Abstract
The nasogastric tube (NGT) has become a frequently used device to alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms. Nasogastric tube syndrome (NTS) is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening complication of an indwelling NGT. NTS is characterized by acute upper airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. We report a case of a 76-year-old man with NTS, induced by an indwelling long intestinal tube. He was admitted to our hospital for treatment of sigmoid colon cancer. He underwent sigmoidectomy to release a bowel obstruction, and had a long intestinal tube inserted to decompress the intestinal tract. He presented acute dyspnea following prolonged intestinal intubation, and bronchoscopy showed bilateral vocal cord paralysis. The NGT was removed immediately, and tracheotomy was performed. The patient was finally discharged in a fully recovered state. NTS be considered in patients complaining of acute upper airway obstruction, not only with a NGT inserted but also with a long intestinal tube.
Keywords: Nasogastric tube syndrome, Nasogastric tube, Long intestinal tube, Acute upper airway obstruction, Tracheotomy
Core tip: Nasogastric tube syndrome (NTS) is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening complication of an indwelling nasogastric tube (NGT). NTS is characterized by acute upper airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. We report a case of a 76-year-old man with NTS, induced by an indwelling long intestinal tube. He presented acute dyspnea following prolonged intestinal intubation, and bronchoscopy showed bilateral vocal cord paralysis. The NGT was removed immediately, and tracheotomy was performed to establish a safe airway. NTS be considered in patients complaining of acute upper airway obstruction, not only with a NGT inserted but also with a long intestinal tube inserted.
INTRODUCTION
Nasogastric tube (NGT) is commonly used for a variety of indications since its first description by Hunter in 1790[1]. Despite extensive adaptation, serious complications have occasionally been reported. Iglauer and Molt first described damage to the larynx due to an indwelling enteric tube in a case series in 1939[2]. NTS was later formally defined by Sofferman et al[3] in 1990. This syndrome consists of throat pain, the presence of a NGT, and vocal cord abductor dysfunction[3]. It is encountered only rarely, but it is potentially life threatening.
To our knowledge, in all of the medical literature, a total of 20 case reports (Table 1) and 2 reviews (including the case report described) of NTS have been published through 2014[3-14]. Of these cases, only one case was induced by indwelling a long intestinal tube[6].
Table 1.
Case reports of nasogastric tube syndrome
| Author | Year | Age (yr), sex | Tube | Treatment | Outcome |
| Sofferman et al[3] | 1990 | 28, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Sofferman et al[3] | 1990 | 42, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Sofferman et al[3] | 1990 | 36, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Death |
| Sofferman et al[3] | 1990 | 45, female | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Apostolakis et al[4] | 2001 | 77, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Not recover |
| Apostolakis et al[4] | 2001 | 73, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Leclerc et al[14] | 2002 | 71, female | NGT | Tracheotomy | Not recover (cricoid necrosis) |
| Nehru et al[5] | 2003 | 60, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Sanaka et al[6] | 2004 | 85, male | Long intestinal tube | Removal of long intestinal tube, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Isozaki et al[7] | 2005 | 73, male | NGT | None | Death |
| Isozaki et al[7] | 2005 | 77, female | NGT | Removal of NGT | Death |
| Isozaki et al[7] | 2005 | 79, female | NGT | Undescribed | Undescribed |
| Isozaki et al[7] | 2005 | 72, female | NGT | Undescribed | Undescribed |
| Marcus et al[9] | 2006 | 72, male | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Vielva del Campo et al[12] | 2010 | 70, female | NGT | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
| Ohshima et al[11] | 2010 | 62, female | NGT | Removal of NGT | Full recover |
| Harmon et al[13] | 2014 | 2 mo, male | NGT | Removal of NGT | Full recover |
| Harmon et al[13] | 2014 | 3 mo, female | NGT | Removal of NGT | Full recover |
| Harmon et al[13] | 2014 | 3 mo, male | NGT | Removal of NGT | Full recover |
| Our case | 2015 | 76, male | Long intestinal tube | Removal of NGT, tracheotomy | Full recover |
NGT: Nasogastric tube.
