Summary
A staggering diversity of endophytic fungi associate with healthy plants in nature, but it is usually unclear whether these represent stochastic encounters or provide host fitness benefits. Although most characterized species of the fungal genus Colletotrichum are destructive pathogens, we show here that C. tofieldiae (Ct) is an endemic endophyte in natural Arabidopsis thaliana populations in central Spain. Colonization by Ct initiates in roots but can also spread systemically into shoots. Ct transfers the macronutrient phosphorus to shoots, promotes plant growth, and increases fertility only under phosphorus-deficient conditions, a nutrient status that might have facilitated the transition from pathogenic to beneficial lifestyles. The host’s phosphate starvation response (PSR) system controls Ct root colonization and is needed for plant growth promotion (PGP). PGP also requires PEN2-dependent indole glucosinolate metabolism, a component of innate immune responses, indicating a functional link between innate immunity and the PSR system during beneficial interactions with Ct.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
Colletotrichum tofieldiae (Ct) is a fungal root endophyte of Arabidopsis
-
•
Ct transfers the macronutrient phosphorus to Arabidopsis shoots
-
•
Ct-mediated plant growth promotion needs an intact phosphate starvation response
-
•
A branch of the plant innate immune system is essential for beneficial Ct activities
In nature, roots of healthy plants are colonized by diverse soil-borne fungi, but it is usually unclear whether this provides host fitness benefits. The fungus Colletotrichum tofieldiae colonizes Arabidopsis roots and transfers the macronutrient phosphorus to its host to boost plant growth and increase fertility under phosphate-deficient conditions.
Introduction
In nature, all healthy, asymptomatic plants live in association with a vast diversity of microbes, comprising bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protists, collectively called the plant microbiota. It is now widely accepted that individual plants of distantly related species assemble taxonomically structured bacterial consortia, characterized by the co-occurrence of a few bacterial phyla, and environmental parameters such as soil nutrients drive diversification of the bacterial microbiota at the species or strain level (Lundberg et al., 2012, Bulgarelli et al., 2013). Similarly, culture-independent community profiling techniques and culture-dependent surveys of surface-sterilized plant tissue revealed an enormous diversity of root-associated fungi, mainly belonging to three phyla, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Glomeromycota (Rodriguez et al., 2009, Coleman-Derr et al., 2016). However, since plant-associated fungal assemblages are hyperdiverse and mainly influenced by the biogeography of the host species (Coleman-Derr et al., 2016), it is difficult to discriminate whether a particular fungal association with a healthy plant is merely the result of a stochastic encounter or has ecophysiological significance. Mycorrhizal fungi of the phylum Glomeromycota are the best-characterized beneficial fungi associated with plant roots, colonize ∼80%–90% of terrestrial plants, and mobilize soil nutrients, including the macronutrient phosphorus, for plant growth (Bonfante and Genre, 2010). This evolutionarily ancient symbiosis evolved ∼450 million years ago, and the plant signaling pathway needed for mycorrhizal symbiosis is conserved in most flowering plants, but was lost in the Brassicaceae lineage, including Arabidopsis thaliana (Bonfante and Genre, 2010).
