Summary
Exosomes are lipid bilayer-enclosed extracellular vesicles (EVs) that contain proteins and nucleic acids. They are secreted by all cells and circulate in the blood. Specific detection and isolation of cancer cell-derived exosomes in circulation is currently lacking. Using mass spectrometry analyses, we identified a cell surface proteoglycan, glypican-1 (GPC1), specifically enriched on cancer cell-derived exosomes. GPC1+ circulating exosomes (crExos) were monitored and isolated using flow cytometry from the serum of cancer patients and mice with cancer. GPC1+ crExos were detected in the serum of patients with pancreas cancer with absolute specificity and sensitivity, distinguishing healthy subjects and patients with a benign pancreas disease from patients with early and late stage pancreas cancer. Levels of GPC1+ crExos correlate with tumor burden and survival in patients pre- and post-surgical tumor resection. GPC1+ crExos from patients and from mice with spontaneous pancreas tumors driven by oncogenic KRAS contained RNA with specific KRAS mutation, and it emerges as a reliable biomarker for the detection of PanIN lesions despite negative signal by MRI in mice. GPC1+ crExos may serve as a potential non-invasive diagnostic and screening tool to detect early stages of pancreas cancer to facilitate possible curative surgical therapy.
Introduction
Exosomes are secreted membrane enclosed vesicles (extracellular vesicles or EVs) of a size range of 50 to 150 nm diameter1. Formed during the inward budding of late endosomes, they develop into intracellular multivesicular endosomes (MVEs)2. During this process, nucleic acids and proteins are encapsulated into exosomes3–6. Exosomes are released into the extracellular space and enter the circulation7,8. Various cell types such as immune cells8, platelets9 or endothelial cells10, release exosomes into the blood stream. Several exosomes-enriched proteins have been described and include members of the tetraspanin family (CD9, CD63 and CD81), members of the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT; TSG101, Alix) and heat shock proteins (Hsp60, Hsp70, Hsp90)11. Epithelial tumor cells secrete exosomes carrying the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)12–14. Melanoma-derived exosomes contain the tumor-associated antigen Mart-1 and tyrosinase-related protein-2 (TYRP2)15–17. Exosomes from gastric, breast and pancreas cancer carry members of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) family18–20. None of these markers are however specific to cancer-derived exosomes. Identification and isolation of cancer specific exosomes in body fluids would aid in the detection and monitoring of cancer and enable specific identification of DNA, RNA and protein content without contamination from non-cancer exosomes. Such possibility could enable the early monitoring of cancer and aid therapy decision.
GPC1 is a cancer exosomes specific protein
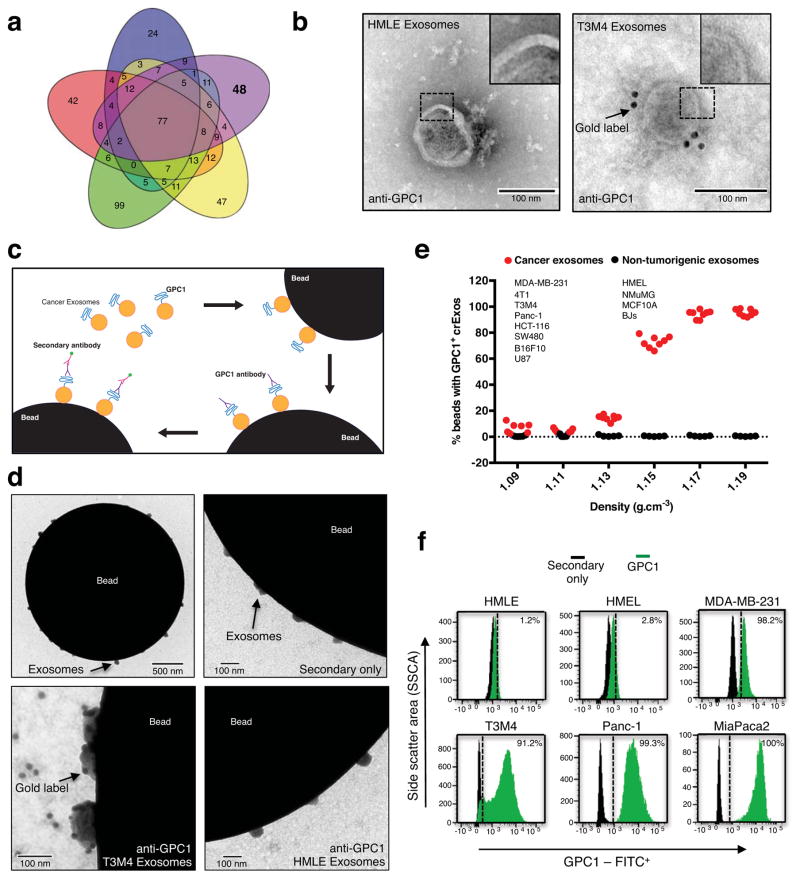
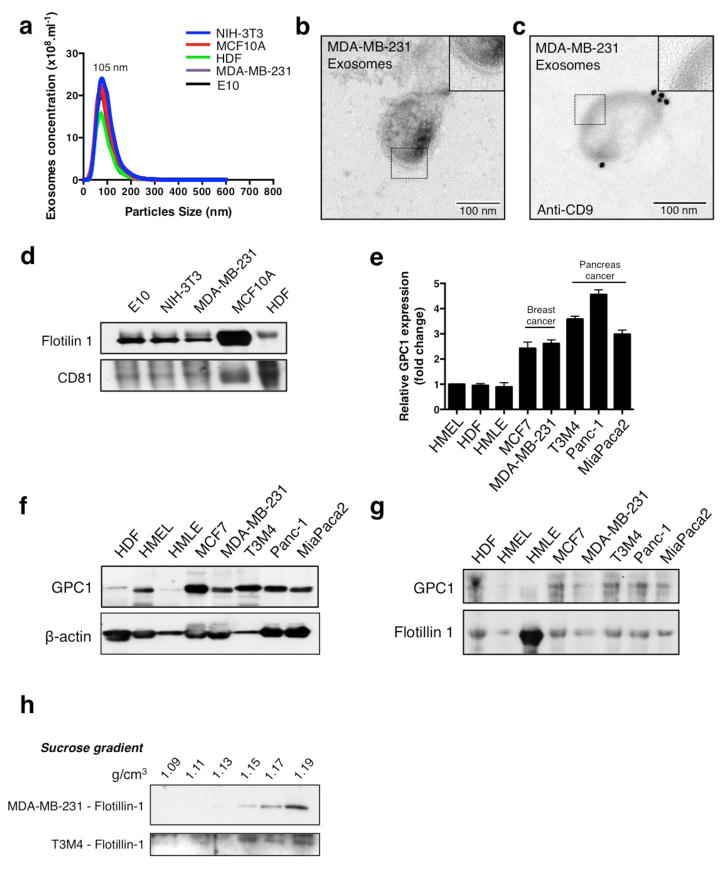
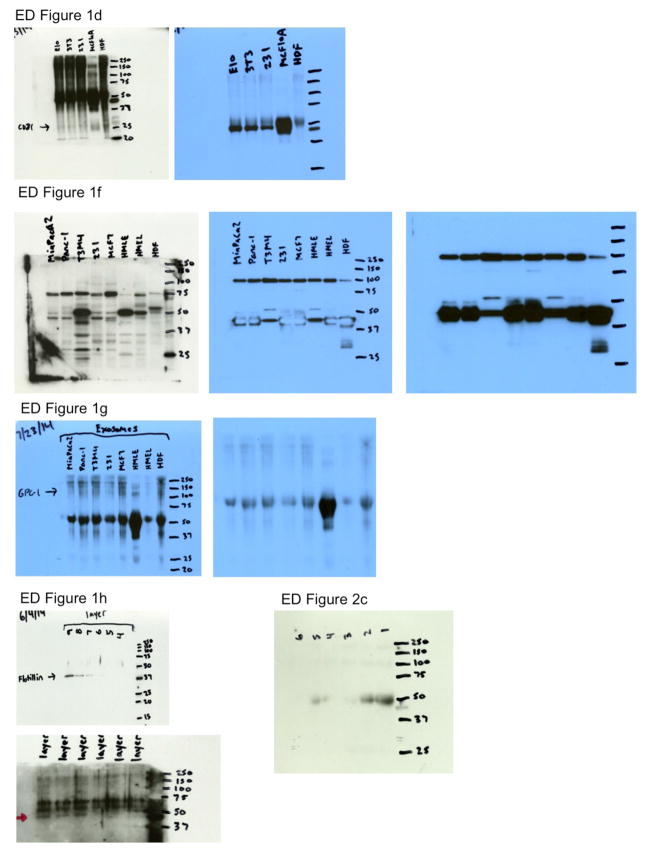
EVs from cancer cells (MDA-MB-231, triple negative human metastatic breast carcinoma), fibroblasts (HDF, human dermal fibroblasts; NIH/3T3, mouse embryonic fibroblasts) and non-tumorigenic epithelial cells (MCF10A, human mammary epithelial cells; E10, mouse lung epithelial cells) were isolated using established ultracentrifugation methods21,22, and called exosomes based on the following observations. NanoSight® nanoparticle tracking analysis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed a range of 105±5 nm and 112±4 nm in diameter, respectively (Extended Data Fig. 1a,b)23. Presence of CD9 on exosomes was shown by immunogold and TEM (Extended Data Fig. 1c) and of flotillin1 and CD81 by immunoblot (Extended Data Fig. 1d, Extended Data Fig. 8)23. The exosomes proteome was evaluated using ultra performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) (Extended Data Table 1)24. Proteins were identified in exosomes derived from different cell types (HDF, NIH/3T3, E10, MCF10A and MDA-MB-231), including the exosomes markers such as TSG101, CD9 and CD63 (total number of proteins identified in exosomes from different cell types were: HDF: 261, NIH/3T3: 171, E10: 232, MCF10A: 214 and MDA-MB-231: 242; Extended Data Table 2). Bioinformatic analyses revealed 48 proteins (25 cytoplasmic, 7 nuclear, 5 transmembrane, 1 membrane-anchored and 7 secreted) as exclusively present in the cancer cell-derived exosomes (MDA-MB-231; Fig. 1a, Extended Data Table 1). Glypican-1 (GPC1) is a membrane anchored protein reported previously as overexpressed in a variety of cancers, including breast and pancreas cancer25,26,27. GPC1 transcripts and protein levels were elevated in several breast and pancreas cancer cell lines compared to non-tumorigenic cells (Extended Data Fig. 1e,f & Extended Data Fig. 8). Therefore, in this study we focused on probing the utility of GPC1 as marker of cancer exosomes. In contrast to exosomes derived from non-tumorigenic cell lines, GPC1 protein was only detected in cancer cell-derived exosomes by immunoblot (Extended Data Fig. 1g & Extended Data Fig. 8). Additionally, GPC1+ exosomes were detected by immunogold TEM in cancer exosomes (T3M4 pancreas cancer line) but not in non-cancer exosomes (HMLE; Fig. 1b).
Figure 1. GPC1 is present specifically on cancer exosomes.
a, Venn diagram of exosomal proteins from NIH/3T3 (blue), MCF 10A (red), HDF (green), E10 (yellow) and MDA-MB-231 (purple) cells. 48 proteins were exclusively detected in exosomes from MDA-MB-231 cells (n=3 protein samples, technical replicates). b, Transmission electron micrographs (TEM; left image) and immunogold TEM (right image) of GPC1. Upper right: digitally zoomed inset (n=2 experiments). c, Diagram of flow cytometry experiment to detect GPC1 on the surface of exosomes bound to beads. d, TEM of bead-bound exosomes and immunogold labeling of GPC1 (n=2 biological replicates). e, Percent beads with GPC1+ exosomes from cancer cells (red) and non-tumorigenic cells (black). f, Flow cytometry analyses of percent beads with GPC1+ exosomes from indicated cell lines (n=2 biological replicates). Negative control: secondary antibody only.
We performed FACS analysis of exosomes coupled to aldehyde/sulphate beads to detect GPC1 protein on their surface (Fig. 1c). Immunogold and TEM identified cancer exosomes at the surface of beads with GPC1 expression while non-tumorigenic exosomes did not exhibit GPC1 expression (Fig. 1d). Exosomes purified using sucrose gradients or ultracentrifugation from cell lines showed GPC1 expression specifically when derived from cancer cell lines (Fig. 1c, e–f; Extended Data Fig. 1h & Extended Data Fig. 8).
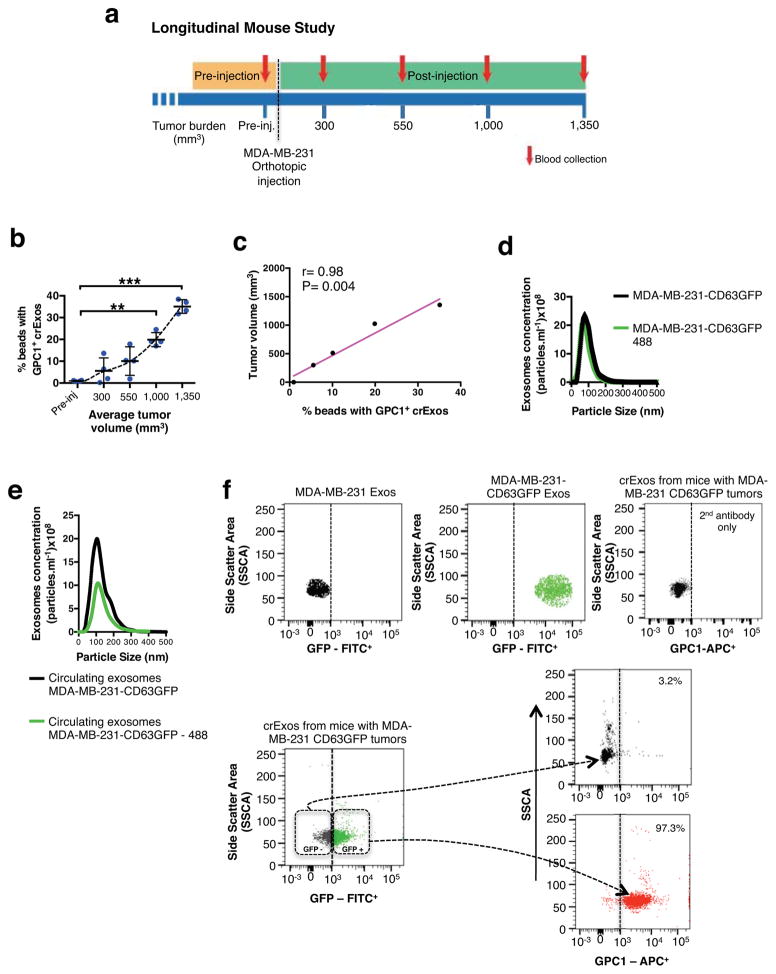
To determine whether GPC1+ exosomes could be isolated from the blood of tumor-bearing mice, we implanted MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in the mammary fat pads of nude mice. The mice were bled prior to cancer cell inoculation, and repeatedly again when tumors reached an average volume of 300, 550, 1000 and 1350 mm3, and circulating exosomes (crExos) were isolated and assessed for the presence of GPC1 (Fig. 2a). The relative percentage of GPC1+ crExos increased proportionally with tumor growth and correlated with tumor burden (Fig. 2b–c; r=0.98, P=0.004). To further confirm the cancer cell origin of GPC1+ crExos, we engineered MDA-MB-231 cells to stably express CD63-GFP fusion protein. CD63 is an established exosomal marker22 and exosomes from these cells (MDA-MB-231-CD63GFP) in culture were uniformly positive for GFP (Fig. 2d). crExos were also collected from mice with orthotopic MDA-MB-231-CD63GFP tumors (~1500 mm3 in size), and a subpopulation of the crExos were GFP+ (Fig. 2e). GPC1 expression was exclusively detected in the GFP+ crExos fraction but not in the GFP− crExos (Fig. 2f).
Figure 2. GPC1+ crExosomes are derived from cancer cells in tumor-bearing mice.
a, Longitudinal blood collection: nude mice with orthotopic MDA-MB-231 tumors (n=4 mice). b, Percentage of beads with GPC1+ exosomes harvested from systemic circulation (crExos) plotted against average tumor volume (n=4 mice, each sample analyzed in technical triplicates for GPC1). ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001. Data is shown as mean ± standard deviation. c, Correlation between tumor volume and percent beads with GPC1+ crExos (Pearson correlation test). d, NanoSight® analyses of exosomes from cultured MDA-MB-231 CD63-GFP cells. Black: all exosomes; green: CD63-GFP+ exosomes (n=3 technical replicates). e, NanoSight® analyses of crExos from mice with MDA-MB-231 CD63-GFP orthotopic tumor. Black: all exosomes; green: CD63-GFP+ exosomes (n=3 technical replicates). f, Flow cytometry analyses of beads with exosomes from cultured MDA-MB-231 (upper left) and MDA-MB-231 CD63-GFP (upper middle) cells, and from crExos of mice with MDA-MB-231 CD63-GFP orthotopic tumors (lower left). Staining of CD63-GFP+ (cancer cell derived) and CD63-GFP− (host derived) crExos for GPC1 (APC+, lower right; n=3 biological replicates and 3 technical replicates). Percent positive beads are listed. Negative control: secondary antibody alone (right upper panel).
GPC1+ circulating exosomes as a biomarker
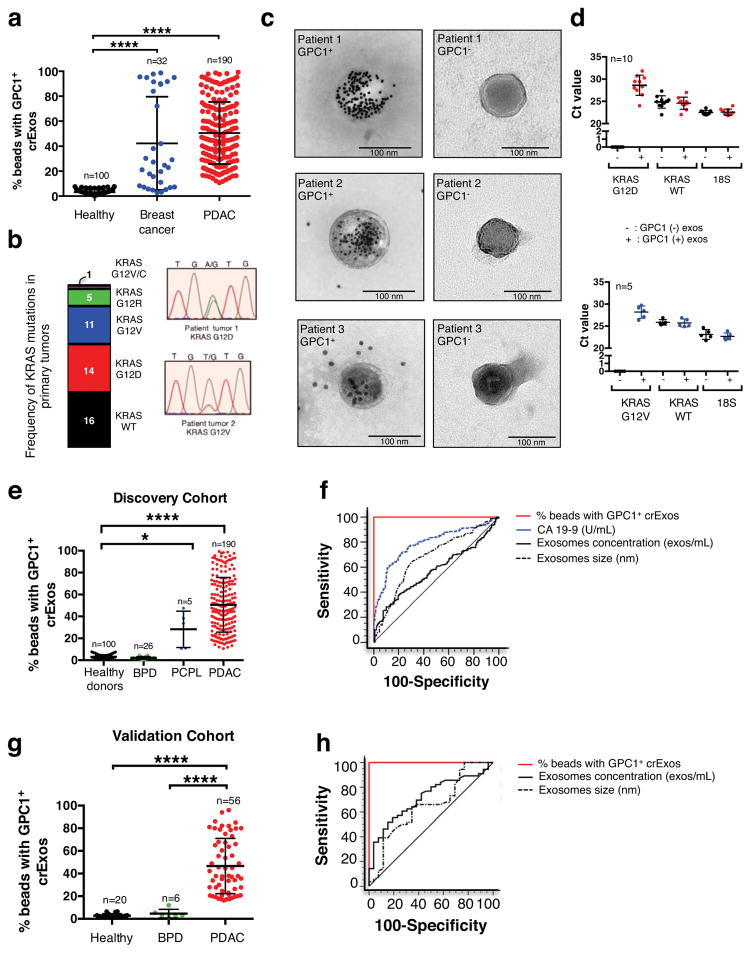
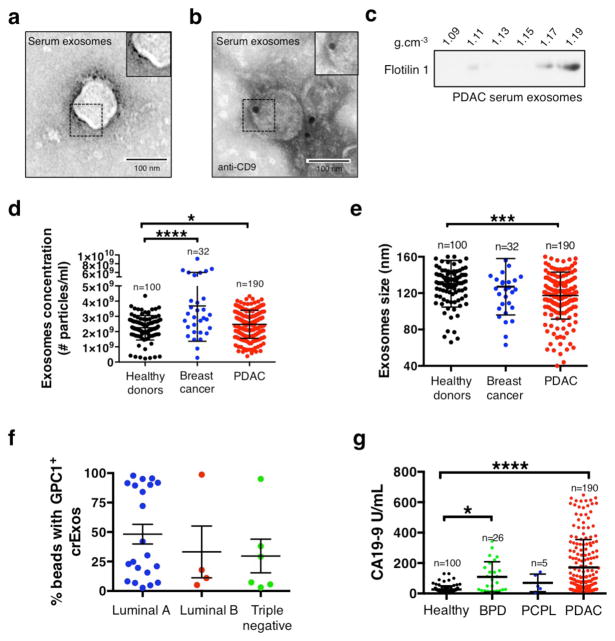
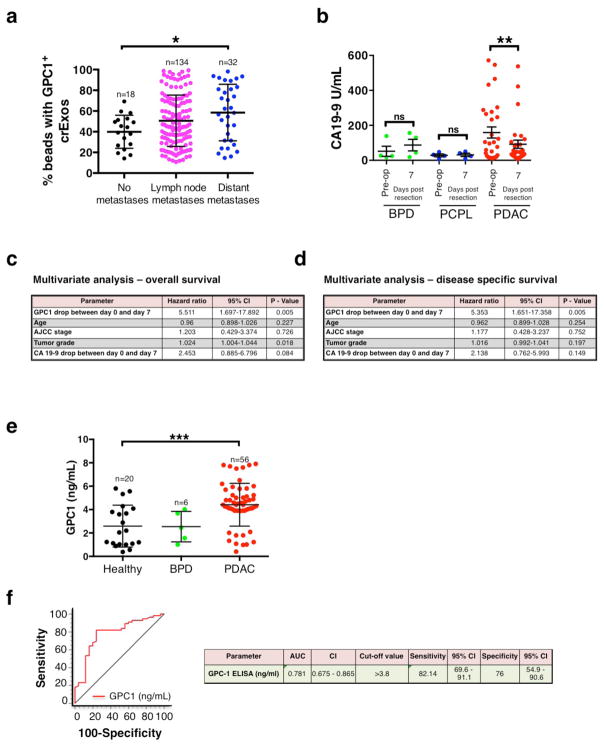
Exosomes derived from cancer cell lines and circulating cancer cell-derived exosomes from tumor-bearing mice were almost exclusively positive for GPC1 (Fig. 1e and Fig. 2f). Next, we isolated crExos from patients with breast cancer (n=32), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, n=190) and healthy donors (n=100) (Patient data is shown in Extended Data Table 3). TEM of crExos isolated from the serum revealed a lipid bilayer and CD9 positivity (Extended Data Fig. 2a–b). crExos isolated using sucrose gradient also showed expression of exosomes marker, flotillin1 (Extended Data Fig. 2c & Extended Data Fig. 8)23,22. The relative concentration of crExos was significantly higher in the sera of cancer patients compared to healthy individuals (Extended Data Fig. 2d), and the average size of PDAC crExos was significantly smaller compared to all other crExos (Extended Data Fig. 2e). Analyses of sera from healthy individuals revealed baseline positivity for GPC1 in crExos, ranging from 0.3 to 4.7% (average of 2.3%; Fig. 3a). We observed that 24 out of 32 (75% of patients) breast cancer patients demonstrated crExos GPC1+ level higher that healthy individuals (P<0.0001; Fig. 3a). Any specific correlation between the level of GPC1+ crExos and breast cancer subtypes was not appreciated in this patient cohort (Luminal A, Luminal B or Triple Negative subtypes; Extended Data Fig. 2f), albeit group size may be too small to conclusively probe such correlation. In contrast, all 190 PDAC crExos revealed levels of GPC1+ crExos higher than levels noted in serum of healthy individuals (P<0.0001; Fig. 3a, Extended Data Fig. 7a–b). These results indicated a strong correlation between GPC1+ crExos and cancer, particularly for PDAC in this analysis. These results encouraged us to perform further analyses to potentially inform on the utility of GPC1+ crExos as a detection and monitoring tool for PDAC.
Figure 3. GPC1+ crExos is a non-invasive biomarker for pancreas cancer.
a, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos in healthy donors (n=100), breast cancer patients (n=32) and patients with PDAC (n=190; ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2, **** P<0.0001). b, Frequency of KRAS mutation in 47 tumor specimens and representative DNA sequencing chromatograms. c, TEM of GPC1 immunogold of crExos from three PDAC patients following flow cytometry isolation of GPC1+ (left column) and GPC1− (right column) crExos (n=3, 3 technical replicates). d, Ct value for KRAS G12D/G12V, KRAS WT mRNA and 18S rRNA expression in GPC1+ (red and blue) and GPC1− (black) crExos (after flow cytometry isolation; n=2, 2 biological replicates and 3 technical replicates each) e, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos, discovery cohort (healthy donors, n=100; patients with a benign pancreatic disease (BPD), n=26; pancreatic cancer precursor lesion (PCPL), n=5; and PDAC patients, n=190; ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2, ** P<0.01, **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates. f, ROC curve of discovery cohort. g, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos, validation cohort (healthy donors, n=20; BPD, n=6; PDAC, n=56; ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates). h, ROC curve of validation cohort. Data is shown as mean ± standard deviation.
GPC1+ crExos contain oncogenic KrasG12D
Exosomes contain DNA and RNA28. KRAS is a frequently mutated gene in pancreas cancer and mutant transcripts have been found in circulation3,29,30. Primary tumor samples of 47 patients with PDAC were sequenced to assess oncogenic KRAS status. Sixteen PDAC tumors contained wild-type KRAS allele, 14 revealed KRASG12Dmutation, 11 with KRASG12Vallele, 5 with KRASG12R allele and 1 with KRASG12V/C mutation (Fig. 3b). Sufficient amount of corresponding serum was available from 10 patients with KrasG12D mutations and 5 with KrasG12V mutation. GPC1+ crExos and GCP1− crExos from the same patient were subjected to immunogold TEM to confirm specific GPC1 expression (Fig. 3c). All 15 GPC1+ crExos with tumor validated oncogenic Kras mutation revealed identical mutation by qPCR analysis of exosomal mRNA using specific primers (Fig. 3d). Wild-type Kras mRNA was found both in GPC1+ and GPC1− crExos, while mutant Kras transcript was only detected in the GPC1+ crExos (Fig. 3d). These results provide further support for the cancer cell origin of the GPC1+ crExos and highlight their potential utility identifying cancer specific genetic defects.
GPC1+ crExos detect early stage pancreas cancer
Further analysis of sera from the discovery cohort of patients revealed that the levels of GPC1+ crExos could distinguish patients with histologically validated pancreatic cancer precursor lesions (PCPL, n=5; Extended Data Table 3) from healthy individuals and patients with benign pancreatic disease (BPD, n=26; Extended Data Table 3, Extended Data Table 4, Fig. 3e). Specifically, the levels of GPC1+ crExos in the PCPL group (intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, IPMN n=5) was consistently higher than the levels of GPC1+ crExos in the healthy donor group, as well as in the BPD group (which includes 18 patients with pancreatitis and 8 with cystic adenomas; Fig. 3e). All patients in PCPL group presented with specific clinical symptoms and exhibited a macroscopic mass imaging using MRI or CT. The BPD group exhibited similar GPC1+ crExos levels (average 2.1% GPC1+ crExos) as healthy individuals (Fig. 3e).
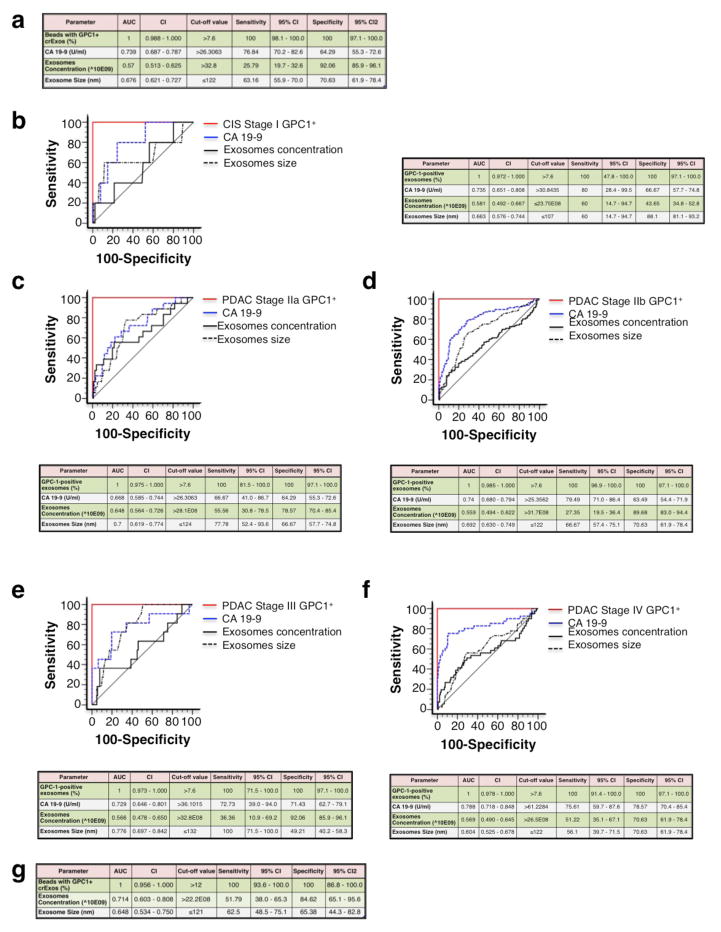
We compared the specificity and sensitivity of GPC1+ crExos detection levels to CA 19-9 levels, a circulating protein currently used as a tumor biomarker for patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma31. CA 19-9 levels were elevated in the serum of patients with PDAC when compared to healthy donors, but CA 19-9 levels were also significantly elevated in the serum of patients with BPD (P<0.0001; Extended Data Fig. 2g). Importantly, CA 19-9 serum levels failed to distinguish patients with PCPL from healthy donors (Extended Data Fig. 2g). When comparing patients with pancreatic cancer from stage I to stage IV, to healthy individuals and patients with BPD, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves show that GPC1+ crExos revealed a near perfect classifier with an AUC of 1.0 (95% CI: 0.988 – 1.0) exhibiting a sensitivity of 100% (95% CI: 98.1–100%) and specificity of 100% (95% CI: 97.1–100%); with a positive predictive value of 100% (95% CI: 98.1–100%) and a negative predictive value of 100% (95%: 86.8–100%; Fig. 3f and Extended Data Fig. 3a–f). In contrast, CA 19–9 was inferior in distinguishing between patients with pancreas cancer and healthy controls (AUC of 0.739, 95% CI: 70.2–82.6%, P<0.001; Fig. 3f and Extended Data Fig. 3a–f). Of note, neither the concentration of exosomes nor the size of exosomes was a valid parameter to stratify patients with pancreas cancer versus control (Fig. 3f and Extended Data Fig. 3a–f). GPC1+ crExos showed a sensitivity and specificity of 100% in each stage of pancreas cancer (carcinoma-in-situ, stage I as well as stages II–IV), supporting its utility as a biomarker for all stages of pancreas cancer progression and its potential use for early detection of pancreas cancer.
