Significance
The flagellar basal body contains a type III protein export machinery to construct the flagellar axial structure. ATP hydrolysis by FliI facilitates the flagellar protein export, and the ATPase activity is regulated by FliH. In this study, the structure of the homodimer of a FliH fragment (FliHC) complexed with FliI has been solved at 3.0-Å resolution. FliHC2 shows a marked structural similarity to the peripheral stalk of the A/V-type ATPases, and the proposed FliHC2–FliI hexamer model resembles in situ electron cryotomographic images. These results suggest that FliH2 functions as a peripheral stalk of the type III ATPase complex and that the flagellar export system and F/A/V-type ATPases share a similar functional mechanism and close evolutionary relationship.
Keywords: bacterial flagellum, type III protein export, crystal structure, F/A/V-type ATPase
Abstract
FliI and FliJ form the FliI6FliJ ATPase complex of the bacterial flagellar export apparatus, a member of the type III secretion system. The FliI6FliJ complex is structurally similar to the α3β3γ complex of F1-ATPase. The FliH homodimer binds to FliI to connect the ATPase complex to the flagellar base, but the details are unknown. Here we report the structure of the homodimer of a C-terminal fragment of FliH (FliHC2) in complex with FliI. FliHC2 shows an unusually asymmetric homodimeric structure that markedly resembles the peripheral stalk of the A/V-type ATPases. The FliHC2–FliI hexamer model reveals that the C-terminal domains of the FliI ATPase face the cell membrane in a way similar to the F/A/V-type ATPases. We discuss the mechanism of flagellar ATPase complex formation and a common origin shared by the type III secretion system and the F/A/V-type ATPases.
For survival and growth, bacteria move in liquid environment by rotating a long filamentous organelle, the flagellum. The bacterial flagellum is a huge extracellular assembly composed of more than 20,000 subunits of about 30 different proteins. Most of the component proteins are translocated into the central channel of the growing flagellum via the flagellar protein export apparatus driven by proton motive force and ATP hydrolysis, and go through the channel to the growing tip for their assembly. The export apparatus consists of a transmembrane export gate complex made up of six integral membrane proteins, FlhA, FlhB, FliO, FliP, FliQ, and FliR, and a cytoplasmic ATPase complex composed of three soluble proteins, FliH, FliI, and FliJ (1–4). These proteins are highly homologous to those of the type III secretion system of pathogenic bacteria, which directly inject virulence factors into eukaryotic host cells (5).
FliI is a Walker-type ATPase (6) and forms a homohexameric ring structure (7, 8). The FliI6 ring has been identified to be located at the base of the flagellum by electron cryotomography (9). The FliI6 ring associates with the basal body through the interactions of FliH with FlhA and FliN, a C-ring component of the basal body (10–12) (Fig. S1). FliI is composed of the N-terminal, ATPase, and C-terminal domains. The entire structure of FliI greatly resembles those of the α and β subunits of F1-ATPase (13). The ring formation and ATPase activity are facilitated by FliJ. FliJ is a small coiled-coil protein similar to the F1-γ subunit. FliJ binds in the central pore of the FliI6 ring to form the FliI6FliJ complex, which resembles the F1-α3β3γ complex (14). Interestingly, FliJ can partially act as a rotor within the central pore of the A3B3 complex of the Thermus thermophilus A-type ATPase (Tt A-ATPase) (15). It has been shown that infrequent ATP hydrolysis is sufficient for processive protein transport during flagellar assembly, suggesting that ATP hydrolysis by the FliI6FliJ complex activates the export gate through an interaction between FliJ and FlhA (16–19).
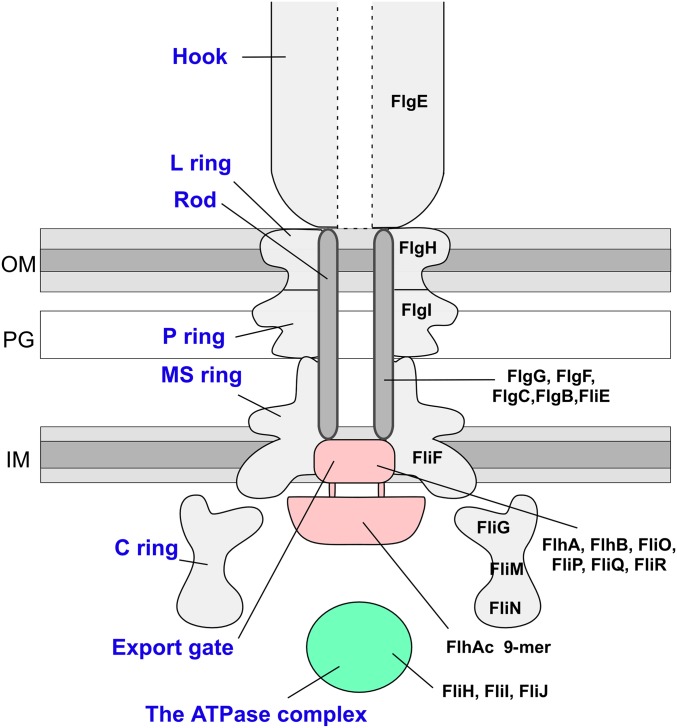
Fig. S1.
Schematic diagram of the flagellar hook–basal body. The name of each part is shown in blue letters (Left), and the name of the component protein(s) is in black letters (Right). IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane; PG, peptidoglycan layer.
FliI also forms a heterotrimeric complex with the FliH homodimer in the cytoplasm when free from the base of the flagellum (20, 21). The FliH dimer binds to the N-terminal region of FliI and inhibits the ring formation of FliI, thereby repressing the ATPase activity in the cytoplasm (20, 22). The chaperone–substrate complexes bind to the FliH2FliI complex through cooperative interactions among FliI, the chaperone, and the export substrate (23–25). FliI labeled with YFP shows rapid turnovers between the basal body and cytoplasmic pool in an ATP-independent manner (12), suggesting that the FliH2FliI complex acts as a dynamic carrier to deliver export substrates or the chaperone–substrate complexes to the docking platform made up of the C-terminal domain of FlhA.
FliH consists of 235 amino acid residues, and can be divided into three regions (20, 26). The N-terminal region composed of residues 1–100 (FliHN) is elongated, and the extreme N-terminal region is responsible for the interaction with FliN and FlhA to allow the FliI6 ring to associate with the export gate (10–12, 27). The middle region, residues 101–140, is essential for homodimer formation. The N-terminal and middle regions are predicted to adopt α-helical coiled-coil structures (21). The C-terminal region contains the binding site for FliI (21, 28). The N- and C-terminal regions of FliH show weak sequence homologies to the b and δ subunits of FOF1-ATP synthase, respectively (29). The b and δ subunits form the peripheral stalk connecting F1 to FO, and thus FliH may be a peripheral stalk that anchors the FliI6FliJ complex to the export gate. However, it remains unclear how FliH works during flagellar protein export, especially as to how FliH binds to FliI and regulates the formation of the cytoplasmic ATPase complex. To answer these questions, we crystallized the full-length FliI in complex with the homodimer of a FliH fragment consisting of residues 99–235 (FliHC) from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (30) and determined the structure of the FliHC2–FliI heterotrimeric complex at 3.0-Å resolution. We show that the FliHC homodimeric structure is highly asymmetric and looks very similar to the peripheral stalk complex of A/V-type ATPases. We discuss the structure of the cytoplasmic ATPase complex in the flagellar type III export apparatus and the evolutionary relationship of the type III ATPase complex with the F/A/V-type ATPases.
Results
Overall Structure of the FliHC2–FliI Complex.