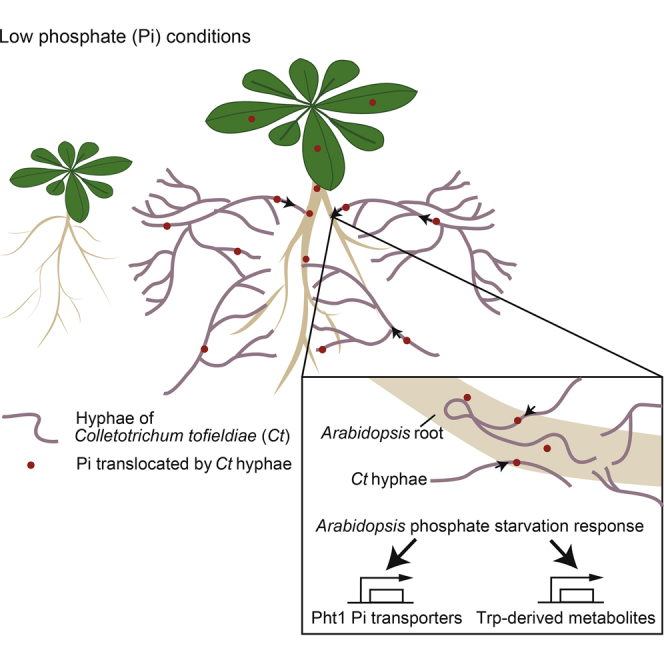
Phosphorus is one of three macronutrients limiting plant growth in natural soils besides nitrogen and potassium, and synthetic fertilizers providing these macronutrients have been critical for crop productivity in intensive agricultural settings for ∼100 years. Plant roots can absorb only inorganic orthophosphate (Pi), although phosphorus is abundant in many natural soil types both as organic and inorganic pools. Pi can be assimilated by plant roots via low-Pi-inducible (high-affinity) and constitutive Pi uptake systems (López-Arredondo et al., 2014). Plant-associated bacteria and fungi such as mycorrhizal fungi can mobilize plant-inaccessible inorganic phosphate in soils such as hydroxyapatite and Ca3(PO4)2 by conversion into bioavailable Pi. In addition, plants have evolved a phosphate starvation response (PSR) system that senses phosphate starvation and adjusts root and shoot growth accordingly (Poirier and Bucher, 2002). The genetic basis of this PSR is well-studied in the model plant A. thaliana (Chiou and Lin, 2011). However, it is currently unknown whether the PSR is coordinated with root colonization by beneficial microbes that mobilize Pi for plant growth under low phosphate conditions.
Flowering plants synthesize and accumulate a vast array of structurally diverse small molecules known as secondary metabolites. The diversification of several secondary metabolite classes and their corresponding biosynthesis pathways in plants is driven by microbes and insects (Dixon, 2001). One of the best-studied and most diversified compound classes in A. thaliana comprises β-thioglucosides, known as glucosinolates, that are synthesized via branch pathways from methionine, tryptophan (Trp), and phenylalanine (Halkier and Gershenzon, 2006). The PEN2 myrosinase-dependent metabolism of Trp-derived indole glucosinolates in A. thaliana is activated upon perception of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system and is needed for broad-spectrum defense to restrict the growth of fungal pathogens (Clay et al., 2009, Bednarek et al., 2009). Although recent findings provided evidence for a metabolic link between the PSR system and glucosinolate biosynthesis (Pant et al., 2015), its functional relevance remains unclear.
Here, we have characterized an ascomycete fungal endophyte, Colletotrichum tofieldiae (Ct), that was originally isolated from asymptomatic A. thaliana plants growing at Las Rozas, Spain after surface disinfection of leaf tissue (García et al., 2013). Colonization experiments with germ-free A. thaliana plants revealed that Ct initiates endophytic growth only via roots and occasionally spreads systemically into shoots without causing discernable disease symptoms. Using 33Pi isotope tracer experiments, we show that Ct, but not the closely related pathogenic species C. incanum (Ci), translocates Pi into the plant via root-associated hyphae only under phosphate starvation conditions. 33Pi translocation is correlated with PGP. Using regulatory mutants of the A. thaliana PSR and mutants of Trp-derived secondary metabolite biosynthetic and regulatory genes, we demonstrate that Ct-mediated PGP needs an intact PEN2 myrosinase-dependent branch pathway for indole glucosinolate hydrolysis and regulatory components of the PSR. Moreover, depletion of all Trp-derived secondary metabolites renders Ct a pathogen of A. thaliana. An analysis of Ct interactions with two A. thaliana relatives, Cardamine hirsuta and Capsella rubella, points to indole glucosinolates as potential determinants of fungal host-range. We hypothesize that Ct is a root endophyte of A. thaliana and other Brassicaceae that might have compensated the loss of components required for mycorrhizal symbiosis in this plant family.
