Abstract
Background:
Not much is known about the role of gastric microbiota except for Helicobacter pylori in human health and disease. In this study, we aimed to detect human gastric microbiota in both gastric mucosa and gastric juice by barcoded 454-pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and to compare the results from mucosa and juice.
Methods:
Gastric biopsies and stomach juices were collected from 4 subjects who underwent standard endoscopy at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. Gastric microbiota of antral mucosa, corpus mucosa samples, and gastric fluids were analyzed by barcoded 454-pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. The analysis focused on bacteria, such as H. pylori and nitrosating or nitrate-reducing bacteria.
Results:
Gastric fluid samples showed higher diversity compared to that of gastric mucosa samples. The mean of operational taxonomic units was higher in gastric fluid than in gastric mucosa. The samples of gastric fluid and gastric mucosa showed different composition of phyla. The composition of H. pylori and Proteobacteria was higher in mucosa samples compared to gastric fluid samples (H. pylori, 66.5% vs. 3.3%, P = 0.033; Proteobacteria, 75.4% vs. 26.3%, P = 0.041), while Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Firmicutes were proportioned relatively less in mucosa samples than gastric fluid. However there was no significant difference. (Actinobacteria, 3.5% vs. 20.2%, P = 0.312; Bacteroidetes, 6.0% vs. 14.8%, P = 0.329; Firmicutes, 12.8% vs. 33.4%, P = 0.246).
Conclusions:
Even though these samples were small, gastric mucosa could be more effective than gastric fluid in the detection of meaningful gastric microbiota by pyrosequencing.
Keywords: Microbiota, Helicobacter pylori, Gastric mucosa, Gastric juice
INTRODUCTION
Human gut, colonized by complex communities of microorganisms, plays essential roles in digestion, absorption of nutrients,1 stimulation of intestinal epithelial regeneration,2 and immune reactions.3 Keeping these microbial communities in balance with host is important for health maintenance and disease prevention.4 Before the discovery of Helicobacter pylori, human stomach environment was considered to be sterile for its acidic gastric environment suppressing the microorganisms from the oral cavity. The detection of H. pylori made a critical change in the existing perspectives that stomach is a sterile organ. After that, more attention was brought to microbial ecosystem of the stomach, along with the development of culture-independent analysis methods such as next-generation sequencing.1,5,6
H. pylori infection is a risk factor for gastric cancer, which causes mucosal atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, and dysplasia.7 Bacteria other than H. pylori alone or simultaneously with H. pylori may also influence atrophic gastritis regulating inflammatory response or N-nitroso compounds (NOC) production.8,9 NOC can be produced from nitrite and secondary amines by nitrosating bacteria of stomach, which have nitrosating enzyme such as cytochrome cd1 nitrite reductase.10 The product of NOC has been suggested to increase the risk of cancers.9 With the development of uncultivated methods, studies focused on non-H. pylori microbiota in human stomach.11 We have conducted a research on an appropriate cutoff value for determining the colonization of H. pylori by the pyrosequencing. We further investigated gastric microbiota and the differences in microbiota according to H. pylori infection status in the presence or absence of gastric cancer using a pyrosequencing method.12,13 We assumed that gastric microbiota could be detected in gastric mucosa and gastric juice as well. However, bacteria recently swallowed through mouth and throat can influence stomach microbiota. Microbiota from oral cavity and esophagus can make it difficult to detect true pathogen in stomach. So we decided to get some information about gastric microbiota in both gastric mucosa and gastric juice. This study aimed to characterize the microbiota of gastric fluid compared with microbiota of gastric mucosa using a pyrosequencing method. This is a sub-group analysis of our previous study that evaluated the composition of human stomach microbiota according to the presence of stomach cancer and H. pylori.12
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Gastric and blood samples
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (B-1112/141-007). Gastric biopsies and fluid samples were collected from 4 subjects who underwent standard endoscopy to screen for premalignant or malignant gastric mucosal lesions or received endoscopy due to dyspepsia. Gastric mucosal (antrum and corpus) biopsies and blood samples were obtained from each patient during endoscopy from October 2008 to March 2013 at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. Ten biopsy specimens per subjects were obtained to perform H. pylori tests and pyrosequencing as our previous study.12,13 The biopsy specimens were assessed for the presence of H. pylori and for the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration, atrophic gastritis, and intestinal metaplasia (hematoxylin and eosin staining). Histological features of gastric mucosa were recorded as the updated Sydney scoring system (i.e., 0 = none, 1 = slight, 2 = moderate, 3 = marked).14 To avoid contamination, the endoscopes were washed and disinfected by immersing in a detergent solution containing 7% proteolytic enzymes and 2% glutaraldehyde. Sterilized gastroscopy forceps were used while gaining another biopsy from the same patient. The biopsies were stored at −80°C. In patients who had clear gastric fluid, the gastric fluid was gained through a catheter connected to 5 mL tube during endoscopy.