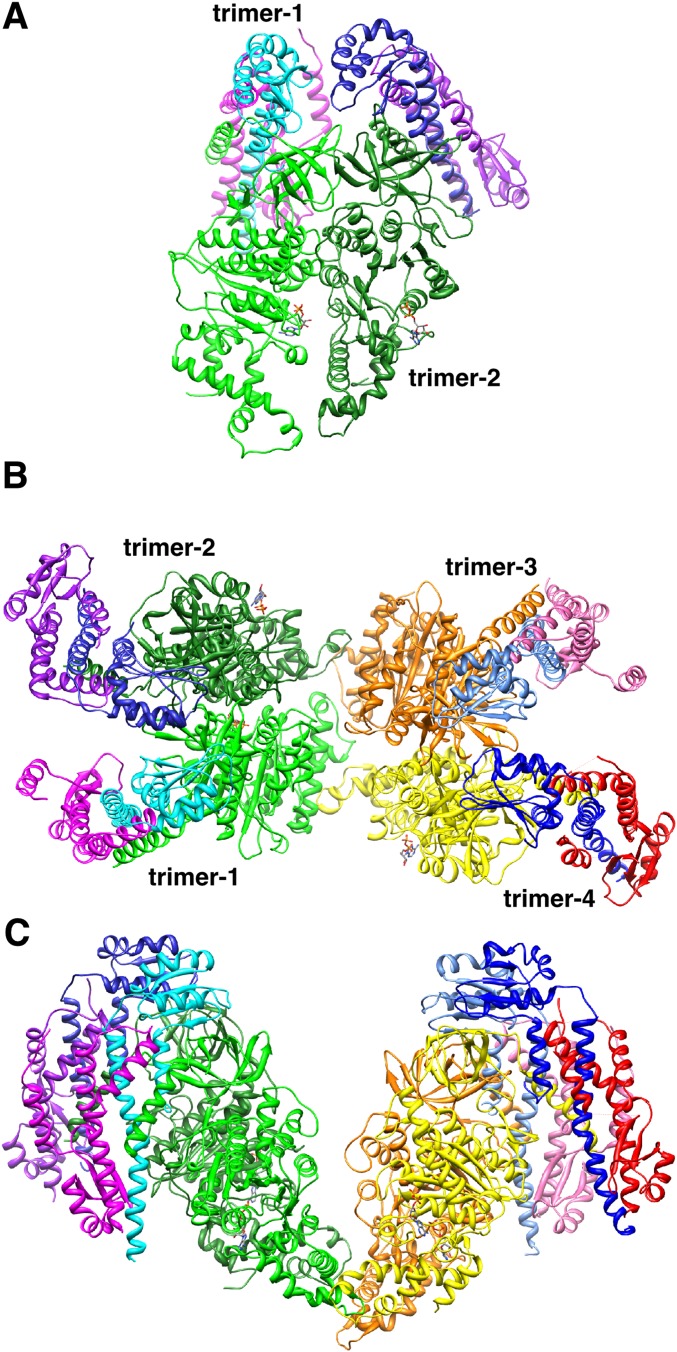
The FliHC homodimer binds to the N-terminal domain of FliI to form a FliHC2–FliI heterotrimeric complex (Fig. 1A). Two heterotrimers form a dimeric unit through the side-by-side interaction of the FliI molecules (Fig. S2A), and two dimeric units related by a local pseudotwofold axis are packed in a crystal asymmetric unit (Fig. S2 B and C). The structures of these four trimer complexes are similar to one another, but there are variations in the relative orientations of the FliHC homodimer and the ATPase domain of FliI to the N-terminal domain of FliI, and in the C-terminal conformation of FliHC2.
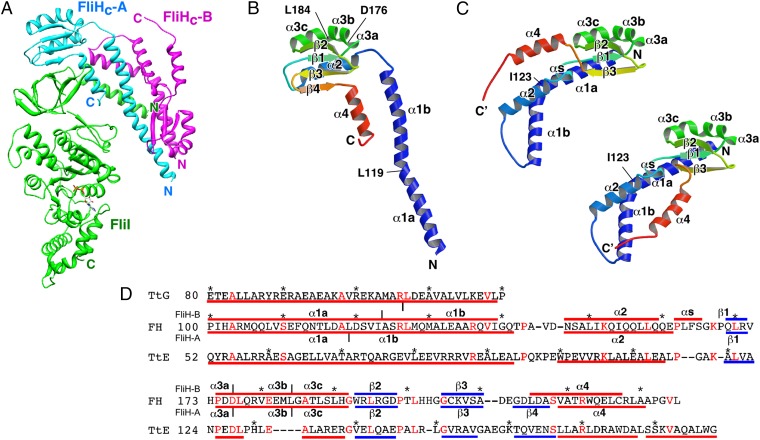
Fig. 1.
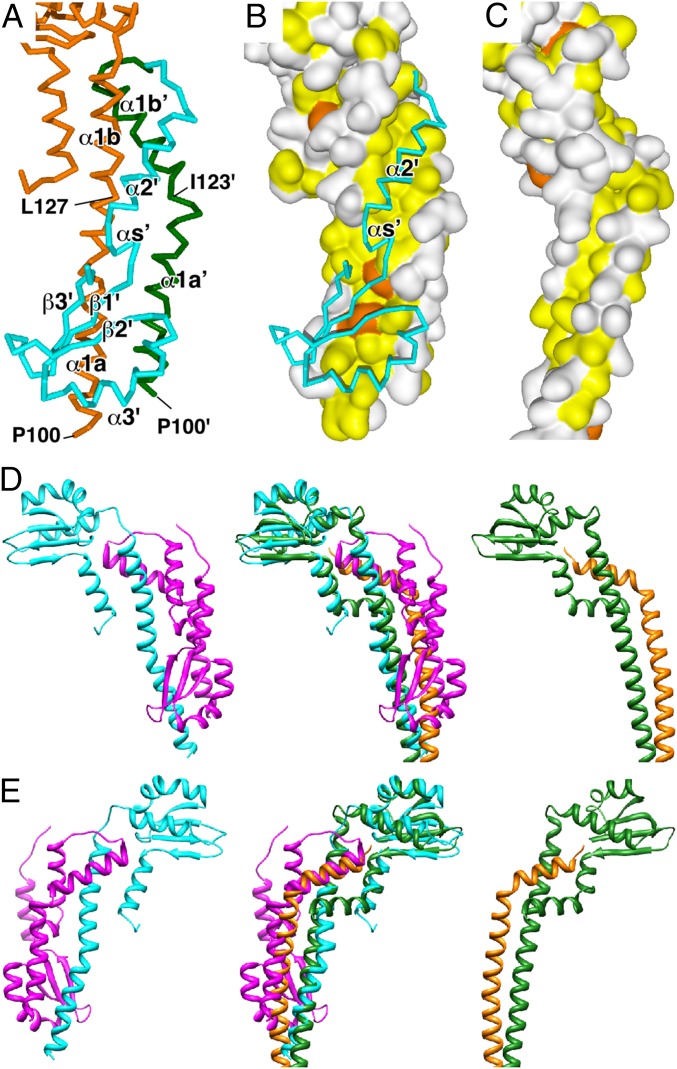
Structure of the FliHC2–FliI complex. (A) Cα ribbon drawing of the FliHC2–FliI complex. FliI and two FliHC subunits (FliHC-A and FliHC-B) are shown in green, cyan, and magenta, respectively. (B and C) Structure of FliHC. Cα ribbon representation of FliHC-A (B) and FliHC-B (C) shown in rainbow colors from the N terminus (blue) to the C terminus (red). The secondary structure elements are labeled. (C) FliHC-B shows two distinct conformations in the dimeric unit. FliHC-B of trimer-1 (trimer-3) (Upper Left) and that of trimer-2 (trimer-4) (Lower Right) are shown. (D) Structure-based amino acid sequence alignment of FliHC and the E (TtE) and G (TtG) subunits of A-ATPase from T. thermophilus (PDB ID code 3V6I). The red and blue bars indicate α-helices and β-strands, respectively. The secondary structures of FliHC-A and FliHC-B are shown below and above the FliH sequence, respectively, with the labels of the secondary structure elements. Conserved residues are highlighted in red characters. Every 10 residues are denoted with asterisks.
Fig. S2.
Structure of the FliHC2–FliI heterotrimeric complex in the crystal. (A) The dimeric unit of the FliHC2–FliI complex. (B) Two dimeric units (trimer-1 and -2, and trimer-3 and -4) in the crystal asymmetric unit. Trimer-1 and -2 are related to trimer-3 and -4, respectively, by a pseudotwofold axis perpendicular to the sheet. (C) Two dimeric units viewed from the bottom of B.
