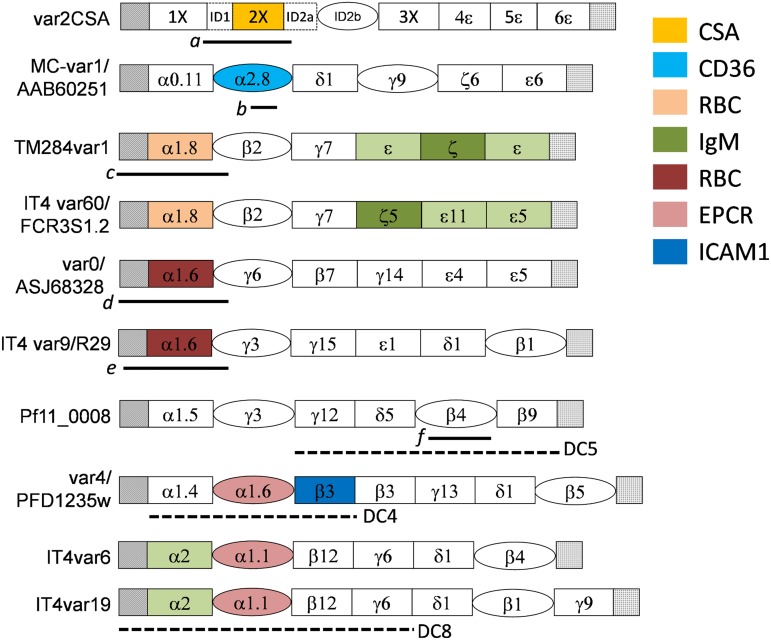
Fig. 2.
The structures of some notable PfEMP1 variants. Duffy-binding domains (DBL) are shown as rectangles and cysteine-rich interdomain regions (CIDR) and the CIDR-like domain of var2CSA are shown as ovals, N-terminal segment and acidic terminal segment (ATS) sequences are shown as hatched and stippled squares, respectively. ID2a and ID2b are interdomain regions within var2CSA that from part of the DBL2X CSA-binding domain (Clausen et al. 2012). Cytoadhesion phenotypes associated with specific domains are shown as colours. Recombinant proteins derived from these PfEMP1 are shown as black horizontal lines under the region of the molecules from which they were derived a, b, c, d, e, f. Domain cassettes are shown as horizontal dashed lines: a, the Id1-DBL2X region can stimulate antibodies in mice that inhibit CSA binding (Bordbar et al. 2012); b, The r179 region of CD36-binding CIDR from the Malayan Camp line used by Baruch et al. (1997) to induce homologous protection in Aotus monkeys; c, the region of the IgM binding, rosette mediating TM284var1 used by Ghumra et al. (2012) to induce cross-reactive, opsonizing antibodies in rabbits; IT4var60 was found to be the rosette mediating var in the well-studied cell line FCR3S1·2 (Albrecht et al. 2011); d,e, constructs from non-IgM-binding, rosette-mediating PfEMP1 found to induce non-cross-reactive, rosette-inhibiting antibodies (Vigan-Womas et al. 2011); (Ghumra et al. 2012); The R29 line was recently found to simultaneously form rosettes and bind to human brain endothelial cells (Adams et al. 2014); f, naturally acquired antibodies to the DBLβ4 domain of pf11_0008 were associated with protection from future malaria in a longitudinal study (Magistrado et al. 2007). A PECAM1-binding domain cassette (DC5) was subsequently identified within this gene (Berger et al. 2013). Also shown are DCs, DC4 found to bind ICAM1 (Bengtsson et al. 2013), identified within var4 previously found to be dominantly expressed in parasites selected for binding to antibodies from semi-immune children (Jensen et al. 2004). Note the additional presence of a CIDRα1.6 within var4, shown to bind to EPCR by Lau et al. (2015) but not by Turner et al. (2013). IT4var6 and IT4var19 were two genes selected for binding to cells lines derived from human brain endothelial cells (Avril et al. 2012; Claessens et al. 2012), within which the DC8 and the EPCR-binding CIDRa1·1 domain was identified (Turner et al. 2013).