Abstract
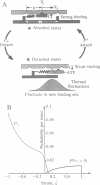
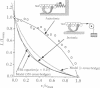
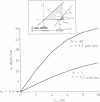
We present a model for single-motor molecules--myosin, dynein, or kinesin--that is powered either by thermal fluctuations or by conformational change. In the thermally driven model, the cross-bridge fluctuates about its equilibrium position against an elastic restoring force. The attachment and detachment of the cross-bridge are determined by modeling the electrostatic attraction between the cross-bridge and the fiber binding sites, so that binding depends on the strain in the cross-bridge and its velocity with respect to the fiber. The model correctly predicts the empirical force-velocity characteristics for populations of motor molecules. For a single motor, the apparent cross-bridge step size per ATP hydrolysis depends nonlinearly on the load. When the elastic energy driving the cross-bridge is generated by a conformational change, the velocity and duty cycle are much larger than is observed experimentally for myosin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brokaw C. J. Computer simulation of movement-generating cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1013–1027. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85752-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaen S., Oiwa K., Shimmen T., Iwamoto H., Sugi H. Simultaneous recordings of force and sliding movement between a myosin-coated glass microneedle and actin cables in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1510–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Hill T. L. Theoretical calculation methods for kinesin in fast axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):431–435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada Y., Sakurada K., Aoki T., Thomas D. D., Yanagida T. Mechanochemical coupling in actomyosin energy transduction studied by in vitro movement assay. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada Y., Yanagida T. The elementary process in the actomyosin energy transduction system. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;315:27–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Chen Y. D., Podolsky R. J. Some self-consistent two-state sliding filament models of muscle contraction. Biophys J. 1975 Apr;15(4):335–372. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85823-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J., Hudspeth A. J., Vale R. D. Movement of microtubules by single kinesin molecules. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):154–158. doi: 10.1038/342154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishijima A., Doi T., Sakurada K., Yanagida T. Sub-piconewton force fluctuations of actomyosin in vitro. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):301–306. doi: 10.1038/352301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. The relation between force and speed in muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1939 Jun 14;96(1):45–64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibler S., Huse D. A. A physical model for motor proteins. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;313(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Caplan S. R., Berg H. C. Dynamics of a tightly coupled mechanism for flagellar rotation. Bacterial motility, chemiosmotic coupling, protonmotive force. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82889-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui T., Ohshima H. A self-induced translation model of myosin head motion in contracting muscle. I. Force-velocity relation and energy liberation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Jun;9(3):248–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01773895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. A model of crossbridge action: the effects of ATP, ADP and Pi. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Jun;10(3):181–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01739809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. A., Sicilia S. The theory of sliding filament models for muscle contraction. I. The two-state model. J Theor Biol. 1987 Jul 7;127(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(87)80158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Warrick H. M., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Quantized velocities at low myosin densities in an in vitro motility assay. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):307–311. doi: 10.1038/352307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Oosawa F. Protein motors and Maxwell's demons: does mechanochemical transduction involve a thermal ratchet? Adv Biophys. 1990;26:97–134. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(90)90009-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Soll D. R., Gibbons I. R. One-dimensional diffusion of microtubules bound to flagellar dynein. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90614-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Arata T., Oosawa F. Sliding distance of actin filament induced by a myosin crossbridge during one ATP hydrolysis cycle. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):366–369. doi: 10.1038/316366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T., Harada Y. Minimum structural unit required for energy transduction in muscle. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;226:277–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]