Structure of FliHC.
FliHC forms a J-shaped, unusually asymmetric homodimer in the complex (Fig. 1A). Although the two FliHC subunits (FliHC-A and FliHC-B) are similar in secondary structure, they are considerably different from each other in 3D arrangement (Fig. 1 B and C and Fig. S3). This is in agreement with a previous result showing the protease sensitivity difference between the two subunits of the FliH homodimer (28). FliHC-A consists of a long N-terminal helix (α1), a globular domain composed of four β-strands (β1–4) and two α-helices (α2 and α3), and a C-terminal helix (α4) (Fig. 1 B and D). α1 is divided into two parts (α1a and α1b) by a small bend at Leu-119. α3 is significantly distorted at Asp-176 and at Leu-184, and can be described as successive three short helices (α3a, α3b, and α3c). α4 is located below the globular domain and interacts with α1b in an antiparallel manner. FliHC-B is composed of five helices (α1–α4 and αs) and three strands (β1–β3). β1–β3 and α3 fold into a globular structure similar to that of FliHC-A, but the arrangement of the other structural components is quite distinct from those in FliHC-A (Fig. 1 C and D). The N-terminal helix (α1) is clearly separated into two parts (α1a and α1b) by the kink between Ile-123 and Ala-124. α2 and β4 are missing in the globular domain of FliHC-B, and therefore the hydrophobic core of the domain is exposed. α2 turns its orientation back to interact with α1b, and the globular structure interacts with α1a to cover its exposed hydrophobic core in part. A short helix (αs) not present in FliHC-A follows α2 and interacts with α1a. β4 changes its conformation to a loop in its N-terminal half and to a helix to become part of α4 in its C-terminal half. α4 of FliHC-B adopts two distinct conformations in the dimeric unit (Fig. 1C and Fig. S3).
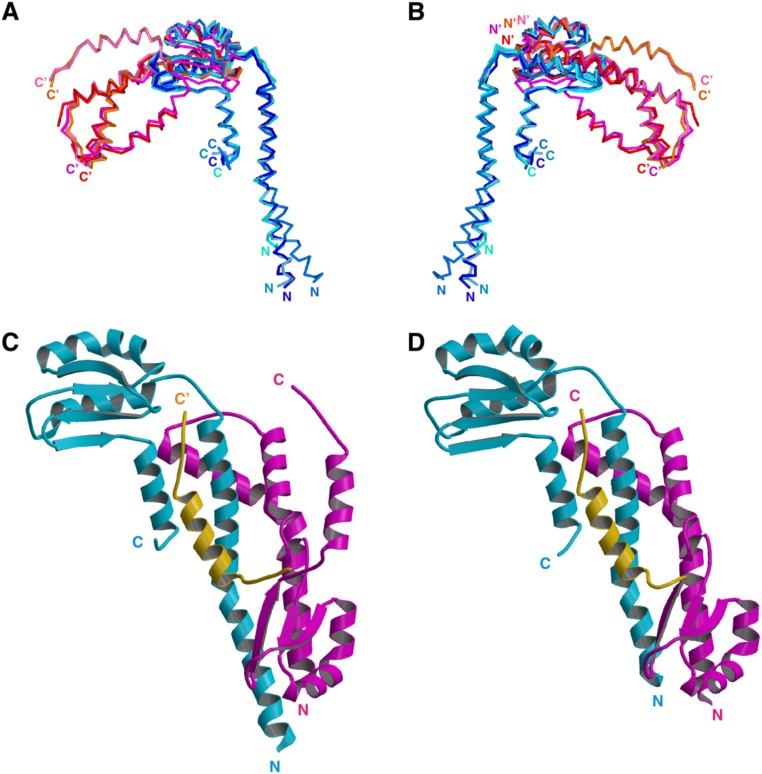
Fig. S3.
Structural variation of FliHC. (A and B) The eight FliHC molecules in the crystallographic asymmetric unit superimposed by fitting the conserved globular domain. (A) Superposition of the Cα backbone trace of FliHC molecules. FliHC-A in trimer-1, -2, -3, and -4 are shown in dark blue, blue, pale blue, and cyan, respectively, and FliHC-B in trimer-1, -2, -3, and -4 are in orange, red, pink, and magenta, respectively. (B) View from the back side of A. The N and C termini are labeled (′ denotes FliHC-B). (C and D) Structural variation in the C-terminal helix of FliHC-B. (C) FliHC2 of trimer-1 shown with the C-terminal helix of FliHC-B of trimer-3 (colored orange). (D) FliHC2 of trimer-2. FliHC-A is colored cyan, FliHC-B is shown in magenta, and the C-terminal helix is highlighted in orange.
Asymmetric Homodimeric Structure of FliHC.
The asymmetric dimer interface is mainly constructed of α1a and α1b of FliHC-A, α1a′, α1b′, and α2′ of FliHC-B (′ denotes FliHC-B hereafter), and the globular structure of FliHC-B (Fig. 2A). α1a and the following eight residues of α1b (Pro-100 to Leu-127) interact with α1a′ (Pro-100 to Ile-123) in a parallel manner, but α1a′ shifts by about 9 Å toward the C-terminal direction relative to α1a with an anticlockwise rotation of 120° around the helix axis. These helices form a loose, right-handed coiled-coil structure. Compared with other right-handed coiled-coil structures, such as the E–G peripheral stalk complex of A/V-ATPases, these helices are arranged nearly side-by-side, and thus the hydrophobic residues are rather exposed on the molecular surface (Fig. 2 B and C). The hydrophobic residues are covered by the exposed hydrophobic core of the partially disrupted globular domain of FliHC-B together with the hydrophobic residues of αs′ (Fig. 2B). The C-terminal half of α1b comes in contact with α1b′ at a relative angle of about 50°. The hydrophobic surface of the amphiphilic helix of α2′ is accommodated in the hydrophobic cleft between α1b and α1b′ (Fig. 2 A and B). These structural features of the dimer interface agree with a previous result showing that the in-frame deletion of residues 101–140, which corresponds to α1, abolishes FliH dimerization (21). α4′ also contributes to the dimer interaction in one of the trimer complexes in the dimeric unit (trimer-1 or -3). α4′ is inlaid into the groove between α1b and α4. The groove of the other trimer (trimer-2 or -4) in the dimeric unit is actually filled by α4′ of the neighboring trimer-2 or -4 related by crystallographic symmetry in the same way as trimer-1 or -3, implying the significance of the interaction (Fig. S3 C and D).
Fig. 2.
Structure of the FliHC homodimer compared with the peripheral stalk complex of A/V-type ATPases. (A) Cα backbone trace of the dimer interface. FliHC-A is shown in orange. α1′a and α1′b′ (′ denotes FliHC-B) of FliHC-B are colored in green, and the other parts of FliHC-B are in cyan. α4 of FliHC-B is removed for better visualization. (B) The hydrophobic surface produced by α1a, α1b, α1a′, and α1b′. The molecular surfaces composed of FliHC-A and α1a′ and α1b′ of FliHC-B are shown with the Cα backbone trace of α2′, αs′, and the following globular domain of FliHC-B. The surfaces of the aromatic and other hydrophobic residues are painted orange and yellow, respectively, and those of the other residues are white. (C) Surface representation of the E–G complex of A-ATPase from T. thermophilus (PDB ID code 3V6I) with the same color coding as B. (D) Ribbon diagrams of the FliHC homodimer and the E–G complex of A-ATPase from T. thermophilus (PDB ID code 3V6I) (Left and Right, respectively). (Middle) Superposition of the two complexes. FliHC-A is shown in cyan, FliHC-B in magenta, the E subunit in green, and the G subunit in orange. (E) View from the back side of D.
FliHC2 Resembles the E–G Complex, the Peripheral Stalk of A/V-Type ATPases.
