Abstract
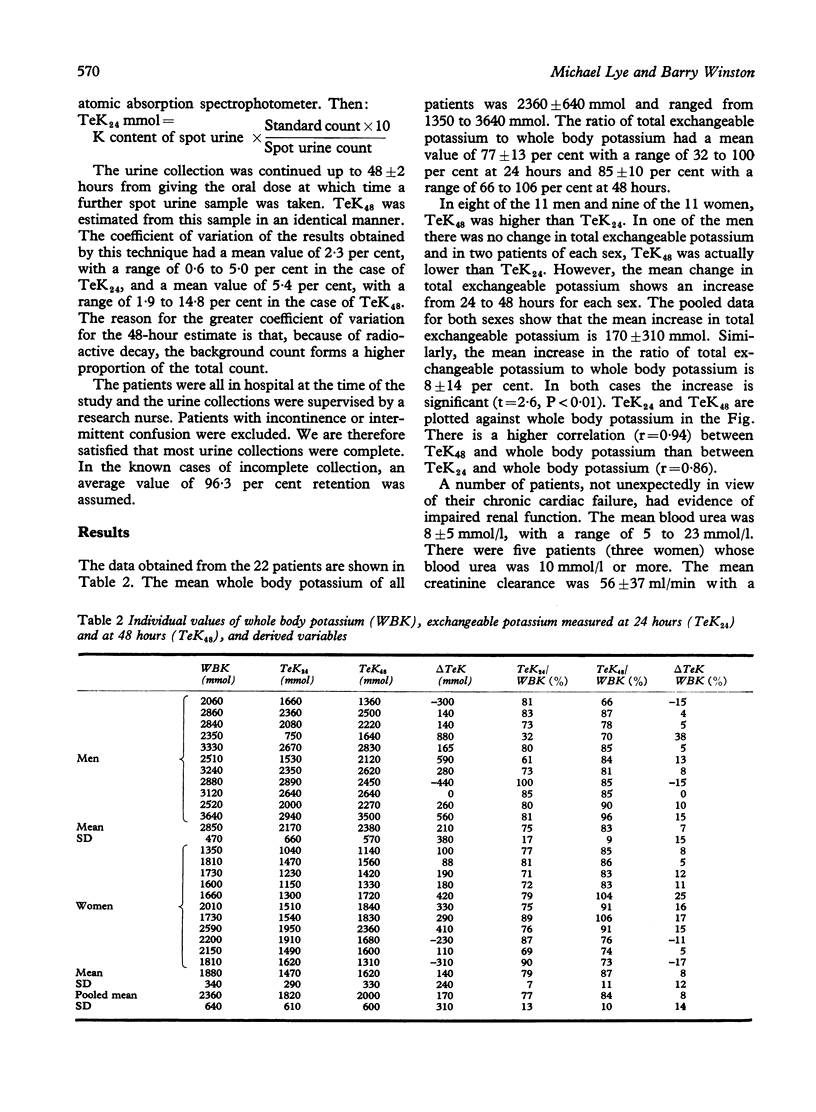
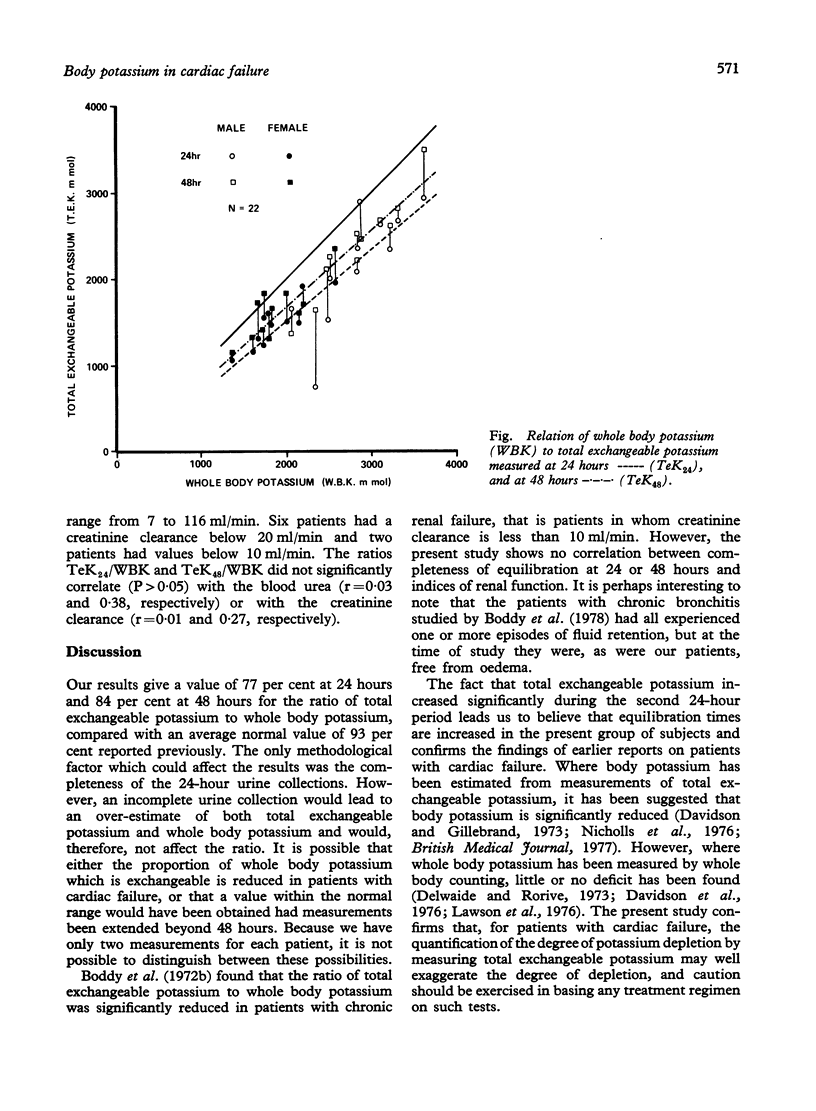
Body potassium status of patients with cardiac failure may be estimated by a number of methods, but increasing reliance is being placed upon radioisotope dilution with 42K which measures the total exchangeable potassium. Total exchangeable potassium comprises between 86 per cent and 97 per cent of whole body potassium in healthy subjects. We have measured total exchangeable potassium in 22 oedema-free elderly patients with stable cardiac failure and compared the results with simultaneously determined measurements of whole body potassium obtained by whole body counting. The mean whole body potassium was 2360 +/- 640 mmol. The mean value of total exchangeable potassium measured at 24 hours was 1820 +/- 610 mmol (77% of whole body potassium) and increased further to 2000 +/- 600 mmol (84%) when measured after 48 hours. In patients with cardiac failure and, perhaps, also other patients with a history of fluid retention, the mixing of a tracer dose may be significantly delayed, which if not appreciated may lead to an overestimate of potassium depletion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boddy K., Davies D. L., Howie A. D., Madkour M. M., Mahaffy M. E., Pack A. I. Total body and exchangeable potassium in chronic airways obstruction: a controversial area? Thorax. 1978 Feb;33(1):62–66. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., King P. C., Hume R., Weyers E. The relation of total body potassium to height, weight, and age in normal adults. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jun;25(6):512–517. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.6.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., King P. C., Lindsay R. M., Winchester J., Kennedy A. C. Exchangeable and total body potassium in patients with chronic renal failure. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 15;1(5793):140–142. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5793.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORSA L., Jr, OLNEY J. M., Jr, STEENBURG R. W., BALL M. R., MOORE F. D. The measurement of exchangeable potassium in man by isotope dilution. J Clin Invest. 1950 Oct;29(10):1280–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI102365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson C., Gillebrand I. M. Use of amiloride as a potassium conserving agent in severe cardiac disease. Br Heart J. 1973 Apr;35(4):456–461. doi: 10.1136/hrt.35.4.