The positivity of H. pylori was confirmed by conventional tests for H. pylori infection: 1) Rapid urease test (Campylobacter-like organism test; Delta West, Bentley, WA, Australia), 2) Histologic examination (modified Giemsa staining), 3) Culture for H. pylori. Current H. pylori infection was positive from any of the former three tests. In order to distinguish if the infection is an existing one, the following two methods were used: Serum H. pylori immunoglobulin G (Genedia H. pylori ELISA; Green Cross Medical Science Co., Eumsung, Korea), and a history of H. pylori infection eradication treatment. If all the 5 tests were negative, we regarded the subject as H. pylori-negative. Using a Latex-enhanced Turbidimetric Immunoassay (Shima Laboratories, Tokyo, Japan), serum concentrations of pepsinogen I and II were evaluated, which are known to be associated with the severity of gastric atrophy.15
2. Barcoded 454-pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene
The mucosal and gastric fluid samples from 4 subjects were subjected to pyrosequencing. Total genomic DNA was separated using a commercial kit (iNtRON Biotechnology, Seongnam, Korea). PCR amplification was done by taking primers targeting the V1 to V3 regions of the 16S rRNA gene with extracted DNA. For bacterial amplification, barcoded primer of 9F (5’-CCTATCCCC-TGTGTGCCTTGGCAGTC-TCAG-AC-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG- 3’; underlined sequence indicates the target region primer) and 541R (5’-CCATCTCATCCCTGCGTGTCTCCGAC-TCAG-X-AC-ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG-3’; ‘X’ presents the unique barcode for each subject) (http://oklbb.ezbiocloud.net/content/1001) as previous study shows. The sequencing was performed at Chunlab (Seoul, Korea) with GS Junior Sequencing system, the modified laboratory benchtop form of 454 sequencing systems (Roche, Branford, CT, USA) as stated in the manufacturer’s directions.
3. Pyrosequencing data analysis
The primary analysis was conducted as described above. Reads taken from different samples were classified by unique barcodes of each PCR product. After identifying the target region in barcoded primers (9F or 541R), all of the linked sequences including adapter, barcode, and linker were eliminated. Low quality sequences such as reads containing two or more indefinite nucleotides, reads with a low quality score (average score < 25), or reads shorter than 300 bp, were eliminated. Potential chimeric sequences were confirmed by the Bellerophon formula, which compares the BLASTN search conclusions between the forward half and reverse half sequences.16 After removing the chimeric sequences, the taxonomic sorting of each read was assigned against the EzTaxon-e database (http://eztaxon-e.ezbiocloud.net),17 which has the 16S rRNA gene sequence of type strains that have valid published names and representative species level phylotypes of either cultured or uncultured entries in the GenBank database with complete hierarchical taxonomic classification from the phylum to the species. Phylogenetic trees were not created as we assigned reads into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) according to BLAST results. The raw 16S rRNA gene sequence originated from our study was deposited in National Center for Biotechnology Information’s Sequence Read Archive (GSE61493).