The FliHC homodimer shows remarkable structural similarities to the E–G heterodimeric peripheral stalk complex of A/V-type ATPases (Fig. 2 D and E) (31, 32). The two dimers can be superimposed with a root-mean-square distance of 2.68 Å for the corresponding 150 Cα atoms. The folding topology of FliHC-A is essentially the same as subunit E of Tt A-ATPase, although the sequence identity of both proteins is only 16% (22/136) (Fig. 1D). The secondary structure arrangement of the globular head group of the E–G heterodimer is almost the same as that of the corresponding region of the FliHC homodimer. α1b of FliHC-B is located in a similar position to the C-terminal helix of subunit G (Fig. 2 D and E). The N-terminal helix of subunit G winds around the N-terminal helix of subunit E to form a right-handed coiled-coil. The orientation of α1a of FliHC-A is nearly identical to that of the N-terminal helix of subunit E, but α1a′ of FliHC-B stands almost in parallel with α1a of FliHC-A. Thus, the helix–helix interaction of the FliHC homodimer is rather loose, and seems to be reinforced by the globular domain of FliHC-B (Fig. 2 B and C).
Interaction Between the FliHC Dimer and FliI.
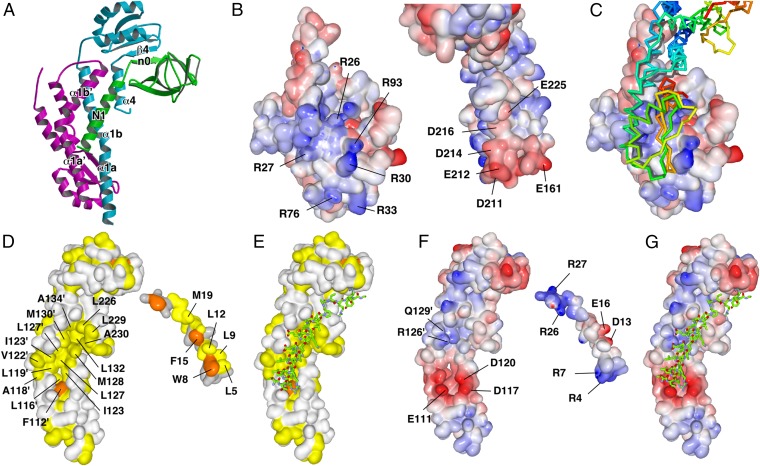
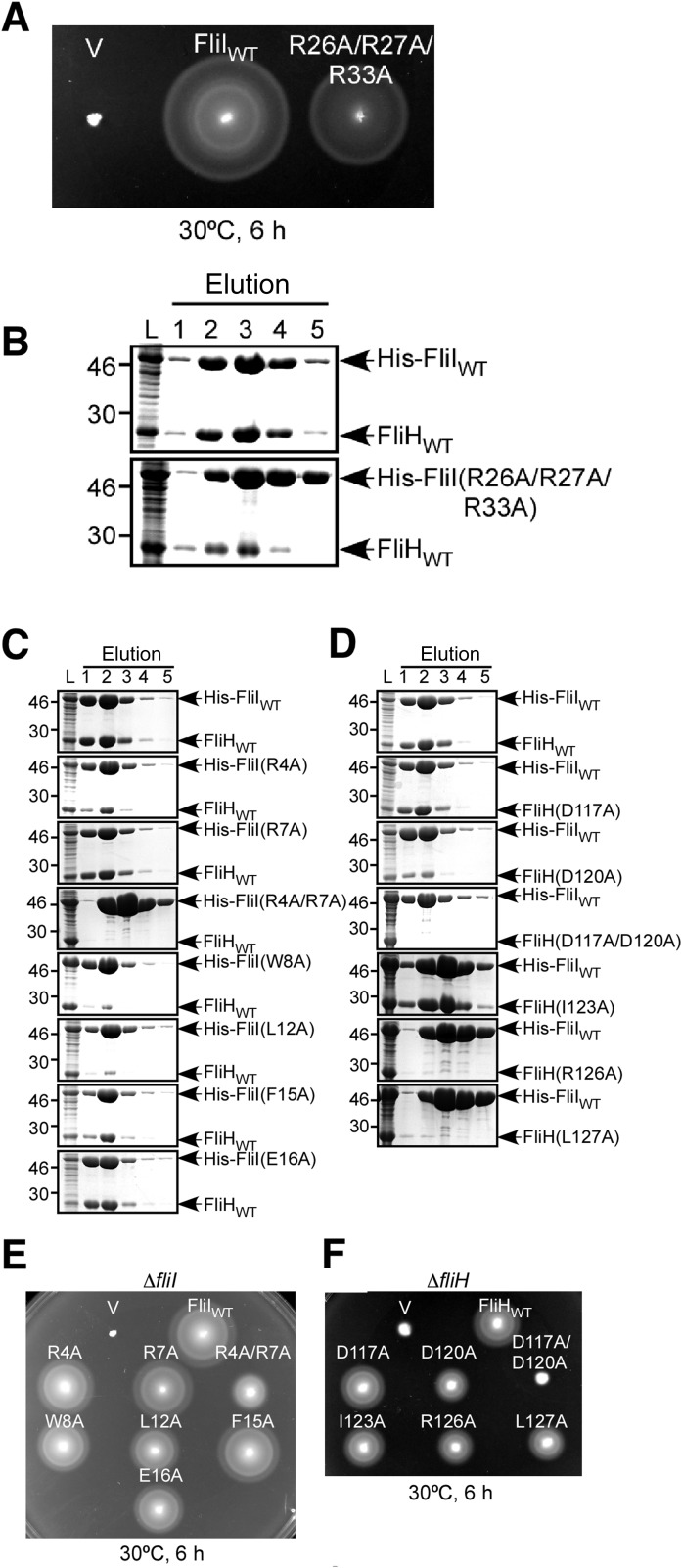
FliHC2 binds to the N-terminal domain of FliI with a buried surface of 1,758 Å2 for the interface. The globular domain of FliHC-A is bound to the top of the N-terminal domain of FliI by creating an intermolecular β-sheet formed by β4 of FliHC-A and β-strand n0 (Val-25 to Tyr-28) of FliI (Fig. 3A and Fig. S4). The interaction surface of FliHC-A is negatively charged with Glu-161, Asp-211, Glu-212, Asp-214, Asp-216, and Glu-225, and its complementary surface of FliI is positively charged with Arg-26, Arg-27, Arg-30, Arg-76, and Arg-93 (Fig. 3 B and C). The electrostatic interactions at the interface stabilize the heterotrimeric structure. In fact, a triple mutant variant of FliI (R26A/R27A/R33A) significantly reduced its binding affinity for FliH, as judged by a pull-down assay with Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, and the motility ring in soft agar of the cells expressing the triple mutant variant was smaller than that of wild-type cells (Fig. S5 A and B). These results suggest the importance of the charge interactions for complex formation.
Fig. 3.
Interaction between FliHC2 and FliI. (A) FliHC2 and the N-terminal region of FliI. FliHC-A, FliHC-B, and FliI are shown in cyan, magenta, and green, respectively. The secondary structure elements involved in the FliH–FliI interaction are labeled. (B and C) Electrostatic interactions between the globular domain of FliHC-A and the N-terminal domain of FliI. (B) The interaction surfaces of the N-terminal domain of FliI (Left) and FliHC2 (Right) colored by electrostatic potential. (C) The complex structure viewed from the same direction as in B, Left. FliHC is shown as a Cα backbone trace with rainbow colors from the N terminus in blue to the C terminus in red. (D and E) Hydrophobic interaction between FliHC2 and the N1 helix of FliI. (D) The interaction surfaces of FliHC2 (Left) and the N1 helix of FliI (Right). Aliphatic and aromatic residues are colored yellow and orange, respectively. (E) The structure of FliHC2 with the N1 helix of FliI viewed from the same direction as in D, Left. The N1 helix of FliI is shown as a Cα backbone trace color-coded as follows: blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen; and green, carbon. (F and G) Electrostatic interactions between FliHC2 and the N1 helix of FliI. (F) The interface of FliHC2 (Left) and the N1 helix of FliI (Right) colored by electrostatic potential. (G) The structure of FliHC2 with the N1 helix of FliI viewed from the same direction as in F, Left. The N1 helix of FliI is shown in the same way as in E.