Next, the discovery findings were validated using an independent patient cohort, composed of 6 patients with histologically validated BPD (chronic pancreatitis), 56 patients with PDAC and 20 healthy individuals (Extended Data Table 3). GPC1+ crExos distinguished patients with PDAC from healthy individuals and patients with BPD (Fig. 3g). The BPD group exhibited similar GPC1+ crExos levels as healthy individuals (Fig. 3g). In complete agreement with the discovery cohort, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves indicated that GPC1+ crExos (from PDAC, BPD patients and healthy individuals) revealed a near perfect classifier with an AUC of 1.0 (95% CI: 0.956 – 1.0) a sensitivity of 100% (95% CI: 93.6–100%), a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 86.8–100%), a positive predictive value of 100% (95% CI: 93.6–100%), and a negative predictive value of 100% (95%: 86.3–100%; Fig.3h, Extended Data Fig. 3g).
GPC1+ crExos inform pancreas cancer burden
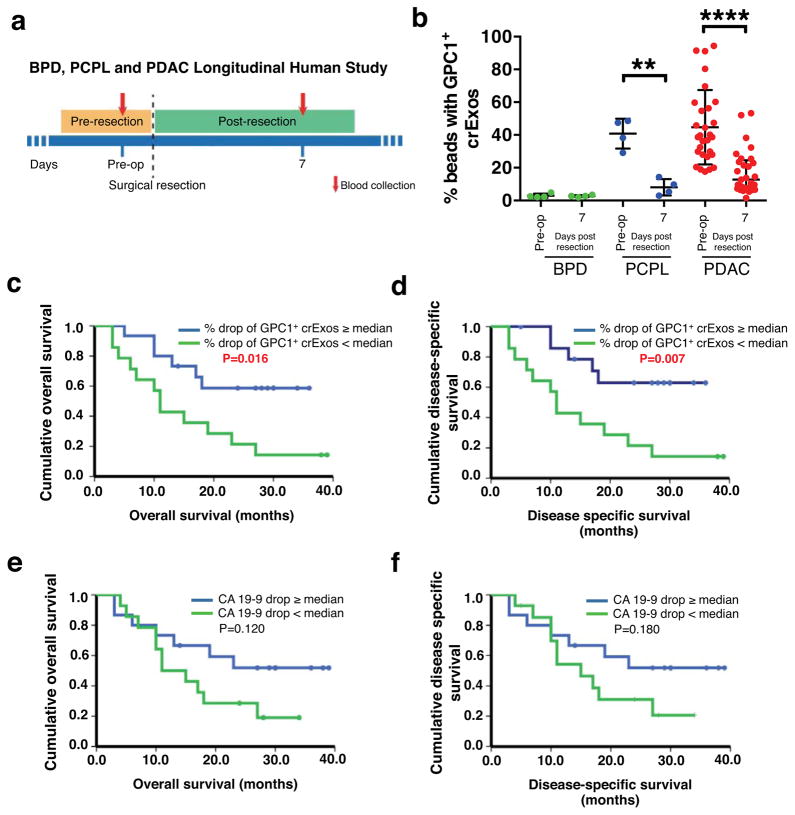
GPC1+ crExos levels correlated with tumor burden in mice (Fig. 2b–c). We next sought to evaluate whether GPC1+ crExos levels could inform on metastatic disease burden of patients with PDAC (Extended Data Table 3). GPC1+ crExos of PDAC patients with distant metastatic disease showed significantly higher levels of bead bound-GPC1+ crExos (average 58.5%) when compared to patients with metastatic disease restricted to lymph nodes (average 50.5%) or no metastases (average 39.9%; Extended Data Fig. 4a). Further, we evaluated GPC1+ crExos in serum of PDAC patients at pre- and post surgery stages (post operative day 7; PDAC n=29, PCPL n=4 and BPD n=4; Fig. 4a). Twenty-eight out of 29 PDAC patients and all PCPL patients with longitudinal blood collections showed a significant decrease in GPC1+ crExos levels following surgical resection (PDAC: P<0.0001; PCPL: P<0.001; Fig. 4b). In contrast, CA 19-9 levels decreased in only 19 out of 29 PDAC patients and in none of the PCPL patients (PDAC: P=0.003; PCPL: P=0.81; Extended Data Fig. 4b). In 4 BPD patients, the levels of neither GPC1+ crExos nor CA 19-9 showed a difference (Fig. 4b and Extended Data Fig. 4b).
Figure 4. Levels of circulating GPC1+ exosomes inform pancreas cancer resection outcome.
a, Longitudinal blood collection pre- (pre-op) and post-operatively (day 7). b, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos from patients with BPD (n=4), PCPL (n=4) or PDAC (n=29) (paired two-tailed Student’s t-test, ** P<0.01, **** P<0.0001). Data is shown as mean ± standard deviation. c–d, Kaplan–Meier curves (log-rank test) displaying overall (c) and disease-specific survival (d) of patients with GPC1+ crExos drop ≥ median (blue) and GPC1+ crExos drop < median (green) drop after resection. e–f, Kaplan–Meier curves (log-rank test) displaying overall (e) and disease-specific survival (f) of patients with a CA 19-9 drop ≥ median (blue) and a CA 19-9 drop < median (green) drop after resection.
To determine the prognostic relevance of GPC1+ crExos in this longitudinal study cohort (Fig. 4a), patients were dichotomized into 2 groups. Group 1 was defined by a decrease of GPC1+ crExos greater or equal (≥) to the median decrease in GPC1+ crExos, and group 2 was defined by a decrease of GPC1+ crExos less (<) than the median decrease of GPC1+ crExos. Group 1 presented with improved overall (26.2 months) and disease specific (27.7 months) survival when compared to group 2 (15.5 months for both overall and disease specific), indicating that a greater decrease in GPC1+ crExos levels after surgery is associated with increased survival (Fig. 4c–d). While a decrease in CA 19-9 levels is noted when comparing pre- and post-resection blood draws, this decrease did not significantly associate with overall and disease-specific survival (Fig. 4e–f and Extended Data Fig. 4b). Using a Cox regression model for a multivariate test to include the decrease in GPC1+ crExos, median age, AJCC stage, tumor grade and CA 19-9 levels, only GPC1+ crExos revealed to be an independent prognostic and predictive marker for disease-specific survival (hazard ratio: 5.353, CI: 1.651–17.358, P=0.005; Extended Data Fig. 4c–d).
Next, we evaluated whether an ELISA for circulating GPC1 could function with the same specificity and sensitivity as GPC1+ crExos. Serum samples of the validation cohort (20 healthy individuals, 6 BPD patients and 56 PDAC patients) were analyzed for circulating GPC1. While GPC1 levels were significantly higher in the PDAC patients when compared to BPD patients and healthy individuals, the sensitivity and specificity of the assay was lower when compared to GPC1+ crExos. The GPC1 ELISA was similar to circulating CA 19-9 assay. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) indicated that GPC1 circulating protein shows an AUC of 0.781 (95% CI: 0.675–0.865) a sensitivity of 82.14% (95% CI: 69.6–91.9%), a specificity of 75% (95% CI: 54.9–90.6%), a positive predictive value of 0.04 (95% CI: 0 – 17.4%), and a negative predictive value of 100% (95%: 94.2 – 100%; Extended Data Fig. 4e–f).
GPC1+ crExos to detect early PanIN lesions
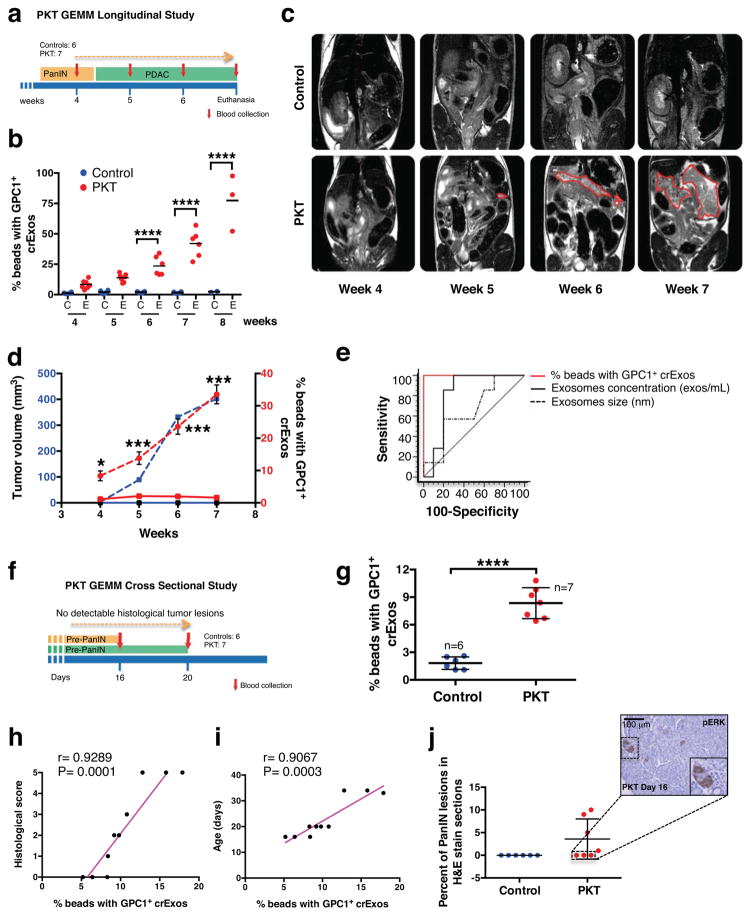
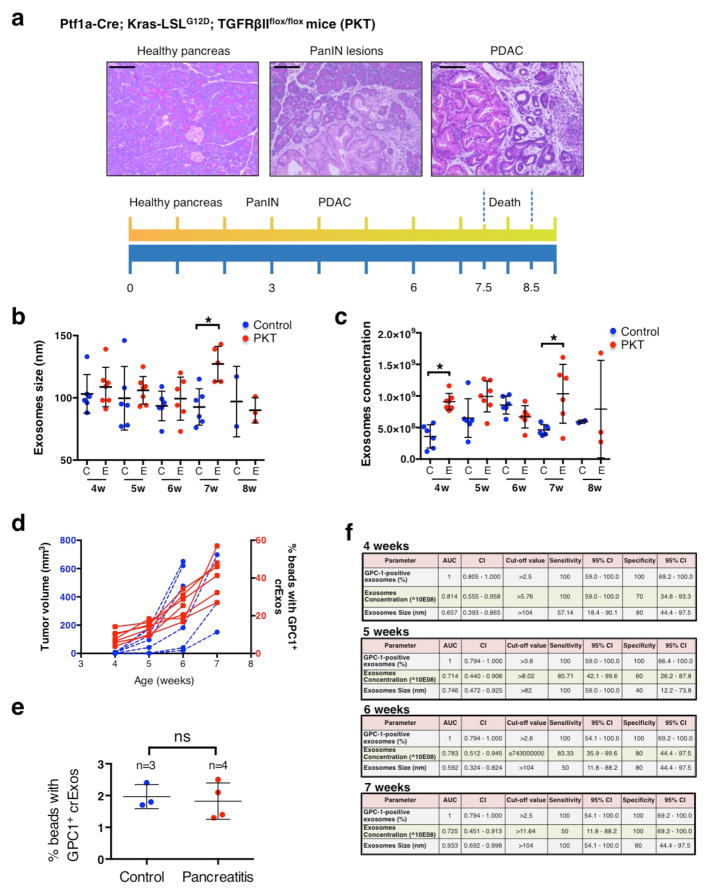
In light of the highly specific and sensitive detection of GPC1+ crExos in pancreas cancer, we next evaluated time course of GPC1+ crExos appearance in the serum relative to pancreas tumor burden. To this end, we employed a genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) for PDAC. The Ptf1acre/+; LSL-KrasG12D/+; Tgfbr2L/L mice (PKT mice)32 develop PDAC with full penetrance that reliably recapitulates the clinical and histopathological features of the human disease32,33. The PKT mice consistently progress from pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) at 4.5 weeks of age and die at 8 weeks of age due to PDAC32,33 (Extended Data Fig. 5a). In a longitudinal study, we bled PKT and littermate control mice repeatedly at 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 weeks of age (n=7 PKT mice and n=6 control mice; Fig. 5a). Three out of 7 PKT mice were euthanized by week 7 along with 4 out of 6 controls, while the remaining 3 PKT mice and 2 controls were euthanized at week 8. At 4 weeks of age PKT mice showed on average an 8.4% GPC1+ crExos, and this increased proportionally with time (and tumor burden) and severity of disease (histopathology), whereas control mice showed an average of 1.2% GPC1+ crExos and this level remained constant with time (Fig. 5b). crExos sizes and concentration did not consistently correlate with disease over time (Extended Data Fig. 5b,c). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), an established imaging modality used for the evaluation of PDAC34, was performed at the same time points when mice were bled to measure GPC1+ crExos (Fig. 5c). When evaluated as a group, GPC1+ crExos levels appeared prior to MRI detectable pancreatic masses (Fig. 5c–d and Extended Data Fig. 5d). GPC1+ crExos size and concentration minimally correlated with pancreas cancer (Extended Data Fig. 5b–c), whereas GPC1+ crExos levels correlated with tumor volume determined by MRI, and appeared to lead the growth of the tumor (Pearson correlation test, r=0.67, P=0.0005, 95% CI: 0.3504–0.8462; Fig. 5c,d and Extended Data Fig. 5d). Importantly, no elevation of GPC1+ crExos was noted in mice cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis, supporting GPC1+ crExos is elevation is pancreas cancer specific (Extended Data Fig. 5e). ROC curve analysis for GPC1+ crExos showed an AUC of 1.0 (95% CI: 0.75–1.0) in PKT mice compared to healthy littermate control mice at all ages evaluated (Fig. 5e and Extended Data Fig. 5f).
Figure 5. GPC1+ circulating exosomes predict pancreas cancer in GEMM.
a, Longitudinal blood collection from control and PKT mice: 4 (n=6 and n=7, respectively), 5 (n=6 and n=7), 6 (n=6 and n=6), 7 (n=6 and n=6) and 8 (n=2 and n=3) weeks of age. b, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos from PKT (red) and control (blue) mice; ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates. c, MRI with tumor encircled in red. d, Tumor volume and percent GPC1+ crExos in PKT mice at indicated age (ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2), *P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001**** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates) e, ROC curve analysis of 4 weeks-old control mice (n=6) and mice with acute pancreatitis (n=4) vs. 4 weeks-old PKT mice (n=7). f, Cross sectional study: blood collected from 16 or 20 days old control (n=6) and PKT (n=7) mice. g, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos from control and PKT (16 – 20 days-old) mice (paired two-tailed Student’s t-test, P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates). h–i, Correlation between histological score (h) or age (i) and percent beads with GPC1+ crExos (Pearson correlation test). j, Relative percent PanIN lesions and representative staining for phosphorylated ERK. Data is shown as mean ± standard deviation.
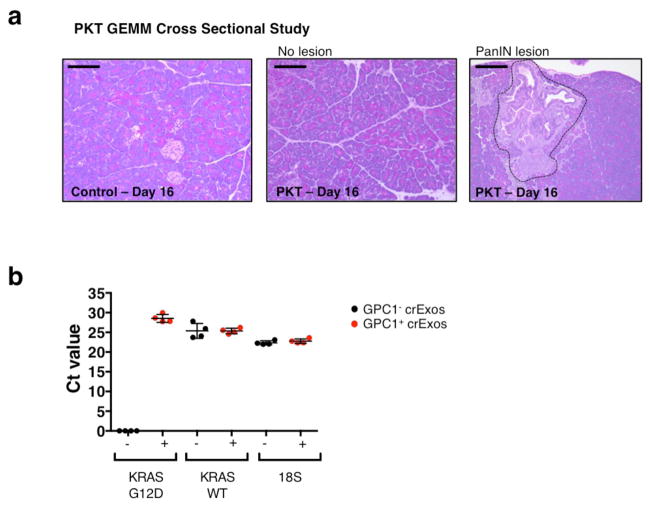
A cross-sectional study was also initiated to assay tumor burden and GPC1+ crExos in PKT mice, as early as 16 and 20 days of age (Fig. 5f). Mice were imaged by MRI, bled and euthanized at these early time points, when mice present with pre-PanIN to early PanIN lesions (Fig. 5f, Extended Data Fig. 6a and Extended Data Table 5). GPC1+ crExos were detected in all PKT mice (PKT: 8.3% average, control: 1.8% average; Fig. 5g and Extended Data Table 5). Histological analysis of PKT mice confirmed pre-PanIN lesions in 4 out of 7 PKT mice, and despite no observed histological lesions in 3 out of 7 PKT mice, GPC1+ crExos predicted future pancreas cancer emergence (Extended Data Table 5). Moreover, we did not observe pancreas-associated masses by MRI in 16 and 20 days old PKT mice. Both histopathological score and age of PKT mice correlated with GPC1+ crExos levels (Fig. 5h–i). Of note, in 4 out of 7 PKT mice with no observed histological lesions, downstream signals for Kras activation, such as phosphorylated ERK (pERK), was detected in the pancreas tissue (Fig. 5j and Extended Data Fig. 6a). We also observed exclusive detection of mutant KrasG12D mRNA in GPC1+ crExos compared to GPC1− crExos (Extended Data Fig. 6b).
Discussion
Tumor-derived exosomes are enriched in GPC1, and GPC1+ crExos exclusively carry mutant Kras mRNA. We show that GPC1+ crExos is a reliable biomarker for detection of early pancreas cancer. GPC1+ crExos are a prognostic marker superior to CA 19-9, the currently employed serum biomarker in pancreas cancer. GPC1+ crExos lead MR imaging as they can be detected in circulation prior to MRI-detectable lesions in GEMM of pancreas cancer.
Routine screening of the general population for a rare cancer such as PDAC using MRI or CT would be prohibitively expensive and associated with a high false positive rate35. GPC1+ crExos detect possibility of pancreas cancer in 16-day-old mice with unremarkable pancreas histology and negative MRI. These results suggest the utility of GPC1+ crExos as a detection and monitoring tool for pancreas cancer, with an emphasis on its application in early detection, a clinical challenge that remains to be addressed.
While oncogenic KRAS mutations are likely driver mutations for pancreas cancer and are detected in early PanIN-1 lesions, it is still estimated that 15 to 20 years may lapse before early PanIN lesions become metastatic PDAC36–38. While this could offer a window for early detection of this disease, PDAC currently presents late with rather non-specific clinical symptoms. Therefore, as many as 80% of patients present with regional and distant metastasis at diagnosis39. Although our understanding of the molecular and genetic details associated with the progression of non-malignant precursor lesions to PDAC is steadily increasing, such knowledge has yet to translate into the development of biomarkers that do not require invasive biopsies. Patients with pancreas cancer exhibit elevated serum levels of CA 19-9, CEA, CA-50, SPan-1, peanut agglutinin, DU-PAN-2, a-fetoprotein, tissue polypeptide antigen and pancreatic oncofetal antigen40. While each of these markers exhibits some utility in tracking biopsy-diagnosed disease they are not tumor specific because they are also elevated in patients with benign diseases of the pancreas. The lack of specific serum-based biomarkers with high degree of sensitivity and specificity and retroperitoneal position of the pancreas further challenges the early detection of pancreas cancer41,42. Pancreatico-duodenectomy (Whipple procedure) can be curative for PDAC patients if tumors are detected early with clear surgical margins43. Due to the late diagnosis of pancreas cancer, only around 15% of patients present with surgically resectable tumors44. Studies comparing stage of disease with outcome following surgery suggests that death rates for PDAC would be reduced if the disease were diagnosed at an earlier stage45.
Specific isolation of exosomes from the serum of cancer patients remains a challenge due to the lack of specific markers that can be used to identify and distinguish cancer exosomes from exosomes produced by other cells. Genetic profiling studies on circulating DNA from cancer patients are cofounded by the fact that the isolated DNA represents all cells of the body, thus making mutation and genetic defects challenging46,47. We previously demonstrated that the DNA in circulation is mainly contained in exosomes6. Therefore a marker for cancer-derived exosomes will significantly increase the sensitivity of detection for low frequency mutations in the circulation. Such mutations are frequently associated with tumor complexity and therapy resistance and relapse, providing a highly specific and sensitive non-invasive tool for genetic monitoring of a tumor. As a proof of concept GPC1+ crExos identified KRAs mutations with 100% correlation with KRAS mutations in the tumor.
Our results provide evidence for GPC1 as a pan-specific marker of cancer exosomes. GPC1 is a cell surface proteoglycan that interacts with many proteins and has diverse functions48. Many cancer cells overexpress glypican-1 with most abundant increase observed in pancreas cancer cells lines and tissue25–27. Many studies have suggested a role of GPC1 as a positive regulator of cancer progression using orthotopic and GEMMs of PDAC49,50. GPC1+ crExos is an attractive candidate for detection and isolation of exosomes in circulation of cancer patients for further genetic analysis of cancer specific alterations in DNA, microRNA, RNA and proteins. Such opportunity offers an unprecedented opportunity for informative early detection of pancreas cancer and help design potential curative surgical options.
Methods
Patient samples and tissue collection
The study was conducted according to the Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK) criteria. The studies using human samples were designed as an explorative study. As there was no interventional approach in this study, a priori power calculation was not applicable. Instead, the number of patients included was assessed based on previous studies investigating the diagnostic relevance of circulating biologicals in pancreatic cancer51.
Serum samples and tissue samples from patients with pancreas cancer, serum samples only from patients with a benign pancreas disease and from healthy donors, who had no evidence of acute or chronic or malignant disease and had no surgery within the past 12 months, were received from the department of General, Visceral and Transplantation Surgery from the University of Heidelberg and from the University Hospital of Dresden after approval by the local institutional review board (Heidelberg: 323/2004, Dresden: EK357112012). The cases were obtained under an IRB-exempt protocol of the MD Anderson Cancer Center (IRB no. PA14-0154). Serum samples from patients with breast cancer were collected at the MD Anderson Cancer Center after approval of the institutional review board (IRB no. LAB10-0690). A written consent for the serum sampling and tumor sampling was obtained pre-operatively from all patients and prior to serum collection from each healthy donor with disclosure of planned analyses regarding potential prognostic markers. The patients included in this study were all consecutive patients who underwent a surgical procedure at the University Hospital of Heidelberg, Germany, at the University Hospital of Dresden, Germany (pancreas disease) or at the MD Anderson Cancer Center (breast cancer). All samples were randomly selected from larger cohorts and were analyzed in a blinded fashion. Unblinding of clinical parameters and corresponding experimental data was performed only after finishing all experiments. Inclusion criteria of patients were a minimum of 18 years of age, histologically verified pancreas cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma), histologically verified benign pancreas disease or breast cancer in a resection specimen, and a negative medical history for any other malignant disease. All blood samples were taken before treatment. Inclusion criteria for healthy control donors were a negative medical history for any malignant disease.
On the day of surgery, 10 ml serum separator tubes were used to collect blood samples before surgical incision. The blood samples were then centrifuged at 2,500g for 10 min to extract the serum, and the serum was stored at −80°C until analyzed. Likewise, blood samples were collected on day 7 after surgery for 29 patients with an adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (PDAC), 4 patients with chronic pancreatitis and 4 patients with an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN).
Patient characteristics and clinical specimens
The pancreatic discovery cohort from the University Hospital of Heidelberg included 190 patients with an adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (PDAC), 18 patients with pancreatitis, 8 patients with a benign serous cystadenoma and 5 patients with an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN). Patients were subjected to surgery between 2006 and 2012 at the Department of General, Visceral, and Transplantation Surgery, University of Heidelberg. Clinical information included age, gender, AJCC tumor stage, tumor size (pT), presence and number of lymph node metastases (pN), tumor grade (G), and treatment with (neo-)/adjuvant chemotherapy. The pancreatic cohort from the University Hospital of Dresden included 56 patients with an adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (PDAC), 6 patients with chronic pancreatitis, and 20 healthy donors. Patients were subjected to surgery between 2007 and 2013 at the Department of Gastrointestinal, Thoracic and Vascular Surgery, University of Dresden. Clinical information included age, gender, AJCC tumor stage, tumor size (pT), presence and number of lymph node metastases (pN), tumor grade (G), and treatment with (neo-)/adjuvant chemotherapy. The breast cancer cohort consisted of 32 women with breast cancer. All breast cancer patients were treated at the MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. Clinical information included age, gender, AJCC tumor stage, tumor size (pT), presence and number of lymph node metastases (pN), tumor grade, and treatment with (neo-)/adjuvant chemotherapy.
Animal Studies
Nude mice (nu/nu) (purchased from Jackson Laboratory) underwent breast pad injections with 0.5 million MDA-MB-231 cells or MDA-MB-231-CD63GFP cells in 20 μl of PBS injected per breast pad. Blood was collected retro-orbitally and exosomes were isolated prior to injection and at tumor volumes of 300, 550, 1000 and 1350mm3. Mice were euthanized when the tumor size reached 1500 mm3 or when severe disease symptoms were present.
The disease progression and genotyping for the Ptf1acre/+; LSL-KrasG12D/+; Tgfbr2L/L (PKT) and the Pdx1cre/+; LSL-KrasG12D/+; p53R172H/+ (KPC) mice was previously described32,33,52. In the PKT longitudinal cohort, retro-orbital blood collections were performed at 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 weeks of age. Mice were euthanized at 8 weeks of age or sooner if severe disease symptoms were noted. Histopathological analysis of mouse pancreas specimen was performed following previously defined criteria4. Four C57BL/6 adult mice were subjected to repeated cerulean injection to induce acute pancreatitis (five hourly repeated i.p. injections of 50 μg cerulein per kg of body weight) and euthanized 24 hrs after injection the last injection. Histological analyses of pancreas of mice was performed according to Hingorani SR et al.52, and an histological score was attributed according to the type of lesions detected: Score 1: PanIN1a, Score 2: PanIN1 a/b, Score 3: PanIN2, Score 4: PanIN3, Score 5: Ductal adenocarcinoma. All mice were housed under standard housing conditions at the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC) animal facilities, and all animal procedures were reviewed and approved by the MDACC institutional animal care and use committee.
Cell lines
The following human cells lines were used: HMLE (American Type Culture Collection – ATCC, Manassas, VA), BJ (ATCC), HDF (ATCC), HMEL (ATCC), MCF-7 (ATCC), MDA-MB-231 (ATTC), Panc-1 (ATTC), SW480 (ATCC), HCT-116 (ATCC), MIA Paca2 (ATCC) and T3M4 cells (Cell Bank, RIKEN BioResource Centre, Japan). The following murine cells lines were used: NIH/3T3 (ATCC), E10 (ATCC), NMuMG (ATTC), 4T1 (ATTC) and B16F10 cells (ATTC). HDF cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 20% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U.ml−1 penicillin and 100 μg.ml−1 streptomycin. HMLE cells and MCF10A cells were grown in DMEM/F12 supplemented with 5% (v/v) horse serum, 100 U.ml−1 penicillin, 100 μg.ml−1 streptomycin, 20 ng.ml−1 EGF, 0.5 mg.ml−1 hydrocortisone, 100 ng.ml−1 cholera toxin and 10 μg.ml−1 insulin. HMEL, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HCT-116, SW480, 4T1, NIH/3T3, E10, U87 and B16F10 cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 100 U.ml−1 penicillin and 100 μg.ml−1 streptomycin. Panc-1, MIA Paca2 and T3M4 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 100 U.ml−1 penicillin and 100 μg.ml−1 streptomycin. NMuMG cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 100 U.ml−1 penicillin, 100 μg.ml−1 streptomycin and 10 μg.ml−1 insulin. All cell lines were kept in a humidifying atmosphere at 5% CO2 at 37°C. MDA-MB-231-CD63GFP cells were engineered by transfection with a plasmid encoding a CD63-GFP fusion protein expressed under the control of a CMV promoter (p-CMV6-CD63-GFP from Origene, RG217238). Transfections were performed using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen).
Exosomes isolation from cells
Exosomes were obtained from supernatant of cells as previously described with some modifications6. Briefly, cells were grown in T225 cm2 flasks in FBS-depleted of exosomes RPMI media until they reached a confluency of 80–90%. Next, the media was collected and centrifuged at 800g for 5 min, followed by a centrifugation step of 2,000g for 10 min to discard cellular debris. Then, the media was filtered using a 0.2 μm pore filter (Syringe filter, Cat. No. 6786-1302, GE Healthcare, UK). The collected media was then ultracentrifuged at 100,000g for 2 hrs at 4°C. The exosomes pellet was washed with 35 ml 1X PBS, followed by a second step of ultracentrifugation at 100,000g for 2 hrs at 4°C. Afterwards, the supernatant was discarded. Exosomes used for RNA extraction were resuspended in 500 μl of Trizol; exosomes used for protein extraction were resuspended in 250 μl of lysis buffer (8M Urea/2.5%SDS, 5 μg.ml−1 leupeptin, 1 μg.ml−1 pepstatin and 1mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride). Exosomes used for flow cytometry analysis (FACS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM; see sections below) and immunogold staining were resuspended in 100 μl 1X PBS. Ten microliters of these exosomes sample were used for NanoSight LM10 (NanoSight Ltd., Minton Park, Amesbury, UK) analysis after dilution 1:100 in 1X PBS.