4. Evaluation of species richness and diversity
To compare species richness between samples of different sizes, rarefaction curve, and diversity indices such as abundance-based coverage estimator, Chao1 estimator, and Jackknife estimator. Simpson diversity index and Shannon diversity index were estimated in the CLcommunity program (Chunlab). Random subsampling was conducted to equalize the read size of samples to compare the different read size within samples. To compare the OTUs between samples, shared OTUs were obtained with the XOR analysis of the CLcommunity program.
5. Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were reported as mean ± SD, and confidence intervals were computed as two-tailed using 95% coverage. Categorical variables were described as frequencies and proportions. Comparisons between continuous parameters were performed by the t-test and Mann-Whitney test. Statistical analyses were done by PASW ver. 18.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA) and P-values < 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant.
RESULTS
1. Patients
Baseline characteristics of clinical and pyrosequencing results of gastric antral mucosal and fluid samples are shown in Table 1. Four subjects (2 gastric cancer, 1 gastritis, and 1 control) were included in this study. The mean age of subjects was 48.7 years (38–59 years). Subject 1 and 3 were male and subject 2 and 4 were female. Sample pH values varied between 1.0 and 7.4 (mean: 2.79). Three samples were found to contain H. pylori, showing positive results. We checked neutrophil infiltration, monocyte infiltration, and intestinal metaplasia to evaluate degree of gastritis. We also evaluated pepsinogen I/II ratio reflecting gastric atrophy. The mean pepsinogen I/II ratio was 3.3.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of 4 subjects
| Subject No. | Sex/Age (yr) | Disease | Gastric pH | Site | Intesinal metaplasia (n) | Neutrophil infiltration (n) | Monocyte infiltration (n) | Atrophy (n) | CLO | H&E | Culture | HP IgG | Eradication history | PG I/II ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M/44 | EGC | 7.4 | Body | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | + | Moderate | Positive | N/A | No | 2.5 |
