Abstract
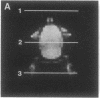
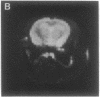
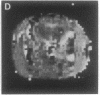
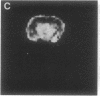
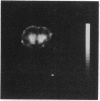
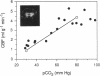
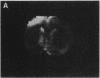
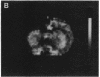
A technique has been developed for proton magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of perfusion, using water as a freely diffusable tracer, and its application to the measurement of cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the rat is demonstrated. The method involves labeling the inflowing water proton spins in the arterial blood by inverting them continuously at the neck region and observing the effects of inversion on the intensity of brain MRI. Solution to the Bloch equations, modified to include the effects of flow, allows regional perfusion rates to be measured from an image with spin inversion, a control image, and a T1 image. Continuous spin inversion labeling the arterial blood water was accomplished, using principles of adiabatic fast passage by applying continuous-wave radiofrequency power in the presence of a magnetic field gradient in the direction of arterial flow. In the detection slice used to measure perfusion, whole brain CBF averaged 1.39 +/- 0.19 ml.g-1.min-1 (mean +/- SEM, n = 5). The technique's sensitivity to changes in CBF was measured by using graded hypercarbia, a condition that is known to increase brain perfusion. CBF vs. pCO2 data yield a best-fit straight line described by CBF (ml.g-1.min-1) = 0.052pCO2 (mm Hg) - 0.173, in excellent agreement with values in the literature. Finally, perfusion images of a freeze-injured rat brain have been obtained, demonstrating the technique's ability to detect regional abnormalities in perfusion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman J. J., Ewy C. S., Becker N. N., Shalwitz R. A. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of blood flow and tissue perfusion employing 2H2O as a freely diffusible tracer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4099–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belliveau J. W., Rosen B. R., Kantor H. L., Rzedzian R. R., Kennedy D. N., McKinstry R. C., Vevea J. M., Cohen M. S., Pykett I. L., Brady T. J. Functional cerebral imaging by susceptibility-contrast NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Jun;14(3):538–546. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Longar S., Fishman R. A. Phospholipid degradation and edema development in cold-injured rat brain. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 31;277(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90941-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detre J. A., Eskey C. J., Koretsky A. P. Measurement of cerebral blood flow in rat brain by 19F-NMR detection of trifluoromethane washout. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Jul;15(1):45–57. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910150106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detre J. A., Subramanian V. H., Mitchell M. D., Smith D. S., Kobayashi A., Zaman A., Leigh J. S., Jr Measurement of regional cerebral blood flow in cat brain using intracarotid 2H2O and 2H NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1990 May;14(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. T., Du L. N., Faul D. D., Gado M., Rossnick S. Projection angiograms of blood labeled by adiabatic fast passage. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Jun;3(3):454–462. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichling J. O., Raichle M. E., Grubb R. L., Jr, Ter-Pogossian M. M. Evidence of the limitations of water as a freely diffusible tracer in brain of the rhesus monkey. Circ Res. 1974 Sep;35(3):358–364. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklöf B., Lassen N. A., Nilsson L., Norberg K., Siesjö B. K., Torlöf P. Regional cerebral blood flow in the rat measured by the tissue sampling technique; a critical evaluation using four indicators C14-antipyrine, C14-ethanol H3-water and xenon. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 May;91(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleff S. M., Schnall M. D., Ligetti L., Osbakken M., Subramanian V. H., Chance B., Leigh J. S., Jr Concurrent measurements of cerebral blood flow, sodium, lactate, and high-energy phosphate metabolism using 19F, 23Na, 1H, and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Aug;7(4):412–424. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910070404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing J. R., Branch C. A., Helpern J. A., Smith M. B., Butt S. M., Welch K. M. Cerebral blood flow measured by NMR indicator dilution in cats. Stroke. 1989 Feb;20(2):259–267. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E., Mintun M. A., Dence C. Nonoxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.3260686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur D., Good W. F., Wolfson S. K., Jr, Yonas H., Shabason L. In vivo mapping of local cerebral blood flow by xenon-enhanced computed tomography. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1267–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.7058347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herscovitch P., Raichle M. E. What is the correct value for the brain--blood partition coefficient for water? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Mar;5(1):65–69. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. A., Quast M. J., Kaplan B. J., Lifsey R. S., Eisenberg H. M. Assessment of a superparamagnetic iron oxide (AMI-25) as a brain contrast agent. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Mar;13(3):434–443. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910130310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii S., Ngai A. C., Ko K. R., Winn H. R. A venous outflow method for continuously monitoring cerebral blood flow in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):H304–H312. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.2.H304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Siesjö B. K. A method for determining blood flow and oxygen consumption in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Jan;96(1):72–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappius H. M. Local cerebral glucose utilization in thermally traumatized rat brain. Ann Neurol. 1981 May;9(5):484–491. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Eriksson L., Stone-Elander S., Widen L. Does mental activity change the oxidative metabolism of the brain? J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2373–2389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]