It is hypothesized that early and adequate investigation of throat pain and hoarseness in patients with an indwelling NGT or a long intestinal tube is critical to the diagnosis and timely management of NTS.
CASE REPORT
A 76-year-old man was admitted to the Tsukuba Medical Center Hospital for the treatment of sigmoid colon cancer. The physiological examination, abdominal X-ray (Figure 1A), and computed tomography (Figure 2) indicated colonic obstruction caused by a tumor in the sigmoid colon. Sigmoidectomy was performed urgently, and a long intestinal tube was placed into the jejunum during surgery for bowel decompression (Figure 1B). Six days after tube placement, the patient developed throat pain, acute inspiratory stridor, and oxygen failure. The long intestinal tube was removed immediately, and the patient was intubated to improve the oxygenation failure. When intubating, post-cricoid ulceration and arytenoid edema were observed. To improve the laryngeal injury, the patient was extubated two days later. Because wheezing persisted even after extubation, the patient was submitted bronchoscopy, which showed bilateral vocal cord dysfunction. Tracheotomy was performed for dyspnea. Four weeks following tracheotomy, bronchoscopy showed improving bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Finally, the patient recovered one month after the onset of NTS and was discharged with the tracheotomy closed.
Figure 1.
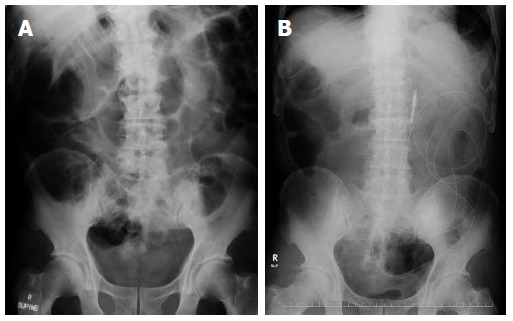
Abdominal X-ray. A: Intestinal obstruction at hospitalization; B: abdominal X-ray after long intestinal intubation.
Figure 2.
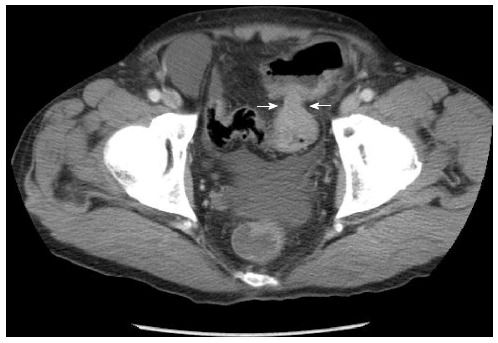
Computed tomography revealed sigmoid colon cancer. The white arrows indicated the site of stenosis due to the cancer.
DISCUSSION
NGT is one of the most commonly used devices in hospital patient care. Most often, NGT is placed for days to weeks before digestive symptoms become manifest. NTS is a rare but potentially fatal complication of nasogastric intubation, comprising acute upper airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. However, due to ignorance of this disease, it is believed that there have been fewer cases reported than have actually occurred. Bilateral vocal cord paralysis is the principal sign that has brought this condition to clinical awareness. We experienced an extremely rare case of NTS induced by indwelling a long intestinal tube[6].
The term NTS was introduced by Sofferman in 1990 to describe the triad of throat pain, nasogastric intubation, and vocal cord paralysis man[3]. Brousseau et al[8] reported that 71% cases of NTS occurred in men, and 29% of cases occurred in women. Harmon et al[13] reported that this syndrome developed in both children and adults. Brousseau et al[8] also estimated a range of NTS onset from 12 h after intubation to 2 wk after extubation. Time to recovery from respiratory symptoms and vocal cords dysfunction has been reported at 1 d to 3 mo[3-6,9,10,12,13]. In our case, the symptoms were present 6 d after long intestinal intubation, and a month was required for complete recovery.