Results
Colletotrichum tofieldiae Is Endemic in Natural A. thaliana Populations in Central Spain
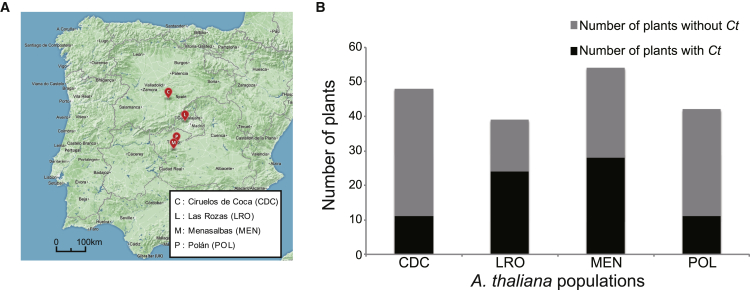
We predicted that Ct should be present in healthy plants throughout the year if the fungus establishes a stable endophytic interaction with A. thaliana. We surveyed the distribution of Ct in plants growing at Las Rozas (“LRO”) using qPCR with a Ct-specific primer pair encompassing coding plus intron sequences of the tubulin gene. Ct was detected in more than half of tested plants from both leaves and roots during two seasons (November, April plus May) and in successive years (2009–2012), suggesting the fungus is wide-spread and persistent in this A. thaliana population (Figures 1A, 1B, and S1A). We also detected Ct in samples from wild populations of A. thaliana at Ciruelos de Coca (“CDC”), Polán (“POL”), and Menasalbas (“MEN”), which are located on the Central Plateau of Spain up to 300 km distant from Las Rozas (Figures 1A and 1B). Thus, Ct appears to be a widely distributed endophyte among A. thaliana populations in Spain. In contrast, we failed to detect Ct in three A. thaliana populations in Germany and France (Figure S1B), suggesting an endemic association of the fungus with natural A. thaliana populations in the Central Plateau of Spain.
Figure 1.
Prevalence of C. tofieldiae in Four Natural A. thaliana Populations in Spain
(A) Geographical location of the sampled sites in Central Spain.
(B) Detection of C. tofieldiae (Ct) in roots and/or leaves of healthy A. thaliana plants (collected in Spring between 2009 and 2012) using qPCR analysis with a specific primer pair targeting the Ct tubulin sequence (CT04_11973).
See also Figure S1.
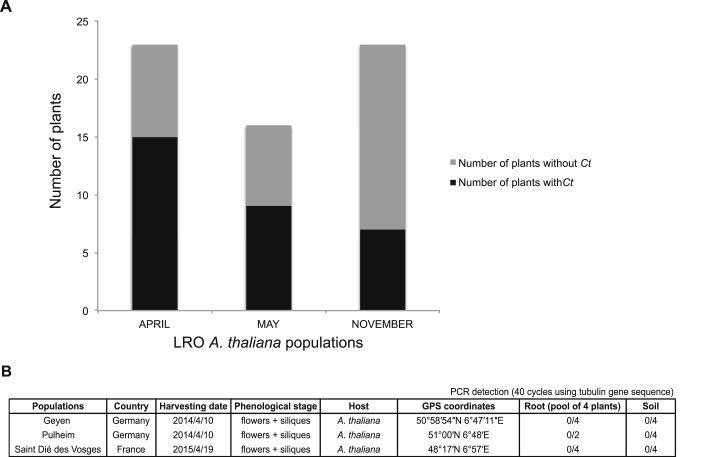
Figure S1.
Distribution of C. tofieldiae at Different Seasons and at Various Sites in Europe, Related to Figure 1
(A) Distribution of C. tofieldiae (Ct) from A. thaliana growing in the Las Rozas (LRO) site in central Spain at two different seasons of the year (April/May, and November). q-PCR analysis using Ct-specific primers detected the presence of Ct in plants at both seasons.
(B) Ct was not detectable in soil and root samples from three A. thaliana populations in France (Saint-Dié des Vosges) and Germany (Geyen and Pulheim).
Ct Colonizes A. thaliana Systemically from Roots without Causing Visible Symptoms
To visualize the infection process of Ct by live-cell confocal imaging, we first generated transgenic fungal strains constitutively expressing cytoplasmic GFP (Ct-GFP) by means of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Conidia of the transgenic strains were then inoculated onto leaves and roots of A. thaliana accession Col-0. On intact leaf surfaces, Ct spores germinated to form melanized appressoria at 8 dpi (Figure 2A). These are specialized infection structures essential for initial host cell entry by pathogenic Colletotrichum species (Deising et al., 2000). However, although Ct was originally isolated from A. thaliana leaves (García et al., 2013), fungal germlings were never seen to enter leaf epidermal cells and form invasive hyphae, even after 8 days. This suggests either that Ct does not use appressoria to invade A. thaliana leaves or that appressorium-mediated entry is terminated by the host.
