Figure 1. PRDM16 with a hypomethylated promoter is overexpressed and correlated with poor prognosis in astrocytoma patients.
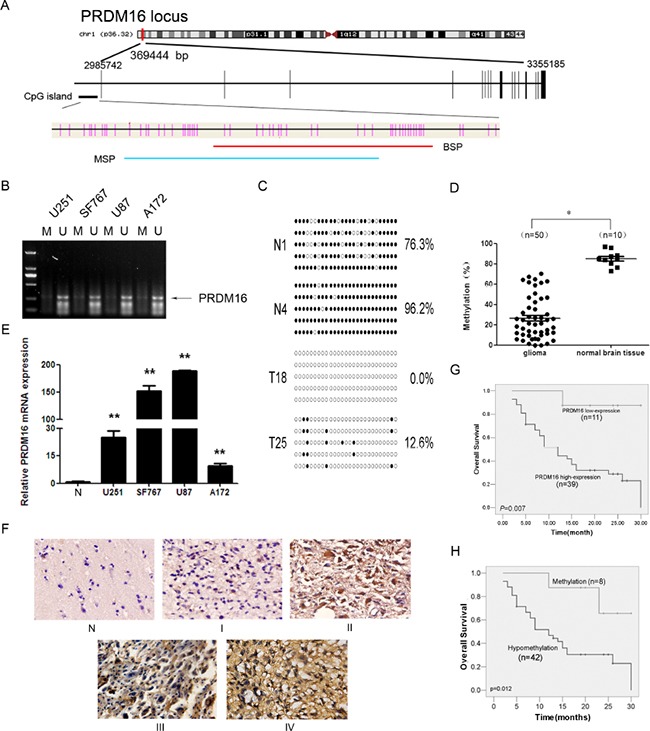
A. A schematic diagram of the CpG dinucleotides within the PRDM16 promoter. The nucleotide number is relative to the transcription start site of PRDM16. The red line indicates the region that was tested with BSP; the blue line indicates the region that was detected with MSP. B. The methylation status of PRDM16 in the astrocytoma cell lines was detected using MSP. U, unmethylated primer; M, methylated primer. C. BSP of the upstream regulatory region of PRDM16 was performed for each representative tissue sample (N, normal brain tissue; T, glioma sample). For each sample, at least five separate clones were sequenced, and the results are shown here. Unmethylated CpG sites are shown as open circles, whereas methylated CpG sites are represented by closed circles. For each row of circles, the sequence results for an individual clone of the bisulfite-PCR product are given. The number of methylated CpGs divided by the total number of true CpGs analyzed is given as a percentage to the right of each BSP result. D. The methylation status of PRDM16 was detected using BSP in astrocytoma (n=50) and normal brain tissue samples (n=10), and the results were verified using an independent samples t-test. *P< 0.05. E. Real-time PCR was used to detect the expression of PRDM16. PRDM16 expression levels in normal brain tissue samples were much lower than in the four astrocytoma cell lines, and this was verified via an independent samples t-test. **P<0.01. F. PRDM16 expression levels in normal brain tissue and astrocytoma tissue samples were tested using ISH. G. The correlation between PRDM16 methylation in tumor tissues and the OS values of astrocytoma patients. Patients with PRDM16 hypomethylation had shorter OS values than patients with normal levels of PRDM16 methylation. For this analysis, the Kaplan-Meier method was used. H. The correlation between tumor PRDM16 protein expression levels and OS values for astrocytoma patients. Patients with high PRDM16 expression levels had poor outcomes. The Kaplan-Meier method was also used for this analysis.
