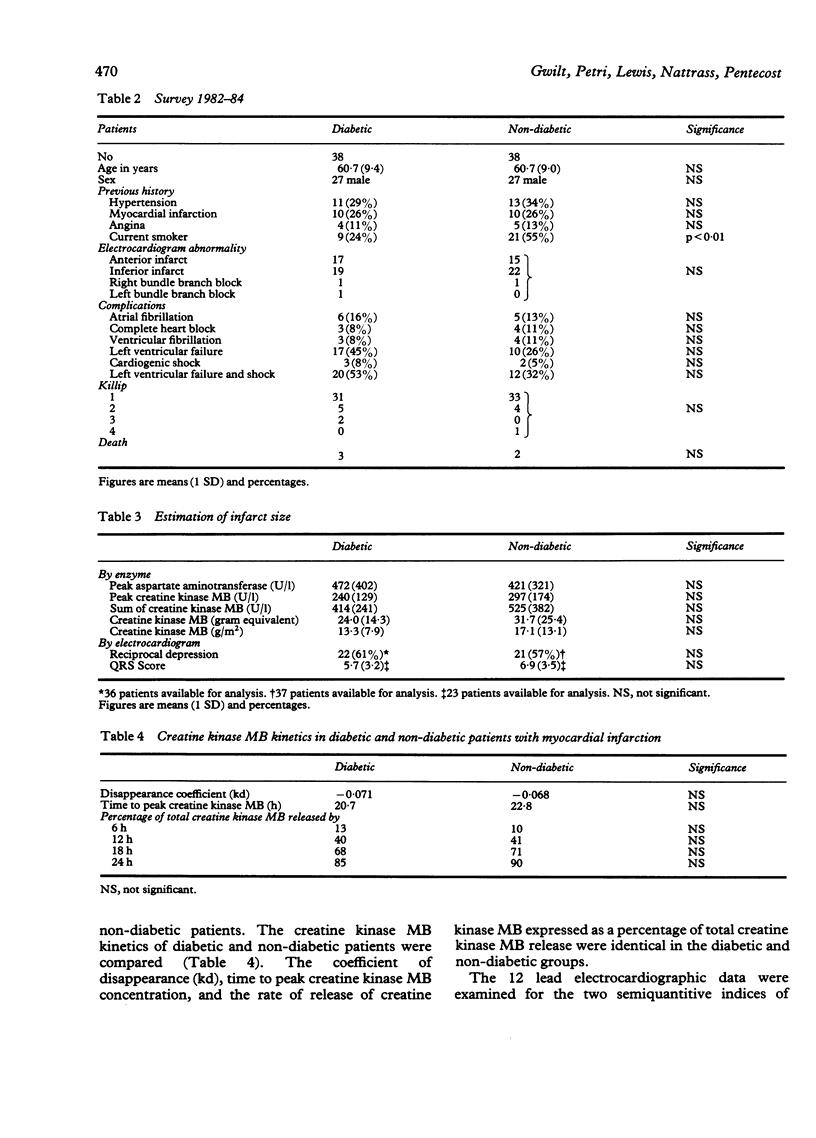
The mortality rate from myocardial infarction is disproportionately high in diabetic patients. One explanation for this may be that diabetic patients incur more extensive myocardial necrosis. This possibility was examined in a three part study. Firstly, peak serum aspartate aminotransferase concentrations of all diabetic and non-diabetic patients admitted with myocardial infarction over a 16 year period were compared retrospectively. Secondly, peak aspartate aminotransferase concentrations in a series of diabetic patients and controls matched by age and sex were examined retrospectively. Thirdly, creatine kinase MB release and electrocardiographic measures of infarct size were investigated prospectively in a case/control study. Although cardiac failure and death were more common in the diabetic groups, there were no significant differences in estimates of infarct size between diabetic and non-diabetic patients in any of the studies. Therefore, the high case fatality rate amongst diabetic patients is not caused by increased myocardial damage. Presumably survival is prejudiced by factors operating before the infarction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison S. P., Chamberlain M. J., Hinton P. Intravenous glucose tolerance, insulin, glucose, and free fatty acid levels after myocardial infarction. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 27;4(5686):776–778. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5686.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman D. G. Statistics and ethics in medical research: III How large a sample? Br Med J. 1980 Nov 15;281(6251):1336–1338. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6251.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J. A., Holder D. A., Tanser P., Missirlis E. Intravenous hyaluronidase therapy for myocardial infarction in man: double-blind trial to assess infarct size limitation. Circulation. 1982 Apr;65(4):764–771. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.4.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crall F. V., Jr, Roberts W. C. The extramural and intramural coronary arteries in juvenile diabetes mellitus: analysis of nine necropsy patients aged 19 to 38 years with onset of diabetes before age 15 years. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer V. W., Barner H. B., Leskiw M. L. Capillary basal laminar thichness in diabetic human myocardium. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):713–719. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint E. J., De Giovanni J., Cadigan P. J., Lamb P., Pentecost B. L. Effect of GL enzyme (a highly purified form of hyaluronidase) on mortality after myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1982 Apr 17;1(8277):871–874. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Keen H., Jarrett R. J., Omer T., Meade T. W., Chakrabarti R., North W. R., Stirling Y. Haemostatic variables associated with diabetes and its complications. Br Med J. 1979 Oct 20;2(6196):964–966. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6196.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to degree of glycaemia: the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. J., McNamara P. M., Gordon T., Kannel W. B. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman J. S., Saltups A. Precordial ST segment depression in patients with inferior myocardial infarction: clinical implications. Br Heart J. 1982 Dec;48(6):560–565. doi: 10.1136/hrt.48.6.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwilt D. J., Petri M., Lamb P., Nattrass M., Pentecost B. L. Effect of intravenous insulin infusion on mortality among diabetic patients after myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1984 Jun;51(6):626–630. doi: 10.1136/hrt.51.6.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husband D. J., Alberti K. G., Julian D. G. "Stress" hyperglycaemia during acute myocardial infarction: an indicator of pre-existing diabetes? Lancet. 