Fig. S4.
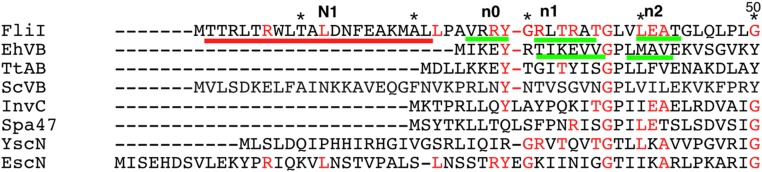
Amino acid sequence alignment of the N-terminal region of the type III ATPases and the B subunit of A/V-type ATPases. The red and green bars indicate α-helices and β-strands, respectively. The conserved residues are colored in red. Every ten residues are denoted by asterisks. FliI form Salmonella typhimurium, FliI; V-ATPase B subunit from Enterococcus hirae, EhVB; A-ATPase B subunit from Thermus thermophilus, TtAB; V-ATPase B subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ScVB; InvC from Salmonella enterica, InvC; Spa47 from Shigella flexneri, Spa47; YscN from Yersinia pestis, YscN; EscN from Escherichia coli O127, EscN.
Fig. S5.
Effect of mutations of residues found in the FliH–FliI interface. (A and B) Effect of a triple mutation of the positively charged residues in the N-terminal domain of FliI on FliH–FliI interaction. (A) Swarming motility of MKM30 (ΔfliI) cells harboring pTrc99A (V), pTrc99A/His-FliI (FliIWT), and pTrc99A/His-FliI(R26A/R27A/R33A) (R26A/R27A/R33A). (B) Interaction of FliH with His-FliI(R26A/R27A/R33A) examined by pull-down assay using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. The eluted fractions were analyzed by CBB (Coomassie Brilliant Blue) staining. (C–F) Effect of mutations of the residues involved in the interaction between FliH and the N1 helix of FliI. (C) Interactions of FliH with His-FliI mutant variants. (D) Interactions of His-FliI with FliH mutant variants. Interactions were examined by pull-down assay using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, and the eluted fractions were analyzed by CBB staining. (E) Motility of fliI mutant cells. Swarming motility of MKM30 (ΔfliI) cells transformed with pET19b-based plasmids: V, pET19b; FliIWT, pMM1701; R4A, pYU21; R7A, pYU22; R4A/R7A, pYU121; W8A, pYU23; L12A, pYU24; F15A, pYU25; E16A, pYU26. (F) Motility of FliH mutant cells. Swarming motility of MKM11 (ΔfliH) cells transformed with pET22b-based plasmids: V, pET22b; FliHWT, pMM307; D117A, pYU102; D120A, pYU104; D117A/D120A, pYU106; I123A, pYU114; R126A, pYU115; L127A, pYU116.
FliHC2 tightly binds to the N-terminal amphiphilic α-helix of FliI (N1; Val-2 to Leu-21), which was not included in the previously determined FliI structure (13). The N1 helix runs along α1b′, and fits into the hydrophobic groove formed by α1b, α1a′, and α1b′ (Fig. 3 A, D, and E). Hydrophobic residues of N1, Trp-8, Leu-12, Phe-15, and Met-19, plunge into the bottom of the hydrophobic groove formed by Ile-123, Leu-127, Met-128, and Leu-132 of FliH α1b, Phe-112′, Leu-116′, and Leu-119′ of FliH α1a′, and Leu-127′, Met-130′, and Ala-134′ of FliH α1b′ (Fig. 3D). Hydrophobic residues of α4 (Leu-226, Leu-229, and Ala-230) also contribute to the interactions with Phe-15 and Met-19 of N1. Other hydrophobic residues of N1, such as Leu-5 and Leu-9, interact with Ala-118′, Val-122′, and Ile-123′ of FliH, which are located on the lateral ridge of the groove (Fig. 3D).
In addition to these hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic interactions greatly contribute to the binding of N1 of FliI to FliH. The N-terminal end of N1 is accommodated in the cleft made up of α1a and α1a′ of FliH. Negatively charged resides of FliH, Glu-111, Asp-117, and Asp-120, are located on both banks of the cleft. These three charged residues of FliH form an electrostatic interaction network with the N-terminal end, Arg-4 and Arg-7 of N1 of FliI (Fig. 3 F and G). These charge interactions seem to be essential for FliHC–FliI heterotrimer formation, because truncation of the N-terminal seven residues of FliI abolishes the binding of FliH (33). Another electrostatic interaction network is found around the middle of N1. Asp-13 and Glu-16 of N1 and Arg-126′ and Gln-129′ of α1b′ are involved in this network, and stabilize the complex structure (Fig. 3F).
Structure-Based Mutational Analyses of Residues Involved in Heterotrimer Formation.
To confirm the contribution of residues found in the interaction surface to heterotrimer formation, we constructed seven alanine-substituted mutant variants of FliI (R4A, R7A, W8A, L12A, F15A, E16A, and R4A/R7A) and examined the complex formation with the FliH homodimer by pull-down assays using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. The amount of coeluted FliH was reduced significantly by the R4A, W8A, L12A, and R4A/R7A mutations and slightly by the R7A, F15A, and E16A mutations, suggesting the contribution of these residues to the complex formation (Fig. S5C). We also prepared six FliH mutants (D117A, D120A, I123A, R126A, L127A, and D117A/D120A) and examined the coelution with His-FliI because these residues were found to interact with those selected for the mutational analysis of FliI. The other FliH residues in the interaction surface were not examined, because their corresponding residues in the other half of the FliH dimer are located on the FliH dimer interface, and therefore the mutation of these residues could affect the dimer formation as well. In agreement with the mutational analysis of FliI, the D120A, R126A, L127A, and D117A/D120A mutant variants showed a lower binding affinity for FliI than the wild-type FliH. However, D117A and I123A bound to FliI at almost the same level as the wild type (Fig. S5D). We further analyzed the motility of the cells expressing these mutant proteins in soft agar. Both double mutants, FliI (R4A/R7A) and FliH (D117A/D120A), indicated severe inhibitory effects on motility in soft agar. The other mutants showed slightly smaller swarm rings than the wild type (Fig. S5 E and F). These results indicate that these residues are involved in complex formation but that the contribution of each residue is rather small.
Discussion
FliI ATPase assembles into a hexameric ring structure. Recent in situ electron cryotomographic studies of the type III secretion system revealed that a globular density corresponding to the ATPase hexamer is located on the axis but below the basal body cup (34, 35). The FliI hexameric ring model was fitted in the density, but there remained extra density around the bottom half of the globular density (35). The FliI ring stably associates with the C ring of the basal body through the interactions of the N-terminal region of FliH with FliN and the C-terminal region of FliH with FliI. Thus, the extra density is thought to be part of FliH (36). Here we built a hexameric ring model of the FliHC2–FliI complex using the hexamer model of F1-ATPase as a template. The shape of the model quite resembles the globular density found in the cytoplasmic side of the basal body (EMDataBank ID code EMD-2521) and FliHC2 filled the extra density, suggesting that the FliHC2–FliI complex is located below the basal body with the C-terminal domains of FliI facing the cell membrane and the C-terminal domain of FliH on the opposite side (Fig. 4). Because the globular density is apart from the bottom of the C ring by more than 100 Å, FliHN should adopt an elongated structure. In fact, previous analytical gel filtration and sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation analyses have shown that the FliH homodimer has an elongated shape (20, 28, 33). The extreme N-terminal region of FliHN is critical for binding to the C ring and is essential for export function (21). The first 10 residues in FliH are crucial to the interaction with FliN, and Trp-7 and Trp-10 directly interact with FliN (11). A recent structural study revealed that the FliH N-terminal 18 residues bind to FliM and FliN in an extended conformation (37). Thus, residues 19–100 in FliH are expected to connect the globular density of the FliHC2–FliI complex and the C ring. Pallen et al. (29) have shown a sequence similarity between the FliH homologs and the E subunits of A/V-type ATPases. Moreover, they also found that the amino acid sequence of FliHN is homologous to that of the b subunit of F1-ATPase, which forms a homodimer with a coiled-coil structure. Secondary structure prediction of FliHN indicated that residues 39–100 have high probability of forming an α-helix and that residues 40–70 are predicted to form a coiled-coil structure. If residues 39–100 adopt an extended α-helix, the estimated length is more than 90 Å. This is long enough to reach the C ring if we also take into account the contribution of residues 19–38 of FliH.
