Abstract
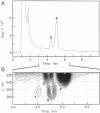
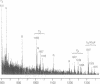
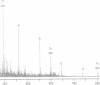
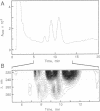
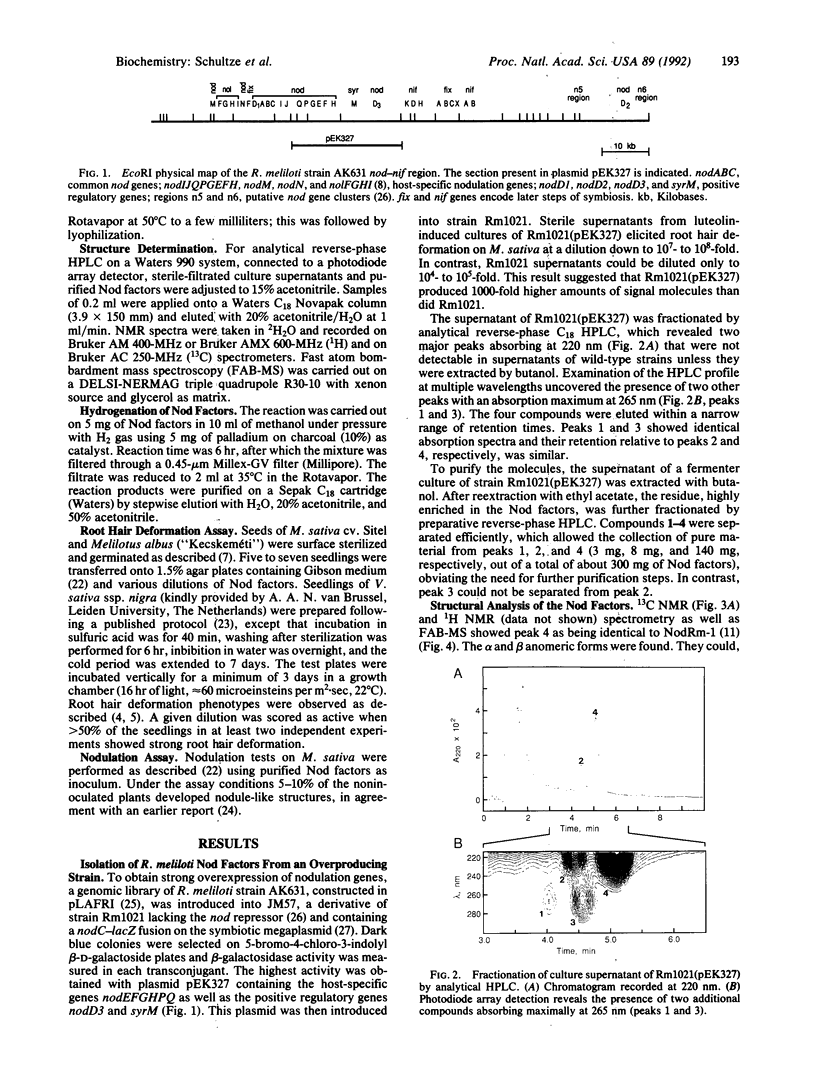
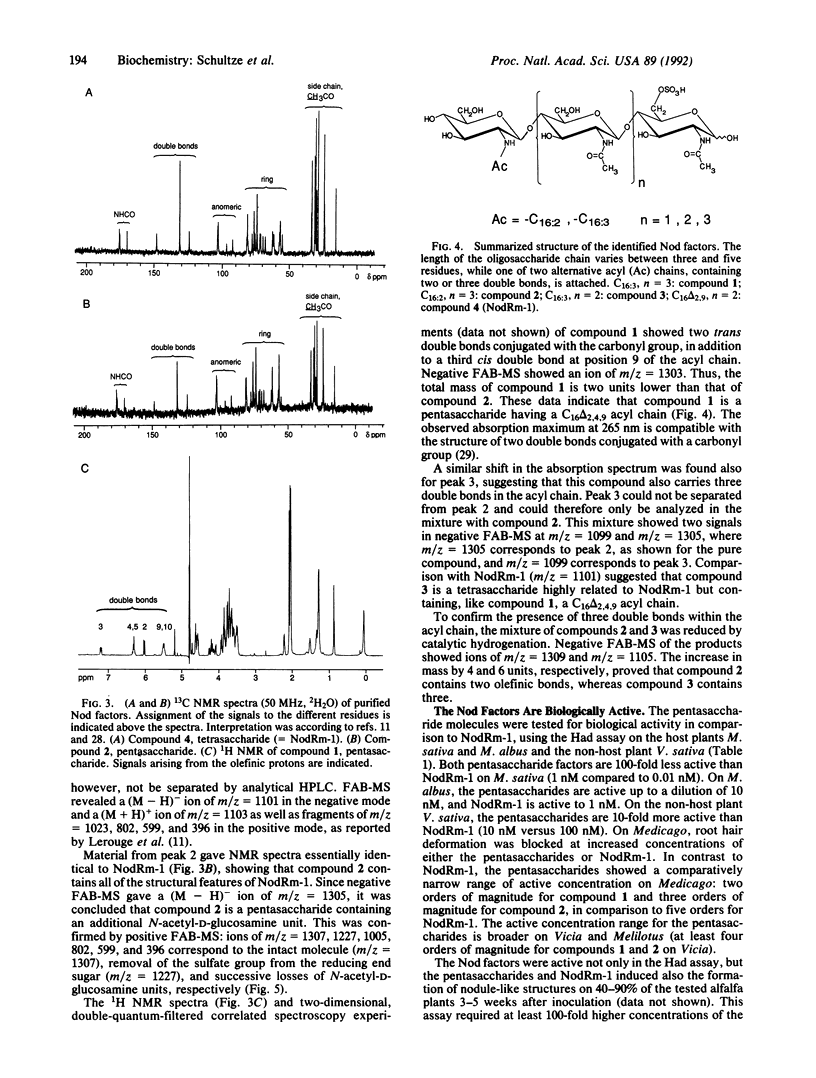
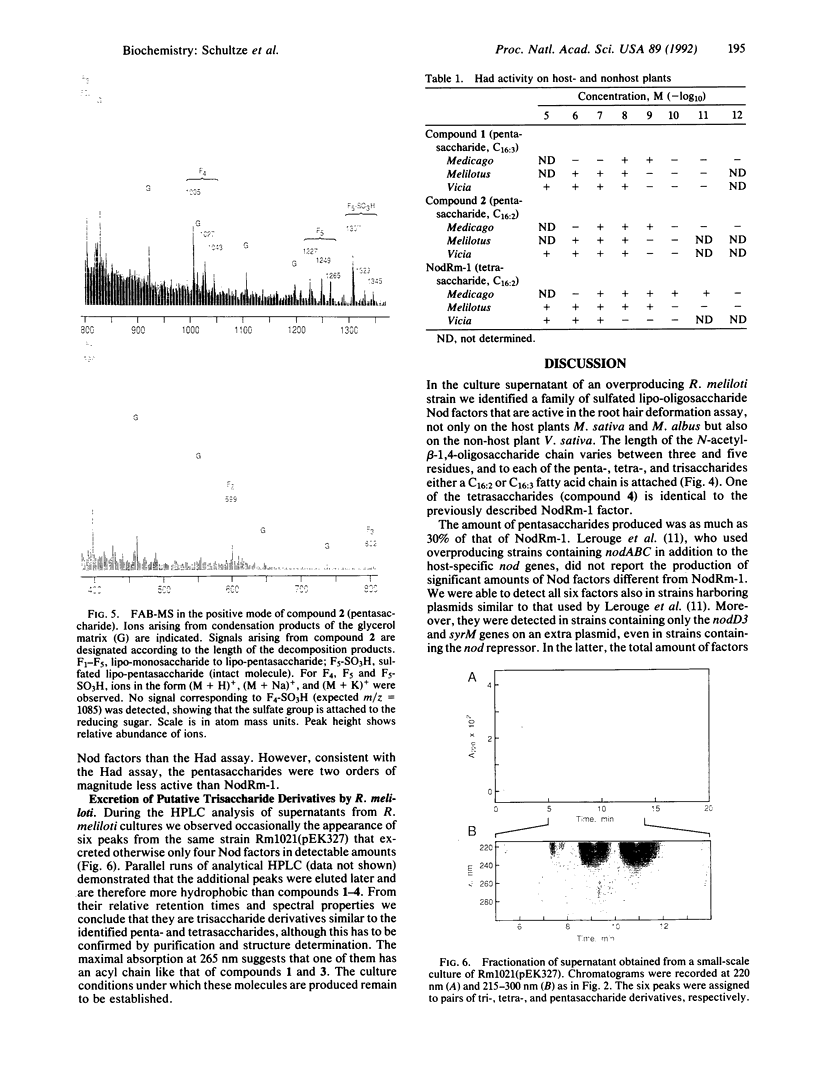
We have shown that a Rhizobium meliloti strain overexpressing nodulation genes excreted high amounts of a family of N-acylated and 6-O-sulfated N-acetyl-beta-1,4-D-glucosamine penta-, tetra-, and trisaccharide Nod factors. Either a C(16:2) or a C(16:3) acyl chain is attached to the nonreducing end subunit, whereas the sulfate group is bound to the reducing glucosamine. One of the tetrasaccharides is identical to the previously described NodRm-1 factor. The two pentasaccharides as well as NodRm-1 were purified and tested for biological activity. In the root hair deformation assay the pentasaccharides show similar activities on the host plants Medicago sativa and Melilotus albus and on the non-host plant Vicia sativa at a dilution of up to 0.01-0.001 microM, in contrast to NodRm-1, which displays a much higher specific activity for Medicago and Melilotus than for Vicia. The active concentration range of the pentasaccharides is more narrow on Medicago than on Melilotus and Vicia. In addition to root hair deformation, the different Nod factors were shown to induce nodule formation on M. sativa. We suggest that the production of a series of active signal molecules with different degrees of specificity might be important in controlling the symbiosis of R. meliloti with several different host plants or under different environmental conditions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baev N., Endre G., Petrovics G., Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Six nodulation genes of nod box locus 4 in Rhizobium meliloti are involved in nodulation signal production: nodM codes for D-glucosamine synthetase. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00282455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Production of root hair deformation factors by Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes in Escherichia coli: HsnD (NodH) is involved in the plant host-specific modification of the NodABC factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00027330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Biró S., Motamedi H., Collins J. F., Hutchinson C. R. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces glaucescens tcmI genes provides key information about the enzymology of polyketide antibiotic biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2727–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Porteous R., Soffe N., Delepierre M. 1H- and 13C-n.m.r. assignments and conformational analysis of some monosaccharide and oligosaccharide substrate-analogues of lysozyme. Carbohydr Res. 1985 Jun 15;139:35–46. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(85)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. J., Downie J. A. The nodI gene product of Rhizobium leguminosarum is closely related to ATP-binding bacterial transport proteins; nucleotide sequence analysis of the nodI and nodJ genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher C., Maillet F., Vasse J., Rosenberg C., van Brussel A. A., Truchet G., Dénarié J. Rhizobium meliloti host range nodH gene determines production of an alfalfa-specific extracellular signal. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5489–5499. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5489-5499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Kondorosi E., John M., Schmidt J., Török I., Györgypal Z., Barabas I., Wieneke U., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Transmembrane orientation and receptor-like structure of the Rhizobium meliloti common nodulation protein NodC. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):583–588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondorosi E., Gyuris J., Schmidt J., John M., Duda E., Hoffmann B., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Positive and negative control of nod gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti is required for optimal nodulation. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1331–1340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheres B., Van De Wiel C., Zalensky A., Horvath B., Spaink H., Van Eck H., Zwartkruis F., Wolters A. M., Gloudemans T., Van Kammen A. The ENOD12 gene product is involved in the infection process during the pea-Rhizobium interaction. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90743-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Wingender R., John M., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti nodA and nodB genes are involved in generating compounds that stimulate mitosis of plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwedock J., Long S. R. ATP sulphurylase activity of the nodP and nodQ gene products of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):644–647. doi: 10.1038/348644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman C. A., Rossen L., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation gene nodF encodes a polypeptide similar to acyl-carrier protein and is regulated by nodD plus a factor in pea root exudate. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):647–652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., van Brussel A. A., Tak T., Pees E., Lugtenberg B. J. Flavonoids induce Rhizobium leguminosarum to produce nodDABC gene-related factors that cause thick, short roots and root hair responses on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3388–3391. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3388-3391.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]