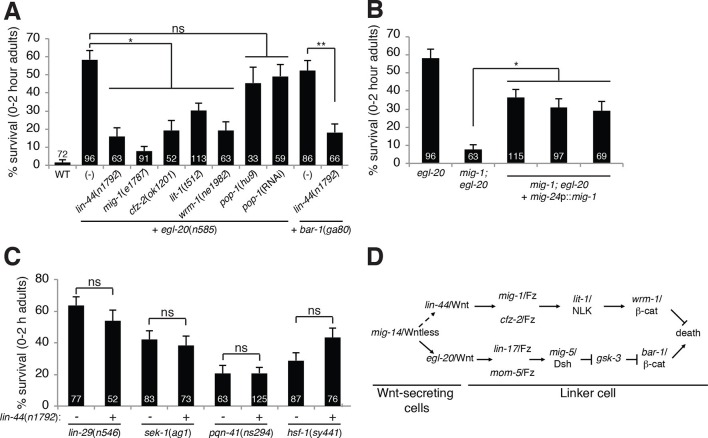
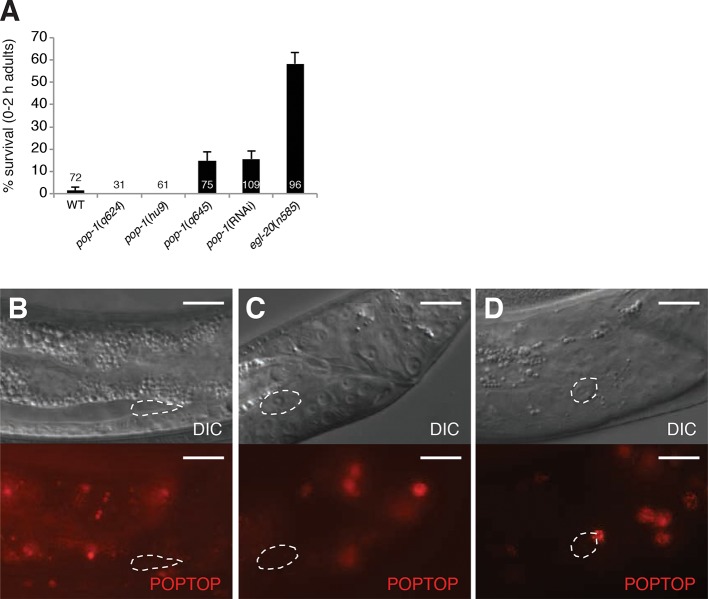
Figure 2. A lin-44/Wnt pathway promotes linker cell survival.
(A) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. In (A-C) strains also contain qIs56 and him-5(e1490). *p<10–3; **p <10–4; ns, not significant; Fisher’s exact test. lit-1(t512) is linked to unc-32(e189). (B) Linker cell survival in egl-20(n585) and mig-1(e1787); egl-20(n585) animals harboring a mig-24p::mig-1 transgene. *p<0.001. (C) Linker cell survival in indicated genotypes. ns, not significant; Fisher’s exact test. (D) Model for Wnt pathway interactions in LCD.