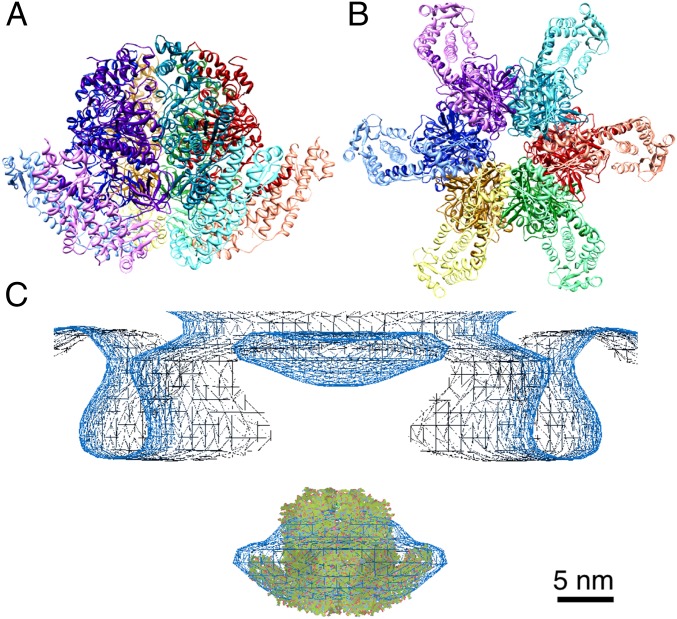
Fig. 4.
Hexameric ring model of the FliHC2–FliI complex. (A) Ribbon diagram of the ring model. Each FliHC2–FliI trimer is shown in a different hue. FliHC2 and FliI in each trimer are indicated in light and dark colors, respectively. (B) View from the bottom of A. (C) The ring model fitted into the globular density below the flagellar basal body obtained by electron cryotomography (35).
Although FliH is needed to form the FliI hexamer below the export gate, it also inhibits FliI oligomerization by forming the stable heterotrimer in solution. In the crystal structure, FliHC does not interact with the possible oligomerization interface of FliI. Therefore, it is still unclear how FliH regulates the FliI oligomerization state. One possible regulatory mechanism is that FliH binding may restrict the movement of the ATPase domain relative to the N-terminal domain to prevent FliI from its oligomerization. In fact, to construct the hexamer model of the FliHC2–FliI complex without collisions, we had to change the relative orientation of the ATPase domains. In F/A/V-type ATPases, the N-terminal domains of the A/B (α/β for F-ATPase) subunits form a rigid ring structure, whereas the orientation of each ATPase domain is different (38, 39). Thus, the flexibility of the ATPase domain relative to the N-terminal domain appears to be important in forming the functional hexamer. In addition, the conformational change of the peripheral stalk is needed for assembly of the A/V-type ATPase complex (40), raising the possibility that the conformational change of FliH affects FliI ring formation. The conformation of FliH may be changed by the interaction with other components, such as the C ring and FlhA, and such conformational changes may allow the movement of the ATPase domain for FliI to assemble into the hexamer.
FliH forms an unusual, globally asymmetric homodimer in the complex. To our knowledge, there is no precedent of such an asymmetric homodimer with distinct subunit structures, except for the N-terminal domain homodimer of nonstructural protein 3 (NSP3) from rotavirus (41). NSP3 binds to the viral mRNA and circularizes it for translation. The NSP3-N is responsible for the binding to mRNA, and its dimerization is important for the strong binding to RNA. The two subunits of NSP3-N are essentially the same in secondary structures but their spatial arrangements are quite distinct, just like the FliHC homodimer. A recent study on asymmetric homodimers showed that the global intrinsic asymmetry is used for strong 2:1 binding to other molecules (42). Because limited proteolysis of purified FliH dimer yielded two different types of cleavage pattern in solution (28), the asymmetry of the FliH dimer seems to be its intrinsic nature. The asymmetric structure may be needed for the FliH dimer to achieve strong binding to FliI.
Although the N-terminal helix of FliI is essential for FliH binding, it is not conserved among type III export ATPases or A/V-type ATPases. The sequence alignment shows a length variation of the N-terminal region (Fig. S4), suggesting a large variation in peripheral stalk binding to the ATPase subunit. The N-terminal regions of InvC, Spa47, and the B subunit of Tt A-ATPase are about 20 residues shorter than that of FliI. They contain residues corresponding to the n0 β-strand but not those corresponding to the N-terminal helix. The N-terminal helix of FliI interacts with the hydrophobic groove formed by α1b, α1a′, and α1b′ of the FliH dimer. The corresponding groove in the E–G complex of T. thermophilus is filled by the C-terminal helix of the E subunit. These observations suggest that the peripheral stalks of these ATPase complexes bind to ATPases only through intersubunit β-sheet formation. The N-terminal regions of EscN, YscN, and the B subunit of yeast V-ATPase, in contrast, are comparable to that of FliI in length and are predicted to contain an α-helix, implying that they bind the peripheral stalk complexes in a similar manner to FliI. Although the hydrophobic groove in the E–G complex of yeast is also occupied by the C-terminal helix of the E subunit, a new hydrophobic groove is made between the C-terminal helices of the G and E subunits (43) [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID codes 4D0L and 4EFA]. Interestingly, this hydrophobic groove interacts with subunit C of the neighboring EGChead complex in the crystal structure of the EGChead complex of yeast V-ATPase (43) (PDB ID codes 4D0L and 4EFA). Therefore, it is possible that the hydrophobic groove binds to the N-terminal region of the B subunit in the yeast V1 complex in a way similar to the FliHC2–FliI complex. It should be noted that the N-terminal helix of the mitochondrial F-ATPase α subunit shows a helix bundle interaction with its peripheral stalk protein OSCP (44) (PDB ID code 2WSS).
The peripheral stalk of A/V-type ATPases is a heterodimer of the E and G subunits, and that of F-type ATPases is composed of the δ subunit and a dimer of b subunits. In contrast, FliH forms a homodimer. We aligned the amino acid sequences of the E and G subunits to FliH on the basis of their structures and compared the sequence similarity of the E and G subunits. The sequence identity was 28.3% (26/92) for the overlapped region (M1–E92 of the E subunit and K29–P120 of the G subunit) and 35% (24/69) for the conserved region (A23–L91 of the E subunit and A51–L119 of the G subunit) (Fig. S6). This sequence similarity suggests that the E–G complex might have been differentiated from a homodimer of an ancestral protein. Similarly, the ATPase ring complex of the flagellar type III secretion system is composed of the homohexamer of FliI, whereas that of A/V-type ATPases is an A3B3 heterohexamer and that of F-ATPases is an α3β3 heterohexamer. These heterohexamers might also have been differentiated from a common ancestral homohexamer. The flagellar type III ATPase complex is composed of only three components, FliH, FliI, and FliJ, and thus involves a much simpler assembly process at the base of the flagellum than those of F/A/V-type ATPases. Therefore, we propose that the flagellar type III ATPase complex may be the closest to the common ancestor of these types of ATPase families.
Fig. S6.
Structure-based sequence alignment of Salmonella FliH (FliH) and T. thermophilus A-ATPase E subunit (TtE) and G subunit (TtG). The overlapped region is underlined and the conserved region is shown in bold lettering. The conserved residues are highlighted in red.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table S1. The FliHC2–FliI complex was expressed and purified as described previously (30). Diffraction data were collected at beamline BL41XU at SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (proposals 2010B1013 and 2010B1901). The statistics of the diffraction data and refinements are summarized in Tables S2 and S3. Full methods are provided in SI Materials and Methods.
