Abstract
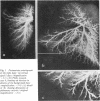
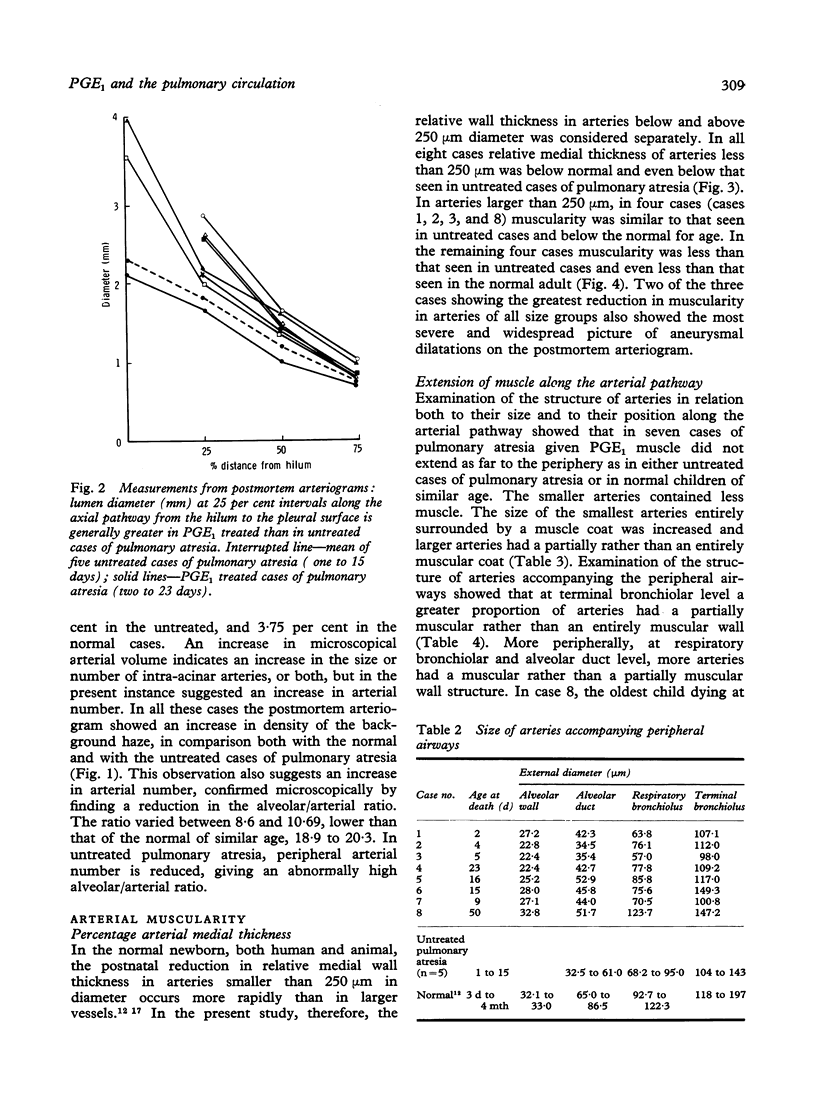
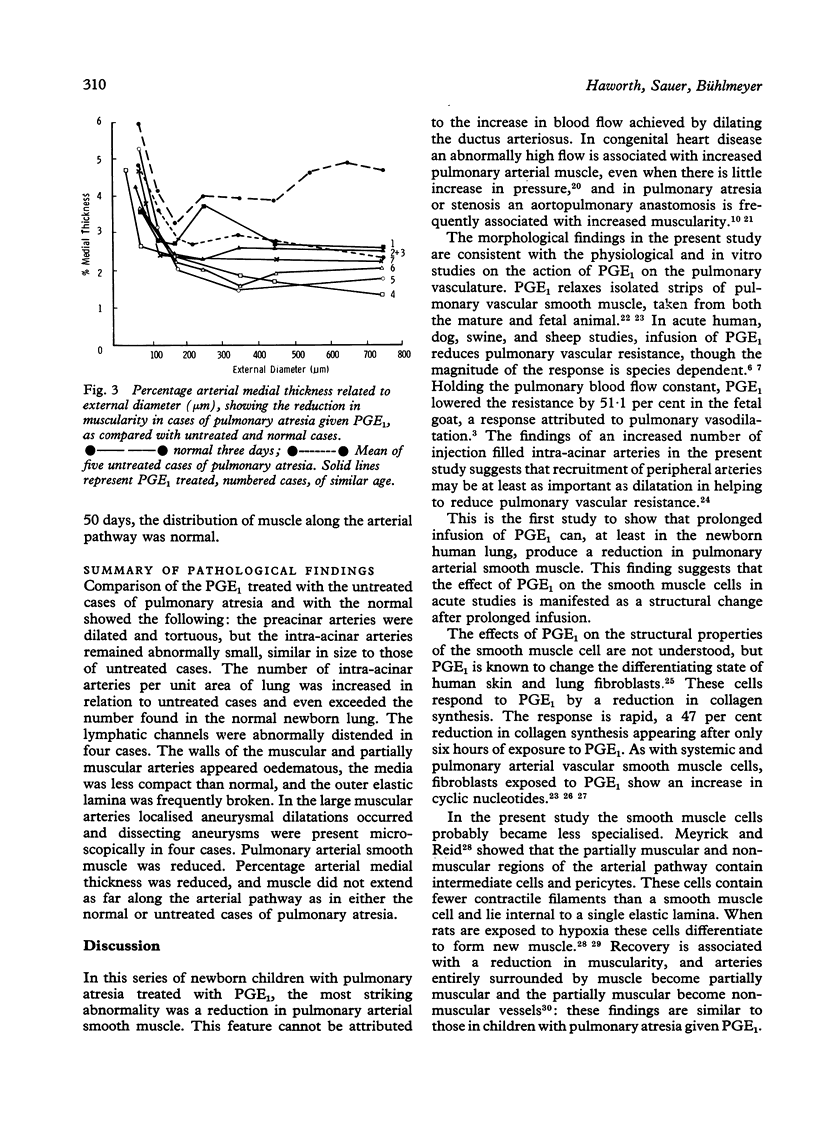
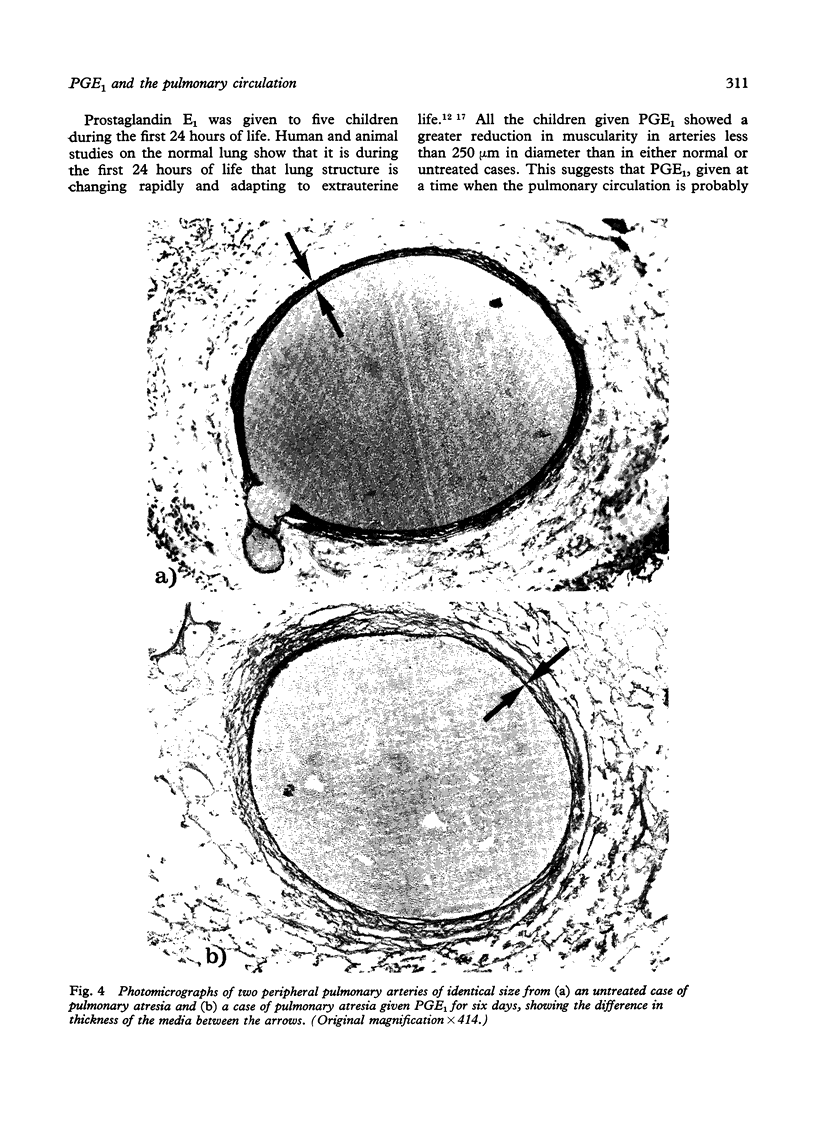
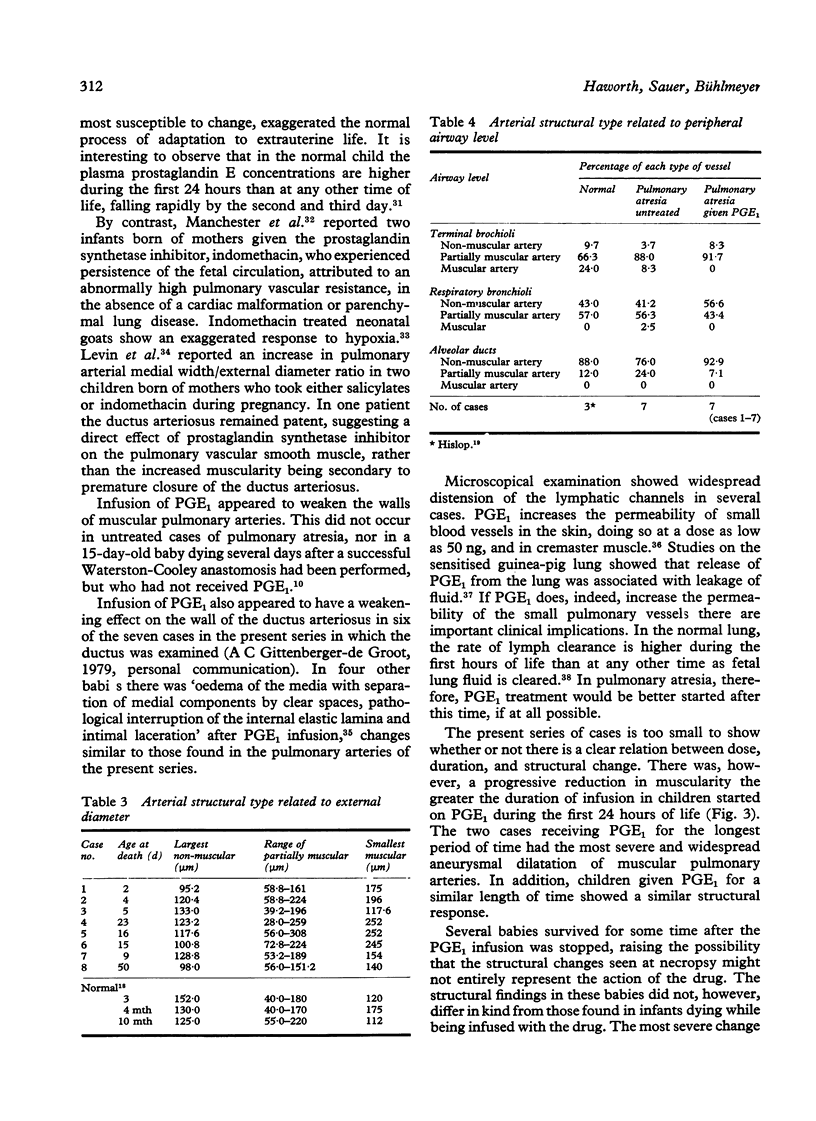
The structural effect of prostaglandin E1 on the pulmonary circulation in pulmonary atresia has been studied by applying quantitative morphometric techniques to the injected and inflated lungs of eight babies who had received prostaglandin E1 for between 30 hours and 12 days. The most striking effect was on the pulmonary arterial smooth muscle. Relative arterial medial thickness was reduced and muscle did not extend as far along the arterial pathway as compared with the normal and with untreated cases of pulmonary atresia, dying at a similar age. The reduction in muscularity tended to increase the longer the duration of infusion. In all cases the thin arterial media was less compact than normal, and localised aneurysmal dilatations occurred, varying in extent and severity between cases. The preacinar arteries were dilated in comparison with the untreated cases, but, by contrast, the intra-acinar arteries remained abnormally small. The number of intra-acinar arteries per unit area of lung was greater in prostaglandin E1 treated than in untreated cases. Infusion of prostaglandin E1 is now the ideal emergency treatment for pulmonary atresia, but the findings in the present study suggest that it should be given for as short a time as possible before the pulmonary blood flow is increased by surgical treatment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum B. J., Moss J., Breul S. D., Crystal R. G. Association in normal human fibroblasts of elevated levels of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate with a selective decrease in collagen production. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3391–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Ekelund L. G., Orö L. Circulatory and respiratory effects of different doses of prostaglandin E1 in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Jan-Feb;75(1):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassin S., Tyler T., Wallis R. The effects of prostaglandin E on fetal pulmonary vascular resistance (38588). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):584–587. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Olley P. M. The response of the ductus arteriosus to prostaglandins. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;51(3):220–225. doi: 10.1139/y73-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G., Reid L. Growth of the alveoli and pulmonary arteries in childhood. Thorax. 1970 Nov;25(6):669–681. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittenberger-de Groot A. C., Moulaert A. J., Harinck E., Becker A. E. Histopathology of the ductus arteriosus after prostaglandin E1 administration in ductus dependent cardiac anomalies. Br Heart J. 1978 Mar;40(3):215–220. doi: 10.1136/hrt.40.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Hamilton R. D., Hopkins N. K. Stimulation of human foreskin fibroblast adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels by prostacyclin (prostaglandin I2). J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1671–1676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth S. G., Reid L. Quantitative structural study of pulmonary circulation in the newborn with pulmonary atresia. Thorax. 1977 Apr;32(2):129–133. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Changes in the pulmonary arteries of the rat during recovery from hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Dec;58(6):653–662. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. New findings in pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Oct;57(5):542–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. New pathological findings in emphysema of childhood. 1. Polyalveolar lobe with emphysema. Thorax. 1970 Nov;25(6):682–690. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.6.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Pulmonary arterial development during childhood: branching pattern and structure. Thorax. 1973 Mar;28(2):129–135. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys P. W., Normand I. C., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Pulmonary lymph flow and the uptake of liquid from the lungs of the lamb at the start of breathing. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):1–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowitz P. J., Joiner P. D., Hyman A. L. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and F2a on the swine pulmonary circulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jan;145(1):53–58. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowitz P. J., Joiner P. D., Hyman A. L., George W. J. Influence of prostaglandins E1 and F2alpha on pulmonary vascular resistance, isolated lobar vessels and cyclic nucleotide levels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Mar;192(3):677–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowitz P. J., Joiner P. D., Hyman A. L. Influence of prostaglandins E1 and F2a on pulmonary vascular resistance in the sheep. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1258–1261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaley G., Weiner R. Prostaglandin E-1: a potential mediator of the inflammatory response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:338–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. L., Fixler D. E., Morriss F. C., Tyson J. Morphologic analysis of the pulmonary vascular bed in infants exposed in utero to prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):478–483. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80453-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester D., Margolis H. S., Sheldon R. E. Possible association between maternal indomethacin therapy and primary pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Oct 15;126(4):467–469. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90640-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maseri A., Caldini P., Harward P., Joshi R. C., Permutt S., Zierler K. L. Determinants of pulmonary vascular volume: recruitment versus distensibility. Circ Res. 1972 Aug;31(2):218–228. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J., Cole B. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and F2-alpha on systemic, pulmonary, and splanchnic circulations in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jul;217(1):222–227. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.1.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olley P. M., Coceani F., Bodach E. E-type prostaglandins: a new emergency therapy for certain cyanotic congenital heart malformations. Circulation. 1976 Apr;53(4):728–731. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.53.4.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Haworth S. G., Castaneda A. R., Nadas A. S., Reid L. M. Lung biopsy in congenital heart disease: a morphometric approach to pulmonary vascular disease. Circulation. 1978 Dec;58(6):1107–1122. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.6.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegler R. L., Walker M. B., Crouch R. H., Christenson P., Jubiz W. Plasma prostaglandin E concentrations from birth through childhood. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):734–737. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling M. B., Elliott R. B. The effects of prostaglandins, prostaglandin inhibitors, and oxygen on the closure of the ductus arteriosus, pulmonary arteries and umbilical vessels in vitro. Prostaglandins. 1974 Nov 10;8(3):187–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczeklik J., Dubiel J. S., Mysik M., Pyzik Z., Krol R., Horzela T. Effects of prostaglandin E1 on pulmonary circulation in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Br Heart J. 1978 Dec;40(12):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/hrt.40.12.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler T., Leffler C., Wallis R., Cassin S. Effects of prostaglandins of the E-series on pulmonary and systemic circulations of newborn goats during normoxia and hypoxia. Prostaglandins. 1975 Dec;10(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler T., Wallis R., Leffler C., Cassin S. The effects of indomethacin on the pulmonary vascular response to hypoxia in the premature and mature newborn goat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Dec;150(3):695–698. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]