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson C., McLachlan M. S., Burkinshaw L., Morgan D. B. Effect of long-term diuretic treatment on body-potassium in heart-disease. Lancet. 1976 Nov 13;2(7994):1044–1047. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90965-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. H., Boddy K., Gray J. M., Mahaffey M., Mills E. Potassium supplements in patients receiving long-term diuretics for oedema. Q J Med. 1976 Jul;45(179):469–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye M., May T., Hammick J., Ackery D. Whole-body and exchangeable potassium measurements in normal elderly subjects. Eur J Nucl Med. 1976 Aug 12;1(3):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00257966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls M. G., Espiner E. A., Hughes H., Rogers T. Effect of potassium-sparing diuretics on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and potassium retention in heart failure. Br Heart J. 1976 Oct;38(10):1025–1030. doi: 10.1136/hrt.38.10.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak L. P., Harrison C. E., Jr Abnormalities of cellular potassium concentration in uncompensated and compensated congestive heart failure. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 Feb;48(2):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'MEARA M. P., BIRKENFELD L. W., GOTCH F. A., EDELMAN I. S. The equilibration of radiosodium (Na24), radiopotassium (K42), and deuterium oxide (D2O) in hydropic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jun;36(6 Pt 1):784–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI103483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNDO J., SAGILD U. Total and exchangeable potassium in humans. Nature. 1955 Apr 30;175(4461):774–774. doi: 10.1038/175774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surveyor I., Hughes D. Discrepancies between whole-body potassium content and exchangeable potassium. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Mar;71(3):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALSO P. J., MILLER C. E., CARBALLO A. J., VASQUEZ I. Exchangeable potassium as a parameter of body composition. Metabolism. 1960 May;9:456–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Chamberlain D. A., Hamer J., McAlister J., Hawkins L. A. Potassium depletion in severe heart disease. Br Med J. 1969 Jun 7;2(5657):606–610. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5657.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