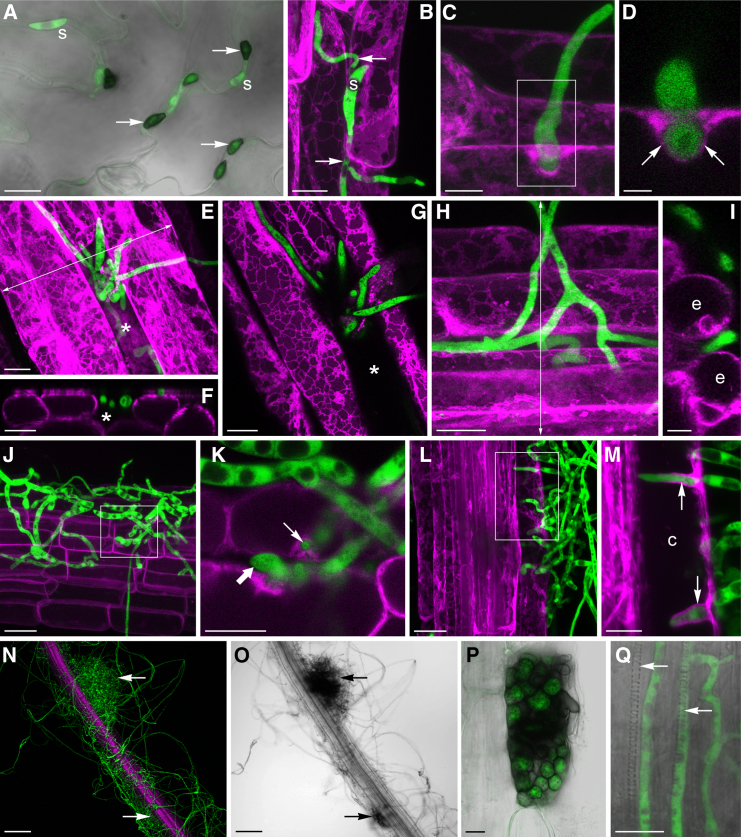
Figure 2.
C. tofieldiae Colonization of A. thaliana Roots
Confocal microscope images of C. tofieldiae (Ct) expressing cytoplasmic GFP (green) and A. thaliana expressing PIP2A-mCherry (magenta).
(A) Spores (s) germinating on a leaf form melanized appressoria (arrows); 8 dpi. Overlay projection of GFP and bright-field channels. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Spore (s) germinating on a root form multiple long germ-tubes (arrows); 2 dpi. Maximum projection of z stack image. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C and D) Undifferentiated hypha penetrating a root epidermal cell enveloped by PIP2A-mCherry-labeled host membranes (arrows); 2 dpi. (C) Maximum projection of z stack image. (D) Enlargement of one optical section from the projection shown in (C). Scale bars, 5 μm (C); 2 μm (D).
(E–G) First infected root epidermal cell (asterisk) containing intracellular hyphae is not labeled by PIP2A-mCherry; 2 dpi. (E) Maximum projection of z stack image. (F) Orthogonal projection of (E). (G) Enlargement of one optical section from the projection shown in (E). Scale bars, 10 μm.
(H and I) Undifferentiated hyphae penetrating between two root epidermal cells (e); 2 dpi. (H) Maximum projection of z stack image. (I) Orthogonal projection of (H). Scale bars, 10 μm (H) and 5 μm (I).
(J and K) Intracellular (small arrow) and intercellular hyphae (large arrow) colonizing the root cortex; 2 dpi. (J) Maximum projection of z stack image. (K) Enlargement of one optical section from the projection shown in (J). Scale bars, 20 μm (J) and 10 μm (K).
(L and M) Intracellular hyphae inside a root cortical cell (c) enveloped by PIP2A-mCherry-labeled host membranes (arrows); 8 dpi. Maximum projections of z stack images. (M) Enlargement of (L) using a subset of optical sections. Scale bars, 20 μm (L) and 10 μm (M).
(N and O) Root enmeshed by a network of extraradical hyphae, with melanized microsclerotia developing (arrows); 8 dpi. (N) Maximum projection of z stack image. (O) Bright-field image corresponding to (N). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(P) Root epidermal cell packed with swollen hyphal cells with melanized cell walls; 28 dpi. Overlay projection of GFP and bright-field channels. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(Q) Hyphae inside the root central cylinder, with xylem tracheids in the same focal plane (arrows); 8 dpi. Overlay projection of GFP and bright-field channels. Scale bar, 20 μm.
See also Figure S2.