Exosomes isolation from human serum samples
As previously described, 250 μl of cell-free serum samples were thawed on ice6. Serum was diluted in 11 ml 1X PBS and filtered through a 0.2 μm pore filter. Afterwards, the samples were ultracentrifuged at 150,000g overnight at 4°C. Next, the exosomes pellet was washed in 11 ml 1X PBS followed by a second step of ultracentrifugation at 150,000g at 4°C for 2 hrs. The supernatant was discarded and pelleted exosomes were resuspended in 500 μl of Trizol for RNA analyses; or in 250 μl of lysis buffer (8M Urea/2.5%SDS, 5 μg.ml−1 leupeptin, 1 μg.ml−1 pepstatin and 1mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride) for protein analyses. Exosomes used for flow cytometry analysis (FACS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM; see sections below) and immunogold staining were resuspended in 100 μl 1X PBS. Ten microliters of this exosomes sample were used for NanoSight LM10 (NanoSight Ltd., Minton Park, Amesbury, UK) analysis after Nano dilution 1:100 in 1X.
Immunogold Labeling and Electron Microscopy
Fixed specimens at an optimal concentration were placed onto a 400 mesh carbon/formvar coated grids and allowed to absorb to the formvar for a minimum of 1 minute. For immunogold staining the grids were placed into a blocking buffer for a block/permeabilization step for 1 hr. Without rinsing, the grids were immediately placed into the primary antibody at the appropriate dilution overnight at 4°C (1:300 anti-CD9 ab92726, Abcam and anti-GPC1 PIPA528055, Thermo Scientific). As controls, some of the grids were not exposed to the primary antibody. The following day, all the grids were rinsed with PBS then floated on drops of the appropriate secondary antibody attached with 10 nm gold particles (AURION, Hatfield, PA) for 2 hrs at room temperature. Grids were rinsed with PBS and were placed in 2.5% Glutaraldehyde in 0.1M Phosphate buffer for 15 min. After rinsing in PBS and distilled water the grids were allowed to dry and stained for contrast using uranyl acetate. The samples were viewed with a Tecnai Bio Twin transmission electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) and images were taken with an AMT CCD Camera (Advanced Microscopy Techniques, Danvers, MA).
Sucrose gradient
Sucrose density gradients were performed to purify exosomes. Exosomes were resuspended in 2 ml of HEPES/sucrose stock solution (2.5M sucrose, 20mM HEPES/NaOH solution, pH 7.4). The exosomes suspension was overlaid with a linear sucrose gradient (2.0-0.25M sucrose, 20mM HEPES/NaOH, pH 7.4) in a SW41 tube (Beckman). The gradients were ultracentrifuged for 16 hrs at 210,000g at 4°C. Gradient fractions of 1 ml were collected from top to bottom and densities of each fractions were evaluated using a refractometer. Next, the exosomes pellets were washed in 1X PBS followed by a second step of ultracentrifugation at 150,000g at 4°C for 2 hrs. Exosomes pellets were resuspended in Laemmli buffer and/or PBS for further immunoblot and flow cytometry analysis.
Flow cytometry analysis of exosomes-bound beads
Exosomes were attached to 4 μm aldehyde/sulfate latex beads (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) by mixing 30 μg exosomes in a 10 μl volume of beads for 15 min at room temperature with continuous rotation. This suspension was diluted to 1 ml with 1X PBS and left for 30 min rotating at room temperature. The reaction was stopped with 100mM glycine and 2% BSA in 1X PBS and left 30 min rotating at room temperature. Exosomes-bound beads were washed 1 time in 1X PBS/2% BSA and centrifuge for 1 min at 10,000 rpm, blocked with 10% BSA with rotation at room temperature for 30 min, washed a second time in 1X PBS/2% BSA and centrifuged for 1 min at 10,000 rpm, and incubated with anti-GPC1 (PIPA528055, Thermo-Scientific, 3 μl of antibody in 20 μl of 2%BSA/1X PBS) during 30 min rotating at 4°C. Beads were centrifuged for 1 min at 10,000 rpm, the supernatant was discarded and beads were washed in 1X PBS/2% BSA and centrifuged for 1 min at 10,000 rpm. Alexa-488 or Alexa-594-tagged secondary antibodies (Life Technologies, NY 14072, USA, 3 μl of antibody in 20 μl of 2%BSA/1X PBS) were used during 30 min with rotation at 4°C. Secondary antibody incubation alone was used as control and to gate the beads with GPC1+ bound exos. The percent positive bead was calculated relative to the total number of beads analyzed per sample (100,000 events). This percentage was therein referred to as the percent beads with GPC1+ exosomes.
Ultra performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS)
Exosomes were mixed with 200 μl of methanol spiked with the Internal Standard tryptophan-d5. After brief vortex mixing, the samples were incubated for 1 hr at −20°C. After centrifugation at 16,000g for 15 min at 4°C, 190 μl of the supernatants was collected and the solvent removed. The dried extracts were then reconstituted in 15 μl of methanol, of which 10 μl were transferred to microtubes and derivatized. Chromatographic separation and mass spectrometric detection conditions employed are summarized below:
| System | SQD |
| Column type | UPLC BEH C18, 1.0 x 100 mm, 1.7 μm |
| Flow rate | 0.14 ml/min |
| Solvent A | H2O + 10mM Ammonium Bicarbonate (+NH4OH until pH: 8.8) |
| Solvent B | ACN |
| (%B), time | 2%, 0 min |
| (%B), time | 8%, 6.5 min |
| (%B), time | 20%, 10 min |
| (%B), time | 30%, 11 min |
| (%B), time | 99.9%, 12 min |
| (%B), time | 2%, 14 min |
| Column temperature | 40°C |
| Injection volume | 1 μl |
| Ionisation | ES+ |
| Source temperature | 120°C |
| Nebulisation N2 flow | 600 l / hour |
| Nebulisation N2 temperature | 350°C |
| Cone N2 flow | 10 l / hour |
| Capillary voltage | 3.2 kV |
| Cone voltage | 30 V |
The mass range, 50 – 1000 m/z, was calibrated with cluster ions of sodium formate. An appropriate test mixture of standard compounds was analyzed before and after the entire set of randomized duplicated sample injections, in order to examine the retention time stability and sensitivity of the LC/MS system throughout the course of the run. Data were processed using the TargetLynx application manager for MassLynx 4.1 software (Waters Corp., Milford, USA). A set of predefined retention time, mass-to-charge ratio pairs, Rt-m/z, corresponding to metabolites included in the analysis are fed into the program. Associated extracted ion chromatograms (mass tolerance window = 0.05 Da) are then peak-detected and noise-reduced in both the LC and MS domains such that only true metabolite related features are processed by the software. A list of chromatographic peak areas is then generated for each sample injection, using the Rt-m/z data pairs (retention time tolerance = 6 s) as identifiers. Normalization factors were calculated for each metabolite by dividing their intensities in each sample by the recorded intensity of the internal standard in that same sample. Visualization of disjoint and overlapping protein data sets was carried out by drawing a VennDiagram of the 5 protein data sets using an R package53.
Cancer Antigen CA 19-9 Human and GPC1 ELISAs
Serum CA 19-9 and GPC1 protein levels in patients with pancreatic cancer, pancreatic cancer precursor lesion, or benign pancreatic disease, and in healthy donors were assessed using the Cancer Antigen CA 19-9 Human ELISA Kit (Abcam, ab108642) and the GPC1 Human ELISA kit (ABIN840422), according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Western blot analyses
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer containing 5 μg.ml−1 leupeptin, 1 μg.ml−1 pepstatin and 1mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. Exosomes were lysed in 8M Urea/2.5% SDS containing 5 μg.ml−1 leupeptin, 1 μg.ml−1 pepstatin and 1mM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. Sample loading was normalized according to Bradford relative protein quantification and proteins separated following an electrophoretic gradient across polyacrylamide gels. Wet electrophoretic transfer was used to transfer the proteins in the gel onto PVDF membranes (ImmobilonP). The protein blot was blocked for 1hr at room temperature with 5% non-fat dry milk in PBS/0,05% Tween and incubated overnight at 4°C with the following primary antibodies: 1:300 anti-GPC1, PIPA528055 (Thermo-Scientific); 1:300 anti-β-Actin A3854 (Sigma-Aldrich); 1:300 anti-CD81 sc-166029 (Santa-Cruz); 1:300 anti-Flottilin1 sc-25506 (Santa-Cruz). Afterwards, HRP conjugated secondary antibodies were incubated for 1 hr at room temperature. Washes after antibody incubations were done on an orbital shaker, four times at 10 min intervals, with 1X PBS 0.05% Tween20. Blots were developed with chemiluminescent reagents from Pierce.
RNA extraction of cells and exosomes
RNA of cells and exosomes was isolated using Trizol Plus RNA purification kit (Life Technologies, 12183555) according to manufactures protocol. RNA was quantified using a Nanodrop® ND-1000 (Thermo Fischer Scientific).
Quantitative real-time-PCR (qRT-PCR)
qRT-PCR was performed on DNase treated RNA using the SuperScript® III Platinum® One-Step Quantitative RT-PCR System (Cat. no. 11732-088, Invitrogen, Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY 14072 USA) according to the manufacturer’s directions on a 7300 Sequence Detector System (Applied Biosystems). 150 ng of RNA extracted from 2.5 × 108 exosomes was used as qPCR input. Primers for KRAS G12D mRNA and KRAS G12V mRNA (both Sigma-Aldrich Corp. St. Louis, MO, USA) were designed as reported previously54. Briefly, the altered base of KRAS G12D and KRAS G12V mutation was kept at the 3′ end of the forward primer. An additional base mutation was included two positions before the Kras mutation in order to increase the specificity of the amplification of the mutant Kras allele. Forward primer sequences for KRAS G12D mRNA: F-5′-ACTTGTGGTAGTTGGAGCAGA-3′. Forward primer sequences for KRAS G12V mRNA: F-5′-ACTTGTGGTAGTTGGAGCAGT-3′. Forward primer sequences for KRAS wild-type mRNA: F-5′-ACTTGTGGTAGTTGGAGCTGG-3′. Reverse primer for all KRAS: R-5′-TTGGATCATATTCGTCCACAA-3′. GPC1 mRNA primer pairs (Cat. No. PPH06045A) and 18S mRNA primer pairs (Cat. No. QF00530467) were purchased as ready specific primer pairs from Qiagen (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Threshold cycle55 (Ct) the fractional cycle number at which the amount of amplified target reached a fixed threshold, was determined and expression was measured using the 2−ΔCt formula, as previously reported56.
DNA extraction from human primary pancreatic cancer tumors and crExos
Immediately after resection, pancreatic tumor samples were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C until further processing. A 10 μm reference section of each sample was cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin by standard methods to evaluate the proportion of tumor tissue and adjacent tumor stroma. Samples with a tumor stroma proportion > 30 % were excluded into this study. DNA isolation was performed using a commercial DNA Extraction Kit (DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit, Cat. No. 69506, Qiagen, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The amount of DNA from tumor samples was quantified using a Nanodrop® 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE 19810, USA).
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Sanger Sequencing
PCR was performed in a 25 μl reaction tube consisting of 10 μl template DNA, 1 μM of each primer, 2.5mM dNTP, 2.5 10 x PCR Buffer, 25mM Mg solution, 0.5 μl H2O and 2.5 μl Taq Polymerase. Amplification was carried out in a T100 ThermoCycler (Bio-Rad) under following conditions: 94°C for 1 min, 2 cycles of 94 °C for 10 s, 67°C for 30 s, 70 °C for 30 s; 2 cycles of 94 °C for 10 s, 64°C for 30 s, 70 °C for 30 s; 2 cycles of 94 °C for 10 s, 61°C for 30 s, 70 °C for 30 s; 35 cycles of 94 °C for 10 s, 59°C for 30 s, 70 °C for 30 s; endless 4 °C. KRAS amplicon were generated using the following primers: forward 5′-AAGGCCTGCTGAAAATGACTG-3′, 5′-AGAATGGTCCTGCACCAGTAA-3′. PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Subsequently, sequencing reaction was performed using BigDye terminator kit (v3.1, Life Technologies, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing products were separated on an ABI 3730 automated sequencer (Life Technologies, USA). KRAS mutation status was evaluated using Finch TV (Geospiza, Inc., Seattle, WA 98119, USA).
MRI imaging
MRI studies were conducted using a 7T small animal MR system, the Biospec USR70/30 (Bruker Biospin MRI, Billerica, MA) is based on an actively-shielded 7T magnet with a 30-cm bore and cryo-refrigeration. The system is equipped with 6 cm inner-diameter gradients that deliver a maximum gradient field of 950 mT/m. A 3.5 cm inner-diameter linear birdcage coil transmits and receives the MR signal. For image acquisition, T2 weighted, respiratory gated, multi-slice imaging will be performed with respiration held to under 25 breaths per minute to minimize motion artifacts in the abdomen. For mice where fat signal might mask the T2 weighted image the fat-suppression pulse module will be utilized. Acquisition parameters were minimally modified from Schmid A et. Al.57. The RARE-T2 weighted pulse sequence was modified to include an effective Te of 56 ms with a total TR of 2265 ms. Between 18 and 20 coronal slices were acquired per mouse with a slice thickness of 0.75 mm and slice spacing of 1 mm. In plane, pixel sizes of 0.156 mm × 0.156 mm with a matrix size of 256×192 (40 mm × 30 mm FOV) was chosen to minimize in plane partial volume effects, maintain a FOV sufficient to cover the abdomen, while also providing sufficient throughput for the experiment.
To measure tumor burden, the region of suspected lesions are drawn blinded on each slice after images intensities were normalized. The volume is calculated by addition of delineated region of interest in mm2 x 1 mm slice distance.
Statistical analysis
The GraphPad Prism version 6.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA 92037 USA) and MedCalc statistical software version 13.0 (MedCalc Software bvba, Acacialaan 22, 8400 Ostend, Belgium) were used for all calculations. Unpaired Student’s t-test was applied to calculate expression differences of the qPCR results (dCt-values). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests were performed to calculate differences of multiple serum factors in murine and human serum samples. As a post-hoc test, a Tukey-Kramer test was applied for pairwise comparison of subgroups when the ANOVA test was positive in case of equal variance. Tamhane T2 test was applied for pairwise comparison of subgroups when the ANOVA test was positive in case of unequal variances. A paired two-tailed Student’s t-test was applied to assay differences in percent bead with GPC1+ crExos and CA 19-9 in the longitudinal cohort between pre-operative and postoperative blood samples. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) were used to determine the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value and to compare area under the curves (AUC) of serum factors using the Delong method58. The cut-off value was determined using the Youden-Index. Univariate analysis using the log-rank test was conducted to visualize (Kaplan Meier curves) and assess disease-specific survival (time from diagnosis to cancer-related death or last follow-up) in the longitudinal cohort of patients with pancreatic cancer. A multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards regression model was performed to evaluate the effect of a decrease of percent bead with GPC1+ crExos in addition to age (continuous variable), AJCC tumor stage, and tumor grade (G) and CA 19-9 levels (U.ml−1). Correlation analysis between murine tumor burden and percent bead with GPC1+ crExos was performed using the Spearman correlation test. Figures were prepared by using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA 92037 USA) and MedCalc statistical software version 13.0 (MedCalc Software bvba, Acacialaan 22, 8400 Ostend, Belgium). All presented P values are two-sided and P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1. Exosomes isolation.
a, Exosomes concentration and size distribution by NanoSight® analysis of culture supernatant from NIH/3T3, MCF10A, HDF, MDA-MB-231 and E10 cells. Size mode: 105 nanometers (nm; 3 technical replicates). b, Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) micrograph of MDA-MB-231-derived exosomes. Upper right image shows a digitally zoomed inset. c, TEM micrograph of MDA-MB-231-derived exosomes following immunogold labeling for CD9. Gold particles are depicted as black dots. Upper right image shows a digitally zoomed inset. d, Immunoblot of flotillin1 and CD81 in exosomal proteins extracted from culture supernatant of E10, NIH/3T3, MDA-MB-231, MCF10A and HDF cells. e, RT–qPCR measurement of GPC1 mRNA levels in HMEL, HDF, HMLE, MCF7, MDA-MB-231, T3M4, Panc-1, MIA Paca2. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation; n=3, 3 biological replicates, with 3 technical replicates each. f, Immunoblot of GPC1 in HMEL, HDF, HMLE, MCF7, MDA-MB-231, T3M4, Panc-1 and MIA Paca2 cell lysates (upper panel). β-actin was used as a loading control (lower panel). g, Immunoblot of GPC1 in exosomal protein lysates derived from the culture supernatant of 3 non-tumorigenic cell lines (HDF, HMEL, HMLE) and 5 tumorigenic cell lines (MCF7, MDA-MB-231, T3M4, Panc-1, MIA Paca2) (upper panel). Immunoblot of flotillin1 was used as loading control (lower panel). h, Immunoblot of flotillin1 in exosomal protein lysates from the culture supernatant of MDA-MB-231 and T3M4 following sucrose gradient purification. The protein content is assayed in each of the density layers listed.
Extended Data Figure 2. NanoSight® analysis in human serum samples.
a, Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) micrograph of cancer patient serum-derived exosomes. Upper right image shows a digitally zoomed inset. b, TEM micrograph of cancer patient serum-derived exosomes following immunogold labeling for CD9. Gold particles are depicted as black dots. Upper right image shows a digitally zoomed inset. c, Immunoblot of flotillin1 of exosomal protein lysates from serum of cancer patient following exosomes purification by sucrose gradient. The protein content is assayed in each of the density layers listed. d, Exosomes concentration by NanoSight® analysis showing the number of exosomes per 1 ml of serum derived from healthy donors (n=100), from breast cancer patients (n=32) and from patients with a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, n=190). ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2, * P<0.05, **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates. e, Exosomes size distribution by NanoSight® analysis showing the mode size of exosomes in 1 ml of serum derived from healthy donors (n=100), from breast cancer patients (n=32) and from patients with a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, n=190). ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, *** P<0.001; 3 technical replicates. f, Scatter dot plots depicting the percentage of beads with GPC1+ bound exosomes purified from the serum of breast cancer patients. The patients are subdivided into three subtypes: Luminal A, Luminal B and Triple Negative breast cancer. g, Scatter plots depicting the serum CA 19-9 concentration (U/mL), evaluated by ELISA, in healthy donors (n=100), patients with benign pancreas disease (BPD, n=26), pancreas cancer precursor lesion (PCPL, n=5) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, n=190). Discovery cohort, ANOVA, post-hoc Tamhane T2 * P<0.05; **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates. Data is presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Extended Data Figure 3. Tumor stage-specific analysis.
a, Table associated with receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis depicted in Figure 1f. b–f, ROC curve analysis for percent GPC1+ crExos (red line), CA 19-9 serum levels (blue scattered line), exosomes concentration (black line) and exosomes size (scattered black line) in patients with carcinoma in situ (CIS) or stage I pancreatic cancer (n=5) (a), stage IIa pancreatic cancer (n=18) (b), stage IIb pancreatic cancer (n=117) (c), stage III pancreatic cancer (n=11) (d), and stage IV pancreas cancer (n=41) (e), compared to control (healthy donors (n=100) and patients with a benign pancreatic disease (n=26), total n=126). g, Table associated with ROC curve analysis depicted in Figure 1h. AUC: Area under the curve, CI: confidence interval.
Extended Data Figure 4. Longitudinal human study.
a, Scatter plots of percent beads with GPC1+ crExos by flow cytometry in patients with pancreas cancer. Patients are divided based on metastatic disease (non-metastatic lesions, lymph node metastases and distant metastases). ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, * P<0.05; 3 technical replicates. b, Scatter plots depicting serum CA 19-9 levels (U/ml) in patients with benign pancreas disease (BPD) (n=4), cancer precursor lesion (PCPL) (n=4), and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) (n=29) on the preoperative day and postoperative day 7 in patients. Paired two-tailed Student’s t-test, ** P<0.01; 3 technical replicates. c–d, Multivariate analysis (Cox proportional hazards regression model) of prognostic parameters for overall (c) and disease-specific (d) survival of patients with pancreas cancer in the longitudinal cohort (n=29). e, Scatter plots depicting serum GPC1 (ng/ml) levels by ELISA in patients with benign pancreas disease (BPD, n=6), pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, n=56) and healthy controls (n=20). ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, **** P<0.0001; 3 technical replicates. f, ROC curve for circulating GPC1 protein (red line) in patients with pancreas cancer (n=56) vs. control (healthy donors (n=20) and patients with a benign pancreatic disease (n=26), total n=6). AUC: Area under the curve, CI: confidence interval.
Extended Data Figure 5. PDAC GEMM longitudinal study.
a, Schematic diagram depicting the spontaneous development and progression of pancreatic cancer in Ptf1acre/+;LSL-KrasG12D/+;Tgfbr2L/L (PKT) mice and H&E of the pancreas at the indicated time points showing healthy pancreas, PanIN lesions, and PDAC lesions. Scale bars: 100 μm. b–c, Exosomes size (b) and concentration (c) assayed by NanoSight® analysis from the serum of PKT mice (E: experimental, red) and control mice (C: control, blue) at 4, 5, 6,7 and 8 weeks of age. ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test, * P<0.05; 3 technical replicates. d, Graph depicting the time wise progression of tumor volume measured by MRI and the % beads with GPC1+ bound crExos in individual PKT mice (blue: tumor volume, red: % GPC1+ crExos). e, Percent beads with GPC1+ crExos on beads from control mice (n=3) and mice with cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis (n=4). Two-tailed Student’s t-test, ns: not significant; 3 technical replicates. f, Results from ROC curves for percent beads with GPC1+ bound crExos, exosomes concentration and exosomes size in 4, 5, 6 and 7 weeks old PKT mice (n=7) vs. control (including age-matched littermate healthy control (n=6) and mice with induced acute pancreatitis (n=4), n=10)). Data is presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Extended Data Figure 6. PDAC GEMM cross sectional studies.
a, Representative micrographs of H&E stained pancreas from 16 days old control mice (left panel) and PKT mice presenting with (right panel, encircled) and without (middle panel) PanIN lesions. Scale bars: 100 μm. b, Ct values following qPCR analyses for oncogenic KRASG12D, wild-type KRAS and 18S internal control RNA from exosomes of 44–48 days old PKT mice serum segregated using FACS for GPC1+ bead bound exos (red) and GPC1− bead bound exos (blue). Data is presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
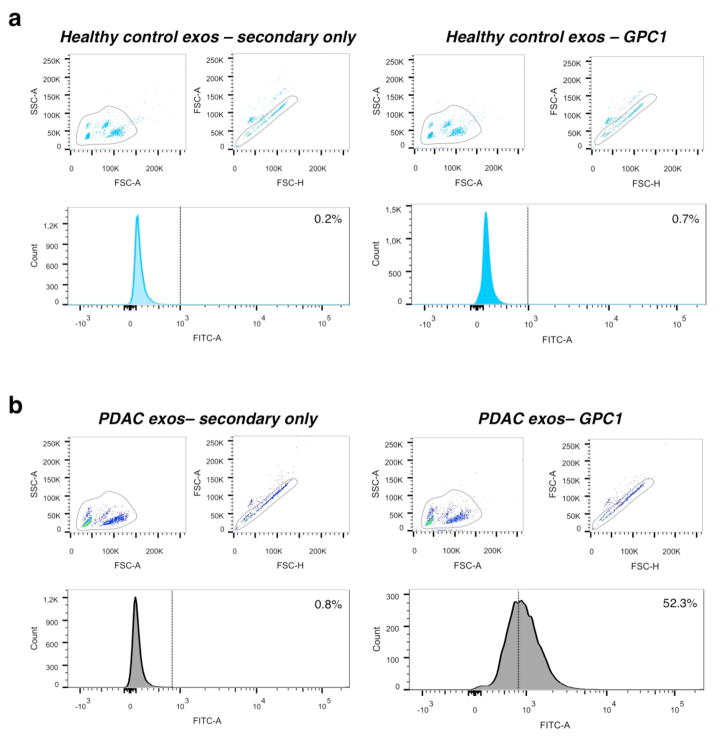
Extended Data Figure 7. Raw scatter dot plot depicting flow cytometry analyses of beads with GPC1+ bound exosomes.
a, Scatter plots and histogram of flow cytometry analyses of serum exosomes on beads of a representative healthy control (left panels are secondary antibody only; right panels are GPC1 antibody and secondary antibody). b, Scatter plots and histogram of flow cytometry analysis of serum exosomes on beads of a representative pancreas cancer sample (left panels are secondary antibody only; right panels are with GPC1 antibody and secondary antibody).
Extended Data Figure 8.
Uncropped Western blots
Extended Data Table 1. List of the 48 proteins exclusive to MDA-MB-231 exosomes.
Listing of the 48 proteins exclusively detected in exosomes from MDA-MB-231 cells determined by ultra performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) and comparative analyses of exosomes derived from NIH/3T3, MCF 10A, HDF, E10 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The proteins are grouped based on cellular location.
| Protein Name | Gene ID | Cellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 6 | ABCA6 | Transmembrane |
| Tetraspanin-4 | TSPAN4 | Transmembrane |
| SLIT and NTRK-like protein 4 | SLITRK4 | Transmembrane |
| Putative protocadherin beta-18 | PCDHB18 | Transmembrane |
| Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 | CD33 | Transmembrane |
| Glypican-1 | GPC1 | Membrane anchored |
| Protein Name | Gene ID | Cellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| Histone H2A type 2-A | HIST1H2AA | Nucleus |
| Histone H2A type 1-A | HIST1H1AA | Nucleus |
| Histone H3.3 | H3F3A | Nucleus |
| Histone H3.1 | HIST1H3A | Nucleus |
| Zinc finger protein 37 homolog | ZFP37 | Nucleus |
| Hypermethylated in cancer 2 protein | HIC2 | Nucleus |
| Zinc finger protein 12 | ZSCAN12 | Nucleus |
| Protein Name | Gene | ID Cellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| Laminin subunit beta-1 | LAMB1 | Secreted |
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like | TINAGL1 | Secreted |
| Peroxiredoxin-4 | PRDX4 | Secreted |
| Collagen alpha-2(IV) chain | COL4A2 | Secreted |
| Putative protein C3P1 | C3P1 | Secreted |
| Collagen alpha-1(II) chain | COL2A1 | Secreted |
| Hemicentin-1 | HMCN1 | Secreted |
| Protein Name | Gene ID | Cellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| Putative rhophilin-2-like protein | RHPN2P1 | Not specified |
| Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 62 | ANKRD62 | Not specified |
| Tripartite motif-containing protein 42 | TRIM42 | Not specified ! |
| Protein Name | Gene ID | Cellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| Junction plakoglobin | JUP | Cytoplasm |
| Tubulin beta-2B chain | TUBB2B | Cytoplasm |
| Endoribonuclease Dicer | DICER1 | Cytoplasm |
| E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | TRIM71 | Cytoplasm |
| Katanin p60 ATPase-containing subunit A-like 2 | KATNAL2 | Cytoplasm |
| Protein S100-A6 | S100A6 | Cytoplasm |
| 5′-nucleotidase domain-containing protein 3 | NT5DC3 | Cytoplasm |
| Valine--tRNA ligase | VARS | Cytoplasm |
| Kazrin | KAZN | Cytoplasm |
| ELAV-like protein 4 | ELAVL4 | Cytoplasm |
| RING finger protein 166 | RNF166 | Cytoplasm |
| FERM and PDZ domain-containing protein 1 | FRMPD1 | Cytoplasm |
| 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein | HSPA5 | Cytoplasm |
| Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 6A | TRAPPC6A | Cytoplasm |
| Squalene monooxygenase | SQLE | Cytoplasm |
| Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein | TSG101 | Cytoplasm |
| Vacuolar protein sorting 28 homolog | VPS28 | Cytoplasm |
| Prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator | PTGFRN | Cytoplasm |
| Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACAD8 | Cytoplasm |
| 26S protease regulatory subunit 6B | PSMC4 | Cytoplasm |
| Elongation factor 1-gamma | EEF1G | Cytoplasm |
| Titin | TTN | Cytoplasm |
| Tyrosine-protein phosphatase type 13 | PTPN13 | Cytoplasm |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | TPI1 | Cytoplasm |
| Carboxypeptidase E | CPE | Cytoplasm |
Extended Data Table 2.
