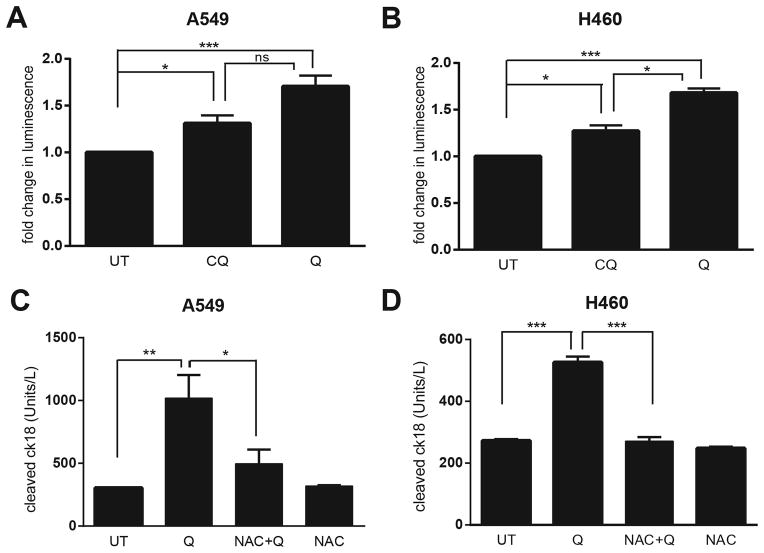
Figure 4. Quinacrine-induced cell death in NSCLC cells is associated with increased reactive oxygen species production (ROS).
(A, B) Cells were treated with 30μM CQ or 10μM Q treatment for 6h. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in A549 (A) or H460 (B) lung cancer cells was measured using a bioluminescence assay to detect intracellular H2O2 levels; results were normalized to those obtained with untreated controls (UT). (C, D) A549 (C) or H460 (D) cells were treated with 30μM CQ or 10μM Q for 24h and cleaved cytokeratin 18 (cCK18) levels were measured using ELISA. UT=untreated controls. NAC= 5 μM N-Acetyl Cysteine. All data represent the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. Statisitical significance was calculated using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001.