Next, we traced the infection of A. thaliana roots by Ct-GFP using transgenic plants expressing the aquaporin PIP2A fused with the fluorescent protein mCherry, providing a plasma membrane/ER marker for living host cells (Nelson et al., 2007). Ct spores germinated at 6 hpi, producing either one or two germ-tubes that became branched (Figure 2B). Around 24 hpi, Ct hyphae were observed to directly enter root epidermal cells, producing intracellular hyphae that were enveloped by mCherry labeling (Figures 2C and 2D), suggesting the host plasma membrane invaginates around the hyphae and that the fungus establishes a biotrophic interaction with living host cells. However, the mCherry fluorescence disappeared from epidermal cells soon after penetration, indicating a loss of viability, although adjacent more recently colonized cells remained alive (Figures 2E–2G). The initial biotrophic interaction of intracellular hyphae with root epidermal cells was therefore transient. Ct also invaded roots via junctions between epidermal cells to form intercellular hyphae (Figures 2H and 2I). Whether penetrating directly into or between epidermal cells, fungal entry was by means of undifferentiated hyphae rather than appressoria, in striking contrast to Colletotrichum species infecting leaves (Deising et al., 2000).
Following invasion of the root epidermis, Ct colonized the underlying cortex by means of both intra- and intercellular hyphae at 2 dpi (Figures 2J–2M, S2A, and S2B). Importantly, the intracellular hyphae in cortical cells remained enveloped by an intact host plasma membrane for longer periods than those infecting epidermal cells (Figures 2L and 2M), suggesting a more stable biotrophic interaction is established with cortical cells. By 8 dpi, extensive networks of extraradical hyphae enveloped the roots (Figures 2N, 2O, and S2A), while in some localized areas, epidermal and cortical cells became packed with black microsclerotia, comprising clusters of swollen, spherical cells with thick, melanized walls (Figures 2N–2P and S2B). In other root-infecting Colletotrichum species, microsclerotia can act as resting structures for long-term survival in soil (Blakeman and Hornby, 1966). TEM revealed that some hyphae colonized the endodermis, but most failed to penetrate the suberized cell walls of the periderm (Figures S2C–S2E). Nevertheless, straight runner hyphae were occasionally seen growing inside the central cylinder parallel to the long axis of the root (Figure 2Q). This shows that some hyphae do overcome the periderm barrier and raises the possibility that Ct colonizes above-ground parts of the plant via the root central cylinder, as reported for Magnaporthe oryzae on rice (Sesma and Osbourn, 2004) and C. graminicola on maize (Sukno et al., 2008). To test this, we grew Arabidopsis plants in a hydroponic culture system in which roots and shoots were physically separated (Strehmel et al., 2014) and inoculated the roots with conidia of Ct-GFP. Using RT-qPCR with GFP-specific primers, we detected the presence of the fungus in 11% of healthy leaves at 28 days after inoculation, increasing to 43% at 38 dpi (Figure S2F). Microscopic analysis at 28 dpi confirmed the presence of hyphae expressing GFP in healthy leaves, mostly restricted to leaf veins (Figure S2G). However, when leaves began to senesce at 48 dpi, the entire leaf was extensively colonized by mycelium, suggesting that Ct growth is limited until host tissues senesce (Figure S2H). Overall, these data suggest that Ct is a root endophyte on A. thaliana, which can also infect shoots systemically, without causing discernible disease symptoms.