Exosomes proteins assayed by ultra performance liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) in indicated cell lines.
| E10 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot_hit | prot_acc | prot_desc | prot_score | prot_mass | prot_matches | prot_sequences_sig | prot_cover | prot_pi |
| 1 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 2721 | 65999 | 68 | 30 | 57.8 | 8.15 |
| 2 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT9 PE=1 SV=3 | 2381 | 62027 | 59 | 24 | 68.2 | 5.14 |
| 3 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 2146 | 58792 | 66 | 29 | 57.9 | 5.13 |
| 4 | P02768 | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 2032 | 69321 | 104 | 9 | 13.5 | 5.92 |
| 5 | P07996 | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1823 | 129300 | 57 | 29 | 37.9 | 4.71 |
| 6 | P02765 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 1784 | 39300 | 50 | 3 | 8.7 | 5.43 |
| 7 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 1719 | 163188 | 62 | 8 | 7.5 | 6.03 |
| 8 | P20742 | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 1562 | 163760 | 48 | 4 | 2.5 | 5.97 |
| 9 | P02751 | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 1186 | 262460 | 37 | 26 | 17.6 | 5.46 |
| 10 | P12111 | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 1113 | 343457 | 51 | 39 | 20.2 | 6.26 |
| 11 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1057 | 65393 | 35 | 21 | 48.4 | 8.07 |
| 12 | P01024 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 978 | 187030 | 43 | 18 | 14.7 | 6.02 |
| 13 | P00734 | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 846 | 69992 | 21 | 6 | 8 | 5.64 |
| 14 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 820 | 41710 | 23 | 12 | 47.5 | 5.29 |
| 15 | P08779 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT16 PE=1 SV=4 | 762 | 51236 | 31 | 18 | 48 | 4.99 |
| 16 | P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 708 | 106397 | 27 | 8 | 9.3 | 6.4 |
| 17 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 579 | 51529 | 25 | 15 | 37.1 | 5.09 |
| 18 | P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4A PE=1 SV=1 | 492 | 192650 | 20 | 9 | 5.6 | 6.65 |
| 19 | P04259 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 446 | 60030 | 18 | 10 | 25.5 | 8.09 |
| 20 | P12109 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 420 | 108462 | 11 | 7 | 11.3 | 5.26 |
| 21 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 419 | 36030 | 12 | 6 | 28.4 | 8.57 |
| 22 | Q07954 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 419 | 504276 | 22 | 10 | 5.8 | 5.16 |
| 23 | P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 419 | 60008 | 18 | 10 | 27.1 | 8.09 |
| 24 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 416 | 78132 | 16 | 3 | 4.8 | 8.5 |
| 25 | P68032 | Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 408 | 41992 | 13 | 6 | 26.8 | 5.23 |
| 26 | P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFP PE=1 SV=1 | 395 | 68633 | 9 | 3 | 5.6 | 5.48 |
| 27 | Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS3BP PE=1 SV=1 | 392 | 65289 | 15 | 10 | 26.7 | 5.13 |
| 28 | P68363 | Tubulin alpha-1B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA1B PE=1 SV=1 | 364 | 50120 | 18 | 9 | 38.4 | 4.94 |
| 29 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 360 | 62340 | 17 | 11 | 23.4 | 7.59 |
| 30 | Q04695 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT17 PE=1 SV=2 | 357 | 48076 | 20 | 10 | 32.6 | 4.97 |
| 31 | Q9BYX7 | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 | 347 | 41989 | 8 | 3 | 13.6 | 5.91 |
| 32 | P06396 | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 340 | 85644 | 11 | 7 | 12.5 | 5.9 |
| 33 | P04114 | Apolipoprotein B-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOB PE=1 SV=2 | 327 | 515283 | 16 | 12 | 2.4 | 6.58 |
| 34 | P03956 | Interstitial collagenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 318 | 53973 | 15 | 11 | 33.5 | 6.47 |
| 35 | Q06033 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 298 | 99787 | 10 | 5 | 5.1 | 5.49 |
| 36 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 297 | 15248 | 13 | 3 | 33.1 | 8.72 |
| 37 | P24821 | Tenascin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNC PE=1 SV=3 | 292 | 240700 | 12 | 10 | 9.4 | 4.79 |
| 38 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 286 | 49639 | 12 | 7 | 34.2 | 4.78 |
| 39 | P68371 | Tubulin beta-2C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB2C PE=1 SV=1 | 278 | 49799 | 10 | 7 | 27.4 | 4.79 |
| 40 | P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 273 | 52929 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 5.4 |
| 41 | Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTBL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 271 | 41976 | 8 | 3 | 16 | 5.39 |
| 42 | P23142 | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 269 | 77162 | 10 | 5 | 7.4 | 5.07 |
| 43 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 256 | 49557 | 13 | 6 | 10.9 | 4.91 |
| 44 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A–I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 255 | 30759 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 5.56 |
| 45 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKM2 PE=1 SV=4 | 228 | 57900 | 9 | 6 | 20.3 | 7.96 |
| 46 | P04004 | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 215 | 54271 | 6 | 1 | 4.2 | 5.55 |
| 47 | P19012 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT15 PE=1 SV=3 | 210 | 49181 | 14 | 6 | 10.3 | 4.71 |
| 48 | Q15582 | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBI PE=1 SV=1 | 196 | 74634 | 8 | 7 | 16.1 | 7.62 |
| 49 | P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 188 | 46283 | 7 | 3 | 12 | 5.97 |
| 50 | Q99715 | Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL12A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 176 | 332941 | 8 | 5 | 4.9 | 5.38 |
| 51 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA1 PE=1 SV=5 | 175 | 84607 | 8 | 4 | 12.8 | 4.94 |
| 52 | P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 174 | 55892 | 7 | 4 | 6.7 | 8.54 |
| 53 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 171 | 16045 | 9 | 2 | 12.9 | 7.85 |
| 54 | P11717 | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 163 | 274199 | 5 | 2 | 0.8 | 5.64 |
| 55 | P51884 | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 161 | 38405 | 9 | 3 | 12.4 | 6.16 |
| 56 | P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 158 | 54531 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.87 |
| 57 | P12259 | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 153 | 251546 | 9 | 6 | 3.5 | 5.68 |
| 58 | P08107 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A/1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1A PE=1 SV=5 | 147 | 70009 | 3 | 3 | 6.2 | 5.48 |
| 59 | P17066 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA6 PE=1 SV=2 | 147 | 70984 | 3 | 3 | 6.2 | 5.81 |
| 60 | P19013 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 146 | 57250 | 6 | 4 | 7.3 | 6.25 |
| 61 | Q8TAA3 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 144 | 28512 | 4 | 3 | 19.5 | 9.07 |
| 62 | Q5XKE5 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 79 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT79 PE=1 SV=2 | 138 | 57800 | 7 | 3 | 6.9 | 6.75 |
| 63 | P0C0S8 | Histone H2A type 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H2AG PE=1 SV=2 | 136 | 14083 | 3 | 2 | 21.5 | 10.9 |
| 64 | Q99816 | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 135 | 43916 | 4 | 2 | 21.8 | 8.2 |
| 65 | P23526 | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 134 | 47685 | 3 | 2 | 9.5 | 5.92 |
| 66 | P00747 | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 132 | 90510 | 7 | 4 | 5.3 | 7.04 |
| 67 | O95678 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 75 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT75 PE=1 SV=2 | 132 | 59524 | 7 | 3 | 7.8 | 7.6 |
| 68 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF2 PE=1 SV=4 | 132 | 95277 | 6 | 4 | 10.3 | 6.41 |
| 69 | Q9UBG0 | C-type mannose receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRC2 PE=1 SV=2 | 128 | 166568 | 2 | 2 | 1.6 | 5.54 |
| 70 | Q15063 | Periostin OS=Homo sapiens GN=POSTN PE=1 SV=2 | 127 | 93255 | 6 | 3 | 10.3 | 7.27 |
| 71 | P62805 | Histone H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H4A PE=1 SV=2 | 127 | 11360 | 5 | 4 | 38.8 | 11.36 |
| 72 | P01008 | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 126 | 52569 | 13 | 3 | 14.9 | 6.32 |
| 73 | P19827 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 124 | 101326 | 4 | 3 | 2.9 | 6.31 |
| 74 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 123 | 70854 | 4 | 4 | 7.6 | 5.37 |
| 75 | P08729 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT7 PE=1 SV=5 | 123 | 51354 | 4 | 2 | 5.1 | 5.4 |
| 76 | P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 122 | 21212 | 4 | 3 | 16.4 | 5.3 |
| 77 | P05787 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT8 PE=1 SV=7 | 122 | 53671 | 4 | 2 | 5.6 | 5.52 |
| 78 | P01031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 122 | 188186 | 5 | 3 | 2.6 | 6.11 |
| 79 | Q5VTE0 | Putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1A1P5 PE=5 SV=1 | 121 | 50153 | 4 | 3 | 14.1 | 9.15 |
| 80 | P05452 | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 121 | 22522 | 5 | 3 | 28.7 | 5.52 |
| 81 | P49327 | Fatty acid synthase OS=Homo sapiens GN=FASN PE=1 SV=3 | 119 | 273254 | 5 | 3 | 3.3 | 6.01 |
| 82 | P07195 | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHB PE=1 SV=2 | 118 | 36615 | 2 | 2 | 6.9 | 5.71 |
| 83 | Q9H4B7 | Tubulin beta-1 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 112 | 50295 | 5 | 3 | 11.8 | 5.05 |
| 84 | P15531 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=NME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 111 | 17138 | 1 | 1 | 11.2 | 5.83 |
| 85 | Q7Z3Y8 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT27 PE=1 SV=2 | 109 | 49792 | 7 | 2 | 7.6 | 4.98 |
| 86 | P08238 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 109 | 83212 | 4 | 2 | 6.2 | 4.97 |
| 87 | P08123 | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A2 PE=1 SV=7 | 105 | 129235 | 2 | 2 | 2.3 | 9.08 |
| 88 | Q86YZ3 | Hornerin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRNR PE=1 SV=2 | 101 | 282228 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 10.05 |
| 89 | P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 99 | 138857 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5.6 |
| 90 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOA PE=1 SV=2 | 98 | 39395 | 2 | 2 | 6.9 | 8.3 |
| 91 | P02787 | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 97 | 77014 | 4 | 2 | 1.7 | 6.81 |
| 92 | P02748 | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 95 | 63133 | 3 | 2 | 3.8 | 5.43 |
| 93 | Q8TEV9_REVERSED | Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosomal region candidate gene 8 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMCR8 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 91 | 104956 | 12 | 1 | 1.2 | 5.36 |
| 94 | P02461 | Collagen alpha-1(III) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL3A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 90 | 138479 | 2 | 2 | 1.6 | 6.21 |
| 95 | P00450 | Ceruloplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CP PE=1 SV=1 | 88 | 122128 | 3 | 3 | 2.9 | 5.44 |
| 96 | P62979 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPS27A PE=1 SV=2 | 88 | 17953 | 4 | 3 | 19.9 | 9.68 |
| 97 | Q14697 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Homo sapiens GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=3 | 84 | 106807 | 2 | 2 | 3.9 | 5.74 |
| 98 | Q08431 | Lactadherin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFGE8 PE=1 SV=2 | 83 | 43095 | 2 | 1 | 3.9 | 8.47 |
| 99 | A6NMY6 | Putative annexin A2-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2P2 PE=5 SV=2 | 82 | 38635 | 2 | 2 | 6.2 | 6.49 |
| 100 | P07355 | Annexin A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 82 | 38580 | 3 | 2 | 10.3 | 7.57 |
| 101 | Q9BYX7_REVERSED | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 80 | 41989 | 4 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.92 |
| 102 | Q8NI35 | InaD-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=INADL PE=1 SV=3 | 79 | 196247 | 8 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.84 |
| 103 | P15169 | Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 79 | 52253 | 1 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.86 |
| 104 | P28074 | Proteasome subunit beta type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB5 PE=1 SV=3 | 79 | 28462 | 2 | 2 | 8.7 | 6.43 |
| 105 | P49720 | Proteasome subunit beta type-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 78 | 22933 | 3 | 2 | 16.6 | 6.14 |
| 106 | Q04756 | Hepatocyte growth factor activator OS=Homo sapiens GN=HGFAC PE=1 SV=1 | 77 | 70636 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 | 6.99 |
| 107 | Q12931 | Heat shock protein 75 kDa, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRAP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 76 | 80060 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8.3 |
| 108 | P05121 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINE1 PE=1 SV=1 | 76 | 45031 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6.68 |
| 109 | P20618 | Proteasome subunit beta type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 74 | 26472 | 2 | 2 | 13.3 | 8.27 |
| 110 | Q14624 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 73 | 103293 | 4 | 1 | 1.9 | 6.51 |
| 111 | Q5D862 | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 72 | 247928 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 8.45 |
| 112 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 71 | 47139 | 3 | 2 | 10.1 | 7.01 |
| 113 | P02790 | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 70 | 51643 | 7 | 1 | 5.4 | 6.55 |
| 114 | P35442 | Thrombospondin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS2 PE=1 SV=2 | 70 | 129908 | 4 | 2 | 3.2 | 4.62 |
| 115 | P13929 | Beta-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO3 PE=1 SV=4 | 69 | 46902 | 2 | 2 | 7.6 | 7.59 |
| 116 | Q8WW52_REVERSED | Protein FAM151A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM151A PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 69 | 63987 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.2 |
| 117 | P12110 | Collagen alpha-2(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 69 | 108512 | 4 | 2 | 3.4 | 5.85 |
| 118 | P04083 | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 68 | 38690 | 1 | 1 | 3.8 | 6.57 |
| 119 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 68 | 46707 | 4 | 1 | 3.3 | 5.37 |
| 120 | P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACHE PE=1 SV=1 | 67 | 67753 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 | 5.87 |
| 121 | P55058 | Phospholipid transfer protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLTP PE=1 SV=1 | 66 | 54705 | 1 | 1 | 2.2 | 6.53 |
| 122 | P00488 | Coagulation factor XIII A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=F13A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 66 | 83215 | 1 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.75 |
| 123 | Q03692 | Collagen alpha-1(X) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL10A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 66117 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 9.68 |
| 124 | P05546 | Heparin cofactor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPIND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 65 | 57034 | 2 | 1 | 2.4 | 6.41 |
| 125 | P01266 | Thyroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TG PE=1 SV=5 | 65 | 304594 | 3 | 3 | 0.8 | 5.4 |
| 126 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHA PE=1 SV=2 | 63 | 36665 | 2 | 1 | 8.1 | 8.44 |
| 127 | O15111_REVERSED | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHUK PE=1 SV=2 -REVERSED | 63 | 84585 | 7 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.28 |
| 128 | Q8NAV2_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein C8orf58 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C8orf58 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 63 | 39636 | 3 | 1 | 4.1 | 8.54 |
| 129 | P28070 | Proteasome subunit beta type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB4 PE=1 SV=4 | 62 | 29185 | 2 | 2 | 7.2 | 5.72 |
| 130 | P07686 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEXB PE=1 SV=3 | 61 | 63071 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 | 6.29 |
| 131 | P05543 | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 61 | 46295 | 2 | 1 | 2.4 | 5.87 |
| 132 | Q9HDC9 | Adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=APMAP PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 46451 | 3 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.82 |
| 133 | P25787 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 25882 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 6.92 |
| 134 | P35125 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=USP6 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 158557 | 12 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.87 |
| 135 | A6NIZ1 | Ras-related protein Rap-1b-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 59 | 20912 | 1 | 1 | 6.5 | 5.37 |
| 136 | B9A064 | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 59 | 23049 | 2 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.08 |
| 137 | Q99456 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT12 PE=1 SV=1 | 58 | 53478 | 6 | 2 | 3.6 | 4.7 |
| 138 | Q86Y46 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 58 | 58887 | 5 | 4 | 6.7 | 6.93 |
| 139 | P20774 | Mimecan OS=Homo sapiens GN=OGN PE=1 SV=1 | 58 | 33901 | 2 | 2 | 9.7 | 5.46 |
| 140 | Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain family 11 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC11A PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 35672 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 5.06 |
| 141 | P10909 | Clusterin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLU PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 52461 | 2 | 1 | 7.8 | 5.89 |
| 142 | Q9NPY3_REVERSED | Complement component C1q receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD93 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 57 | 68515 | 2 | 1 | 1.1 | 5.27 |
| 143 | P81605 | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 56 | 11277 | 2 | 2 | 22.7 | 6.08 |
| 144 | P03973 | Antileukoproteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLPI PE=1 SV=2 | 55 | 14316 | 1 | 1 | 9.1 | 9.11 |
| 145 | Q6YHK3 | CD109 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD109 PE=1 SV=2 | 55 | 161587 | 2 | 2 | 1.8 | 5.59 |
| 146 | P04180 | Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCAT PE=1 SV=1 | 55 | 49546 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 5.71 |
| 147 | Q9BXJ4 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1QTNF3 PE=2 SV=1 | 55 | 26977 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 6.04 |
| 148 | P16070 | CD44 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD44 PE=1 SV=3 | 53 | 81487 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.13 |
| 149 | P02649 | Apolipoprotein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOE PE=1 SV=1 | 53 | 36132 | 1 | 1 | 2.8 | 5.65 |
| 150 | P29353_REVERSED | SHC-transforming protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHC1 PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 51 | 62782 | 6 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.01 |
| 151 | P35580 | Myosin-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH10 PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 228858 | 2 | 2 | 1.2 | 5.44 |
| 152 | P28066 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 50 | 26394 | 1 | 1 | 4.1 | 4.74 |
| 153 | O95445 | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 49 | 21239 | 4 | 1 | 6.9 | 5.66 |
| 154 | P04745 | Alpha-amylase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY1A PE=1 SV=2 | 49 | 57731 | 1 | 1 | 2.3 | 6.47 |
| 155 | Q13454 | Tumor suppressor candidate 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUSC3 PE=2 SV=1 | 49 | 39650 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 9.93 |
| 156 | P49721 | Proteasome subunit beta type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB2 PE=1 SV=1 | 49 | 22822 | 3 | 1 | 19.9 | 6.51 |
| 157 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX2 PE=1 SV=5 | 49 | 21878 | 1 | 1 | 9.1 | 5.66 |
| 158 | Q6ZU45 | Putative C-type lectin domain-containing protein NCRNA00083 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCRNA00083 PE=5 SV=1 | 49 | 25796 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 6.3 |
| 159 | O43264_REVERSED | Centromere/kinetochore protein zw10 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZW10 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 49 | 88773 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 5.89 |
| 160 | Q9Y490 | Talin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 48 | 269599 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5.77 |
| 161 | Q96CD0_REVERSED | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXL8 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 48 | 40490 | 11 | 1 | 1.9 | 7.03 |
| 162 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 47 | 13234 | 1 | 1 | 13.2 | 5.71 |
| 163 | Q6P1X5_REVERSED | Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAF2 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 47 | 136883 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 8.46 |
| 164 | Q16853 | Membrane primary amine oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AOC3 PE=1 SV=3 | 47 | 84568 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.05 |
| 165 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 47 | 44586 | 3 | 1 | 8.4 | 8.3 |
| 166 | P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 46 | 38273 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 | 8.34 |
| 167 | A8MPT4 | Glutathione S-transferase theta-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTT4 PE=3 SV=2 | 45 | 27941 | 2 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.25 |
| 168 | Q8N6V9_REVERSED | Testis-expressed sequence 9 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TEX9 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 45 | 44798 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.2 |
| 169 | Q9Y2U8_REVERSED | Inner nuclear membrane protein Man1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LEMD3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 45 | 99935 | 2 | 1 | 0.7 | 7.31 |
| 170 | P05154 | Plasma serine protease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 45 | 45646 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 9.3 |
| 171 | Q8NDM7_REVERSED | WD repeat-containing protein 96 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR96 PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 45 | 191861 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.71 |
| 172 | Q6NXT2 | Histone H3.3C OS=Homo sapiens GN=H3F3C PE=1 SV=3 | 44 | 15204 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 | 11.1 |
| 173 | O95248 | Myotubularin-related protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SBF1 PE=1 SV=3 | 44 | 208184 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 6.46 |
| 174 | Q9UK61_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein C3orf63 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3orf63 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 44 | 188914 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.55 |
| 175 | Q9Y6X9_REVERSED | MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MORC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 43 | 117750 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 8.6 |
| 176 | P06746 | DNA polymerase beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=POLB PE=1 SV=3 | 43 | 38154 | 1 | 1 | 1.8 | 9.01 |
| 177 | Q92820 | Gamma-glutamyl hydrolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GGH PE=1 SV=2 | 43 | 35941 | 1 | 1 | 4.1 | 6.67 |
| 178 | Q9TNN7 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, Cw-5 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-C PE=2 SV=1 | 43 | 40886 | 1 | 1 | 3.6 | 7.11 |
| 179 | Q12968_REVERSED | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NFATC3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 115522 | 3 | 1 | 0.7 | 5.91 |
| 180 | Q96M89 | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 138 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCDC138 PE=1 SV=1 | 41 | 76171 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 8.75 |
| 181 | Q9Y5E4_REVERSED | Protocadherin beta-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB5 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 86369 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4.87 |
| 182 | Q9NU02_REVERSED | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANKRD5 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 86610 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | 8.51 |
| 183 | Q7Z5M8 | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 12B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD12B PE=2 SV=1 | 41 | 40750 | 4 | 1 | 1.7 | 8.57 |
| 184 | Q15020_REVERSED | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SART3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 109865 | 4 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.45 |
| 185 | P10643 | Complement component C7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C7 PE=1 SV=2 | 41 | 93457 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6.09 |
| 186 | P61769 | Beta-2-microglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=B2M PE=1 SV=1 | 40 | 13706 | 1 | 1 | 8.4 | 6.06 |
| 187 | Q9BY43 | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP4A PE=1 SV=3 | 40 | 25083 | 2 | 1 | 6.3 | 4.65 |
| 188 | O60312 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase VA OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP10A PE=2 SV=2 | 40 | 167582 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| 189 | Q8NBM4 | Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBAC2 PE=2 SV=1 | 40 | 38938 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.21 |
| 190 | Q99798 | Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACO2 PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 85372 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7.36 |
| 191 | Q14849 | StAR-related lipid transfer protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STARD3 PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 50471 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 8.52 |
| 192 | Q8NFY9 | Kelch repeat and BTB domain-containing protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KBTBD8 PE=2 SV=2 | 39 | 68778 | 1 | 1 | 1.8 | 5.88 |
| 193 | Q96K21 | Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZFYVE19 PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 51514 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.57 |
| 194 | P02760 | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 39 | 38974 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5.95 |
| 195 | P53675_REVERSED | Clathrin heavy chain 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLTCL1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 39 | 186910 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.57 |
| 196 | P0C869 | Cytosolic phospholipase A2 beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLA2G4B PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 87922 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5.64 |
| 197 | Q8WUM4 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6IP PE=1 SV=1 | 39 | 95963 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.13 |
| 198 | P05156 | Complement factor I OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFI PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 65707 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 7.72 |
| 199 | P00736 | Complement C1r subcomponent OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1R PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 80067 | 2 | 1 | 3.4 | 5.82 |
| 200 | Q00535_REVERSED | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK5 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 38 | 33283 | 1 | 1 | 3.1 | 7.9 |
| 201 | Q9ULT0 | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 7A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTC7A PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 96123 | 2 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.03 |
| 202 | P25786 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 29537 | 1 | 1 | 4.6 | 6.15 |
| 203 | Q9Y2C9_REVERSED | Toll-like receptor 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLR6 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 91820 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6.83 |
| 204 | Q14C86_REVERSED | GTPase-activating protein and VPS9 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPVD1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 164876 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.09 |
| 205 | Q5T1B0 | Axonemal dynein light chain domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AXDND1 PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 117953 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.49 |
| 206 | Q9P2G4_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein KIAA1383 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA1383 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 100283 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 6.77 |
| 207 | Q6NUP7 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 4 regulatory subunit 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPP4R4 PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 99389 | 2 | 1 | 0.7 | 7.96 |
| 208 | Q16348 | Solute carrier family 15 member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC15A2 PE=2 SV=2 | 38 | 81730 | 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 8.4 |
| 209 | Q9P2E9 | Ribosome-binding protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RRBP1 PE=1 SV=4 | 38 | 152381 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 8.69 |
| 210 | P04920 | Anion exchange protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC4A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 38 | 136923 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.9 |
| 211 | Q99819 | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARHGDIG PE=2 SV=2 | 38 | 25082 | 1 | 1 | 2.7 | 5.45 |
| 212 | O95071_REVERSED | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBR5 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 309158 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.59 |
| 213 | P22352 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPX3 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 25537 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 8.26 |
| 214 | P29401 | Transketolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TKT PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 67835 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 | 7.58 |
| 215 | P35443 | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 105802 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.44 |
| 216 | Q14028_REVERSED | Cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNGB1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 139590 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 4.76 |
| 217 | Q14573_REVERSED | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITPR3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 303912 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 6.05 |
| 218 | Q9C0B2 | Uncharacterized protein KIAA1751 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA1751 PE=2 SV=2 | 37 | 86902 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.39 |
| 219 | Q6ZUT9_REVERSED | DENN domain-containing protein 5B OS=Homo sapiens GN=DENND5B PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 144927 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6.29 |
| 220 | O94991 | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLITRK5 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 107418 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.48 |
| 221 | O94868_REVERSED | FCH and double SH3 domains protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCHSD2 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 37 | 84224 | 2 | 1 | 1.9 | 5.55 |
| 222 | Q4G0X9_REVERSED | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 40 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CCDC40 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 130033 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.21 |
| 223 | Q9UC07_REVERSED | Zinc finger protein 69 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF69 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 65718 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 9.13 |
| 224 | Q9Y496_REVERSED | Kinesin-like protein KIF3A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF3A PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 37 | 79991 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 6.16 |
| 225 | Q14997 | Proteasome activator complex subunit 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSME4 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 211199 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 6.45 |
| 226 | Q92841 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDX17 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 72326 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 8.82 |
| 227 | Q8N6K7 | Sterile alpha motif domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SAMD3 PE=2 SV=2 | 37 | 61197 | 7 | 1 | 2.1 | 6.67 |
| 228 | Q9NU22 | Midasin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MDN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 632420 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.46 |
| 229 | A8MW92_REVERSED | PHD finger protein 20-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHF20L1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 114938 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.4 |
| 230 | O95613 | Pericentrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCNT PE=1 SV=4 | 36 | 377806 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.4 |
| 231 | P10242_REVERSED | Transcriptional activator Myb OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYB PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 72296 | 3 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.35 |
| 232 | Q7L8A9 | Vasohibin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=VASH1 PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 40931 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 9.5 |
| HDF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot_hit | prot_acc | prot_desc | prot_score | prot_mass | prot_matches | prot_sequences_sig | prot_cover | prot_pi |
| 1 | P02751 | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 16183 | 262460 | 423 | 86 | 66 | 5.46 |
| 2 | P07996 | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 3990 | 129300 | 115 | 42 | 49.4 | 4.71 |
| 3 | P12111 | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 3014 | 343457 | 118 | 59 | 33.3 | 6.26 |
| 4 | P02768 | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 2557 | 69321 | 114 | 8 | 11.8 | 5.92 |
| 5 | P02765 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 2385 | 39300 | 60 | 4 | 8.7 | 5.43 |
| 6 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 2277 | 65999 | 62 | 25 | 51.1 | 8.15 |
| 7 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 2109 | 58792 | 64 | 27 | 54.8 | 5.13 |
| 8 | P03956 | Interstitial collagenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 1904 | 53973 | 57 | 20 | 60.8 | 6.47 |
| 9 | P07093 | Glia-derived nexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINE2 PE=1 SV=1 | 1820 | 43974 | 53 | 17 | 59.8 | 9.35 |
| 10 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1740 | 65393 | 52 | 23 | 56.2 | 8.07 |
| 11 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 1729 | 163188 | 56 | 11 | 7.5 | 6.03 |
| 12 | P24821 | Tenascin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNC PE=1 SV=3 | 1664 | 240700 | 47 | 31 | 25.3 | 4.79 |
| 13 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT9 PE=1 SV=3 | 1625 | 62027 | 36 | 20 | 62.6 | 5.14 |
| 14 | P08253 | 72 kDa type IV collagenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1609 | 73835 | 50 | 24 | 60.5 | 5.26 |
| 15 | P20742 | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 1393 | 163760 | 42 | 5 | 4 | 5.97 |
| 16 | P43235 | Cathepsin K OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSK PE=1 SV=1 | 1336 | 36942 | 26 | 9 | 53.5 | 8.72 |
| 17 | P01024 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 1296 | 187030 | 53 | 13 | 15.4 | 6.02 |
| 18 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 951 | 41710 | 31 | 14 | 47.5 | 5.29 |
| 19 | P12109 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 940 | 108462 | 21 | 13 | 19.6 | 5.26 |
