Figure 1. RKIP negatively regulates Notch1 activation in lung and cervical cancer cell lines.
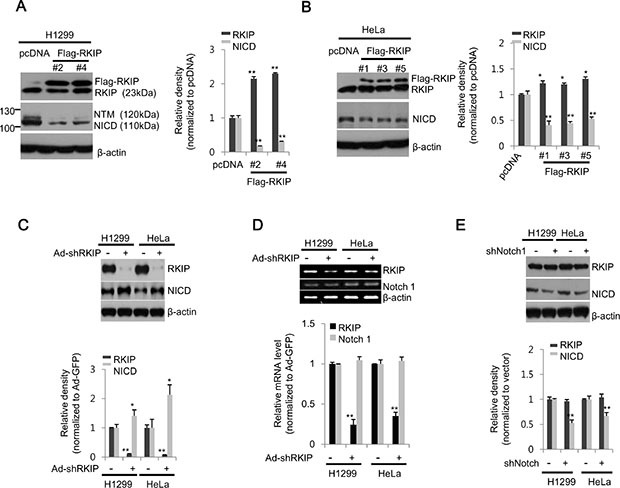
(A, B) Stable cell lines expressing FLAG-tagged RKIP (FLAG-RKIP) or control vector (pcDNA) were established in H1299 (clones #2 and 4) and HeLa (clones #1, 3, and 5) cells. (Left) Total cell extracts (30 μg) were separated on 10% SDS gels and analyzed by western blot analysis using anti-RKIP or -Notch1 antibodies. β-actin was used as a loading control. (Right) The expression levels of RKIP or NICD in H1299 (A) and HeLa (B) cells were quantified and represented graphically. (C) In H1299 and HeLa cells, RKIP expression was either knocked down with adenoviral shRNA-RKIP (Ad-shRKIP) or unaffected using a control vector (Ad-GFP). The expression levels of RKIP and Notch1 (NICD) in total cell extracts were analyzed by western blot analysis using specific antibodies to each protein (top) and represented graphically (bottom). (D) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Notch1 in RKIP- knocked down H1299 or HeLa cells. PCR products (295 bp for β-actin, 564 bp for RKIP, and 365 bp for Notch1) were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel (top) and quantified (bottom). (E) Expression of Notch1 in H1299 or HeLa cells was either abolished by transient transfection with Notch1 shRNA or unaffected in control vector transfections for 24 h. Each protein was analyzed by western blot analysis (top) and quantified (bottom). All data indicate the mean values ± standard deviation (S.D.) of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 compared to normalized controls.