Throat pain is an important symptom. Most often, the discomfort is correctly attributed to the NGT, but its significance is usually minimized. Unless the pain is closely followed by stridor, otolaryngologic consultation can be delayed by several days to more than a week after the initial complaint. Odynophagia and referred otalgia are additional symptoms that coexist within the broad framework of this syndrome.
Diabetes mellitus and immunocompromised states have been suggested as risk factors for NTS[3]. Moreover, time to recovery have been reported to be longer in diabetic patients[3]. In our case, the patient did not have diabetes mellitus. Because the number of NTS case reports is very small, the risk factors for the disease are currently unclear. It is necessary to accumulate further case reports.
It is important first to diagnose NTS accurately. If it is not suspected at the time of intubation, bronchoscopy might be omitted and the correct diagnosis missed. The diagnosis of vocal cord paralysis and a post-cricoid ulcer can be excluded only by direct visualization of the entire post-cricoid area[4]. The most common findings, using the scope of the pharynx and the larynx in all of the published cases, have been bilateral vocal cord paralysis and ulceration of the post-cricoid region[8]. In our case, bronchoscopy showed only bilateral vocal cord paralysis induced by an indwelling long intestinal tube. The assessment of suspected cases of vocal cords paralysis in the setting of NGT or a long intestinal tube should include a full head and neck examination to exclude other causes and bronchoscopy to evaluate vocal cord function, ulceration, and the post-cricoid area, as well as ultrasound or computed tomography of the neck to exclude compressive pathologies.
The mechanisms of NTS can be explained in three parts[3,8,9,12]. First, the mobile laryngeal structures rub against the fixed NGT. Second, while the patient is supine, the cricoid bone compresses the tube against the supine. Finally, tonic contraction of the cricopharyngeus muscle pulls the tube against the delicate and thin post-cricoid mucosa. This combination generates local irritation, edema and eventual ulceration of the tissues, leading to impaired vocal cord function. It is believed that the upper airway is closed by the swelling that occurs due to the above mechanism.
The key treatment of NTS is removal of the NGT or long intestinal tube because it can lead to rapid resolution of respiratory distress. If a patient suffering from NTS requires prolonged bowel decompression, a percutaneous gastrostomy is an option. There have also been cases that improved only with the removal of the tube. However, when removal of the tube does not improve symptoms, tracheotomy will be required. Nehru et al[5] reported that 77% of all NTS cases required tracheotomy. Tracheotomy is preferable to prolonged endotracheal intubation because the latter can delay the recovery of vocal cord function for several months. With regard to other treatments, parenteral corticosteroids should be used to reduce inflammation, and antibiotics should be used to prevent the formation of retro-cricoid abscesses. Moreover, the patient should refrain from oral ingestion for several days, with daily inspection of the larynx to detect reduction in arytenoid edema. If necessary, intravenous fluids, hyperalimentation, or gastrostomy could be required during this interval. In our case, the long intestinal tube was removed immediately, and tracheotomy was performed.
To prevent the onset of NTS, adaptation of the NGT or long intestinal tube insertion should be carefully determined. Moreover, a more narrow tube diameter should be chosen to reduce the pressure with which the tube presses against the organization. Friedman et al[15] reported that midline tube placement generated severe inflammation in the post-cricoid region more often than lateral tube placement. A long intestinal tube with a large diameter might be more easily placed in the midline than a NGT and lead to NTS.
In summary, we have reported a very rare but life-threatening case of the NTS induced by a long intestinal tube. We believe that this is only the second report of a case of NTS associated with a long intestinal tube for postoperative bowel decompression. NTS should be considered in all patients who present with throat pain, hoarseness, or shortness of breath after a nasogastric or a long intestinal intubation. It is hoped that careful attention to these conditions will prevent the full syndrome from becoming manifest. NTS requires prompt treatment, such as removal of the tube and tracheotomy, and close follow-up with bronchoscopy. If patients are properly diagnosed, almost all of them will eventually recover.
COMMENTS
Case characteristics
A 76-year-old man presented acute upper airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis.
Clinical diagnosis
The patients present acute upper airway obstruction following prolonged intestinal intubation, and bronchoscopy showed bilateral vocal cord paralysis.