| 20 | P98160 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPG2 PE=1 SV=4 | 933 | 468532 | 48 | 30 | 13.6 | 6.06 |
| 21 | P00734 | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 818 | 69992 | 18 | 8 | 10.9 | 5.64 |
| 22 | P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 799 | 106397 | 24 | 8 | 9.3 | 6.4 |
| 23 | P06396 | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 746 | 85644 | 26 | 11 | 14.3 | 5.9 |
| 24 | P26022 | Pentraxin-related protein PTX3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTX3 PE=1 SV=3 | 727 | 41949 | 16 | 8 | 30.2 | 4.94 |
| 25 | P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 680 | 46283 | 23 | 5 | 12.2 | 5.97 |
| 26 | Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS3BP PE=1 SV=1 | 667 | 65289 | 21 | 12 | 30.3 | 5.13 |
| 27 | Q15582 | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBI PE=1 SV=1 | 604 | 74634 | 17 | 14 | 28.8 | 7.62 |
| 28 | Q99715 | Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL12A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 550 | 332941 | 23 | 19 | 11.7 | 5.38 |
| 29 | Q14393 | Growth arrest-specific protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAS6 PE=1 SV=2 | 527 | 79625 | 16 | 10 | 19.4 | 5.84 |
| 30 | P68032 | Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 521 | 41992 | 19 | 9 | 26.8 | 5.23 |
| 31 | Q07954 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 455 | 504276 | 16 | 13 | 4.5 | 5.16 |
| 32 | P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFP PE=1 SV=1 | 433 | 68633 | 13 | 4 | 6.7 | 5.48 |
| 33 | P12110 | Collagen alpha-2(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 430 | 108512 | 19 | 12 | 18.1 | 5.85 |
| 34 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 429 | 78132 | 18 | 3 | 4.8 | 8.5 |
| 35 | P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4A PE=1 SV=1 | 405 | 192650 | 15 | 8 | 5.6 | 6.65 |
| 36 | P08254 | Stromelysin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP3 PE=1 SV=2 | 403 | 53943 | 15 | 9 | 24.9 | 5.77 |
| 37 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 386 | 15248 | 18 | 5 | 34.5 | 8.72 |
| 38 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 376 | 51529 | 13 | 9 | 23.5 | 5.09 |
| 39 | P35442 | Thrombospondin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS2 PE=1 SV=2 | 331 | 129908 | 13 | 8 | 9.2 | 4.62 |
| 40 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 323 | 36030 | 9 | 5 | 26.3 | 8.57 |
| 41 | P05121 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINE1 PE=1 SV=1 | 323 | 45031 | 12 | 9 | 41.5 | 6.68 |
| 42 | Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTBL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 320 | 41976 | 11 | 4 | 13 | 5.39 |
| 43 | Q8WUJ3 | Protein KIAA1199 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA1199 PE=1 SV=2 | 308 | 152900 | 13 | 9 | 12 | 7.98 |
| 44 | O00391 | Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=QSOX1 PE=1 SV=3 | 301 | 82526 | 9 | 6 | 14.5 | 9.13 |
| 45 | P07355 | Annexin A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 298 | 38580 | 8 | 6 | 31 | 7.57 |
| 46 | Q06033 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 294 | 99787 | 11 | 4 | 8.8 | 5.49 |
| 47 | P07339 | Cathepsin D OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSD PE=1 SV=1 | 282 | 44524 | 13 | 7 | 25.2 | 6.1 |
| 48 | Q08431 | Lactadherin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFGE8 PE=1 SV=2 | 281 | 43095 | 12 | 8 | 26.6 | 8.47 |
| 49 | P08123 | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A2 PE=1 SV=7 | 262 | 129235 | 7 | 7 | 8.4 | 9.08 |
| 50 | P15144 | Aminopeptidase N OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANPEP PE=1 SV=4 | 254 | 109471 | 12 | 6 | 13 | 5.31 |
| 51 | P08758 | Annexin A5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA5 PE=1 SV=2 | 249 | 35914 | 9 | 5 | 19.1 | 4.94 |
| 52 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 246 | 62340 | 14 | 7 | 14.6 | 7.59 |
| 53 | P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 244 | 52929 | 9 | 5 | 12 | 5.4 |
| 54 | P51884 | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 239 | 38405 | 14 | 6 | 21.9 | 6.16 |
| 55 | Q13219 | Pappalysin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAPPA PE=1 SV=3 | 238 | 180856 | 6 | 4 | 6.1 | 5.76 |
| 56 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKM2 PE=1 SV=4 | 238 | 57900 | 7 | 7 | 21.3 | 7.96 |
| 57 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 234 | 70854 | 5 | 5 | 10.2 | 5.37 |
| 58 | P04114 | Apolipoprotein B-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOB PE=1 SV=2 | 231 | 515283 | 15 | 6 | 2.2 | 6.58 |
| 59 | P98095 | Fibulin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN2 PE=1 SV=2 | 221 | 126489 | 7 | 4 | 8.4 | 4.73 |
| 60 | P04259 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 216 | 60030 | 12 | 5 | 10.1 | 8.09 |
| 61 | Q15063 | Periostin OS=Homo sapiens GN=POSTN PE=1 SV=2 | 215 | 93255 | 11 | 7 | 15.1 | 7.27 |
| 62 | P00747 | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 212 | 90510 | 9 | 5 | 8.5 | 7.04 |
| 63 | P12259 | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 210 | 251546 | 10 | 6 | 4.2 | 5.68 |
| 64 | Q16363 | Laminin subunit alpha-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMA4 PE=1 SV=4 | 210 | 202397 | 4 | 3 | 4.1 | 5.89 |
| 65 | P04004 | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 209 | 54271 | 4 | 1 | 3.1 | 5.55 |
| 66 | P55268 | Laminin subunit beta-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMB2 PE=1 SV=2 | 207 | 195854 | 11 | 6 | 6.4 | 6.07 |
| 67 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 204 | 30759 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 5.56 |
| 68 | P23142 | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 202 | 77162 | 11 | 5 | 10.2 | 5.07 |
| 69 | Q9Y6C2 | EMILIN-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EMILIN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 198 | 106601 | 5 | 4 | 8.8 | 5.07 |
| 70 | Q99816 | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 43916 | 15 | 5 | 19.2 | 5.2 |
| 71 | P05543 | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 197 | 46295 | 6 | 3 | 8.2 | 5.87 |
| 72 | Q13510 | Acid ceramidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ASAH1 PE=1 SV=5 | 197 | 44631 | 5 | 5 | 18.5 | 7.52 |
| 73 | P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 188 | 138857 | 8 | 4 | 5.2 | 5.6 |
| 74 | P11047 | Laminin subunit gamma-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 179 | 177489 | 6 | 4 | 3.8 | 5.01 |
| 75 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 176 | 16045 | 11 | 2 | 12.9 | 7.85 |
| 76 | P35443 | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 171 | 105802 | 6 | 5 | 7.3 | 4.44 |
| 77 | P49747 | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMP PE=1 SV=2 | 167 | 82808 | 6 | 5 | 7.1 | 4.36 |
| 78 | P19827 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 166 | 101326 | 3 | 3 | 2.9 | 6.31 |
| 79 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 165 | 47139 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 7.01 |
| 80 | P13929 | Beta-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO3 PE=1 SV=4 | 163 | 46902 | 2 | 2 | 7.6 | 7.59 |
| 81 | P01031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 162 | 188186 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 6.11 |
| 82 | P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 159 | 60008 | 9 | 4 | 9.9 | 8.09 |
| 83 | P02100 | Hemoglobin subunit epsilon OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBE1 PE=1 SV=2 | 159 | 16192 | 7 | 2 | 12.9 | 8.67 |
| 84 | P07858 | Cathepsin B OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSB PE=1 SV=3 | 159 | 37797 | 5 | 4 | 15 | 5.88 |
| 85 | Q6YHK3 | CD109 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD109 PE=1 SV=2 | 158 | 161587 | 6 | 5 | 5.3 | 5.59 |
| 86 | P42785 | Lysosomal Pro-X carboxypeptidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRCP PE=1 SV=1 | 155 | 55764 | 2 | 1 | 4.2 | 6.75 |
| 87 | P02649 | Apolipoprotein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOE PE=1 SV=1 | 154 | 36132 | 6 | 3 | 9.1 | 5.65 |
| 88 | P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 154 | 21212 | 5 | 4 | 38.3 | 5.3 |
| 89 | P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 154 | 55892 | 3 | 2 | 3.9 | 8.54 |
| 90 | Q92626 | Peroxidasin homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=PXDN PE=1 SV=2 | 153 | 165170 | 5 | 4 | 4.9 | 6.79 |
| 91 | P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 150 | 54531 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.87 |
| 92 | P00736 | Complement C1r subcomponent OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1R PE=1 SV=2 | 150 | 80067 | 6 | 5 | 13 | 5.82 |
| 93 | Q9Y4K0 | Lysyl oxidase homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LOXL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 148 | 86668 | 3 | 3 | 5.7 | 5.95 |
| 94 | Q13103 | Secreted phosphoprotein 24 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 147 | 24322 | 2 | 1 | 5.7 | 8.59 |
| 95 | P34931 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1L PE=1 SV=2 | 145 | 70331 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 5.76 |
| 96 | P04083 | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 141 | 38690 | 3 | 3 | 16.2 | 6.57 |
| 97 | Q9Y490 | Talin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 140 | 269599 | 7 | 4 | 4.2 | 5.77 |
| 98 | P68363 | Tubulin alpha-1B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA1B PE=1 SV=1 | 139 | 50120 | 8 | 4 | 19.7 | 4.94 |
| 99 | P15169 | Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 139 | 52253 | 2 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.86 |
| 100 | P07686 | Beta-hexosaminidase subunit beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEXB PE=1 SV=3 | 137 | 63071 | 8 | 3 | 15.8 | 6.29 |
| 101 | P02748 | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 135 | 63133 | 3 | 2 | 3.8 | 5.43 |
| 102 | P19013 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 130 | 57250 | 8 | 4 | 7.3 | 6.25 |
| 103 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 129 | 49639 | 6 | 4 | 18.5 | 4.78 |
| 104 | Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain family 11 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC11A PE=1 SV=1 | 128 | 35672 | 3 | 1 | 8 | 5.06 |
| 105 | P51888 | Prolargin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRELP PE=1 SV=1 | 124 | 43782 | 6 | 4 | 15.2 | 9.47 |
| 106 | Q9UBG0 | C-type mannose receptor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MRC2 PE=1 SV=2 | 123 | 166568 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 5.54 |
| 107 | P00742 | Coagulation factor X OS=Homo sapiens GN=F10 PE=1 SV=2 | 122 | 54697 | 5 | 3 | 7.6 | 5.68 |
| 108 | Q86YZ3 | Hornerin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRNR PE=1 SV=2 | 115 | 282228 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 10.05 |
| 109 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 112 | 49557 | 5 | 4 | 6.1 | 4.91 |
| 110 | P09871 | Complement C1s subcomponent OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1S PE=1 SV=1 | 111 | 76635 | 5 | 4 | 6.8 | 4.86 |
| 111 | P10619 | Lysosomal protective protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSA PE=1 SV=2 | 106 | 54431 | 4 | 3 | 12.5 | 6.16 |
| 112 | P62979 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPS27A PE=1 SV=2 | 100 | 17953 | 7 | 3 | 28.2 | 9.68 |
| 113 | Q02809 | Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLOD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 98 | 83497 | 4 | 2 | 8.4 | 6.47 |
| 114 | P07602 | Proactivator polypeptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSAP PE=1 SV=2 | 96 | 58074 | 4 | 3 | 7.6 | 5.06 |
| 115 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA1 PE=1 SV=5 | 96 | 84607 | 5 | 2 | 5.9 | 4.94 |
| 116 | P49746 | Thrombospondin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS3 PE=1 SV=1 | 94 | 104135 | 7 | 2 | 8.1 | 4.43 |
| 117 | P08294 | Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOD3 PE=1 SV=2 | 94 | 25835 | 1 | 1 | 5.4 | 6.14 |
| 118 | P00450 | Ceruloplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CP PE=1 SV=1 | 94 | 122128 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5.44 |
| 119 | P08473 | Neprilysin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MME PE=1 SV=2 | 93 | 85460 | 2 | 2 | 3.2 | 5.54 |
| 120 | P04745 | Alpha-amylase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY1A PE=1 SV=2 | 91 | 57731 | 2 | 2 | 5.5 | 6.47 |
| 121 | P08238 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 91 | 83212 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4.97 |
| 122 | P21333 | Filamin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLNA PE=1 SV=4 | 89 | 280564 | 5 | 3 | 2.6 | 5.7 |
| 123 | Q8NI35 | InaD-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=INADL PE=1 SV=3 | 89 | 196247 | 8 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.84 |
| 124 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 88 | 44586 | 2 | 1 | 7.9 | 8.3 |
| 125 | P48723 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA13 PE=1 SV=1 | 88 | 51895 | 3 | 3 | 8.1 | 5.52 |
| 126 | Q8TEV9_REVERSED | Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosomal region candidate gene 8 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMCR8 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 86 | 104956 | 10 | 1 | 1.2 | 5.36 |
| 127 | P09486 | SPARC OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPARC PE=1 SV=1 | 85 | 34610 | 3 | 2 | 16.5 | 4.73 |
| 128 | P68371 | Tubulin beta-2C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB2C PE=1 SV=1 | 85 | 49799 | 5 | 3 | 15.7 | 4.79 |
| 129 | P27487 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 85 | 88222 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5.67 |
| 130 | P09238 | Stromelysin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP10 PE=1 SV=1 | 84 | 54117 | 4 | 2 | 6.1 | 5.49 |
| 131 | Q8N436 | Inactive carboxypeptidase-like protein X2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPXM2 PE=2 SV=3 | 84 | 85816 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6.4 |
| 132 | O95497 | Pantetheinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VNN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 81 | 56975 | 1 | 1 | 3.7 | 5.32 |
| 133 | Q06828 | Fibromodulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FMOD PE=1 SV=2 | 80 | 43152 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.66 |
| 134 | O00560 | Syntenin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SDCBP PE=1 SV=1 | 79 | 32424 | 4 | 2 | 21.1 | 7.05 |
| 135 | P23526 | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 79 | 47685 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 5.92 |
| 136 | P33908 | Mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase IA OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN1A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 78 | 72922 | 3 | 2 | 6.4 | 6.04 |
| 137 | O14773 | Tripeptidyl-peptidase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 77 | 61210 | 1 | 1 | 4.8 | 6.01 |
| 138 | P01008 | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 77 | 52569 | 5 | 2 | 7.3 | 6.32 |
| 139 | P16035 | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TIMP2 PE=1 SV=2 | 77 | 24383 | 4 | 2 | 12.7 | 7.45 |
| 140 | P11717 | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 77 | 274199 | 4 | 3 | 2.2 | 5.64 |
| 141 | Q12860 | Contactin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CNTN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 75 | 113249 | 3 | 2 | 3.4 | 5.62 |
| 142 | Q92743 | Serine protease HTRA1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HTRA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 75 | 51255 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 | 8.09 |
| 143 | P05067 | Amyloid beta A4 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=APP PE=1 SV=3 | 74 | 86888 | 2 | 1 | 2.6 | 4.73 |
| 144 | Q8TAA3 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 74 | 28512 | 1 | 1 | 5.5 | 9.07 |
| 145 | Q5D862 | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 72 | 247928 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8.45 |
| 146 | O00300 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFRSF11B PE=1 SV=3 | 71 | 45996 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 | 8.66 |
| 147 | P02790 | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 71 | 51643 | 4 | 1 | 1.9 | 6.55 |
| 148 | O15111_REVERSED | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHUK PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 71 | 84585 | 6 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.28 |
| 149 | P28799 | Granulins OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRN PE=1 SV=2 | 69 | 63500 | 4 | 2 | 6.2 | 6.43 |
| 150 | O75508 | Claudin-11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLDN11 PE=1 SV=2 | 69 | 21978 | 1 | 1 | 6.8 | 8.22 |
| 151 | P81605 | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 68 | 11277 | 2 | 2 | 20 | 6.08 |
| 152 | P55058 | Phospholipid transfer protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLTP PE=1 SV=1 | 68 | 54705 | 1 | 1 | 2.2 | 6.53 |
| 153 | P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 68 | 38273 | 3 | 1 | 4.3 | 8.34 |
| 154 | P60033 | CD81 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD81 PE=1 SV=1 | 67 | 25792 | 2 | 1 | 18.2 | 5.09 |
| 155 | Q8WXE9 | Stonin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=STON2 PE=1 SV=1 | 67 | 101102 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 |
| 156 | O95445 | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 21239 | 5 | 1 | 6.9 | 5.66 |
| 157 | Q7Z304 | MAM domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAMDC2 PE=2 SV=3 | 66 | 77506 | 3 | 2 | 3.9 | 5.05 |
| 158 | Q12931 | Heat shock protein 75 kDa, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRAP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 65 | 80060 | 3 | 1 | 2.8 | 8.3 |
| 159 | P19883 | Follistatin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FST PE=1 SV=2 | 65 | 37981 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 5.53 |
| 160 | P61224 | Ras-related protein Rap-1b OS=Homo sapiens GN=RAP1B PE=1 SV=1 | 64 | 20812 | 2 | 2 | 12.5 | 5.65 |
| 161 | P20908 | Collagen alpha-1(V) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL5A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 64 | 183447 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 4.94 |
| 162 | P10599 | Thioredoxin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TXN PE=1 SV=3 | 64 | 11730 | 1 | 1 | 12.4 | 4.82 |
| 163 | P08133 | Annexin A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA6 PE=1 SV=3 | 62 | 75826 | 2 | 2 | 4.2 | 5.42 |
| 164 | Q9NZP8 | Complement C1r subcomponent-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1RL PE=1 SV=2 | 62 | 53464 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.75 |
| 165 | Q03692 | Collagen alpha-1(X) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL10A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 61 | 66117 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 9.68 |
| 166 | P26447 | Protein S100-A4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A4 PE=1 SV=1 | 61 | 11721 | 2 | 2 | 16.8 | 5.85 |
| 167 | P14550 | Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 61 | 36550 | 1 | 1 | 3.1 | 6.32 |
| 168 | P15121 | Aldose reductase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AKR1B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 61 | 35830 | 1 | 1 | 3.2 | 6.51 |
| 169 | P22105 | Tenascin-X OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNXB PE=1 SV=3 | 60 | 464034 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.19 |
| 170 | Q9BYX7_REVERSED | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 57 | 41989 | 9 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.92 |
| 171 | P05546 | Heparin cofactor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPIND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 57 | 57034 | 2 | 1 | 3.8 | 6.41 |
| 172 | P02461 | Collagen alpha-1(III) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL3A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 57 | 138479 | 3 | 1 | 2.9 | 6.21 |
| 173 | P07585 | Decorin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCN PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 39722 | 2 | 1 | 9.7 | 8.75 |
| 174 | Q03135 | Caveolin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CAV1 PE=1 SV=4 | 56 | 20458 | 1 | 1 | 7.9 | 5.65 |
| 175 | O43264_REVERSED | Centromere/kinetochore protein zw10 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZW10 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 55 | 88773 | 2 | 1 | 0.8 | 5.89 |
| 176 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=PPIA PE=1 SV=2 | 55 | 18001 | 2 | 1 | 13.9 | 7.68 |
| 177 | P07737 | Profilin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PFN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 55 | 15045 | 2 | 2 | 12.1 | 8.44 |
| 178 | P02760 | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 55 | 38974 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5.95 |
| 179 | B9A064 | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 54 | 23049 | 1 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.08 |
| 180 | P18206 | Vinculin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCL PE=1 SV=4 | 54 | 123722 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5.5 |
| 181 | P10643 | Complement component C7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C7 PE=1 SV=2 | 54 | 93457 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6.09 |
| 182 | Q9UK55 | Protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA10 PE=1 SV=1 | 53 | 50674 | 4 | 1 | 4.1 | 8.28 |
| 183 | Q8NBM4 | Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBAC2 PE=2 SV=1 | 52 | 38938 | 5 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.21 |
| 184 | Q14624 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 52 | 103293 | 6 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.51 |
| 185 | Q86VH2 | Kinesin-like protein KIF27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF27 PE=2 SV=1 | 51 | 160184 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 6.9 |
| 186 | P28300 | Protein-lysine 6-oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LOX PE=1 SV=2 | 51 | 46915 | 1 | 1 | 3.1 | 8.36 |
| 187 | P05452 | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 22522 | 1 | 1 | 10.4 | 5.52 |
| 188 | Q8NAV2_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein C8orf58 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C8orf58 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 51 | 39636 | 3 | 1 | 4.1 | 8.54 |
| 189 | P08962 | CD63 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD63 PE=1 SV=2 | 51 | 25619 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 | 8.14 |
| 190 | P61769 | Beta-2-microglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=B2M PE=1 SV=1 | 51 | 13706 | 1 | 1 | 8.4 | 6.06 |
| 191 | P15311 | Ezrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=EZR PE=1 SV=4 | 50 | 69370 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 5.94 |
| 192 | P04439 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A-3 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-A PE=1 SV=2 | 50 | 40815 | 3 | 2 | 9.3 | 5.66 |
| 193 | Q86Y46 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 50 | 58887 | 8 | 3 | 8.5 | 6.93 |
| 194 | P26038 | Moesin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MSN PE=1 SV=3 | 50 | 67778 | 2 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.08 |
| 195 | O60312 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase VA OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP10A PE=2 SV=2 | 50 | 167582 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| 196 | Q9HDC9 | Adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=APMAP PE=1 SV=2 | 50 | 46451 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.82 |
| 197 | Q16394 | Exostosin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EXT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 49 | 86200 | 3 | 1 | 8.6 | 9.16 |
| 198 | Q15751_REVERSED | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HERC1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 48 | 531891 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.69 |
| 199 | P02787 | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 47 | 77014 | 2 | 1 | 1.7 | 6.81 |
| 200 | Q13454 | Tumor suppressor candidate 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUSC3 PE=2 SV=1 | 47 | 39650 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 9.93 |
| 201 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHA PE=1 SV=2 | 47 | 36665 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 8.44 |
| 202 | P60903 | Protein S100-A10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A10 PE=1 SV=2 | 47 | 11196 | 1 | 1 | 17.5 | 6.82 |
| 203 | P29353_REVERSED | SHC-transforming protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHC1 PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 46 | 62782 | 5 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.01 |
| 204 | P01042 | Kininogen-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KNG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 46 | 71912 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.34 |
| 205 | Q76LX8 | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAMTS13 PE=1 SV=1 | 45 | 153505 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 6.96 |
| 206 | Q9UHL4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DPP7 PE=1 SV=3 | 45 | 54307 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 | 5.91 |
| 207 | P07225 | Vitamin K-dependent protein S OS=Homo sapiens GN=PROS1 PE=1 SV=1 | 45 | 75074 | 2 | 1 | 2.4 | 5.48 |
| 208 | Q99456 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT12 PE=1 SV=1 | 45 | 53478 | 3 | 1 | 3.2 | 4.7 |
| 209 | Q96CD0_REVERSED | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXL8 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 44 | 40490 | 6 | 1 | 1.9 | 7.03 |
| 210 | Q6ZU45 | Putative C-type lectin domain-containing protein NCRNA00083 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCRNA00083 PE=5 SV=1 | 44 | 25796 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 6.3 |
| 211 | Q3KQU3 | MAP7 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP7D1 PE=1 SV=1 | 44 | 92764 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 10.12 |
| 212 | Q5U5X0 | LYR motif-containing protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYRM7 PE=1 SV=1 | 44 | 11947 | 1 | 1 | 5.8 | 9.67 |
| 213 | Q8N7B9_REVERSED | EF-hand calcium-binding domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFCAB3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 44 | 50114 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 9.31 |
| 214 | Q8NB25_REVERSED | Protein FAM184A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM184A PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 44 | 132883 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.59 |
| 215 | P06732 | Creatine kinase M-type OS=Homo sapiens GN=CKM PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 43074 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.77 |
| 216 | Q93096_REVERSED | Protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTP4A1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 44 | 19802 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 | 9.17 |
| 217 | Q8IWC1 | MAP7 domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP7D3 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 98368 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 9.34 |
| 218 | P11137 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP2 PE=1 SV=4 | 42 | 199404 | 2 | 1 | 1.1 | 4.82 |
| 219 | Q16348 | Solute carrier family 15 member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC15A2 PE=2 SV=2 | 42 | 81730 | 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 8.4 |
| 220 | P15531 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=NME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 42 | 17138 | 1 | 1 | 11.2 | 5.83 |
| 221 | Q14566_REVERSED | DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MCM6 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 92831 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 5.28 |
| 222 | O75830 | Serpin I2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINI2 PE=2 SV=1 | 41 | 46116 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.08 |
| 223 | O60568 | Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLOD3 PE=1 SV=1 | 41 | 84731 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 5.69 |
| 224 | Q8NHP8 | Putative phospholipase B-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLBD2 PE=1 SV=2 | 41 | 65430 | 2 | 1 | 3.2 | 6.34 |
| 225 | Q99466_REVERSED | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NOTCH4 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 209480 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.43 |
| 226 | P17936 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGFBP3 PE=1 SV=2 | 41 | 31654 | 1 | 1 | 3.8 | 9.03 |
| 227 | Q14789_REVERSED | Golgin subfamily B member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GOLGB1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 375790 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.96 |
| 228 | Q9BXJ4 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1QTNF3 PE=2 SV=1 | 40 | 26977 | 1 | 1 | 2.8 | 6.04 |
| 229 | P25789 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA4 PE=1 SV=1 | 40 | 29465 | 2 | 2 | 6.5 | 7.57 |
| 230 | Q8WZ42 | Titin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTN PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 3813810 | 5 | 1 | 0.1 | 6.01 |
| 231 | P02750 | Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 38154 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 6.45 |
| 232 | Q9GZR7 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX24 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DDX24 PE=1 SV=1 | 40 | 96271 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 9.14 |
| 233 | Q92616_REVERSED | Translational activator GCN1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GCN1L1 PE=1 SV=6 - REVERSED | 40 | 292572 | 6 | 1 | 0.5 | 7.28 |
| 234 | Q03923_REVERSED | Zinc finger protein 85 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF85 PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 40 | 68691 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 9.45 |
| 235 | Q8IVF5_REVERSED | T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TIAM2 PE=2 SV=4 - REVERSED | 40 | 189985 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 6.8 |
| 236 | A2RRP1_REVERSED | Neuroblastoma-amplified sequence OS=Homo sapiens GN=NBAS PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 40 | 268401 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.65 |
| 237 | P55083 | Microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFAP4 PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 28630 | 1 | 1 | 7.1 | 5.38 |
| 238 | O14782 | Kinesin-like protein KIF3C OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF3C PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 89371 | 3 | 1 | 1.1 | 8.28 |
| 239 | O14556 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, testis-specific OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDHS PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 44473 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 8.38 |
| 240 | P05156 | Complement factor I OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFI PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 65707 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 7.72 |
| 241 | Q6IWH7 | Anoctamin-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANO7 PE=1 SV=1 | 39 | 105463 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8.33 |
| 242 | Q14C86_REVERSED | GTPase-activating protein and VPS9 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPVD1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 39 | 164876 | 2 | 1 | 1.1 | 5.09 |
| 243 | P02792 | Ferritin light chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTL PE=1 SV=2 | 38 | 20007 | 2 | 1 | 19.4 | 5.51 |
| 244 | Q15022 | Polycomb protein SUZ12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SUZ12 PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 83003 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 8.98 |
| 245 | P33981 | Dual specificity protein kinase TTK OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTK PE=1 SV=2 | 38 | 97011 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 8.41 |
| 246 | P27105 | Erythrocyte band 7 integral membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=STOM PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 31711 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 | 7.71 |
| 247 | P28066 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 26394 | 1 | 1 | 4.1 | 4.74 |
| 248 | Q12968_REVERSED | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NFATC3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 37 | 115522 | 3 | 1 | 0.7 | 5.91 |
| 249 | O00754 | Lysosomal alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 113672 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 6.84 |
| 250 | P24347 | Stromelysin-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP11 PE=1 SV=3 | 36 | 54556 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.38 |
| 251 | A6H8Y1 | Transcription factor TFIIIB component B~~ homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=BDP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 36 | 293705 | 2 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.06 |
| 252 | O95071_REVERSED | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBR5 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 309158 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.59 |
| 253 | Q9UDT6 | CAP-Gly domain-containing linker protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLIP2 PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 115767 | 4 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.29 |
| 254 | Q9C093_REVERSED | Sperm flagellar protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SPEF2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 209680 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.4 |
| 255 | Q9NW08 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase III subunit RPC2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POLR3B PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 127702 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.77 |
| 256 | Q5VWK0 | Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NBPF6 PE=2 SV=2 | 36 | 72194 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 4.84 |
| 257 | O15264 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAPK13 PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 42063 | 4 | 1 | 1.9 | 8.48 |
| 258 | P21580_REVERSED | Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNFAIP3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 36 | 89556 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 8.61 |
| 259 | P10242_REVERSED | Transcriptional activator Myb OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYB PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 72296 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.35 |
| 260 | Q96IF1 | Protein ajuba OS=Homo sapiens GN=JUB PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 56897 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.86 |
| 261 | Q96RD9_REVERSED | Fc receptor-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCRL5 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 36 | 106371 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 6.72 |
| MCF 10A | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot_hit | prot_acc | prot_desc | prot_score | prot_mass | prot_matches | prot_sequences_sig | prot_cover | prot_pi |
| 1 | P02751 | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 3184 | 262460 | 89 | 44 | 34.2 | 5.46 |
| 2 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 3099 | 65999 | 85 | 33 | 58.1 | 8.15 |
| 3 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 2577 | 58792 | 82 | 31 | 61.6 | 5.13 |
| 4 | P12111 | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 2447 | 343457 | 101 | 65 | 32.7 | 6.26 |
| 5 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT9 PE=1 SV=3 | 2240 | 62027 | 64 | 25 | 59.9 | 5.14 |
| 6 | P02768 | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 2090 | 69321 | 94 | 11 | 11.8 | 5.92 |
| 7 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1977 | 65393 | 59 | 28 | 58.5 | 8.07 |
| 8 | Q99715 | Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL12A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1875 | 332941 | 84 | 55 | 28.3 | 5.38 |
| 9 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 1827 | 163188 | 60 | 9 | 7.7 | 6.03 |
| 10 | P07996 | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 1802 | 129300 | 68 | 33 | 38.1 | 4.71 |
| 11 | P02765 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 1724 | 39300 | 54 | 5 | 8.7 | 5.43 |
| 12 | P20742 | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 1283 | 163760 | 43 | 6 | 4.3 | 5.97 |
