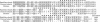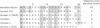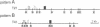Abstract
A full-length cDNA clone specifying sandbar shark (Carcharhinus plumbeus) immunoglobulin light chain has been isolated and sequenced. By alignment with human lambda chains, the leader, framework, complementarity-determining, joining, and constant regions are clearly identified in the shark light chain. Approximately 40-50% identity is shared between the human and shark sequences in the variable and constant regions. We have performed sequence comparisons of the individual segments and constructed phylogenetic trees for the variable region. These studies identify the shark protein as a lambda chain. In addition, the sandbar shark light chain is only distantly related to that of horned shark (Heterodontus francisci) [Shamblott, M. J. & Litman, G. W. (1989) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 4684-4688], demonstrating that the long evolutionary time of divergence among shark species has led to the generation of substantial differences in sequence. The positions of the variable, joining, and constant gene segments in 14 genomic clones have been mapped. The segments are linked in individual clusters (variable, joining, constant) occupying 3-7 kilobases. Cluster arrangement can be grouped into two patterns based upon spacing between the genes in the individual clones. This arrangement is fundamentally different from that observed in higher vertebrates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. L., Szajnert M. F., Kaplan J. C., McColl L., Young B. D. The isolation of a human Ig V lambda gene from a recombinant library of chromosome 22 and estimation of its copy number. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6647–6661. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer S. R., Huebner K., Budarf M., Finan J., Erikson J., Emanuel B. S., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M., Melchers F. The human Vpre B gene is located on chromosome 22 near a cluster of V lambda gene segments. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(5):328–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00364231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berinstein N., Levy S., Levy R. Activation of an excluded immunoglobulin allele in a human B lymphoma cell line. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):337–339. doi: 10.1126/science.2496466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chersi A., Appella E., Carta S., Mage R. The amino acid sequence of a variable region of rabbit b4 chain from an anti-SIII antibody: comparison with light chains of the same sub-group from anti-A-variant carbohydrate antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1979 Aug;16(8):589–595. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F. Aligning amino acid sequences: comparison of commonly used methods. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):112–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02100085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley R. C., Beh K. J. Isolation and sequence of sheep Ig H and L chain cDNA. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):708–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Mutation data matrix and its uses. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:333–351. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayzer D. J. Immunoglobulin lambda light chain evolution: Igl and Igl-like sequences form three major groups. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(3):157–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02114969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayzer D. J., Jaton J. C. Cloning and sequencing of two functional rabbit germ-line immunoglobulin V lambda genes. Gene. 1989 Aug 1;80(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Somatic mutation creates diversity in the major group of mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chains. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the variable domains of two homogeneous rabbit antibodies to type III pneumococcal polysaccharide. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):235–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1470235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Noonan D. J., Strohal R., Balderas R. S., Møller N. P., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Molecular analysis of the murine lupus-associated anti-self response: involvement of a large number of heavy and light chain variable region genes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jan;17(1):91–95. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Strohal R., Balderas R. S., Johnson M. E., Noonan D. J., Duchosal M. A., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region gene complex organization and immunoglobulin genes encoding anti-DNA autoantibodies in lupus mice. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI113689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Melchers F. A second gene, VpreB in the lambda 5 locus of the mouse, which appears to be selectively expressed in pre-B lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2267–2272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Rudikoff S., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Scharff M. D. Nucleic acid and protein sequences of phosphocholine-binding light chains. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1366–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz W., Schäble K. F., Thiebe R., Stavnezer J., Zachau H. G. The J kappa proximal region of the human K locus contains three uncommon V kappa genes which are arranged in opposite transcriptional polarities. Mol Immunol. 1988 May;25(5):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Schluter S. F. Evolution of variable and constant domains and joining segments of rearranging immunoglobulins. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2469–2479. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2509274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvari R., Ziv E., Lantner F., Heller D., Schechter I. Somatic diversification of chicken immunoglobulin light chains by point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3072–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Höchtl J., Schnell H., Zachau H. G. Differences between germ-line and rearranged immunoglobulin V kappa coding sequences suggest a localized mutation mechanism. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):668–670. doi: 10.1038/291668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez P., Marche P. N., Le Guern C., Cazenave P. A. Structure of a third murine immunoglobulin lambda light chain variable region that is expressed in laboratory mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9185–9188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Capra J. D. V kappa and J kappa gene segments of A/J Ars-A antibodies: somatic recombination generates the essential arginine at the junction of the variable and joining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1085–1089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluter S. F., Beischel C. J., Martin S. A., Marchalonis J. J. Sequence analysis of homogeneous peptides of shark immunoglobulin light chains by tandem mass spectrometry: correlation with gene sequence and homologies among variable and constant region peptides of sharks and mammals. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jan;27(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluter S. F., Hohman V. S., Edmundson A. B., Marchalonis J. J. Evolution of immunoglobulin light chains: cDNA clones specifying sandbar shark constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9961–9965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamblott M. J., Litman G. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of primitive vertebrate immunoglobulin light chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamblott M. J., Litman G. W. Genomic organization and sequences of immunoglobulin light chain genes in a primitive vertebrate suggest coevolution of immunoglobulin gene organization. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3733–3739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen M. L., Hellman L., Pettersson U. The immunoglobulin lambda locus in rat consists of two C lambda genes and a single V lambda gene. Gene. 1987;55(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger B., Thiebe R., Huber C., Osterholzer E., Zachau H. G. Two unusual human immunoglobulin V kappa genes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Jul;369(7):601–607. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.2.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohal R., Helmberg A., Kroemer G., Kofler R. Mouse Vk gene classification by nucleic acid sequence similarity. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(6):475–493. doi: 10.1007/BF02421180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg A. L., Kindt T. J. Amino acid sequence of rabbit light chains: variable region of a light chain from a homogeneous immunoglobulin raised by streptococcal immunization. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 6;15(7):1381–1386. doi: 10.1021/bi00652a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoegaerden M., Strosberg A. D. Sequence of a rabbit anti-Micrococcus lysodeikticus antibody light chain. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4311–4317. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma M. Use of ammonium sulfate precipitation and guanidine isothiocyanate lysis to isolate lambda DNA. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):230–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]