Table S1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strains and plasmids | Relevant properties | Source |
| Salmonella | ||
| SJW1368 | ∆cheW-flhD | (50) |
| MKM11 | ∆fliH | (21) |
| MKM30 | ∆fliI | (8) |
| Plasmids | ||
| pET19b | Expression vector | Novagen |
| pET22b | Expression vector | Novagen |
| pTrc99A | Expression vector | GE Healthcare |
| pMM307 | pET22b/FliH | (26) |
| pMM1701 | pET19b/His-FliI | (26) |
| pMM1702 | pTrc99A/His-FliI | (26) |
| pMKM177 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(R26A/R27A/R33A) | This study |
| pMKM186 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(R26A/R27A/R33A) + FliH | This study |
| pMKM1702iH | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH | This study |
| pYU003 | pET-Duet-1/His-FliHC2 + FliI | (30) |
| pYU21 | pET19b/His-FliI(R4A) | This study |
| pYU22 | pET19b/His-FliI(R7A) | This study |
| pYU23 | pET19b/His-FliI(W8A) | This study |
| pYU24 | pET19b/His-FliI(L12A) | This study |
| pYU25 | pET19b/His-FliI(F15A) | This study |
| pYU26 | pET19b/His-FliI(E16A) | This study |
| pYU95 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(R4A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU96 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(R7A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU97 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(W8A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU98 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(L12A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU99 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(F15A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU100 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(E16A) + FliH | This study |
| pYU102 | pET22b/FliH(D117A) | This study |
| pYU104 | pET22b/FliH(D120A) | This study |
| pYU106 | pET22b/FliH(D117A/D120A) | This study |
| pYU108 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(D117A) | This study |
| pYU110 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(D120A) | This study |
| pYU112 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(D117A/D120A) | This study |
| pYU114 | pET22b/FliH(I123A) | This study |
| pYU115 | pET22b/FliH(R126A) | This study |
| pYU116 | pET22b/FliH(L127A) | This study |
| pYU117 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(I123A) | This study |
| pYU118 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(R126A) | This study |
| pYU119 | pTrc99A/His-FliI + FliH(L127A) | This study |
| pYU121 | pET19b/His-FliI(R4A/R7A) | This study |
| pYU123 | pTrc99A/His-FliI(R4A/R7A) + FliH | This study |
Table S2.
X-ray data collection statistics
| Space group | P212121 |
| Cell dimensions, a, b, c, Å | 133.7, 147.3, 164.2 |
| Wavelength, Å | 1.000 |
| Resolution, Å | 60.0–3.0 (3.61–3.0) |
| Rmerge | 8.1 (39.7) |
| I/σI | 5.6 (2.9) |
| Completeness, % | 99.4 (99.6) |
| Redundancy | 4.6 (4.2) |
Values in parentheses are for the highest resolution shell.
Table S3.
X-ray refinement statistics
| Resolution range, Å | 51.3–3.0 (3.04–3.0) |
| No. of reflections working | 61,698 (2,562) |
| No. of reflections test | 3,292 (125) |
| Rw, %* | 21.8 (29.5) |
| Rfree, %† | 27.0 (38.8) |
| Rms deviation bond length, Å | 0.005 |
| Rms deviation bond angle, ° | 1.0 |
| B factors | |
| Protein atoms | 73.2 |
| Ligand atoms | 69.4 |
| Ramachandran plot, % | |
| Most favored | 96.8 |
| Additionally allowed | 3.0 |
| Generously allowed | 0.2 |
| Disallowed | 0 |
| No. of protein atoms | 21,874 |
| No. of ligand atoms | 108 |
| No. of solvent atoms | 0 |
Values in parentheses are for the highest resolution shell.
Rw = Σ || Fo | − | Fc ||/Σ | Fo |.
Rfree = Σ || Fo | − | Fc ||/Σ | Fo |.
SI Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Media.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table S1. L broth (LB) and soft tryptone agar plates were prepared as described (20, 45). Ampicillin was added at a final concentration of 100 μg/mL if needed.
DNA Manipulations.
Site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis method as described in the manufacturer’s instructions (Stratagene). DNA sequencing was performed using BigDye version 3.1 (Applied Biosystems), and the reaction mixtures were analyzed by a 3130 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Purification and Crystallization of the FliHC2–FliI Complex.
Details of the expression, purification, and crystallization of the FliHC2–FliI complex were previously described (30). BL21(DE3) cells carrying a plasmid pYU003, which encodes both His-FliHC2 and FliI, were used for expression of the FliHC2–FliI complex. Crystallization of the FliHC2–FliI complex was conducted by the sitting-drop vapor-diffusion method. Crystals suitable for X-ray data collection were grown from drops prepared by mixing 2 μL protein solution (7 mg mL−1) containing 10 mM Hepes-NaOH (pH 8.0), 10 mM NaCl, and 2 mM ADP with 2 μL reservoir solution containing 0.1 M Hepes-NaOH (pH 7.2), 5% (vol/vol) PEG-400, and 0.1 M magnesium acetate at 285 K. Orthorhombic P212121 crystals of the FliHC2–FliI complex with unit-cell dimensions a = 133.7 Å, b = 147.3 Å, and c = 164.2 Å appeared within 1 wk after microseeding and grew to typical dimensions of 0.1 × 0.05 × 0.2 mm.
Data Collection and Structure Determination.
X-ray diffraction data were collected at synchrotron beamline BL41XU at SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (proposals 2010B1013 and 2010B1901). Details of the X-ray data collection and processing were described previously (30). Crystals were frozen in liquid nitrogen and mounted in helium gas flow at 40 K. The X-ray diffraction data were collected on a Quantum 315 CCD detector (Area Detector Systems), processed with Mosflm (46), and scaled with SCALA (47). The statistics of the diffraction data were described previously (30) and are summarized again in Table S2. The structure was determined by a molecular replacement method with PHENIX (48). The atomic model of FliI (PDB ID code 2DPY) was used as a search model. The atomic model of the FliHc2–FliI complex was constructed with Coot (49) and refined to 3.0 Å with PHENIX (48). During the refinement process, manual modification was repeated using “omit map.” The refinement R factor and the free R factor were converged to 21.8% and 27.0%, respectively. The Ramachandran plot indicated that 96.8% and 3.0% of residues were located in the most favorable and allowed regions, respectively. Structural refinement statistics are summarized in Table S3.
Motility Assay.
Fresh colonies were inoculated on soft tryptone agar plates and incubated at 30 °C to evaluate the swarm ring size.
Pull-Down Assay by Ni-NTA Affinity Chromatography.
SJW1368 cells transformed with a pTrc99A-based plasmid cooverproducing both His-FliI and FliH or its point mutant variants were grown overnight in LB containing ampicillin. The cells were collected by centrifugation (8,000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C), suspended in binding buffer (20 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl) containing 25 mM imidazole, and sonicated (ASTRASON model XL2020 sonicator; Misonix) After centrifugation (13,000 × g, 30 min, 4 °C), the supernatants were loaded onto a nickel-nitrilacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose column (bed volume, 1 mL) preequilibrated with the binding buffer with 25 mM imidazole. After washing the column with 20 mL of the binding buffer with 50 mM imidazole, proteins were eluted with 5 mL of the binding buffer containing 500 mM imidazole.