| 13 | P01024 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 756 | 187030 | 35 | 17 | 15.6 | 6.02 |
| 14 | P12109 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 726 | 108462 | 23 | 10 | 18.9 | 5.26 |
| 15 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 718 | 51529 | 32 | 14 | 32.8 | 5.09 |
| 16 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 676 | 41710 | 28 | 10 | 47.5 | 5.29 |
| 17 | P00734 | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 607 | 69992 | 17 | 6 | 10.5 | 5.64 |
| 18 | P08779 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT16 PE=1 SV=4 | 585 | 51236 | 29 | 13 | 32.1 | 4.99 |
| 19 | P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 534 | 106397 | 15 | 7 | 9.3 | 6.4 |
| 20 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 529 | 78132 | 20 | 3 | 4.8 | 8.5 |
| 21 | Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=LGALS3BP PE=1 SV=1 | 520 | 65289 | 20 | 13 | 30.4 | 5.13 |
| 22 | P24821 | Tenascin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TNC PE=1 SV=3 | 429 | 240700 | 21 | 11 | 13.8 | 4.79 |
| 23 | P04259 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 426 | 60030 | 21 | 12 | 21.3 | 8.09 |
| 24 | P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 401 | 60008 | 21 | 12 | 21.1 | 8.09 |
| 25 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 387 | 62340 | 23 | 13 | 23.7 | 7.59 |
| 26 | P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4A PE=1 SV=1 | 356 | 192650 | 15 | 8 | 5.2 | 6.65 |
| 27 | Q15582 | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TGFBI PE=1 SV=1 | 344 | 74634 | 18 | 10 | 25.2 | 7.62 |
| 28 | P68032 | Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 332 | 41992 | 16 | 6 | 26.8 | 5.23 |
| 29 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 330 | 49557 | 16 | 6 | 12.9 | 4.91 |
| 30 | P06396 | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 324 | 85644 | 13 | 5 | 11.4 | 5.9 |
| 31 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 324 | 36030 | 10 | 5 | 28.4 | 8.57 |
| 32 | P68363 | Tubulin alpha-1B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA1B PE=1 SV=1 | 318 | 50120 | 14 | 10 | 28.8 | 4.94 |
| 33 | Q04695 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT17 PE=1 SV=2 | 309 | 48076 | 19 | 8 | 22 | 4.97 |
| 34 | P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFP PE=1 SV=1 | 303 | 68633 | 10 | 4 | 6.7 | 5.48 |
| 35 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 291 | 15248 | 14 | 4 | 33.1 | 8.72 |
| 36 | P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 282 | 52929 | 11 | 5 | 11.6 | 5.4 |
| 37 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLTC PE=1 SV=5 | 280 | 191493 | 7 | 6 | 6.2 | 5.48 |
| 38 | P19012 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT15 PE=1 SV=3 | 256 | 49181 | 17 | 6 | 12.1 | 4.71 |
| 39 | P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 254 | 46283 | 6 | 3 | 9.1 | 5.97 |
| 40 | P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 243 | 138857 | 10 | 6 | 9.6 | 5.6 |
| 41 | P04114 | Apolipoprotein B-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOB PE=1 SV=2 | 237 | 515283 | 15 | 9 | 2.2 | 6.58 |
| 42 | P12110 | Collagen alpha-2(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 235 | 108512 | 15 | 7 | 15.3 | 5.85 |
| 43 | P07355 | Annexin A2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 220 | 38580 | 7 | 6 | 23.9 | 7.57 |
| 44 | Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTBL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 213 | 41976 | 10 | 3 | 16 | 5.39 |
| 45 | P68366 | Tubulin alpha-4A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA4A PE=1 SV=1 | 208 | 49892 | 10 | 7 | 19 | 4.95 |
| 46 | P04004 | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 196 | 54271 | 6 | 1 | 4.2 | 5.55 |
| 47 | P23142 | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 180 | 77162 | 7 | 4 | 5.7 | 5.07 |
| 48 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 180 | 49639 | 8 | 5 | 19.6 | 4.78 |
| 49 | Q5XKE5 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 79 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT79 PE=1 SV=2 | 179 | 57800 | 8 | 4 | 6.9 | 6.75 |
| 50 | P62805 | Histone H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H4A PE=1 SV=2 | 173 | 11360 | 7 | 5 | 50.5 | 11.36 |
| 51 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 171 | 16045 | 10 | 2 | 12.9 | 7.85 |
| 52 | P05787 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT8 PE=1 SV=7 | 170 | 53671 | 7 | 4 | 5.8 | 5.52 |
| 53 | Q07954 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 167 | 504276 | 9 | 4 | 2.6 | 5.16 |
| 54 | P49747 | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMP PE=1 SV=2 | 165 | 82808 | 6 | 4 | 5.8 | 4.36 |
| 55 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 164 | 30759 | 4 | 1 | 8.2 | 5.56 |
| 56 | P19013 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 163 | 57250 | 8 | 4 | 7.3 | 6.25 |
| 57 | P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 145 | 54531 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.87 |
| 58 | P01008 | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 144 | 52569 | 11 | 5 | 10.3 | 6.32 |
| 59 | P68371 | Tubulin beta-2C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB2C PE=1 SV=1 | 140 | 49799 | 7 | 4 | 16.2 | 4.79 |
| 60 | Q06033 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 139 | 99787 | 6 | 3 | 4.2 | 5.49 |
| 61 | P12259 | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 135 | 251546 | 8 | 4 | 3.2 | 5.68 |
| 62 | P23526 | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 133 | 47685 | 3 | 2 | 9 | 5.92 |
| 63 | P51884 | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 130 | 38405 | 6 | 2 | 9.8 | 6.16 |
| 64 | Q8NI35 | InaD-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=INADL PE=1 SV=3 | 129 | 196247 | 11 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.84 |
| 65 | P19827 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 120 | 101326 | 3 | 2 | 3.8 | 6.31 |
| 66 | Q05707 | Collagen alpha-1(XIV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL14A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 119 | 193394 | 11 | 4 | 7.6 | 5.16 |
| 67 | P12035 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT3 PE=1 SV=3 | 118 | 64378 | 6 | 4 | 5.6 | 6.12 |
| 68 | P15169 | Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 116 | 52253 | 2 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.86 |
| 69 | P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 114 | 55892 | 5 | 3 | 5.3 | 8.54 |
| 70 | P02748 | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 113 | 63133 | 2 | 2 | 3.8 | 5.43 |
| 71 | P11717 | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 111 | 274199 | 4 | 2 | 0.8 | 5.64 |
| 72 | P00747 | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 110 | 90510 | 6 | 2 | 4.3 | 7.04 |
| 73 | P81605 | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 110 | 11277 | 4 | 3 | 22.7 | 6.08 |
| 74 | P05543 | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 105 | 46295 | 4 | 2 | 4.8 | 5.87 |
| 75 | P0C0S8 | Histone H2A type 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H2AG PE=1 SV=2 | 105 | 14083 | 3 | 2 | 21.5 | 10.9 |
| 76 | Q86YZ3 | Hornerin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRNR PE=1 SV=2 | 102 | 282228 | 2 | 2 | 1.3 | 10.05 |
| 77 | P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 101 | 38273 | 4 | 1 | 5.2 | 8.34 |
| 78 | Q08431 | Lactadherin OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFGE8 PE=1 SV=2 | 101 | 43095 | 2 | 1 | 3.9 | 8.47 |
| 79 | P01031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 101 | 188186 | 6 | 2 | 2.6 | 6.11 |
| 80 | Q5D862 | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 100 | 247928 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8.45 |
| 81 | P07195 | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHB PE=1 SV=2 | 99 | 36615 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 5.71 |
| 82 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 98 | 46707 | 4 | 1 | 3.3 | 5.37 |
| 83 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCP PE=1 SV=4 | 96 | 89266 | 5 | 2 | 8.8 | 5.14 |
| 84 | O43854 | EGF-like repeat and discoidin I-like domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EDIL3 PE=1 SV=1 | 93 | 53730 | 4 | 4 | 7.5 | 7.08 |
| 85 | P08238 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 92 | 83212 | 3 | 2 | 4.1 | 4.97 |
| 86 | O14818 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA7 PE=1 SV=1 | 91 | 27870 | 3 | 3 | 13.7 | 8.6 |
| 87 | O15111_REVERSED | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHUK PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 87 | 84585 | 7 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.28 |
| 88 | P08107 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A/1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1A PE=1 SV=5 | 82 | 70009 | 4 | 3 | 8.3 | 5.48 |
| 89 | Q86Y46 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 81 | 58887 | 6 | 4 | 6.7 | 6.93 |
| 90 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKM2 PE=1 SV=4 | 81 | 57900 | 6 | 3 | 14.1 | 7.96 |
| 91 | P02461 | Collagen alpha-1(III) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL3A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 80 | 138479 | 3 | 2 | 2.3 | 6.21 |
| 92 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOA PE=1 SV=2 | 80 | 39395 | 4 | 2 | 10.7 | 8.3 |
| 93 | P61204 | ADP-ribosylation factor 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ARF3 PE=1 SV=2 | 79 | 20588 | 1 | 1 | 8.3 | 6.84 |
| 94 | Q14764 | Major vault protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MVP PE=1 SV=4 | 77 | 99266 | 4 | 3 | 5.6 | 5.34 |
| 95 | P02787 | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 77 | 77014 | 3 | 2 | 1.7 | 6.81 |
| 96 | Q5QNW6 | Histone H2B type 2-F OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H2BF PE=1 SV=3 | 76 | 13912 | 3 | 2 | 15.9 | 10.31 |
| 97 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA1 PE=1 SV=5 | 76 | 84607 | 3 | 2 | 4.9 | 4.94 |
| 98 | Q8N7M0_REVERSED | Tctex1 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TCTEX1D1 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 75 | 20717 | 13 | 1 | 3.9 | 9.04 |
| 99 | P04083 | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 74 | 38690 | 2 | 1 | 8.4 | 6.57 |
| 100 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 73 | 70854 | 4 | 2 | 8.7 | 5.37 |
| 101 | P04180 | Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase OS=Homo sapiens GN=LCAT PE=1 SV=1 | 70 | 49546 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 5.71 |
| 102 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 70 | 13234 | 3 | 1 | 24.6 | 5.71 |
| 103 | Q9BXJ4 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1QTNF3 PE=2 SV=1 | 68 | 26977 | 2 | 2 | 8.1 | 6.04 |
| 104 | P02753 | Retinol-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBP4 PE=1 SV=3 | 66 | 22995 | 2 | 1 | 16.4 | 5.76 |
| 105 | P29353_REVERSED | SHC-transforming protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHC1 PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 66 | 62782 | 11 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.01 |
| 106 | Q08554 | Desmocollin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 99924 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.25 |
| 107 | Q16853 | Membrane primary amine oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AOC3 PE=1 SV=3 | 66 | 84568 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.05 |
| 108 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHA PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 36665 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 8.44 |
| 109 | P00488 | Coagulation factor XIII A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=F13A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 65 | 83215 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 5.75 |
| 110 | Q5VTE0 | Putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1A1P5 PE=5 SV=1 | 64 | 50153 | 3 | 2 | 5.2 | 9.15 |
| 111 | Q9H4B7 | Tubulin beta-1 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB1 PE=1 SV=1 | 64 | 50295 | 3 | 1 | 9.5 | 5.05 |
| 112 | P62979 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPS27A PE=1 SV=2 | 63 | 17953 | 1 | 1 | 10.3 | 9.68 |
| 113 | P35443 | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 62 | 105802 | 5 | 2 | 3.9 | 4.44 |
| 114 | P02760 | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 61 | 38974 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5.95 |
| 115 | P21333 | Filamin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLNA PE=1 SV=4 | 60 | 280564 | 3 | 2 | 1.3 | 5.7 |
| 116 | P35579 | Myosin-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH9 PE=1 SV=4 | 59 | 226392 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 5.5 |
| 117 | Q15063 | Periostin OS=Homo sapiens GN=POSTN PE=1 SV=2 | 59 | 93255 | 3 | 1 | 5.9 | 7.27 |
| 118 | P02649 | Apolipoprotein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOE PE=1 SV=1 | 59 | 36132 | 4 | 2 | 8.2 | 5.65 |
| 119 | Q14624 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 59 | 103293 | 3 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.51 |
| 120 | P08758 | Annexin A5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA5 PE=1 SV=2 | 58 | 35914 | 4 | 2 | 10.6 | 4.94 |
| 121 | P02786 | Transferrin receptor protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TFRC PE=1 SV=2 | 58 | 84818 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.18 |
| 122 | A6NIZ1 | Ras-related protein Rap-1b-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 57 | 20912 | 1 | 1 | 6.5 | 5.37 |
| 123 | Q93070 | Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ART4 PE=2 SV=2 | 57 | 35854 | 8 | 1 | 2.2 | 9.31 |
| 124 | Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain family 11 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC11A PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 35672 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 5.06 |
| 125 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX2 PE=1 SV=5 | 55 | 21878 | 1 | 1 | 9.1 | 5.66 |
| 126 | Q99456 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT12 PE=1 SV=1 | 55 | 53478 | 4 | 1 | 3.2 | 4.7 |
| 127 | P01591 | Immunoglobulin J chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGJ PE=1 SV=4 | 54 | 18087 | 1 | 1 | 6.3 | 5.12 |
| 128 | Q6ZU45 | Putative C-type lectin domain-containing protein NCRNA00083 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCRNA00083 PE=5 SV=1 | 53 | 25796 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 6.3 |
| 129 | Q86TI0_REVERSED | TBC1 domain family member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TBC1D1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 53 | 133000 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 6.52 |
| 130 | Q99436 | Proteasome subunit beta type-7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB7 PE=1 SV=1 | 53 | 29946 | 1 | 1 | 3.6 | 7.57 |
| 131 | P15144 | Aminopeptidase N OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANPEP PE=1 SV=4 | 53 | 109471 | 3 | 1 | 3.8 | 5.31 |
| 132 | P28066 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 52 | 26394 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 4.74 |
| 133 | Q07092 | Collagen alpha-1(XVI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL16A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 52 | 157653 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 8.14 |
| 134 | Q9BYX7_REVERSED | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 51 | 41989 | 3 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.92 |
| 135 | P05452 | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 22522 | 1 | 1 | 5.9 | 5.52 |
| 136 | P35125 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=USP6 PE=1 SV=2 | 50 | 158557 | 11 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.87 |
| 137 | O95445 | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 50 | 21239 | 2 | 1 | 6.9 | 5.66 |
| 138 | P02790 | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 50 | 51643 | 4 | 1 | 3.2 | 6.55 |
| 139 | Q13454 | Tumor suppressor candidate 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUSC3 PE=2 SV=1 | 50 | 39650 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.93 |
| 140 | Q8NA29_REVERSED | Major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 2A OS=Homo sapiens GN=MFSD2A PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 50 | 60131 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.55 |
| 141 | Q9TNN7 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, Cw-5 alpha chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=HLA-C PE=2 SV=1 | 49 | 40886 | 1 | 1 | 3.6 | 7.11 |
| 142 | P12036 | Neurofilament heavy polypeptide OS=Homo sapiens GN=NEFH PE=1 SV=4 | 49 | 112411 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.99 |
| 143 | Q8N1N4 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT78 PE=1 SV=2 | 49 | 56830 | 2 | 1 | 2.7 | 5.79 |
| 144 | Q9Y490 | Talin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLN1 PE=1 SV=3 | 49 | 269599 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.77 |
| 145 | Q9UBR2 | Cathepsin Z OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSZ PE=1 SV=1 | 49 | 33846 | 1 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.7 |
| 146 | P49720 | Proteasome subunit beta type-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 48 | 22933 | 2 | 1 | 12.2 | 6.14 |
| 147 | P05546 | Heparin cofactor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPIND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 48 | 57034 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 | 6.41 |
| 148 | P01042 | Kininogen-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KNG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 48 | 71912 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.34 |
| 149 | Q96Q89_REVERSED | Kinesin-like protein KIF20B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF20B PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 48 | 210500 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.54 |
| 150 | P03956 | Interstitial collagenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MMP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 48 | 53973 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6.47 |
| 151 | Q8NDM7_REVERSED | WD repeat-containing protein 96 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR96 PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 47 | 191861 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.71 |
| 152 | Q71DI3 | Histone H3.2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H3A PE=1 SV=3 | 46 | 15379 | 4 | 1 | 14.7 | 11.27 |
| 153 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF2 PE=1 SV=4 | 46 | 95277 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.41 |
| 154 | Q9Y6X9_REVERSED | MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MORC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 46 | 117750 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 8.6 |
| 155 | P28074 | Proteasome subunit beta type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB5 PE=1 SV=3 | 46 | 28462 | 1 | 1 | 4.6 | 6.43 |
| 156 | Q9ULC6 | Protein-arginine deiminase type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PADI1 PE=1 SV=2 | 46 | 74618 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.07 |
| 157 | Q8NBM4 | Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBAC2 PE=2 SV=1 | 46 | 38938 | 3 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.21 |
| 158 | Q2VWP7 | Protogenin OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRTG PE=2 SV=1 | 46 | 126996 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 7.37 |
| 159 | Q9NPY3_REVERSED | Complement component C1q receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD93 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 45 | 68515 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 5.27 |
| 160 | Q9NRY4 | Glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding factor 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GRLF1 PE=1 SV=2 | 45 | 172121 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 6.33 |
| 161 | Q9NU02_REVERSED | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANKRD5 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 45 | 86610 | 5 | 1 | 1.8 | 8.51 |
| 162 | B9A064 | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 45 | 23049 | 1 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.08 |
| 163 | Q5T764_REVERSED | Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=IFIT1B PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 45 | 54958 | 2 | 1 | 3.4 | 7.69 |
| 164 | P07339 | Cathepsin D OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSD PE=1 SV=1 | 45 | 44524 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 6.1 |
| 165 | P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 45 | 21212 | 2 | 1 | 9.3 | 5.3 |
| 166 | Q9UKT8_REVERSED | F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXW2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 45 | 51479 | 2 | 1 | 3.1 | 6.11 |
| 167 | P29803_REVERSED | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDHA2 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 44 | 42906 | 3 | 1 | 4.1 | 8.76 |
| 168 | Q9BY43 | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP4A PE=1 SV=3 | 44 | 25083 | 3 | 1 | 6.3 | 4.65 |
| 169 | Q00013 | 55 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MPP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 52264 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.91 |
| 170 | Q13477_REVERSED | Mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MADCAM1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 43 | 40130 | 2 | 1 | 2.6 | 5 |
| 171 | Q8NFM7_REVERSED | Interleukin-17 receptor D OS=Homo sapiens GN=IL17RD PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 43 | 82358 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 6.81 |
| 172 | Q92609 | TBC1 domain family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TBC1D5 PE=1 SV=1 | 43 | 88949 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 |
| 173 | Q96CD0_REVERSED | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXL8 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 43 | 40490 | 9 | 1 | 1.9 | 7.03 |
| 174 | P04745 | Alpha-amylase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY1A PE=1 SV=2 | 43 | 57731 | 1 | 1 | 2.3 | 6.47 |
| 175 | Q9NZM4 | Glioma tumor suppressor candidate region gene 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GLTSCR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 42 | 158393 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 6.17 |
| 176 | P10643 | Complement component C7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C7 PE=1 SV=2 | 42 | 93457 | 2 | 1 | 1.1 | 6.09 |
| 177 | Q6ZUT9_REVERSED | DENN domain-containing protein 5B OS=Homo sapiens GN=DENND5B PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 144927 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 6.29 |
| 178 | Q86UQ0_REVERSED | Zinc finger protein 589 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZNF589 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 41163 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 8.62 |
| 179 | P43652 | Afamin OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFM PE=1 SV=1 | 41 | 69024 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 5.64 |
| 180 | Q96RD9_REVERSED | Fc receptor-like protein 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FCRL5 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 41 | 106371 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 6.72 |
| 181 | Q16563 | Synaptophysin-like protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SYPL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 41 | 28547 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 | 8.69 |
| 182 | Q58FF6 | Putative heat shock protein HSP 90-beta 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB4P PE=5 SV=1 | 40 | 58228 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 4.65 |
| 183 | Q9ULT0 | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 7A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTC7A PE=1 SV=3 | 40 | 96123 | 3 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.03 |
| 184 | P98160 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPG2 PE=1 SV=4 | 39 | 468532 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 6.06 |
| 185 | O14782 | Kinesin-like protein KIF3C OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF3C PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 89371 | 3 | 1 | 1.1 | 8.28 |
| 186 | Q99816 | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 43916 | 3 | 1 | 2.4 | 9.4 |
| 187 | P11166 | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC2A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 54049 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 8.93 |
| 188 | Q00535_REVERSED | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK5 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 39 | 33283 | 2 | 1 | 3.1 | 7.9 |
| 189 | Q8N3E9 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase delta-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLCD3 PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 89202 | 5 | 1 | 1.9 | 6.52 |
| 190 | P43235 | Cathepsin K OS=Homo sapiens GN=CTSK PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 36942 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 | 8.72 |
| 191 | P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACHE PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 67753 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 | 5.87 |
| 192 | Q9P2G4_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein KIAA1383 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIAA1383 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 100283 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 6.77 |
| 193 | Q9BZP6 | Acidic mammalian chitinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHIA PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 52237 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.54 |
| 194 | Q9ULI3_REVERSED | Protein HEG homolog 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HEG1 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 38 | 147369 | 5 | 1 | 0.9 | 5.81 |
| 195 | O43264_REVERSED | Centromere/kinetochore protein zw10 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZW10 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 38 | 88773 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 5.89 |
| 196 | P48436_REVERSED | Transcription factor SOX-9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOX9 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 38 | 56102 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.33 |
| 197 | Q5TAH2 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 11 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC9A11 PE=2 SV=1 | 38 | 128969 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 6.5 |
| 198 | Q03518 | Antigen peptide transporter 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 87163 | 10 | 1 | 1.9 | 8.24 |
| 199 | P06746 | DNA polymerase beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=POLB PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 38154 | 1 | 1 | 1.8 | 9.01 |
| 200 | Q7Z5M8 | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 12B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD12B PE=2 SV=1 | 37 | 40750 | 3 | 1 | 1.7 | 8.57 |
| 201 | Q15020_REVERSED | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SART3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 37 | 109865 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.45 |
| 202 | Q9NX14 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 11, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=NDUFB11 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 17306 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 | 5.17 |
| 203 | Q9H115_REVERSED | Beta-soluble NSF attachment protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=NAPB PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 33535 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5.32 |
| 204 | Q14573_REVERSED | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITPR3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 303912 | 3 | 1 | 0.4 | 6.05 |
| 205 | P00742 | Coagulation factor X OS=Homo sapiens GN=F10 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 54697 | 1 | 1 | 1.8 | 5.68 |
| 206 | P26006 | Integrin alpha-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITGA3 PE=1 SV=4 | 37 | 118680 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 6.51 |
| 207 | Q6DHV7_REVERSED | Adenosine deaminase-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ADAL PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 40239 | 1 | 1 | 3.1 | 5.89 |
| 208 | P21462_REVERSED | fMet-Leu-Phe receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=FPR1 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 37 | 38420 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 9.23 |
| 209 | Q9UGM3 | Deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DMBT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 260569 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.18 |
| 210 | Q14CM0_REVERSED | FERM and PDZ domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FRMPD4 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 36 | 144289 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.12 |
| 211 | O00754 | Lysosomal alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 36 | 113672 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 6.84 |
| 212 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A8 PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 10828 | 1 | 1 | 7.5 | 6.51 |
| 213 | O75691_REVERSED | Small subunit processome component 20 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=UTP20 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 36 | 318182 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 7.09 |
| 214 | Q96ED9_REVERSED | Protein Hook homolog 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HOOK2 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 36 | 83155 | 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 5.36 |
| MDA-MB-231 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot_hit | prot_acc | prot_desc | prot_score | prot_mass | prot_matches | prot_sequences_sig | prot_cover | prot_pi |
| 1 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 3363 | 65999 | 84 | 31 | 57.3 | 8.15 |
| 2 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 2875 | 58792 | 85 | 31 | 58.7 | 5.13 |
| 3 | P02751 | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 2436 | 262460 | 88 | 40 | 25.6 | 5.46 |
| 4 | P02765 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 2048 | 39300 | 52 | 4 | 7.1 | 5.43 |
| 5 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT9 PE=1 SV=3 | 1994 | 62027 | 55 | 23 | 65.7 | 5.14 |
| 6 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1865 | 65393 | 55 | 25 | 57.9 | 8.07 |
| 7 | P02768 | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 1781 | 69321 | 112 | 8 | 11.8 | 5.92 |
| 8 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 1613 | 163188 | 57 | 6 | 5.2 | 6.03 |
| 9 | P20742 | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 1346 | 163760 | 41 | 4 | 3.8 | 5.97 |
| 10 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VCP PE=1 SV=4 | 906 | 89266 | 35 | 21 | 37.1 | 5.14 |
| 11 | Q5QNW6 | Histone H2B type 2-F OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H2BF PE=1 SV=3 | 881 | 13912 | 22 | 5 | 35.7 | 10.31 |
| 12 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 647 | 41710 | 25 | 13 | 47.5 | 5.29 |
| 13 | P00734 | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 613 | 69992 | 15 | 6 | 9.5 | 5.64 |
| 14 | P07996 | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 580 | 129300 | 27 | 13 | 13.2 | 4.71 |
| 15 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 575 | 51529 | 25 | 15 | 32.4 | 5.09 |
| 16 | P01024 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 509 | 187030 | 23 | 11 | 8.8 | 6.02 |
| 17 | P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 468 | 106397 | 15 | 8 | 9.3 | 6.4 |
| 18 | Q6FI13 | Histone H2A type 2-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H2AA3 PE=1 SV=3 | 456 | 14087 | 14 | 4 | 49.2 | 10.9 |
| 19 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 450 | 62340 | 22 | 13 | 25.3 | 7.59 |
| 20 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 441 | 49639 | 20 | 13 | 45 | 4.78 |
| 21 | Q07954 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 439 | 504276 | 15 | 8 | 3.6 | 5.16 |
| 22 | P98160 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPG2 PE=1 SV=4 | 439 | 468532 | 20 | 13 | 4.7 | 6.06 |
| 23 | P08779 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT16 PE=1 SV=4 | 394 | 51236 | 19 | 10 | 18 | 4.99 |
| 24 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 380 | 78132 | 16 | 3 | 4.8 | 8.5 |
| 25 | P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4A PE=1 SV=1 | 367 | 192650 | 15 | 7 | 5.6 | 6.65 |
| 26 | P62805 | Histone H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H4A PE=1 SV=2 | 363 | 11360 | 15 | 6 | 51.5 | 11.36 |
| 27 | P04259 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 349 | 60030 | 15 | 8 | 14 | 8.09 |
| 28 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 346 | 70854 | 12 | 7 | 16.7 | 5.37 |
| 29 | Q86YZ3 | Hornerin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRNR PE=1 SV=2 | 344 | 282228 | 3 | 3 | 2.1 | 10.05 |
| 30 | P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 339 | 60008 | 15 | 8 | 15.6 | 8.09 |
| 31 | P68032 | Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 333 | 41992 | 17 | 9 | 26.8 | 5.23 |
| 32 | P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFP PE=1 SV=1 | 310 | 68633 | 9 | 3 | 5.6 | 5.48 |
| 33 | Q9BQE3 | Tubulin alpha-1C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA1C PE=1 SV=1 | 285 | 49863 | 18 | 6 | 31.8 | 4.96 |
| 34 | P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 277 | 52929 | 10 | 6 | 11.8 | 5.4 |
| 35 | P04004 | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 277 | 54271 | 6 | 1 | 4.2 | 5.55 |
| 36 | Q9BVA1 | Tubulin beta-2B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB2B PE=1 SV=1 | 270 | 49921 | 17 | 10 | 36.9 | 4.78 |
| 37 | Q04695 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT17 PE=1 SV=2 | 257 | 48076 | 16 | 9 | 15 | 4.97 |
| 38 | P68366 | Tubulin alpha-4A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA4A PE=1 SV=1 | 256 | 49892 | 13 | 5 | 22.5 | 4.95 |
| 39 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 254 | 49557 | 12 | 6 | 9.2 | 4.91 |
| 40 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 231 | 15248 | 8 | 3 | 33.1 | 8.72 |
| 41 | P04114 | Apolipoprotein B-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOB PE=1 SV=2 | 227 | 515283 | 14 | 7 | 1.9 | 6.58 |
| 42 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 222 | 36030 | 5 | 2 | 17.6 | 8.57 |
| 43 | Q5XKE5 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 79 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT79 PE=1 SV=2 | 221 | 57800 | 10 | 4 | 6.9 | 6.75 |
| 44 | P23142 | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 214 | 77162 | 11 | 4 | 7.3 | 5.07 |
| 45 | P08238 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AB1 PE=1 SV=4 | 193 | 83212 | 8 | 4 | 10.4 | 4.97 |
| 46 | Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTBL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 189 | 41976 | 12 | 4 | 16 | 5.39 |
| 47 | P06396 | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 185 | 85644 | 6 | 5 | 9.5 | 5.9 |
| 48 | Q96QV6 | Histone H2A type 1-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H2AA PE=1 SV=3 | 183 | 14225 | 6 | 3 | 29.8 | 10.86 |
| 49 | P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 181 | 46283 | 6 | 3 | 8.6 | 5.97 |
| 50 | Q5VTE0 | Putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1A1P5 PE=5 SV=1 | 175 | 50153 | 8 | 6 | 21 | 9.15 |
| 51 | Q06033 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 168 | 99787 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 5.49 |
| 52 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSP90AA1 PE=1 SV=5 | 165 | 84607 | 9 | 4 | 10.7 | 4.94 |
| 53 | P08107 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A/1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1A PE=1 SV=5 | 162 | 70009 | 4 | 3 | 6.2 | 5.48 |
| 54 | P17066 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA6 PE=1 SV=2 | 162 | 70984 | 4 | 3 | 6.2 | 5.81 |
| 55 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PKM2 PE=1 SV=4 | 157 | 57900 | 7 | 6 | 16 | 7.96 |
| 56 | P19013 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 155 | 57250 | 8 | 4 | 7.3 | 6.25 |
| 57 | P05556 | Integrin beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITGB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 155 | 88357 | 7 | 4 | 9.6 | 5.27 |
| 58 | Q9UPY3 | Endoribonuclease, Dicer OS=Homo sapiens GN=DICER PE=1 SV=2 | 154 | 218682 | 9 | 4 | 6.6 | 8.38 |
| 59 | P62979 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPS27A PE=1 SV=2 | 154 | 17953 | 8 | 5 | 34 | 9.68 |
| 60 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 150 | 16045 | 9 | 2 | 12.9 | 7.85 |