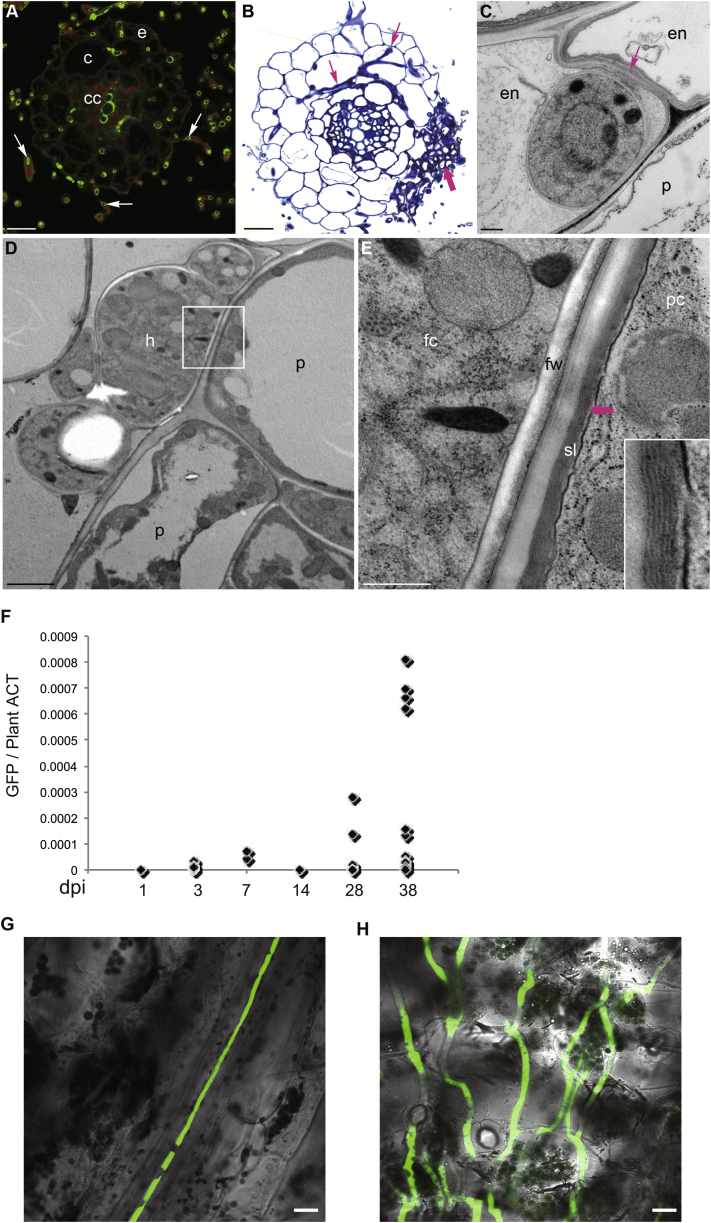
Figure S2.
C. tofieldiae Colonization of A. thaliana Roots and Systemic Colonization of A. thaliana Shoots, Related to Figure 2
(A) Epi-fluorescence micrograph of a root cross-section at 7 dpi. The section was stained with wheat germ lectin-FITC, which labels N-acetylglucosamine residues in fungal cell walls green, but also the secondary cell walls of xylem vessels in the central cylinder (cc). The root cortex (c), epidermis (e) and root hairs (arrows) are extensively colonized by intraradical hyphae, while abundant extraradical hyphae envelope the root at this stage.
(B) Bright-field micrograph of a root cross-section stained with Toluidine blue (7 dpi). Note the microsclerotium (thick arrows) developing in the epidermis and cortex and long intracellular hyphae spreading in the cortex (thin arrows).
(C–E) Transmission electron micrographs of ultrathin sections. (C) Cross-section of a hypha inside a root endodermal cell (en) as indicated by the presence of Casparian strip cell wall alterations in the anticlinal cell wall (arrow). 5 dpi. (D and E) Hypha (h) in contact with the root periderm (p) as indicated by the presence of layered suberin lamellae (sl) in the peridermal cell wall (arrow and inset). 7 dpi. fw, fungal wall; fc, fungal cytoplasm; pc, plant cytoplasm. Scale bars, 20 μm (A and B), 2 μm (D), 500 nm (C and E).
(F) Detection of C. tofieldiae (Ct) in healthy shoots of A. thaliana following root inoculation. A. thaliana Col-0 plants were grown hydroponically and the 20-day-old roots were infected with Ct-GFP spores. q-RT-PCR analysis with GFP-specific primers detected the presence of Ct-GFP in some healthy leaves. Approximately10 leaves per time point were collected.
(G) Confocal microscope image showing Ct-GFP hypha growing in vein tissue of a healthy leaf at 28 days post inoculation (dpi) of roots. Bar = 20 μm.
(H) Confocal microscope image showing Ct-GFP hyphae growing in a senescent leaf at 48 dpi. Bar = 20 μm.