1983 Jul 23;2(8343):179–181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe A. S., Spadaro J. J., Schechtman K., Roberts R., Geltman E. M., Sobel B. E. Increased congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction of modest extent in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am Heart J. 1984 Jul;108(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibe O., Nilsson N. J. Observations on the diagnostic and prognostic value of some enzyme tests in myocardial infarction. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Nov;182(5):597–610. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb10886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killip T., 3rd, Kimball J. T. Treatment of myocardial infarction in a coronary care unit. A two year experience with 250 patients. Am J Cardiol. 1967 Oct;20(4):457–464. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(67)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke A. J. Alterations of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the acutely ischemic heart. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1981 Mar-Apr;23(5):321–336. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(81)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan D. E. Plasma protein changes, blood viscosity, and diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetes. 1976;25(2 Suppl):858–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris R. M., Whitlock R. M., Barratt-Boyes C., Small C. W. Clinical measurement of myocardial infarct size. Modification of a method for the estimation of total creatine phosphokinase release after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1975 Apr;51(4):614–620. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.51.4.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opie L. H., Tansey M. J., Kennelly B. M. The heart in diabetes mellitus. Part II. Acute myocardial infarction and diabetes. S Afr Med J. 1979 Aug 18;56(7):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opie L. H., Tansey M., Kennelly B. M. Proposed metabolic vicious circle in patients with large myocardial infarcts and high plasma-free-fatty-acid concentrations. Lancet. 1977 Oct 29;2(8044):890–892. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90830-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald G. A., Corcoran S., Yudkin J. S. Prevalence and risks of hyperglycaemia and undiagnosed diabetes in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1984 Jun 9;1(8389):1264–1267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmeri S. T., Harrison D. G., Cobb F. R., Morris K. G., Harrell F. E., Ideker R. E., Selvester R. H., Wagner G. S. A QRS scoring system for assessing left ventricular function after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jan 7;306(1):4–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198201073060102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pell S., D'Alonzo C. A. Factors associated with long-term survival of diabetics. JAMA. 1970 Dec 7;214(10):1833–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shell W. E., Kjekshus J. K., Sobel B. E. Quantitative assessment of the extent of myocardial infarction in the conscious dog by means of analysis of serial changes in serum creatine phosphokinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2614–2625. doi: 10.1172/JCI106762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel B. E., Bresnahan G. F., Shell W. E., Yoder R. D. Estimation of infarct size in man and its relation to prognosis. Circulation. 1972 Oct;46(4):640–648. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.46.4.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler N. G., Pentecost B. L., Bennett M. A., FitzGerald M. G., Lamb P., Malins J. M. Coronary care for myocardial infarction in diabetics. Lancet. 1974 Mar 23;1(7856):475–477. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92785-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vague P., Juhan I. Red cell deformability, platelet aggregation, and insulin action. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):88–91. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