| 61 | P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 148 | 54531 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.87 |
| 62 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 146 | 30759 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 5.56 |
| 63 | Q7Z3Y8 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT27 PE=1 SV=2 | 142 | 49792 | 6 | 3 | 7.4 | 4.98 |
| 64 | Q9P2B2 | Prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTGFRN PE=1 SV=2 | 140 | 98495 | 5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6.16 |
| 65 | P13497 | Bone morphogenetic protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BMP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 133 | 111178 | 3 | 2 | 3.1 | 6.48 |
| 66 | P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 132 | 55892 | 4 | 3 | 4.7 | 8.54 |
| 67 | Q9Y6L7 | Tolloid-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 132 | 113484 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | 5.6 |
| 68 | P00747 | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 131 | 90510 | 6 | 3 | 4.4 | 7.04 |
| 69 | Q8WUM4 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6IP PE=1 SV=1 | 126 | 95963 | 6 | 3 | 8.3 | 6.13 |
| 70 | Q71DI3 | Histone H3.2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST2H3A PE=1 SV=3 | 121 | 15379 | 6 | 4 | 44.9 | 11.27 |
| 71 | P84243 | Histone H3.3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=H3F3A PE=1 SV=2 | 111 | 15318 | 6 | 4 | 44.9 | 11.27 |
| 72 | Q86Y46 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 110 | 58887 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 6.93 |
| 73 | P12259 | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 109 | 251546 | 6 | 4 | 2.3 | 5.68 |
| 74 | P01008 | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 108 | 52569 | 7 | 3 | 10.1 | 6.32 |
| 75 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ENO1 PE=1 SV=2 | 108 | 47139 | 3 | 3 | 10.8 | 7.01 |
| 76 | P19827 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 106 | 101326 | 4 | 2 | 2.9 | 6.31 |
| 77 | Q8NI35 | InaD-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=INADL PE=1 SV=3 | 106 | 196247 | 10 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.84 |
| 78 | Q8TAA3 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 106 | 28512 | 3 | 2 | 19.5 | 9.07 |
| 79 | P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 104 | 138857 | 2 | 2 | 1.6 | 5.6 |
| 80 | P68431 | Histone H3.1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIST1H3A PE=1 SV=2 | 103 | 15394 | 6 | 4 | 44.9 | 11.13 |
| 81 | P07942 | Laminin subunit beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 102 | 197909 | 3 | 2 | 1.9 | 4.83 |
| 82 | P05787 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT8 PE=1 SV=7 | 102 | 53671 | 5 | 3 | 7.2 | 5.52 |
| 83 | P51884 | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 101 | 38405 | 3 | 2 | 8.3 | 6.16 |
| 84 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLTC PE=1 SV=5 | 97 | 191493 | 2 | 2 | 2.9 | 5.48 |
| 85 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 93 | 44586 | 3 | 2 | 8.4 | 8.3 |
| 86 | P15531 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=NME1 PE=1 SV=1 | 92 | 17138 | 1 | 1 | 11.2 | 5.83 |
| 87 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALDOA PE=1 SV=2 | 92 | 39395 | 5 | 2 | 12.4 | 8.3 |
| 88 | P05452 | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 91 | 22522 | 3 | 3 | 21.8 | 5.52 |
| 89 | P02787 | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 91 | 77014 | 3 | 2 | 1.7 | 6.81 |
| 90 | A6NIZ1 | Ras-related protein Rap-1b-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 89 | 20912 | 2 | 1 | 6.5 | 5.37 |
| 91 | Q9GZM7 | Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=TINAGL1 PE=1 SV=1 | 88 | 52353 | 1 | 1 | 2.8 | 6.54 |
| 92 | P11021 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA5 PE=1 SV=2 | 87 | 72288 | 3 | 2 | 3.1 | 5.07 |
| 93 | P16870 | Carboxypeptidase E OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPE PE=1 SV=1 | 87 | 53117 | 2 | 2 | 4.8 | 5.03 |
| 94 | P81605 | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 86 | 11277 | 2 | 2 | 20 | 6.08 |
| 95 | P15169 | Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 84 | 52253 | 1 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.86 |
| 96 | P11717 | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 83 | 274199 | 4 | 2 | 1.2 | 5.64 |
| 97 | P07195 | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHB PE=1 SV=2 | 81 | 36615 | 2 | 1 | 7.5 | 5.71 |
| 98 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 80 | 13234 | 2 | 1 | 24.6 | 5.71 |
| 99 | Q5D862 | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 79 | 247928 | 2 | 1 | 0.9 | 8.45 |
| 100 | P28066 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 78 | 26394 | 1 | 1 | 7.9 | 4.74 |
| 101 | Q92743 | Serine protease HTRA1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HTRA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 78 | 51255 | 3 | 2 | 6.5 | 8.09 |
| 102 | P23526 | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 78 | 47685 | 2 | 2 | 6.3 | 5.92 |
| 103 | P02760 | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 77 | 38974 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5.95 |
| 104 | P05543 | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 75 | 46295 | 3 | 1 | 2.4 | 5.87 |
| 105 | P43686 | 26S protease regulatory subunit 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMC4 PE=1 SV=2 | 74 | 47337 | 2 | 1 | 2.9 | 5.09 |
| 106 | Q7RTS7 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 74 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT74 PE=1 SV=2 | 74 | 57830 | 4 | 2 | 4.2 | 7.59 |
| 108 | Q99456 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT12 PE=1 SV=1 | 73 | 53478 | 7 | 2 | 3.6 | 4.7 |
| 109 | P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase OS=Homo sapiens GN=TPI1 PE=1 SV=2 | 72 | 26653 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 | 6.45 |
| 110 | P05156 | Complement factor I OS=Homo sapiens GN=CFI PE=1 SV=2 | 71 | 65707 | 2 | 2 | 3.4 | 7.72 |
| 111 | Q12931 | Heat shock protein 75 kDa, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRAP1 PE=1 SV=3 | 71 | 80060 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8.3 |
| 112 | P08962 | CD63 OS=HOMO SAPIENS GN=CD63 PE=4 SV=2 | 71 | 25637 | 3 | 3 | 16.4 | 5.3 |
| 113 | P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 67 | 38273 | 3 | 1 | 5.2 | 8.34 |
| 114 | B9A064 | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 66 | 23049 | 2 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.08 |
| 115 | P12109 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 66 | 108462 | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | 5.26 |
| 116 | P04745 | Alpha-amylase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY1A PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 57731 | 2 | 1 | 2.3 | 6.47 |
| 117 | P35052 | Glypican-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 66 | 61641 | 4 | 1 | 10.9 | 7.07 |
| 118 | P08133 | Annexin A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA6 PE=1 SV=3 | 65 | 75826 | 4 | 2 | 5.9 | 5.42 |
| 119 | P01031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 65 | 188186 | 4 | 2 | 1.8 | 6.11 |
| 120 | P29353_REVERSED | SHC-transforming protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHC1 PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 65 | 62782 | 10 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.01 |
| 121 | O15111_REVERSED | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHUK PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 65 | 84585 | 6 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.28 |
| 123 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 64 | 46707 | 3 | 2 | 3.3 | 5.37 |
| 124 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF2 PE=1 SV=4 | 64 | 95277 | 3 | 2 | 6.9 | 6.41 |
| 125 | A6NMY6 | Putative annexin A2-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA2P2 PE=5 SV=2 | 63 | 38635 | 2 | 1 | 6.2 | 6.49 |
| 126 | Q99816 | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 43916 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 | 6.06 |
| 127 | P02461 | Collagen alpha-1(III) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL3A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 59 | 138479 | 2 | 2 | 1.5 | 6.21 |
| 128 | Q14624 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 58 | 103293 | 5 | 2 | 3.3 | 6.51 |
| 129 | P02649 | Apolipoprotein E OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOE PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 36132 | 1 | 1 | 2.8 | 5.65 |
| 130 | P26641 | Elongation factor 1-gamma OS=Homo sapiens GN=EEF1G PE=1 SV=3 | 56 | 50087 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 6.25 |
| 131 | P35125 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=USP6 PE=1 SV=2 | 55 | 158557 | 13 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.87 |
| 132 | P02790 | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 54 | 51643 | 6 | 1 | 5.4 | 6.55 |
| 133 | Q9BYX7_REVERSED | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 54 | 41989 | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.92 |
| 135 | P14923 | Junction plakoglobin OS=Homo sapiens GN=JUP PE=1 SV=3 | 53 | 81693 | 1 | 1 | 2.7 | 5.75 |
| 136 | Q14764 | Major vault protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MVP PE=1 SV=4 | 52 | 99266 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 5.34 |
| 138 | P01042 | Kininogen-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KNG1 PE=1 SV=2 | 52 | 71912 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.34 |
| 139 | Q8N139 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABCA6 PE=1 SV=2 | 52 | 184167 | 2 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.05 |
| 141 | Q96Q89_REVERSED | Kinesin-like protein KIF20B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF20B PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 51 | 210500 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.54 |
| 142 | Q2Q1W2_REVERSED | Tripartite motif-containing protein 71 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRIM71 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 51 | 93326 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 7.62 |
| 143 | Q9BY43 | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP4A PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 25083 | 2 | 1 | 3.2 | 4.65 |
| 144 | Q8NAV2_REVERSED | Uncharacterized protein C8orf58 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C8orf58 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 51 | 39636 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 8.54 |
| 145 | P02748 | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 51 | 63133 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.43 |
| 146 | O00754 | Lysosomal alpha-mannosidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAN2B1 PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 113672 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 6.84 |
| 147 | O14817 | Tetraspanin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSPAN4 PE=1 SV=1 | 50 | 26100 | 2 | 1 | 10.5 | 6.07 |
| 148 | P11047 | Laminin subunit gamma-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LAMC1 PE=1 SV=3 | 50 | 177489 | 3 | 3 | 1.9 | 5.01 |
| 149 | P21333 | Filamin-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLNA PE=1 SV=4 | 50 | 280564 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.7 |
| 150 | A8MT19_REVERSED | Putative rhophilin-2-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=5 SV=2 - REVERSED | 49 | 65903 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.53 |
| 151 | P12111 | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 48 | 343457 | 3 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.26 |
| 152 | Q00013 | 55 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=MPP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 47 | 52264 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.91 |
| 153 | Q8IW52 | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLITRK4 PE=2 SV=1 | 47 | 94271 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 7.95 |
| 154 | O95445 | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 47 | 21239 | 1 | 1 | 3.7 | 5.66 |
| 155 | Q13162 | Peroxiredoxin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX4 PE=1 SV=1 | 46 | 30521 | 1 | 1 | 4.1 | 5.86 |
| 156 | P00488 | Coagulation factor XIII A chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=F13A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 46 | 83215 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5.75 |
| 157 | P08572 | Collagen alpha-2(IV) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL4A2 PE=1 SV=4 | 46 | 167449 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.89 |
| 158 | O14782 | Kinesin-like protein KIF3C OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF3C PE=1 SV=3 | 46 | 89371 | 4 | 1 | 1.1 | 8.28 |
| 159 | P35443 | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 45 | 105802 | 2 | 1 | 2.8 | 4.44 |
| 161 | P49747 | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMP PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 82808 | 2 | 1 | 2.8 | 4.36 |
| 162 | Q14573_REVERSED | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITPR3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 44 | 303912 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 6.05 |
| 163 | Q8IWC1 | MAP7 domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP7D3 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 98368 | 2 | 1 | 2.1 | 9.34 |
| 164 | Q3KQU3 | MAP7 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP7D1 PE=1 SV=1 | 44 | 92764 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 10.12 |
| 165 | Q5U5X0 | LYR motif-containing protein 7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LYRM7 PE=1 SV=1 | 44 | 11947 | 1 | 1 | 5.8 | 9.67 |
| 166 | Q8N7B9_REVERSED | EF-hand calcium-binding domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFCAB3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 44 | 50114 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 9.31 |
| 167 | Q8NB25_REVERSED | Protein FAM184A OS=Homo sapiens GN=FAM184A PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 44 | 132883 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.59 |
| 168 | P06732 | Creatine kinase M-type OS=Homo sapiens GN=CKM PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 43074 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.77 |
| 169 | Q93096_REVERSED | Protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTP4A1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 44 | 19802 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 | 9.17 |
| 170 | Q6YHK3 | CD109 antigen OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD109 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 161587 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.59 |
| 171 | Q8IYT4 | Katanin p60 ATPase-containing subunit A-like 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KATNAL2 PE=2 SV=3 | 43 | 61214 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 7.22 |
| 172 | A8MPT4 | Glutathione S-transferase theta-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTT4 PE=3 SV=2 | 43 | 27941 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.25 |
| 173 | Q8N6V9_REVERSED | Testis-expressed sequence 9 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TEX9 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 43 | 44798 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.2 |
| 174 | Q9Y2U8_REVERSED | Inner nuclear membrane protein Man1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LEMD3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 43 | 99935 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 7.31 |
| 175 | P05154 | Plasma serine protease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 43 | 45646 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 9.3 |
| 176 | Q92609 | TBC1 domain family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TBC1D5 PE=1 SV=1 | 42 | 88949 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 |
| 177 | Q9H2G4 | Testis-specific Y-encoded-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSPYL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 42 | 79387 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.45 |
| 178 | Q00535_REVERSED | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CDK5 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 42 | 33283 | 1 | 1 | 3.1 | 7.9 |
| 179 | P06703 | Protein S100-A6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A6 PE=1 SV=1 | 41 | 10173 | 2 | 1 | 8.9 | 5.33 |
| 180 | Q6ZMU1 | Putative protein C3P1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3P1 PE=5 SV=3 | 41 | 40171 | 2 | 1 | 5.5 | 6.32 |
| 183 | Q86UY8_REVERSED | 5~-nucleotidase domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NT5DC3 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 41 | 63379 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 8.47 |
| 184 | O75460_REVERSED | Serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease IRE1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERN1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 109666 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.98 |
| 186 | Q9Y6X9_REVERSED | MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MORC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 40 | 117750 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 8.6 |
| 187 | Q96TA0_REVERSED | Putative protocadherin beta-18 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PCDHB18 PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 40 | 80423 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 4.87 |
| 188 | P02458 | Collagen alpha-1(II) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL2A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 40 | 141698 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 6.58 |
| 191 | Q8NBM4 | Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBAC2 PE=2 SV=1 | 40 | 38938 | 1 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.21 |
| 193 | Q7Z5M8 | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 12B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD12B PE=2 SV=1 | 40 | 40750 | 5 | 1 | 1.7 | 8.57 |
| 194 | Q15020_REVERSED | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SART3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 40 | 109865 | 5 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.45 |
| 196 | O60312 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase VA OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP10A PE=2 SV=2 | 39 | 167582 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| 197 | Q9Y6Q3_REVERSED | Zinc finger protein 37 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZFP37 PE=2 SV=3 - REVERSED | 39 | 71164 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 9.26 |
| 198 | Q96RW7 | Hemicentin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HMCN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 39 | 613001 | 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 6.07 |
| 199 | Q13183_REVERSED | Solute carrier family 13 member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC13A2 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 38 | 64368 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.61 |
| 200 | Q9UK41 | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 28 homolog OS=Homo sapiens GN=VPS28 PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 25409 | 2 | 1 | 6.8 | 5.37 |
| 201 | Q14C86_REVERSED | GTPase-activating protein and VPS9 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPVD1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 164876 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.09 |
| 206 | P26640 | Valyl-tRNA synthetase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VARS PE=1 SV=4 | 38 | 140387 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 7.53 |
| 207 | Q96JB3 | Hypermethylated in cancer 2 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HIC2 PE=1 SV=2 | 38 | 66114 | 1 | 1 | 1.6 | 5.95 |
| 208 | O43309 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZSCAN12 PE=2 SV=1 | 38 | 70178 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6.28 |
| 209 | Q96K21 | Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 19 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ZFYVE19 PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 51514 | 2 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.57 |
| 210 | Q8WZ42_REVERSED | Titin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TTN PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 3813810 | 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 6.01 |
| 211 | O75865_REVERSED | Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRAPPC6A PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 17593 | 1 | 1 | 3.8 | 5.14 |
| 213 | P04083 | Annexin A1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANXA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 38690 | 1 | 1 | 2.3 | 6.57 |
| 214 | P28070 | Proteasome subunit beta type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB4 PE=1 SV=4 | 37 | 29185 | 1 | 1 | 3.8 | 5.72 |
| 216 | P02753 | Retinol-binding protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RBP4 PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 22995 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 5.76 |
| 217 | Q12923 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTPN13 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 276733 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.99 |
| 218 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A8 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 10828 | 1 | 1 | 11.8 | 6.51 |
| 220 | Q5SYB0 | FERM and PDZ domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FRMPD1 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 173328 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.14 |
| 221 | A6NC57_REVERSED | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 62 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANKRD62 PE=2 SV=4 - REVERSED | 37 | 106379 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 6.26 |
| 222 | Q8IWZ5_REVERSED | Tripartite motif-containing protein 42 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TRIM42 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 82690 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 8.31 |
| 223 | Q9UKU7_REVERSED | Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACAD8 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 37 | 45040 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 8.16 |
| 224 | Q674X7_REVERSED | Kazrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=KAZN PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 86298 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 | 6.59 |
| 225 | Q14534 | Squalene monooxygenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=SQLE PE=2 SV=3 | 37 | 63882 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8.8 |
| 226 | P20138 | Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD33 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 39800 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 8.69 |
| 227 | A2RRP1_REVERSED | Neuroblastoma-amplified sequence OS=Homo sapiens GN=NBAS PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 268401 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 5.65 |
| 231 | O95714_REVERSED | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HERC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 526895 | 6 | 1 | 0.4 | 5.88 |
| 232 | Q9UGM3 | Deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DMBT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 260569 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.18 |
| 233 | P26378 | ELAV-like protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ELAVL4 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 41743 | 2 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.45 |
| 234 | Q96A37 | RING finger protein 166 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RNF166 PE=2 SV=1 | 36 | 26105 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 | 8.42 |
| 236 | P22352 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GPX3 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 25537 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 8.26 |
| 237 | Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain family 11 member A OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC11A PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 35672 | 1 | 1 | 5.3 | 5.06 |
| 240 | P25789 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA4 PE=1 SV=1 | 36 | 29465 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 7.57 |
| 241 | P10242_REVERSED | Transcriptional activator Myb OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYB PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 72296 | 2 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.35 |
| 242 | P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 35 | 21226 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 8.2 |
| NIH 3T3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot_hit | prot_acc | prot_desc | prot_score | prot_mass | prot_matches | prot_sequences_sig | prot_cover | prot_pi |
| 1 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT1 PE=1 SV=6 | 2826 | 65999 | 70 | 31 | 55.3 | 8.15 |
| 2 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT10 PE=1 SV=6 | 2816 | 58792 | 83 | 29 | 57.9 | 5.13 |
| 3 | P02768 | Serum albumin OS=Homo sapiens GN=ALB PE=1 SV=2 | 2011 | 69321 | 114 | 8 | 13.5 | 5.92 |
| 4 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=A2M PE=1 SV=3 | 1949 | 163188 | 70 | 8 | 5.7 | 6.03 |
| 5 | P02765 | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHSG PE=1 SV=1 | 1830 | 39300 | 50 | 4 | 8.7 | 5.43 |
| 6 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT9 PE=1 SV=3 | 1822 | 62027 | 44 | 22 | 68.7 | 5.14 |
| 7 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT2 PE=1 SV=2 | 1641 | 65393 | 46 | 24 | 58.1 | 8.07 |
| 8 | P02751 | Fibronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 1564 | 262460 | 50 | 29 | 18.1 | 5.46 |
| 9 | P20742 | Pregnancy zone protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PZP PE=1 SV=4 | 1547 | 163760 | 48 | 5 | 4.3 | 5.97 |
| 10 | P01024 | Complement C3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C3 PE=1 SV=2 | 704 | 187030 | 25 | 11 | 8.9 | 6.02 |
| 11 | P07996 | Thrombospondin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS1 PE=1 SV=2 | 622 | 129300 | 26 | 15 | 19.1 | 4.71 |
| 12 | P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH2 PE=1 SV=2 | 593 | 106397 | 18 | 7 | 9.2 | 6.4 |
| 13 | P00734 | Prothrombin OS=Homo sapiens GN=F2 PE=1 SV=2 | 527 | 69992 | 11 | 6 | 8 | 5.64 |
| 14 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT5 PE=1 SV=3 | 514 | 62340 | 23 | 16 | 28.8 | 7.59 |
| 15 | P0C0L4 | Complement C4-A OS=Homo sapiens GN=C4A PE=1 SV=1 | 467 | 192650 | 18 | 7 | 5.2 | 6.65 |
| 16 | Q07954 | Prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LRP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 415 | 504276 | 14 | 11 | 3.5 | 5.16 |
| 17 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=LTF PE=1 SV=6 | 406 | 78132 | 18 | 3 | 4.8 | 8.5 |
| 18 | P04259 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6B PE=1 SV=5 | 394 | 60030 | 17 | 11 | 23 | 8.09 |
| 19 | P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT6A PE=1 SV=3 | 388 | 60008 | 17 | 12 | 24.6 | 8.09 |
| 20 | P06396 | Gelsolin OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSN PE=1 SV=1 | 360 | 85644 | 11 | 7 | 12.8 | 5.9 |
| 21 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT14 PE=1 SV=4 | 353 | 51529 | 17 | 9 | 20.3 | 5.09 |
| 22 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTB PE=1 SV=1 | 315 | 41710 | 12 | 8 | 33.6 | 5.29 |
| 23 | P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein OS=Homo sapiens GN=AFP PE=1 SV=1 | 288 | 68633 | 8 | 3 | 6.7 | 5.48 |
| 24 | P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=GC PE=1 SV=1 | 271 | 52929 | 12 | 5 | 12 | 5.4 |
| 25 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBA1 PE=1 SV=2 | 252 | 15248 | 13 | 4 | 33.1 | 8.72 |
| 26 | Q7Z794 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1b OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT77 PE=1 SV=3 | 248 | 61864 | 7 | 3 | 4.8 | 5.73 |
| 27 | P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF1 PE=1 SV=4 | 233 | 46283 | 10 | 3 | 12 | 5.97 |
| 28 | P04004 | Vitronectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=VTN PE=1 SV=1 | 226 | 54271 | 6 | 1 | 4.2 | 5.55 |
| 29 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 226 | 30759 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 5.56 |
| 30 | P62736 | Actin, aortic smooth muscle OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTA2 PE=1 SV=1 | 220 | 41982 | 7 | 5 | 18.8 | 5.23 |
| 31 | Q04695 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT17 PE=1 SV=2 | 205 | 48076 | 12 | 6 | 14.6 | 4.97 |
| 32 | Q5XKE5 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 79 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT79 PE=1 SV=2 | 200 | 57800 | 7 | 4 | 6.9 | 6.75 |
| 33 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT13 PE=1 SV=4 | 198 | 49557 | 8 | 4 | 6.1 | 4.91 |
| 34 | Q06033 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH3 PE=1 SV=2 | 196 | 99787 | 9 | 3 | 6.3 | 5.49 |
| 35 | Q86YZ3 | Hornerin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HRNR PE=1 SV=2 | 193 | 282228 | 3 | 2 | 2.3 | 10.05 |
| 36 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBD PE=1 SV=2 | 189 | 16045 | 10 | 2 | 12.9 | 7.85 |
| 37 | Q15063 | Periostin OS=Homo sapiens GN=POSTN PE=1 SV=2 | 174 | 93255 | 7 | 2 | 7.4 | 7.27 |
| 38 | P23142 | Fibulin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBLN1 PE=1 SV=4 | 172 | 77162 | 9 | 4 | 7.3 | 5.07 |
| 39 | P02100 | Hemoglobin subunit epsilon OS=Homo sapiens GN=HBE1 PE=1 SV=2 | 160 | 16192 | 7 | 1 | 12.9 | 8.67 |
| 40 | P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINF2 PE=1 SV=3 | 143 | 54531 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 5.87 |
| 41 | P00747 | Plasminogen OS=Homo sapiens GN=PLG PE=1 SV=2 | 139 | 90510 | 6 | 3 | 4.3 | 7.04 |
| 42 | P02675 | Fibrinogen beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGB PE=1 SV=2 | 136 | 55892 | 5 | 3 | 6.7 | 8.54 |
| 43 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPDH PE=1 SV=3 | 134 | 36030 | 3 | 3 | 17.6 | 8.57 |
| 44 | P05556 | Integrin beta-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITGB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 131 | 88357 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 5.27 |
| 45 | Q9BQE3 | Tubulin alpha-1C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBA1C PE=1 SV=1 | 130 | 49863 | 7 | 4 | 14.9 | 4.96 |
| 46 | P01008 | Antithrombin-III OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINC1 PE=1 SV=1 | 130 | 52569 | 10 | 4 | 14.7 | 6.32 |
| 47 | P02452 | Collagen alpha-1(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A1 PE=1 SV=5 | 124 | 138857 | 3 | 3 | 2.4 | 5.6 |
| 48 | P01031 | Complement C5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C5 PE=1 SV=4 | 122 | 188186 | 6 | 2 | 2.9 | 6.11 |
| 49 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA8 PE=1 SV=1 | 122 | 70854 | 3 | 3 | 5.3 | 5.37 |
| 50 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUBB PE=1 SV=2 | 121 | 49639 | 5 | 4 | 24.8 | 4.78 |
| 51 | P19013 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT4 PE=1 SV=4 | 120 | 57250 | 7 | 3 | 7.3 | 6.25 |
| 52 | P08107 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1A/1B OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA1A PE=1 SV=5 | 119 | 70009 | 2 | 2 | 4.2 | 5.48 |
| 53 | P17066 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPA6 PE=1 SV=2 | 119 | 70984 | 2 | 2 | 4.2 | 5.81 |
| 54 | P12109 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A1 PE=1 SV=3 | 117 | 108462 | 2 | 2 | 2.4 | 5.26 |
| 55 | P02748 | Complement component C9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C9 PE=1 SV=2 | 114 | 63133 | 3 | 2 | 3.8 | 5.43 |
| 56 | P19827 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH1 PE=1 SV=3 | 113 | 101326 | 4 | 2 | 2.9 | 6.31 |
| 57 | Q8TAA3 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7-like OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA8 PE=1 SV=3 | 113 | 28512 | 2 | 2 | 10.9 | 9.07 |
| 58 | Q7Z3Y8 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 27 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT27 PE=1 SV=2 | 111 | 49792 | 6 | 3 | 7.4 | 4.98 |
| 59 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A9 PE=1 SV=1 | 109 | 13234 | 4 | 2 | 43 | 5.71 |
| 60 | P05787 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT8 PE=1 SV=7 | 109 | 53671 | 4 | 3 | 5.6 | 5.52 |
| 61 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A8 PE=1 SV=1 | 109 | 10828 | 3 | 3 | 31.2 | 6.51 |
| 62 | P02787 | Serotransferrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=TF PE=1 SV=3 | 109 | 77014 | 5 | 2 | 1.7 | 6.81 |
| 63 | Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACTBL2 PE=1 SV=2 | 108 | 41976 | 5 | 3 | 13.8 | 5.39 |
| 64 | P62979 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a OS=Homo sapiens GN=RPS27A PE=1 SV=2 | 102 | 17953 | 7 | 3 | 30.1 | 9.68 |
| 65 | P12035 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT3 PE=1 SV=3 | 99 | 64378 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 6.12 |
| 66 | Q8NI35 | InaD-like protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=INADL PE=1 SV=3 | 98 | 196247 | 10 | 1 | 0.3 | 4.84 |
| 67 | Q8TEV9_REVERSED | Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosomal region candidate gene 8 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=SMCR8 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 97 | 104956 | 10 | 1 | 1.2 | 5.36 |
| 68 | Q5D862 | Filaggrin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG2 PE=1 SV=1 | 96 | 247928 | 2 | 2 | 1.3 | 8.45 |
| 69 | P12111 | Collagen alpha-3(VI) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL6A3 PE=1 SV=5 | 96 | 343457 | 3 | 3 | 1.1 | 6.26 |
| 70 | P49747 | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=COMP PE=1 SV=2 | 94 | 82808 | 3 | 2 | 4.5 | 4.36 |
| 71 | A6NIZ1 | Ras-related protein Rap-1b-like protein OS=Homo sapiens PE=2 SV=1 | 91 | 20912 | 2 | 1 | 6.5 | 5.37 |
| 72 | P12259 | Coagulation factor V OS=Homo sapiens GN=F5 PE=1 SV=4 | 89 | 251546 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5.68 |
| 73 | Q14624 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ITIH4 PE=1 SV=4 | 87 | 103293 | 5 | 2 | 3.3 | 6.51 |
| 74 | Q6KB66 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 80 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT80 PE=1 SV=2 | 86 | 50494 | 3 | 1 | 5.1 | 5.58 |
| 75 | P13497 | Bone morphogenetic protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=BMP1 PE=1 SV=2 | 83 | 111178 | 4 | 3 | 3.1 | 6.48 |
| 76 | Q86Y46 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 73 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT73 PE=1 SV=1 | 78 | 58887 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 6.93 |
| 77 | P04114 | Apolipoprotein B-100 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOB PE=1 SV=2 | 77 | 515283 | 3 | 3 | 0.5 | 6.58 |
| 78 | P02790 | Hemopexin OS=Homo sapiens GN=HPX PE=1 SV=2 | 76 | 51643 | 6 | 1 | 3.2 | 6.55 |
| 79 | P35443 | Thrombospondin-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=THBS4 PE=1 SV=2 | 75 | 105802 | 2 | 2 | 2.5 | 4.44 |
| 80 | P08123 | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL1A2 PE=1 SV=7 | 75 | 129235 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | 9.08 |
| 81 | P15169 | Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=CPN1 PE=1 SV=1 | 73 | 52253 | 1 | 1 | 3.3 | 6.86 |
| 82 | Q92743 | Serine protease HTRA1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HTRA1 PE=1 SV=1 | 73 | 51255 | 2 | 2 | 4.4 | 8.09 |
| 83 | Q9Y6L7 | Tolloid-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TLL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 72 | 113484 | 3 | 2 | 2.2 | 5.6 |
| 84 | P05452 | Tetranectin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CLEC3B PE=1 SV=3 | 69 | 22522 | 2 | 2 | 12.9 | 5.52 |
| 85 | Q96Q89_REVERSED | Kinesin-like protein KIF20B OS=Homo sapiens GN=KIF20B PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 68 | 210500 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.54 |
| 86 | P51884 | Lumican OS=Homo sapiens GN=LUM PE=1 SV=2 | 68 | 38405 | 4 | 1 | 6.8 | 6.16 |
| 87 | P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOH PE=1 SV=3 | 67 | 38273 | 3 | 1 | 5.2 | 8.34 |
| 88 | P63104 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta OS=Homo sapiens GN=YWHAZ PE=1 SV=1 | 67 | 27728 | 1 | 1 | 4.9 | 4.73 |
| 89 | O15111_REVERSED | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHUK PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 66 | 84585 | 7 | 1 | 1.6 | 6.28 |
| 90 | Q03692 | Collagen alpha-1(X) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL10A1 PE=1 SV=2 | 64 | 66117 | 1 | 1 | 1.9 | 9.68 |
| 91 | B9A064 | Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGLL5 PE=2 SV=2 | 63 | 23049 | 2 | 1 | 3.7 | 9.08 |