Ct Promotes Plant Growth under Low Pi Conditions by Translocating Pi to the Host
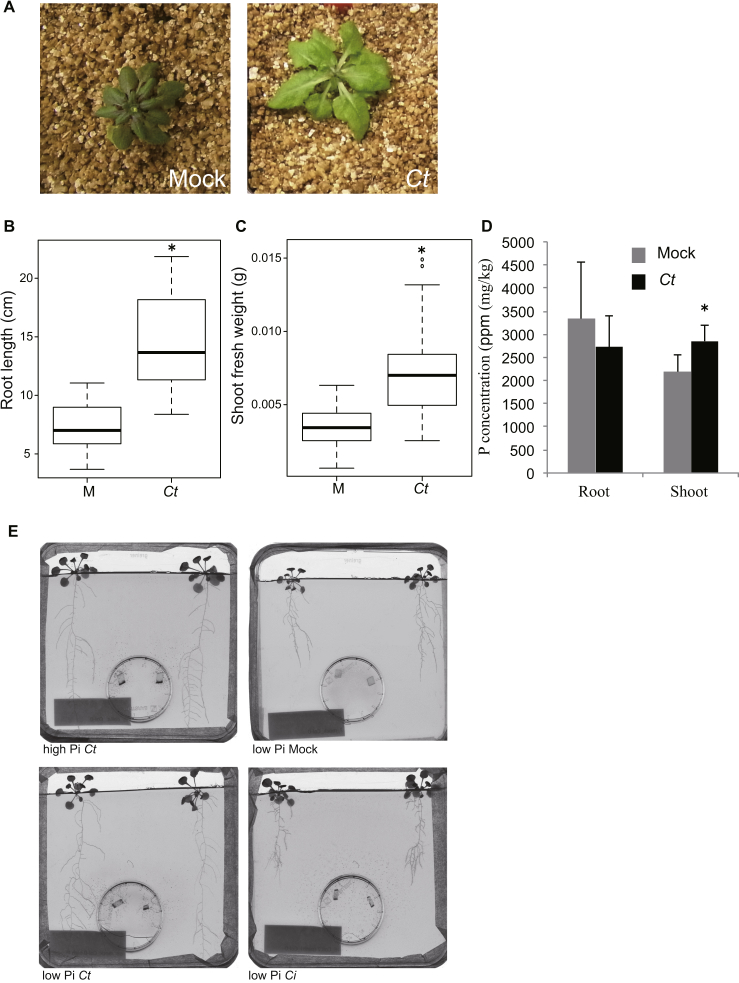
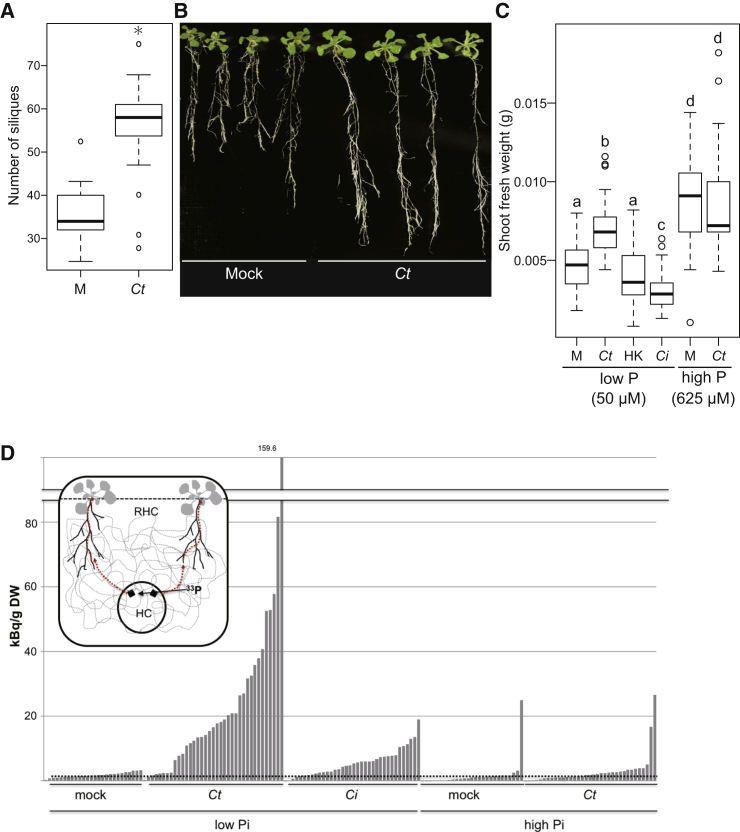
To address the long-term impacts of Ct colonization on plant growth, we co-cultivated A. thaliana plants with Ct in vermiculite, a naturally occurring mica mineral, without supplying additional nutrients. After 30 days, mock-treated plants appeared stunted and accumulated anthocyanin in their shoots, a well-known abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis (Kovinich et al., 2014). In contrast, plants co-cultivated with Ct had larger shoots that did not accumulate anthocyanins (Figure S3A), suggesting the fungus can promote plant growth in this low-nutrient soil-free system. We also measured silique production as an index of fertility and plant fitness. The Ct-treated plants produced significantly more siliques (Figure 3A), indicating that the fungus enhances both plant growth and fitness under low nutrient conditions.