| Antrum | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 2 | F/59 | Gastritis | 1.25 | Body | 0 | 2 | 2 | Ina | + | Moderate | Positive | 1.975 | No | 1.9 |
| Antrum | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 3 | M/54 | AGC | 1 | Body | 0 | 2 | 2 | Ina | + | Mild | N/A | N/A | No | 3.0 |
| Antrum | 2 | |||||||||||||
| 4 | F/38 | Control | 1.51 | Body | 0 | 0 | 1 | Ina | - | - | N/A | N/A | No | 5.7 |
| Antrum | 0 |
CLO, Campylobacter-like organism; HP IgG, Helicobacter pylori immunoglobulin G; PG, pepsinogen; M, male; F, female; EGC, early gastric cancer; AGC; advancedgastric cancer; Ina, inadequate to assess atrophy; N/A, not assessed.
2. Gastric fluid vs. gastric mucosa
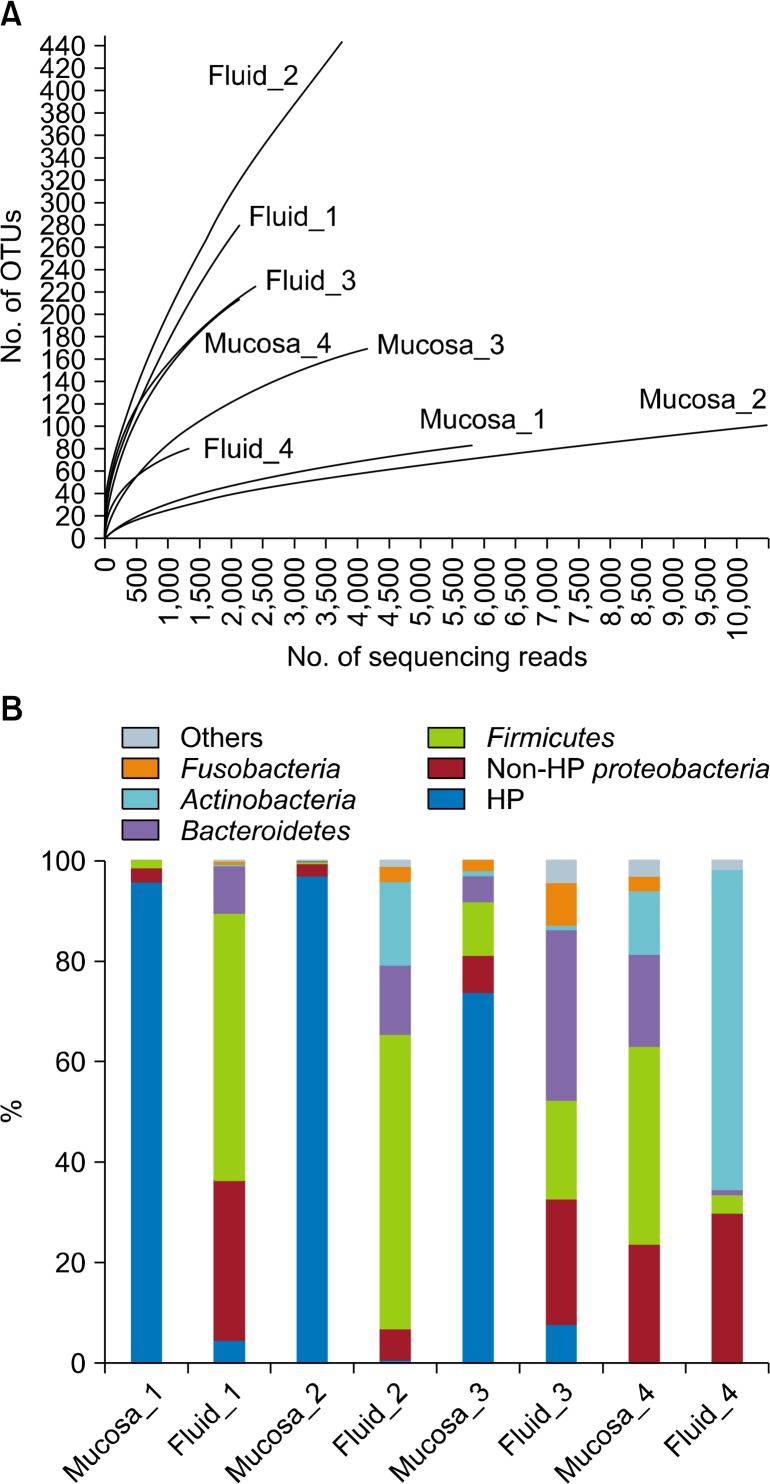
Though there was no statistical significance, the mean of total number of reads was lower in gastric fluid samples than gastric mucosa samples. However, the mean of OTUs was higher in gastric fluid (Fig. 1A). Generally, gastric fluid samples show higher diversity compared to gastric mucosa samples (Fig. 1B). At the phylum level, members of Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Bacteroidetes were identified. The difference in the composition of phyla between gastric mucosa and fluid samples is shown in Fig. 1B and Table 2. The composition of H. pylori and Proteobacteria was higher in mucosa samples than gastric fluid samples (H. pylori, 66.5% vs. 3.3%, P = 0.033; Proteobacteria, 75.4% vs. 26.3%, P = 0.041), Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Firmicutes were proportioned relatively less in mucosa samples compared to gastric fluid. It showed no statistically significant difference. (Actinobacteria, 3.5% vs. 20.2%, P = 0.312; Bacteroidetes, 6.0% vs. 14.8%, P = 0.329; Firmicutes, 12.8% vs. 33.4%, P = 0.246) (Fig. 1B, Table 2).
Figure 1.
(A) Rarefaction curve and composition of phylum in the gastric mucosa and gastric fluid samples. The rarefaction curve indicates the bacterial community in the gastric fluid samples and mucosa samples (1–3, Helicobacter pylori [HP] (+) sample; 4, HP (−) sample). OTUs stands for operational taxonomic units. (B) The phylum composition between gastric mucosa samples and gastric fluid samples.
Table 2.
