Abstract
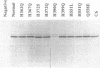
Recombinant human 5-lipoxygenase (arachidonate:oxygen 5-oxidoreductase, EC 1.13.11.34) was expressed in Escherichia coli. In incubations of E. coli supernatants with arachidonic acid, 5-hydroxy-7,9,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid and leukotriene A4 were formed, while incubation with 8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid gave 8-hydroxy-9,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid. Six conserved histidine residues in 5-lipoxygenase were subjected to site-directed mutagenesis. Exchanges of His-367, -372, or -551 gave mutants for which no enzyme activities were detectable. On the other hand, exchanges of His-362, -390, or -399 gave mutants that were enzymatically active, but less so than the nonmutated control. For two of these (exchanges of His-390 or -399), the activities of the mutants were dependent on the expression temperature. Thus, the histidines in the first group (His-367, -372, -551) were crucial for 5-lipoxygenase activity, possibly because of a function of these residues as metal ligands. Mutagenesis aimed at two other conserved elements in 5-lipoxygenase, Gln-558 and the C terminus, gave mutated proteins with only a small residual activity (substitution of Gln-558), or with no detectable activity (deletion of six C-terminal amino acids), indicating that these regions are important for the function of 5-lipoxygenase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balcarek J. M., Theisen T. W., Cook M. N., Varrichio A., Hwang S. M., Strohsacker M. W., Crooke S. T. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding rat 5-lipoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13937–13941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7816–7820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis D., Falgueyret J. P., Riendeau D., Abramovitz M. Characterization of the activity of purified recombinant human 5-lipoxygenase in the absence and presence of leukocyte factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5072–5079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Jones R. E., Diehl R. E., Bennett C. D., Kargman S., Rouzer C. A. Cloning of the cDNA for human 5-lipoxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):416–420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham W. R., Carroll R. T., Thompson J. F., Sands R. H., Funk M. O., Jr The initial characterization of the iron environment in lipoxygenase by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):611–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealing P. M., Casey R. The complete amino acid sequence of a pea (Pisum sativum) seed lipoxygenase predicted from a near full-length cDNA. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):915–918. doi: 10.1042/bj2530915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J., Thiele B. J., Chester J., O'Prey J., Janetzki S., Aitken A., Anton I. A., Rapoport S. M., Harrison P. R. The complete sequence of the rabbit erythroid cell-specific 15-lipoxygenase mRNA: comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of the erythrocyte lipoxygenase with other lipoxygenases. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk C. D., Furci L., FitzGerald G. A. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human platelet/erythroleukemia cell 12-lipoxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5638–5642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk C. D., Gunne H., Steiner H., Izumi T., Samuelsson B. Native and mutant 5-lipoxygenase expression in a baculovirus/insect cell system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2592–2596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk C. D., Hoshiko S., Matsumoto T., Rdmark O., Samuelsson B. Characterization of the human 5-lipoxygenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Hoshiko S., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Cloning of the cDNA for human 12-lipoxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7477–7481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Funk C. D., Rådmark O., Hög J. O., Jörnvall H., Samuelsson B. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of human 5-lipoxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Matsumoto T., Noguchi M., Yamashita I., Noma M. Expression of a cDNA encoding human 5-lipoxygenase under control of the STA1 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90010-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navaratnam S., Feiters M. C., Al-Hakim M., Allen J. C., Veldink G. A., Vliegenthart J. F. Iron environment in soybean lipoxygenase-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 31;956(1):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J. The nitric oxide complex of ferrous soybean lipoxygenase-1. Substrate, pH, and ethanol effects on the active-site iron. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12137–12142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Matsumoto T., Nakamura M., Noma M. Expression of human 5-lipoxygenase cDNA in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80638-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival M. D. Human 5-lipoxygenase contains an essential iron. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10058–10061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Rands E., Kargman S., Jones R. E., Register R. B., Dixon R. A. Characterization of cloned human leukocyte 5-lipoxygenase expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10135–10140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Samuelsson B. Leukocyte arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase: isolation and characterization. Methods Enzymol. 1990;187:312–319. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)87036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1171–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.2820055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Steczko J., Dixon J. E., Andrews P. C., Hermodson M., Axelrod B. Primary structure of soybean lipoxygenase L-2. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6816–6821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Steczko J., Dixon J. E., Hermodson M., Yazdanparast R., Axelrod B. Primary structure of soybean lipoxygenase-1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10080–10085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Izumi T., Seyama Y., Tadokoro K., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Characterization of leukotriene A4 synthase from murine mast cells: evidence for its identity to arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4175–4179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Enzyme with dual lipoxygenase activities catalyzes leukotriene A4 synthesis from arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirano Y., Shibata D. Low temperature cultivation of Escherichia coli carrying a rice lipoxygenase L-2 cDNA produces a soluble and active enzyme at a high level. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):128–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80388-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal E., Craik C. S., Highland E., Grunberger D., Costello L. L., Dixon R. A., Nadel J. A. Molecular cloning and primary structure of human 15-lipoxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):457–464. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Suzuki H., Yamamoto S., Takai T., Yokoyama C., Tanabe T. Cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase of porcine leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2142–2146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]