Acknowledgments
We thank K. Hasegawa at SPring-8 for technical help in the use of the beamlines. This work was supported in part by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grants 15H02386 (to K.I.), 21227006 and 25000013 (to K.N.), and 26293097 (to T.M.) and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology KAKENHI Grants 23115008 (to K.I.) and 24117004, 25121718, and 15H01640 (to T.M.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: The crystallography, atomic coordinates, and structure factors reported in this paper have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, www.pdb.org (PDB ID code 5B0O).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1524025113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Macnab RM. Type III flagellar protein export and flagellar assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1694(1–3):207–217. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Minamino T, Namba K. Self-assembly and type III protein export of the bacterial flagellum. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;7(1–2):5–17. doi: 10.1159/000077865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. Mechanisms of type III protein export for bacterial flagellar assembly. Mol Biosyst. 2008;4(11):1105–1115. doi: 10.1039/b808065h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Minamino T. Protein export through the bacterial flagellar type III export pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843(8):1642–1648. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cornelis GR. The type III secretion injectisome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006;4(11):811–825. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fan F, Macnab RM. Enzymatic characterization of FliI. An ATPase involved in flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(50):31981–31988. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.31981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Claret L, Calder SR, Higgins M, Hughes C. Oligomerization and activation of the FliI ATPase central to bacterial flagellum assembly. Mol Microbiol. 2003;48(5):1349–1355. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Minamino T, et al. Oligomerization of the bacterial flagellar ATPase FliI is controlled by its extreme N-terminal region. J Mol Biol. 2006;360(2):510–519. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen S, et al. Structural diversity of bacterial flagellar motors. EMBO J. 2011;30(14):2972–2981. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.González-Pedrajo B, Minamino T, Kihara M, Namba K. Interactions between C ring proteins and export apparatus components: A possible mechanism for facilitating type III protein export. Mol Microbiol. 2006;60(4):984–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Minamino T, et al. Roles of the extreme N-terminal region of FliH for efficient localization of the FliH-FliI complex to the bacterial flagellar type III export apparatus. Mol Microbiol. 2009;74(6):1471–1483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bai F, et al. Assembly dynamics and the roles of FliI ATPase of the bacterial flagellar export apparatus. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6528. doi: 10.1038/srep06528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Imada K, Minamino T, Tahara A, Namba K. Structural similarity between the flagellar type III ATPase FliI and F1-ATPase subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(2):485–490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608090104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ibuki T, et al. Common architecture of the flagellar type III protein export apparatus and F- and V-type ATPases. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(3):277–282. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kishikawa J, et al. Common evolutionary origin for the rotor domain of rotary ATPases and flagellar protein export apparatus. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Minamino T, Namba K. Distinct roles of the FliI ATPase and proton motive force in bacterial flagellar protein export. Nature. 2008;451(7177):485–488. doi: 10.1038/nature06449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Paul K, Erhardt M, Hirano T, Blair DF, Hughes KT. Energy source of flagellar type III secretion. Nature. 2008;451(7177):489–492. doi: 10.1038/nature06497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Minamino T, Morimoto YV, Hara N, Namba K. An energy transduction mechanism used in bacterial flagellar type III protein export. Nat Commun. 2011;2:475. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Minamino T, Morimoto YV, Kinoshita M, Aldridge PD, Namba K. The bacterial flagellar protein export apparatus processively transports flagellar proteins even with extremely infrequent ATP hydrolysis. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7579. doi: 10.1038/srep07579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Minamino T, Macnab RM. FliH, a soluble component of the type III flagellar export apparatus of Salmonella, forms a complex with FliI and inhibits its ATPase activity. Mol Microbiol. 2000;37(6):1494–1503. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.González-Pedrajo B, Fraser GM, Minamino T, Macnab RM. Molecular dissection of Salmonella FliH, a regulator of the ATPase FliI and the type III flagellar protein export pathway. Mol Microbiol. 2002;45(4):967–982. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Okabe M, Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K, Kihara M. Role of the N-terminal domain of FliI ATPase in bacterial flagellar protein export. FEBS Lett. 2009;583(4):743–748. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Thomas J, Stafford GP, Hughes C. Docking of cytosolic chaperone-substrate complexes at the membrane ATPase during flagellar type III protein export. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(11):3945–3950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307223101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Imada K, Minamino T, Kinoshita M, Furukawa Y, Namba K. Structural insight into the regulatory mechanisms of interactions of the flagellar type III chaperone FliT with its binding partners. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(19):8812–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001866107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Minamino T, Kinoshita M, Imada K, Namba K. Interaction between FliI ATPase and a flagellar chaperone FliT during bacterial flagellar protein export. Mol Microbiol. 2012;83(1):168–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Minamino T, Macnab RM. Interactions among components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and its substrates. Mol Microbiol. 2000;35(5):1052–1064. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hara N, Morimoto YV, Kawamoto A, Namba K, Minamino T. Interaction of the extreme N-terminal region of FliH with FlhA is required for efficient bacterial flagellar protein export. J Bacteriol. 2012;194(19):5353–5360. doi: 10.1128/JB.01028-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Minamino T, González-Pedrajo B, Oosawa K, Namba K, Macnab RM. Structural properties of FliH, an ATPase regulatory component of the Salmonella type III flagellar export apparatus. J Mol Biol. 2002;322(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00754-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pallen MJ, Bailey CM, Beatson SA. Evolutionary links between FliH/YscL-like proteins from bacterial type III secretion systems and second-stalk components of the FoF1 and vacuolar ATPases. Protein Sci. 2006;15(4):935–941. doi: 10.1110/ps.051958806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Uchida Y, Minamino T, Namba K, Imada K. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the FliH-FliI complex responsible for bacterial flagellar type III protein export. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2012;68(Pt 11):1311–1314. doi: 10.1107/S1744309112030801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee LK, Stewart AG, Donohoe M, Bernal RA, Stock D. The structure of the peripheral stalk of Thermus thermophilus H+-ATPase/synthase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(3):373–378. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stewart AG, Lee LK, Donohoe M, Chaston JJ, Stock D. The dynamic stator stalk of rotary ATPases. Nat Commun. 2012;3:687. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Minamino T, Tame JR, Namba K, Macnab RM. Proteolytic analysis of the FliH/FliI complex, the ATPase component of the type III flagellar export apparatus of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 2001;312(5):1027–1036. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hu B, et al. Visualization of the type III secretion sorting platform of Shigella flexneri. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(4):1047–1052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411610112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kawamoto A, et al. Common and distinct structural features of Salmonella injectisome and flagellar basal body. Sci Rep. 2013;3:3369. doi: 10.1038/srep03369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lin T, Gao L, Zhao X, Liu J, Norris SJ. Mutations in the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellar type III secretion system genes fliH and fliI profoundly affect spirochete flagellar assembly, morphology, motility, structure, and cell division. MBio. 2015;6(3):e00579-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00579-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Notti RQ, Bhattacharya S, Lilic M, Stebbins CE. A common assembly module in injectisome and flagellar type III secretion sorting platforms. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7125. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Abrahams JP, Leslie AGW, Lutter R, Walker JE. Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 1994;370(6491):621–628. doi: 10.1038/370621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Arai S, et al. Rotation mechanism of Enterococcus hirae V1-ATPase based on asymmetric crystal structures. Nature. 2013;493(7434):703–707. doi: 10.1038/nature11778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bernal RA, Stock D. Three-dimensional structure of the intact Thermus thermophilus H+-ATPase/synthase by electron microscopy. Structure. 2004;12(10):1789–1798. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Deo RC, Groft CM, Rajashankar KR, Burley SK. Recognition of the rotavirus mRNA 3′ consensus by an asymmetric NSP3 homodimer. Cell. 2002;108(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00632-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Swapna LS, Srikeerthana K, Srinivasan N. Extent of structural asymmetry in homodimeric proteins: Prevalence and relevance. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oot RA, Huang LS, Berry EA, Wilkens S. Crystal structure of the yeast vacuolar ATPase heterotrimeric EGC(head) peripheral stalk complex. Structure. 2012;20(11):1881–1892. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rees DM, Leslie AGW, Walker JE. The structure of the membrane extrinsic region of bovine ATP synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(51):21597–21601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910365106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Minamino T, Macnab RM. Components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and classification of export substrates. J Bacteriol. 1999;181(5):1388–1394. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.5.1388-1394.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Leslie AGW, Powell HR. 2007. Processing diffraction data with Mosflm. Evolving Methods for Macromolecular Crystallography, NATO Science Series, eds Read RJ, Sussman JL (Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands), Vol 245, pp 41–51.
- 47.Winn MD, et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011;67(Pt 4):235–242. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910045749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Adams PD, et al. PHENIX: Building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002;58(Pt 11):1948–1954. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902016657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60(Pt 12 Pt 1):2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ohnishi K, Ohto Y, Aizawa S, Macnab RM, Iino T. FlgD is a scaffolding protein needed for flagellar hook assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1994;176(8):2272–2281. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.8.2272-2281.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]