The phylum composition between gastric mucosa samples and gastric fluid samples
| Subject No. | Acidobacteria | Actinobacteria | Bacteroidetes | Firmicutes | Fusobacteria | Proteobacteria | Helicobacter pylori |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||||
| Mucosa | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.05 | 98.31 | 95.55 |
| Gastric juice | 0.00 | 0.52 | 9.25 | 52.79 | 0.56 | 36.36 | 4.51 |
| 2 | |||||||
| Mucosa | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 99.09 | 96.76 |
| Gastric juice | 0.00 | 16.60 | 13.81 | 58.48 | 2.95 | 6.68 | 0.40 |
| 3 | |||||||
| Mucosa | 0.00 | 1.02 | 5.27 | 10.65 | 2.13 | 80.57 | 73.76 |
| Gastric juice | 0.00 | 0.50 | 34.63 | 19.03 | 8.36 | 32.54 | 7.90 |
| 4 | |||||||
| Mucosa | 0.07 | 12.67 | 18.36 | 38.91 | 2.78 | 23.79 | 0.00 |
| Gastric juice | 0.37 | 63.25 | 1.41 | 3.42 | 0.00 | 29.77 | 0.30 |
Values are presented as percentage only.
DISCUSSION
Stomach plays an important role in maintaining gastrointestinal (GI) health, as a barrier against ingested infectious disease agents of the lower GI tract.18 In healthy subjects, swallowed pathogens are inactivated by gastric fluid, which contains both hydrochloric acid and proteolytic enzymes.19 Atrophic gastritis, gastric surgery, or drugs that inhibit acid secretion can cause hypochlorhydria.18 Decreased gastric acid secretion is responsible for an increased risk of infection.20 There were few studies related to gastric juice. von Rosenvinge et al.21 reported the microbiota composition of gastric fluid in relation to various human host parameters, including immune status, gastric fluid pH, use of proton pump inhibitors, and antibiotic medications.
Previous research has primarily focused on the microbiota of gastric mucosal biopsies and applied only-DNA-based methodologies; yet it was unable to distinguish between transcriptionally active, inactive, or dead bacteria. Analysis by the 16S rRNA gene contents of microbial samples after amplification by PCR has changed the characterization of microbial communities.5,11,22 Using a 16S rRNA transcript amplicon sequencing strategy, we can differentiate transcriptionally active RNA microbiota from the total DNA microbiota compositions.23
Our results reveal that human gastric fluid harbors a diverse microbiota dominated by Fusobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria including H. pylori, demonstrating a similar overall composition at the phylum level as previously found in other study.5,20,24
Contrary to previous studies about stomach environment based on biopsy samples from the mucosa,5,6 H. pylori was not the dominant species in the gastric fluid microbiota, similar to other reports.21,25 This finding is consistent with the literature showing that H. pylori colonizes the mucous layer and adheres to gastric epithelial cells.26 Delgado et al.1 also demonstrated that the ratio of culture recovery from gastric fluid (5/12) was about half compared to that from gastric mucosa (10/12).
In contrast to that, in gastric mucosa, the proportion of the Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria was relatively increased in the gastric fluid samples, and the proportion of Proteobacteria was decreased in the present study, similar to other reports.5,25
Higher microbioal diversity of gastric fluid compared to gastric mucosa was observed in H. pylori (+) patients; however these pattern was not shown in the H. pylori (−) patient. The number of sequencing reads was lower in the fluid sample than mucosa. That is, microorganism in the gastric fluid was diverse, but small compared to mucosa. In addition, because there are some bacteria that come through oral cavity and esophagus in gastric fluid, it can be concluded that such bacteria simply pass through the stomach, instead of actually inhabiting in stomach. Therefore, pyrosequencing of mucosa could reflect more accurate information about gastric microbiota. This conclusion is also supported by a number of researches done using pyrosequencing to examine microbiota on gastric mucosa.1,5 However, this study has a limitation due to small sample size, and further research with more samples would be needed.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant for the Global Core Research Center (GCRC) funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2011-0030001).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
REFERENCES
- 1.Delgado S, Cabrera-Rubio R, Mira A, Suárez A, Mayo B. Microbiological survey of the human gastric ecosystem using culturing and pyrosequencing methods. Microb Ecol. 2013;65:763–72. doi: 10.1007/s00248-013-0192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004;118:229–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mazmanian SK, Liu CH, Tzianabos AO, Kasper DL. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell. 2005;122:107–18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hattori M, Taylor TD. The human intestinal microbiome: a new frontier of human biology. DNA Res. 2009;16:1–12. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bik EM, Eckburg PB, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Purdom EA, Francois F, et al. Molecular analysis of the bacterial microbiota in the human stomach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:732–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506655103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Andersson AF, Lindberg M, Jakobsson H, Bäckhed F, Nyrén P, Engstrand L. Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Correa P, Houghton J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:659–72. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sanduleanu S, Jonkers D, De Bruïne A, Hameeteman W, Stockbrügger RW. Double gastric infection with Helicobacter pylori and non-Helicobacter pylori bacteria during acid-suppressive therapy: increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines and development of atrophic gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1163–75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.01029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mowat C, Williams C, Gillen D, Hossack M, Gilmour D, Carswell A, et al. Omeprazole, Helicobacter pylori status, and alterations in the intragastric milieu facilitating bacterial N-nitrosation. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:339–47. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.9367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ziebarth D, Spiegelhalder B, Bartsch H. N-nitrosation of medicinal drugs catalysed by bacteria from human saliva and gastro-intestinal tract, including Helicobacter pylori. Carcinogenesis. 1997;18:383–9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.2.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Kemsley EK, Lund EK, Jamieson C, et al. Ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel patients exhibit distinct abnormalities of the gut microbiota. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jo HJ, Kim J, Kim N, Park JH, Nam RH, Seok YJ, et al. Analysis of gastric microbiota by pyrosequencing: minor role of bacteria other than Helicobacter pylori in the gastric carcinogenesis [published online ahead of print February 24, 2016] Helicobacter. doi: 10.1111/hel.12293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim J, Kim N, Jo HJ, Park JH, Nam RH, Seok YJ, et al. An appropriate cutoff value for determining the colonization of Helicobacter pylori by the pyrosequencing method: comparison with conventional methods. Helicobacter. 2015;20:370–80. doi: 10.1111/hel.12214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis. The updated Sydney System. International Workshop on the Histopathology of Gastritis, Houston 1994. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996;20:1161–81. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199610000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yoon H, Kim N, Lee HS, Shin CM, Park YS, Lee DH, et al. Helicobacter pylori-negative gastric cancer in South Korea: incidence and clinicopathologic characteristics. Helicobacter. 2011;16:382–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2011.00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P. Bellerophon: a program to de tect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:2317–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, et al. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2012;62:716–21. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Martinsen TC, Bergh K, Waldum HL. Gastric juice: a barrier against infectious diseases. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96:94–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto960202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tennant SM, Hartland EL, Phumoonna T, Lyras D, Rood JI, Robins-Browne RM, et al. Influence of gastric acid on susceptibility to infection with ingested bacterial pathogens. Infect Immun. 2008;76:639–45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01138-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Howden CW, Hunt RH. Relationship between gastric secretion and infection. Gut. 1987;28:96–107. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.von Rosenvinge EC, Song Y, White JR, Maddox C, Blanchard T, Fricke WF. Immune status, antibiotic medication and pH are associated with changes in the stomach fluid microbiota. ISME J. 2013;7:1354–66. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Verma R, Verma AK, Ahuja V, Paul J. Real-time analysis of mucosal flora in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in India. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4279–82. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01360-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zoetendal EG, Akkermans AD, De Vos WM. Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA from human fecal samples reveals stable and host-specific communities of active bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64:3854–9. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.10.3854-3859.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Anderson CM, Langford RF. Bacterial content of small intestine of children in health, in coeliac disease, and in fibrocystic disease of pancreas. Br Med J. 1958;1:803–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5074.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wu WM, Yang YS, Peng LH. Microbiota in the stomach: new insights. J Dig Dis. 2014;15:54–61. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Amieva MR, El-Omar EM. Host-bacterial interactions in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:306–23. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]