Differential diagnosis
Diseases that cause acute upper airway obstruction such as the infection and foreign substances may be the main differential diagnosis.
Laboratory diagnosis
Except for desaturation, most laboratory values were within normal limits.
Imaging diagnosis
Bronchoscopy showed bilateral vocal cord paralysis.
Treatment
The key treatment is removal of the nasogastric tube or long intestinal tube. When removal of the tube does not improve symptoms, tracheotomy will be required.
Related reports
Very few cases of nasogastric tube syndrome have been reported in the literature. In most of the cases have been induced by an indwelling the nasogastric tube. The authors report a case induced by an indwelling long intestinal tube.
Term explanation
NTS is defined as nasogastric tube syndrome and NGT is defined as nasogastric tube.
Peer-review
The authors have described a case of nasogastric tube syndrome, which is rare and should, therefore, be reported. The patient was finally discharged in a fully recovered state by treatment with the appropriate diagnosis.
Footnotes
Institutional review board statement: This case report was reviewed and approved by the University of Tsukuba Institutional Review Board.
Informed consent statement: Informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: August 31, 2015
First decision: September 29, 2015
Article in press: December 30, 2015
P- Reviewer: Perakath B S- Editor: Gong ZM L- Editor: A E- Editor: Liu XM
References
- 1.Sofferman RA, Hubbell RN. Laryngeal complications of nasogastric tubes. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1981;90:465–468. doi: 10.1177/000348948109000510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Iglauer S, Molt WF. Severe Injury to the Larynx Resulting from the Indwelling Duodenal Tube. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1939;48:886–904. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sofferman RA, Haisch CE, Kirchner JA, Hardin NJ. The nasogastric tube syndrome. Laryngoscope. 1990;100:962–968. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199009000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Apostolakis LW, Funk GF, Urdaneta LF, McCulloch TM, Jeyapalan MM. The nasogastric tube syndrome: two case reports and review of the literature. Head Neck. 2001;23:59–63. doi: 10.1002/1097-0347(200101)23:1<59::aid-hed9>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nehru VI, Al Shammari HJ, Jaffer AM. Nasogastric tube syndrome: the unilateral variant. Med Princ Pract. 2003;12:44–46. doi: 10.1159/000068162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sanaka M, Kishida S, Yoritaka A, Sasamura Y, Yamamoto T, Kuyama Y. Acute upper airway obstruction induced by an indwelling long intestinal tube: attention to the nasogastric tube syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:913. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200411000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Isozaki E, Tobisawa S, Naito R, Mizutani T, Hayashi H. A variant form of nasogastric tube syndrome. Intern Med. 2005;44:1286–1290. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.44.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brousseau VJ, Kost KM. A rare but serious entity: nasogastric tube syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135:677–679. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2006.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marcus EL, Caine Y, Hamdan K, Gross M. Nasogastric tube syndrome: a life-threatening laryngeal obstruction in a 72-year-old patient. Age Ageing. 2006;35:538–539. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afl042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brousseau VJ, Kost KM. Nasogastric tube syndrome. J Otolaryngol. 2007;36:E96–E97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ohshima M, Hori E, Suzuki A, Katoh H, Itagaki T, Adachi Y, Doi M, Sato S. [Nasogastric tube syndrome suspected at the end of anesthesia] Masui. 2010;59:495–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vielva del Campo B, Moráis Pérez D, Saldaña Garrido D. Nasogastric tube syndrome: a case report. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2010;61:85–86. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harmon J, Balakrishnan K, de Alarcon A, Hart CK. The nasogastric tube syndrome in infants. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;78:882–884. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leclerc C, Perhirin M, De Rugy MG, Valdazo A. [Severe laryngeal injury due to a nasogastric tube] Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2002;21:306–309. doi: 10.1016/s0750-7658(02)00608-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Friedman M, Baim H, Shelton V, Stobnicki M, Chilis T, Ferrara T, Skolnik E. Laryngeal injuries secondary to nasogastric tubes. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1981;90:469–474. doi: 10.1177/000348948109000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


