Figure 3. DNA damage.
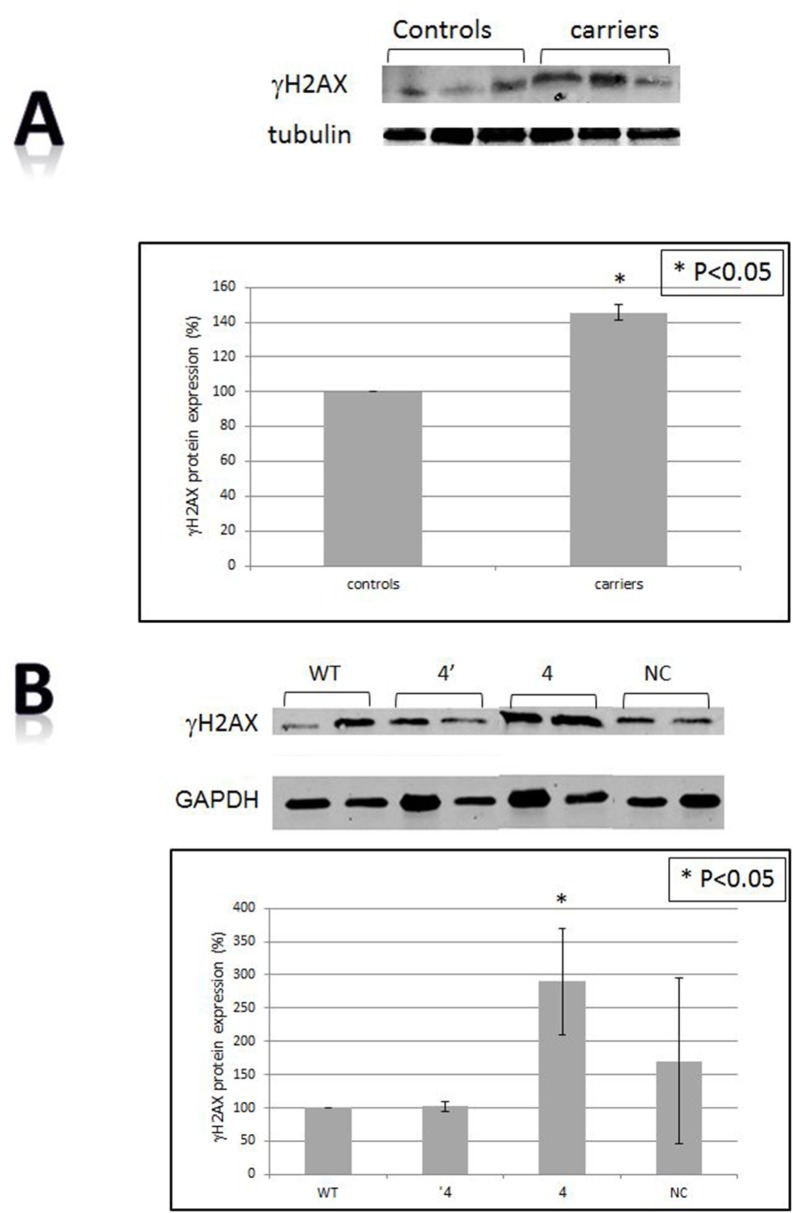
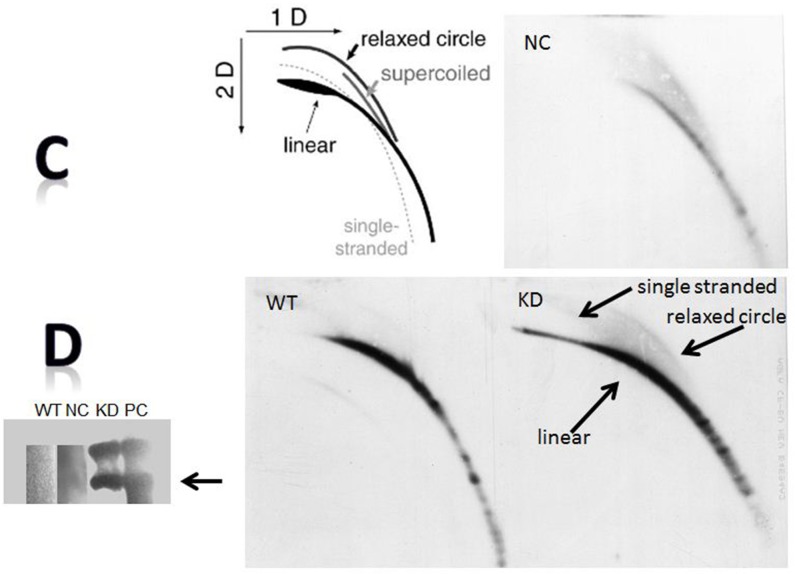
A. The levels of γH2AX in BRCA1/2 mutations carriers by Western blot. The upper panel is an example of a Western blot and the lower one presents quantitation of three independent measurements. Calculations were done by using tubulin signal as the reference protein. B. The levels of γH2AX after BRCA1 silencing as measured by Western blot. The upper panel is an example of a Western blot and the lower one is a quantitation of three independent measurements. Calculations were done by using the GAPDH signal as the reference protein. “WT”- the wild type cells; “NC”- cells transfected with the negative control shRNA plasmid; “4’ “- clone # 4 in which BRCA1 silencing was optimal one month post shRNA transfection. “4” is clone # 4 in which BRCA1 silencing was optimal 6 months post shRNA transfection. C. t-circles in cells after BRCA1 silencing. Genomic DNA was extracted from the different clones and was separated in 2D gel system. Subsequently, gels were blotted onto a positively charged membrane and blotted with a probe containing a complementary sequence to that of telomeric repeats. The upper left panel is a cartoon explaining the migration of t-circles in agarose gels. The arrows point to the linear double stranded DNA, the single stranded telomere and the telomeric circles (relaxed circle). WT”- the wild type intact cells; “NC”- cells transfected with the negative control shRNA plasmid; “KD” is clone # 4 in which BRCA1 silencing was optimal one month post shRNA transfection. D. t-circles formed by phi29 DNA polymerase. Genomic DNA was extracted from the different clones and was subjected to phi29 DNA polymerase which replicated telomere circles to concatameres that migrate as a very heavy band in an agarose gel. PC- a positive control from a telomerase negative cell line, U2OS which is rich in t-circles.