| 92 | Q7RTS7 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 74 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT74 PE=1 SV=2 | 62 | 57830 | 3 | 2 | 4.2 | 7.59 |
| 93 | Q99456 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 12 OS=Homo sapiens GN=KRT12 PE=1 SV=1 | 62 | 53478 | 5 | 2 | 3.6 | 4.7 |
| 94 | Q9BYX7_REVERSED | Putative beta-actin-like protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=POTEKP PE=5 SV=1 - REVERSED | 61 | 41989 | 6 | 1 | 3.5 | 5.92 |
| 95 | P00450 | Ceruloplasmin OS=Homo sapiens GN=CP PE=1 SV=1 | 59 | 122128 | 3 | 2 | 2.9 | 5.44 |
| 96 | P23526 | Adenosylhomocysteinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AHCY PE=1 SV=4 | 59 | 47685 | 2 | 1 | 6.3 | 5.92 |
| 97 | P20618 | Proteasome subunit beta type-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB1 PE=1 SV=2 | 58 | 26472 | 1 | 1 | 5.8 | 8.27 |
| 98 | P98160 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=HSPG2 PE=1 SV=4 | 57 | 468532 | 2 | 2 | 0.6 | 6.06 |
| 99 | Q8WUM4 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDCD6IP PE=1 SV=1 | 57 | 95963 | 2 | 1 | 2.2 | 6.13 |
| 100 | P35125 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 OS=Homo sapiens GN=USP6 PE=1 SV=2 | 56 | 158557 | 12 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.87 |
| 101 | P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FGG PE=1 SV=3 | 56 | 51479 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5.37 |
| 102 | P29353_REVERSED | SHC-transforming protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SHC1 PE=1 SV=4 - REVERSED | 56 | 62782 | 9 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.01 |
| 103 | P05546 | Heparin cofactor 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPIND1 PE=1 SV=3 | 55 | 57034 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 | 6.41 |
| 104 | P01344 | Insulin-like growth factor II OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2 PE=1 SV=1 | 54 | 20127 | 1 | 1 | 8.9 | 9.5 |
| 105 | P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=FTH1 PE=1 SV=2 | 54 | 21212 | 1 | 1 | 5.5 | 5.3 |
| 106 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA1 PE=1 SV=3 | 52 | 46707 | 3 | 1 | 3.3 | 5.37 |
| 107 | Q16853 | Membrane primary amine oxidase OS=Homo sapiens GN=AOC3 PE=1 SV=3 | 52 | 84568 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.05 |
| 108 | P20930 | Filaggrin OS=Homo sapiens GN=FLG PE=1 SV=3 | 51 | 434922 | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 9.24 |
| 109 | Q13454 | Tumor suppressor candidate 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TUSC3 PE=2 SV=1 | 49 | 39650 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 9.93 |
| 110 | Q9BXJ4 | Complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C1QTNF3 PE=2 SV=1 | 48 | 26977 | 2 | 2 | 6.5 | 6.04 |
| 111 | Q9HAV0 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GNB4 PE=1 SV=3 | 48 | 37543 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 | 5.6 |
| 112 | Q9NWT1_REVERSED | p21-activated protein kinase-interacting protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PAK1IP1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 48 | 43936 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | 9.07 |
| 113 | Q6ZU45 | Putative C-type lectin domain-containing protein NCRNA00083 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NCRNA00083 PE=5 SV=1 | 48 | 25796 | 1 | 1 | 3.4 | 6.3 |
| 114 | Q92609 | TBC1 domain family member 5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TBC1D5 PE=1 SV=1 | 47 | 88949 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 |
| 115 | O95497 | Pantetheinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=VNN1 PE=1 SV=2 | 47 | 56975 | 1 | 1 | 3.7 | 5.32 |
| 116 | O95714_REVERSED | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HERC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 47 | 526895 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.88 |
| 117 | P11717 | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=IGF2R PE=1 SV=3 | 47 | 274199 | 2 | 1 | 0.8 | 5.64 |
| 118 | Q9NPY3_REVERSED | Complement component C1q receptor OS=Homo sapiens GN=CD93 PE=1 SV=3 - REVERSED | 46 | 68515 | 1 | 1 | 1.1 | 5.27 |
| 119 | P31151 | Protein S100-A7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=S100A7 PE=1 SV=4 | 46 | 11464 | 2 | 1 | 31.7 | 6.28 |
| 120 | P19961 | Alpha-amylase 2B OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMY2B PE=1 SV=1 | 46 | 57673 | 2 | 1 | 5.1 | 6.64 |
| 121 | P02760 | Protein AMBP OS=Homo sapiens GN=AMBP PE=1 SV=1 | 46 | 38974 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5.95 |
| 122 | Q9H4M9 | EH domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EHD1 PE=1 SV=2 | 46 | 60589 | 2 | 1 | 4.9 | 6.35 |
| 123 | Q96CD0_REVERSED | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 8 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXL8 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 45 | 40490 | 11 | 1 | 1.9 | 7.03 |
| 124 | Q08554 | Desmocollin-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=DSC1 PE=1 SV=2 | 45 | 99924 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 5.25 |
| 125 | P49720 | Proteasome subunit beta type-3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMB3 PE=1 SV=2 | 45 | 22933 | 2 | 2 | 16.6 | 6.14 |
| 126 | P05543 | Thyroxine-binding globulin OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA7 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 46295 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 | 5.87 |
| 127 | Q9H2G4 | Testis-specific Y-encoded-like protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSPYL2 PE=1 SV=1 | 44 | 79387 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.45 |
| 128 | P25787 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA2 PE=1 SV=2 | 44 | 25882 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 6.92 |
| 129 | P02461 | Collagen alpha-1(III) chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=COL3A1 PE=1 SV=4 | 43 | 138479 | 3 | 2 | 1.4 | 6.21 |
| 130 | P81605 | Dermcidin OS=Homo sapiens GN=DCD PE=1 SV=2 | 43 | 11277 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 6.08 |
| 131 | Q9Y6X9_REVERSED | MORC family CW-type zinc finger protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MORC2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 43 | 117750 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 8.6 |
| 132 | Q8NBM4 | Ubiquitin-associated domain-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=UBAC2 PE=2 SV=1 | 43 | 38938 | 4 | 1 | 2.3 | 9.21 |
| 133 | P10643 | Complement component C7 OS=Homo sapiens GN=C7 PE=1 SV=2 | 43 | 93457 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 6.09 |
| 134 | Q12968_REVERSED | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=NFATC3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 43 | 115522 | 3 | 1 | 0.7 | 5.91 |
| 135 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRDX2 PE=1 SV=5 | 42 | 21878 | 1 | 1 | 9.1 | 5.66 |
| 136 | Q9UGM3 | Deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=DMBT1 PE=1 SV=2 | 42 | 260569 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.18 |
| 137 | O75460_REVERSED | Serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease IRE1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=ERN1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 109666 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.98 |
| 138 | Q9UKT8_REVERSED | F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=FBXW2 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 41 | 51479 | 2 | 1 | 3.1 | 6.11 |
| 139 | O95445 | Apolipoprotein M OS=Homo sapiens GN=APOM PE=1 SV=2 | 41 | 21239 | 2 | 1 | 6.9 | 5.66 |
| 140 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PGK1 PE=1 SV=3 | 40 | 44586 | 2 | 1 | 8.4 | 8.3 |
| 141 | O14578_REVERSED | Citron Rho-interacting kinase OS=Homo sapiens GN=CIT PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 40 | 231286 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 6.16 |
| 142 | Q7Z5M8 | Abhydrolase domain-containing protein 12B OS=Homo sapiens GN=ABHD12B PE=2 SV=1 | 40 | 40750 | 3 | 1 | 1.7 | 8.57 |
| 143 | Q15020_REVERSED | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by T-cells 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SART3 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 40 | 109865 | 3 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.45 |
| 144 | P29803_REVERSED | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=PDHA2 PE=1 SV=1 - REVERSED | 40 | 42906 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | 8.76 |
| 145 | Q14914 | Prostaglandin reductase 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PTGR1 PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 35847 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 | 8.45 |
| 146 | Q9NQX4 | Myosin-Vc OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYO5C PE=1 SV=2 | 40 | 202682 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 7.69 |
| 147 | Q13183_REVERSED | Solute carrier family 13 member 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SLC13A2 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 40 | 64368 | 2 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.61 |
| 148 | A8MPT4 | Glutathione S-transferase theta-4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GSTT4 PE=3 SV=2 | 39 | 27941 | 2 | 1 | 2.5 | 6.25 |
| 149 | Q8N6V9_REVERSED | Testis-expressed sequence 9 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TEX9 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 39 | 44798 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 6.2 |
| 150 | Q9Y2U8_REVERSED | Inner nuclear membrane protein Man1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=LEMD3 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 39 | 99935 | 2 | 1 | 0.7 | 7.31 |
| 151 | P05154 | Plasma serine protease inhibitor OS=Homo sapiens GN=SERPINA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 45646 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 9.3 |
| 152 | P11137 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAP2 PE=1 SV=4 | 39 | 199404 | 4 | 1 | 1.4 | 4.82 |
| 153 | Q9BY43 | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a OS=Homo sapiens GN=CHMP4A PE=1 SV=3 | 39 | 25083 | 1 | 1 | 3.2 | 4.65 |
| 154 | P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase OS=Homo sapiens GN=ACHE PE=1 SV=1 | 39 | 67753 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 | 5.87 |
| 155 | P07864 | L-lactate dehydrogenase C chain OS=Homo sapiens GN=LDHC PE=2 SV=4 | 38 | 36288 | 3 | 1 | 6.6 | 7.08 |
| 156 | P28066 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS=Homo sapiens GN=PSMA5 PE=1 SV=3 | 38 | 26394 | 2 | 1 | 12 | 4.74 |
| 157 | Q14C86_REVERSED | GTPase-activating protein and VPS9 domain-containing protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=GAPVD1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 164876 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 5.09 |
| 158 | O75808 | Calpain-15 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SOLH PE=1 SV=1 | 38 | 117239 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 6.27 |
| 159 | Q15751_REVERSED | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC1 OS=Homo sapiens GN=HERC1 PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 38 | 531891 | 1 | 1 | 0.2 | 5.69 |
| 160 | Q6R2W3_REVERSED | SCAN domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=SCAND3 PE=2 SV=1 - REVERSED | 38 | 151570 | 3 | 1 | 0.7 | 6.3 |
| 161 | Q6ZNE9_REVERSED | RUN and FYVE domain-containing protein 4 OS=Homo sapiens GN=RUFY4 PE=2 SV=2 - REVERSED | 37 | 64309 | 1 | 1 | 1.4 | 6.43 |
| 162 | Q8N7B9 | EF-hand calcium-binding domain-containing protein 3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=EFCAB3 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 50114 | 3 | 1 | 2.1 | 9.31 |
| 163 | O60312 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase VA OS=Homo sapiens GN=ATP10A PE=2 SV=2 | 37 | 167582 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 8.7 |
| 164 | O15264 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MAPK13 PE=1 SV=1 | 37 | 42063 | 3 | 1 | 1.9 | 8.48 |
| 165 | Q9H2K8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase TAO3 OS=Homo sapiens GN=TAOK3 PE=1 SV=2 | 37 | 105340 | 5 | 1 | 1.9 | 6.83 |
| 166 | P48634 | Protein PRRC2A OS=Homo sapiens GN=PRRC2A PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 228724 | 4 | 1 | 0.3 | 9.48 |
| 167 | Q8IVF6 | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 18A OS=Homo sapiens GN=ANKRD18A PE=1 SV=3 | 37 | 115525 | 4 | 1 | 0.7 | 7.92 |
| 168 | P35580 | Myosin-10 OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYH10 PE=1 SV=3 | 36 | 228858 | 1 | 1 | 0.6 | 5.44 |
| 169 | P10242_REVERSED | Transcriptional activator Myb OS=Homo sapiens GN=MYB PE=1 SV=2 - REVERSED | 36 | 72296 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 | 6.35 |
| 170 | Q9BV38 | WD repeat-containing protein 18 OS=Homo sapiens GN=WDR18 PE=1 SV=2 | 36 | 47375 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 | 6.21 |
| 171 | Q99816 | Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein OS=Homo sapiens GN=TSG101 PE=1 SV=2 | 60 | 43916 | 1 | 1 | 6.4 | 8.21 |
Extended Data Table 3.
Demographics of Patients and Healthy Participants
| DISCOVERY COHORT | VALIDATION COHORT | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants (n=321) | % of participants | No. of participants (n=82) | % of participants | No. of participants (n=32) | % of participants | ||||
| Pancreatic Cancer | Pancreatic Cancer | Breast cancer | |||||||
| Total | 190 | 59.19% | 56 | 68.29% | 32 | 100% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Sex | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Men | 104 | 54.74% | 28 | 50.00% | 0 | 0% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Women | 86 | 45.26% | 28 | 50.00% | 32 | 100% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Median Age (range) | 66 (37 – 86) | 70 (40 – 85) | 57 (30 – 85) | ||||||
|
| |||||||||
| AJCC stage | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| 0 | n.a. | - | n.a. | - | 2 | 6% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| I | 2 | 1.05% | 2 | 3.57% | 12 | 38% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| II | n.a | - | n.a | - | 17 | 53% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| IIa | 19 | 10.00% | 15 | 26.79% | n.a. | - | |||
|
| |||||||||
| IIb | 117 | 61.58% | 36 | 64.29% | n.a. | - | |||
|
| |||||||||
| III | 11 | 5.79% | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | 3% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| IV | 41 | 21.58% | 3 | 5.36% | n.a. | - | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Tumor grade | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 0.53% | 1 | 1.79% | 8 | 25% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| 2 | 91 | 47.89% | 35 | 62.5% | 13 | 41% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| 3 | 49 | 25.79% | 19 | 33.93% | 10 | 31% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.53% | 0 | 0.00% | n.a. | - | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Unknown | 48 | 25.26% | 1 | 1.79% | 1 | 3% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Tumor resected | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Yes | 152 | 80.00% | 54 | 96.43% | 32 | 100% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| No | 38 | 20.00% | 2 | 3.57% | 0 | 0% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Neoadjuvant Radio- /Chemotherapy | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Received | 10 | 5.26% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Not received | 180 | 94.74% | 56 | 100.00% | 32 | 100% | |||
|
| |||||||||
| Benign Pancreatic disease (BPD) | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Total | 26 | 8.15% | |||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Sex | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Men | 18 | 69.23% | 3 | 50.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Women | 8 | 30.77% | 3 | 50.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Median Age (range) | 58.5 (31 – 77) | 49 (43 – 56) | |||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Diagnosis | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Chronic pancreatits | 15 | 57.69% | 6 | 100% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Autoimmune pancreatitis | 3 | 11.54% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Serous cystadenoma | 8 | 30.77% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Pancreatic cancer precursor lesion (PCPL) | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Total | 5 | 1.55% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Sex | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Men | 2 | 40.00% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Women | 3 | 60.00% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Median Age (range) | 65 (59 – 74) | - | - | - | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Neoplasms | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| * IPMN | 5 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.00% | |||||
|
| |||||||||
| Healthy donors | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Total | 100 | 31.15% | 20 | 24.39% | |||||
n.a. - non applicable
Abbreviations: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PanIN).
The group of IPMNs consist of 2 IPMN associated with a carcinoma in situ, 1 IPMN associated with an early adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (pT1), an IPMN with intermediate dysplasia and an IPMN with low-grade dysplasia.
Extended Data Table 4. Histological report of patients with chronic pancreatitis.
The histopathological report is listed for the 15 patients with chronic pancreatitis in the discovery cohort.
| Patient No. | PanIN described | Histopathological report |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | Pancreatic tissue with chronic pancreatitis and extensive fibrosis and focal necrosis lipolytic and triptolytic areas. |
| 0 | No | Diffuse periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates; severe periductal fibrosis and duct obstruction/disappearance; severe interlobular and acinar involvement; severe inflammatory storiform fibrosis and diffuse sclerosis; frequent venulitis and occasional arteritis; scattered and occasionally prominent lymphoid follicles |
| 3 | No | Chronic pancreatitis with periductal, inter- and intralobular fibrosis |
| 4 | No | Chronic pancreatitis and extensive fibrosis |
| 5 | No | Chronic recurrent and acute pancreatitis with plurifocal tryptolytic and lipolytic necrosis |
| 6 | No | Low-grade chronic pancreatitis with periductal fibrosis, in the present material no evidence of neoplastic events, no evidence of malignancy. |
| 7 | No | Chronic recurrent pancreatitis with some more pronounced fibrosis and intraductal calcifications. Chronic pancreatitis extends to the pancreas resection margin. |
| 8 | No | Chronic pancreatitis, cholangitis and papillitis with focally histomorphological aspect of an autoimmune, chronic sclerosing pancreatitis. |
| 9 | PanIN 1a | Pancreatic parenchyma (head of the pancreas) and peripancreatic fat and connective tissue with chronic recurrent pancreatitis with some areas fibrosis and abscesses. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) Grade 1A. |
| 10 | No | Pancreatic parenchyma with perilobular fibrosis as well as dilated pancreatic ducts. In addition, peripancreatic fat and connective tissue with fibrosis. The finding represents a chronic pancreatitis. |
| 11 | PanIN 1a | Chronic-recurrent pancreatitis with pronounced fibrosis and dilated pancreatic ducts with focal inflammatory reactive epithelial cells. Older areas of organized necrosis and focal pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) Grade 1A. Chronic pancreatitis also affects the pancreas resection margin. |
| 12 | No | Pancreatitis with focally accentuated, periductal, perilobular and intralobular fibrosis as well as smaller areas of organized fatty necrosis and presence of singel giant cells of foreign body type. |
| 13 | No | Chronic recurrent and acute pancreatitis with plurifocal tryptolytic and lipolytic necrosis with extensive destruction of the pancreatic parenchyma. Smaller secretion - and obliteration of pancreatic ducts with periductal fibrosis and localized squamous metaplasia. Peri- and interlobular fibrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma. Pancreatitis reaches the resection margin. At present, no neoplastic tissue, no evidence of malignancy. |
| 14 | No | Pancreatic tissue with some scarring chronic inflammation and chronic pancreatits. In the present material, no evidence of malignancy. |
| 15 | No | Tumor -free pancreatic tissue (surgical margins) with low periductal and interlobular fibrosis. |
Extended Data Table 5. Histopathological findings and scoring in PKT mice in the cross sectional study.
The mouse ID, age, genotype and percent bead with GPC1+ crExos of mice in the cross sectional study are listed. A description of the histopathological findings and associated histological score is listed for PKT mice. Score 1: PanIN1a, Score 2: PanIN1 a/b, Score 3: PanIN2, Score 4: PanIN3, Score 5: Ductal adenocarcinoma (DCA). P: present (lesions were detected). 0: no lesion detected.
| Mouse ID | Age (days) | Sex | Genotype | GPC1 (%) | Normal (% area) | Involved (% area) | PanIN1a | PanIN1b | PanIN2 | PanIN3 | DCA | Other (defined) | Pathological score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T187 | 16 | M | Healthy+control | 0.6 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T188 | 16 | M | Healthy+control | 1.1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T157 | 20 | M | Healthy+control | 0.2 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T158 | 20 | M | Healthy+control | 0.2 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T163 | 20 | M | Healthy+control | 0.2 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T164 | 20 | M | Healthy+control | 0.4 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| T183 | 16 | M | PKT | 8.4 | 98.6 | 1.4 | P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| T190 | 16 | F | PKT | 5.2 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | reactive+ducts | 0 |
| T191 | 16 | F | PKT | 6.4 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | reactive+ducts | 0 |
| T156 | 20 | M | PKT | 8.3 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| T159 | 20 | F | PKT | 10.8 | 95.1 | 4.9 | P | P | P | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| T160 | 20 | F | PKT | 9.8 | 99.3 | 0.7 | P | P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| T165 | 20 | F | PKT | 9.2 | 96.1 | 3.9 | P | P | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
P : present
0 : not detected
Acknowledgments
This work was primarily supported by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas and UT MD Anderson Cancer Center. RK is also supported by NIH Grants CA-155370, CA-151925, DK 081576 and Metastasis Research Center at the MD Anderson Cancer Center (P30CA016672). VSL is supported by the NIH/NCI under the award number P30CA016672 and the UT MDACC Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahya Foundation. DPW and STG are supported by the NIH P50-CA094056. Institutional Core Grant CA16672 for High Resolution Electron Microscopy Facility. The Flow Cytometry MDACC core facility is partially funded by NIH P30CA16672. The MDACC Small Animal Imaging Facility is partially funded by NIH grants P30-CA016672 and 5U24-CA126577. SAM is a Human Frontiers Science Program Fellow. CK is funded by a Research Fellowship of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaf (DFG). We thank Paul A. Kurywchak for the help with immunoblots and sucrose gradients, and Sushrut Kamerkar for the help with the sucrose gradients. We thank Kenneth Dunner Jr. for the help with the transmission electron microscopy and immunogold techniques.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information is linked to the online version of the paper at www.nature.com/nature.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author contribution: S.A.M. conceptually designed and carried out most of the experiments, generated the data and the figures, and wrote the manuscript; L.B.L. carried out most of the experiments; C.K. performed sequencing of primary tumors, performed most of the statistical analysis of the manuscript and support in manuscript writing; A.F.F. optimized, performed and analyzed the UPLC-MS data; S.T.G. performed mouse MRI and analyzed the data; J.K. GEMMs breeding, bleeding, euthanasia and material collection; V.S.L. GEMMs breeding, bleeding, euthanasia, material collection and support in manuscript editing; E.A.M. provided breast cancer patient samples and patient history; J.W., N.R., C.R. and C.P. collected and provided serum samples and patient history for analysis; M.F.F. optimized, performed and analyzed the UPLC-MS data; D.P.W. mouse MRI interpretation and provided support in data interpretation and analysis; R.K. conceived the idea, conceptually designed the study, supervised the project and wrote the manuscript.
References
- 1.Pan BT, Teng K, Wu C, Adam M, Johnstone RM. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. The Journal of cell biology. 1985;101:942–948. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Trajkovic K, et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science. 2008;319:1244–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.1153124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Skog J, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nature cell biology. 2008;10:1470–1476. doi: 10.1038/ncb1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Al-Nedawi K, et al. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nature cell biology. 2008;10:619–624. doi: 10.1038/ncb1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Demory Beckler M, et al. Proteomic analysis of exosomes from mutant KRAS colon cancer cells identifies intercellular transfer of mutant KRAS. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP. 2013;12:343–355. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.022806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kahlert C, et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2014;289:3869–3875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C113.532267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ostrowski M, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nature cell biology. 2010;12:19–30. doi: 10.1038/ncb2000. sup pp 11–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thery C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2009;9:581–593. doi: 10.1038/nri2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al. Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. International journal of cancer. Journal international du cancer. 2005;113:752–760. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hergenreider E, et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nature cell biology. 2012;14:249–256. doi: 10.1038/ncb2441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. Exosomes/microvesicles: mediators of cancer-associated immunosuppressive microenvironments. Seminars in immunopathology. 2011;33:441–454. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecologic oncology. 2008;110:13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Silva J, et al. Analysis of exosome release and its prognostic value in human colorectal cancer. Genes, chromosomes & cancer. 2012;51:409–418. doi: 10.1002/gcc.21926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Runz S, et al. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecologic oncology. 2007;107:563–571. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.08.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Peinado H, et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nature medicine. 2012;18:883–891. doi: 10.1038/nm.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mears R, et al. Proteomic analysis of melanoma-derived exosomes by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics. 2004;4:4019–4031. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200400876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andre F, et al. Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived exosomes. Lancet. 2002;360:295–305. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Adamczyk KA, et al. Characterization of soluble and exosomal forms of the EGFR released from pancreatic cancer cells. Life sciences. 2011;89:304–312. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Baran J, et al. Circulating tumour-derived microvesicles in plasma of gastric cancer patients. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII. 2010;59:841–850. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0808-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ciravolo V, et al. Potential role of HER2-overexpressing exosomes in countering trastuzumab-based therapy. Journal of cellular physiology. 2012;227:658–667. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Luga V, et al. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell. 2012;151:1542–1556. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. In: Bonifacino Juan S, et al., editors. Current protocols in cell biology / editorial board. Unit 3. Chapter 3. 2006. p. 22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Thery C, Zitvogel L, Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2002;2:569–579. doi: 10.1038/nri855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wilson ID, et al. High resolution “ultra performance” liquid chromatography coupled to oa-TOF mass spectrometry as a tool for differential metabolic pathway profiling in functional genomic studies. Journal of proteome research. 2005;4:591–598. doi: 10.1021/pr049769r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Matsuda K, et al. Glypican-1 is overexpressed in human breast cancer and modulates the mitogenic effects of multiple heparin-binding growth factors in breast cancer cells. Cancer research. 2001;61:5562–5569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kleeff J, et al. The cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan glypican-1 regulates growth factor action in pancreatic carcinoma cells and is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1998;102:1662–1673. doi: 10.1172/JCI4105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Su G, et al. Glypican-1 is frequently overexpressed in human gliomas and enhances FGF-2 signaling in glioma cells. The American journal of pathology. 2006;168:2014–2026. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kahlert C, Kalluri R. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2013;91:431–437. doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morris JPt, Wang SC, Hebrok M. KRAS, Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2010;10:683–695. doi: 10.1038/nrc2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chen WW, et al. BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis of Mutant IDH1 mRNA in Glioma Patient Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids. 2013;2:e109. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2013.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Del Villano BC, et al. Radioimmunometric assay for a monoclonal antibody-defined tumor marker, CA 19–9. Clinical chemistry. 1983;29:549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ozdemir BC, et al. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer cell. 2014;25:719–734. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ijichi H, et al. Aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice caused by pancreas-specific blockade of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cooperation with active Kras expression. Genes & development. 2006;20:3147–3160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1475506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee ES, Lee JM. Imaging diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A state-of-the-art review. World journal of gastroenterology : WJG. 2014;20:7864–7877. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rickes S, Unkrodt K, Neye H, Ocran KW, Wermke W. Differentiation of pancreatic tumours by conventional ultrasound, unenhanced and echo-enhanced power Doppler sonography. Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology. 2002;37:1313–1320. doi: 10.1080/003655202761020605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Murphy SJ, et al. Genetic alterations associated with progression from pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia to invasive pancreatic tumor. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1098–1109 e1091. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.07.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2002;2:897–909. doi: 10.1038/nrc949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yachida S, et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2010;467:1114–1117. doi: 10.1038/nature09515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2010;362:1605–1617. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0901557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ballehaninna UK, Chamberlain RS. Biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: promising new markers and options beyond CA 19-9. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine. 2013;34:3279–3292. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jazieh KA, Foote MB, Diaz LA., Jr The clinical utility of biomarkers in the management of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Seminars in radiation oncology. 2014;24:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2013.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Locker GY, et al. ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24:5313–5327. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Okano K, Suzuki Y. Strategies for early detection of resectable pancreatic cancer. World journal of gastroenterology : WJG. 2014;20:11230–11240. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Conlon KC, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF. Long-term survival after curative resection for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 5-year survivors. Annals of surgery. 1996;223:273–279. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199603000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bilimoria KY, et al. National failure to operate on early stage pancreatic cancer. Annals of surgery. 2007;246:173–180. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3180691579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Murtaza M, et al. Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature. 2013;497:108–112. doi: 10.1038/nature12065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yong E. Cancer biomarkers: Written in blood. Nature. 2014;511:524–526. doi: 10.1038/511524a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.David G, et al. Molecular cloning of a phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan from human lung fibroblasts. The Journal of cell biology. 1990;111:3165–3176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Whipple CA, Young AL, Korc M. A KrasG12D-driven genetic mouse model of pancreatic cancer requires glypican-1 for efficient proliferation and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2012;31:2535–2544. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Aikawa T, et al. Glypican-1 modulates the angiogenic and metastatic potential of human and mouse cancer cells. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2008;118:89–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI32412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Brand RE, et al. Serum biomarker panels for the detection of pancreatic cancer. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2011;17:805–816. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hingorani SR, et al. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer cell. 2003;4:437–450. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen H, Boutros PC. VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC bioinformatics. 2011;12:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rachagani S, et al. Activated KrasG(1)(2)D is associated with invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through inhibition of E-cadherin. British journal of cancer. 2011;104:1038–1048. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rothstein DM, et al. Targeting signal 1 through CD45RB synergizes with CD40 ligand blockade and promotes long term engraftment and tolerance in stringent transplant models. J Immunol. 2001;166:322–329. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Schmid A, Braumuller H, Wehrl HF, Rocken M, Pichler BJ. Non-invasive monitoring of pancreatic tumor progression in the RIP1-Tag2 mouse by magnetic resonance imaging. Molecular imaging and biology : MIB : the official publication of the Academy of Molecular Imaging. 2013;15:186–193. doi: 10.1007/s11307-012-0548-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44:837–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]