Figure S3.
C. tofieldiae-Mediated Plant Growth Promotion in Phosphate Limiting Conditions, Related to Figure 3
(A) A. thaliana vegetative growth in nutrient-poor vermiculite was improved in the presence of C. tofieldiae (Ct). Col-0 plants grown in half MS medium containing 0.8% sucrose were transferred to vermiculite soil either with or without the addition of Ct mycelium. The photographs were taken after co-cultivation for four weeks.
(B) Root growth promotion by Ct in low Pi conditions. Root length was measured 24 days after sterilized Col-0 seeds were inoculated with Ct spores (24 dpi). Ct treatment significantly increased root length (two-tailed t test, p < 0.0001). The graph represents combined data from three independent experiments.
(C) Shoot growth promotion by Ct when hydroxyapatite provided the sole Pi source. Shoot fresh weights were measured at 24 dpi. Ct treatment significantly increased the shoot fresh weight (two-tailed t test, p < 0.0001). The graph shows combined data from two independent experiments.
(D) The concentration of phosphorus (P) in A. thaliana shoots was significantly increased after growth in the presence of Ct. The P content of plants incubated with Ct for 24 days was measured by ICP-MS and was calculated in ppm based on the shoot dry weight. Ct treatment significantly increased the P content of shoots (two-tailed t test, p < 0.01). Similar results were obtained from one additional independent experiment.
(E) Illustration of the two-compartment co-cultivation system used for 33P translocation experiments. Seven-day-old A. thaliana seedlings were transferred to half MS agar medium providing either high or low Pi conditions in square (12 × 12 cm) Petri plates. Two agar plugs with or without C. tofieldiae mycelium were placed into the small circular Petri plates. After 7 days, 33P was added to the small plates, and the two-compartment system was further incubated for 17 days, when the photographs were taken and shoots harvested for scintillation counting.
Figure 3.
C. tofieldiae Promotes Plant Growth in Low Phosphate Conditions
(A) Number of siliques produced by A. thaliana growing in vermiculite. Plants grown with Ct had significantly more siliques than those grown without C. tofieldiae (Ct) (t test, p < 0.01).
(B) A representative image of A. thaliana plants grown in low phosphate (Pi) conditions with and without Ct. Seven-day-old plants were inoculated with Ct or water and grown in low Pi MS medium for 18 days.
(C) Shoot fresh weight (SFW) of plants incubated with beneficial Ct or pathogenic C. incanum (Ci) in high or low Pi conditions. A. thaliana Col-0 seeds were inoculated with Ct, heat-killed Ct or Ci, or water (mock), and SFW was determined 24 days later (15 plants per experiment). The boxplot shows combined data from three independent experiments. Different letters indicate significantly different statistical groups (Tukey-HSD, p < 0.01).
(D) Translocation of 33P-labeled orthophosphate from Ct to A. thaliana shoots. Col-0 plants were grown on low Pi medium without (mock, n = 26) or with Ct (n = 37) or Ci (n = 36) or on high Pi medium without (mock, n = 27) or with Ct (n = 35) in a two-compartment system (cartoon). 33P was added to the hyphal compartment (HC) and after 17 days 33P -incorporation into shoots was measured by scintillation counting. Columns represent counts in kBq 33P /g dry weight (DW) of individual plants. The dotted line shows the median level of 33P background counts from mock inoculations. RHC, root hyphal compartment.
See also Figure S3.
To address whether Ct helps plants to assimilate nutrients, we used an agarose gel-based medium in which the concentration of specific nutrients, such as phosphorus, nitrogen, and iron, can be tightly controlled (Gruber et al., 2013). In this system, we found that Ct promoted plant growth under low Pi conditions (50 μM bioavailable KH2PO4). Thus, after 18 days co-cultivation with Ct, plants developed longer roots and larger shoots, as measured by shoot fresh-weight, whereas plants co-cultivated with heat-killed fungus showed no growth promotion (Figures 3B, 3C, and S3B). Moreover, Ct also promoted plant growth when plant-inaccessible hydroxyapatite provided the sole Pi source, indicating that the fungus can dissolve this insoluble form of phosphate (Figure S3C). However, Ct did not promote plant growth under Pi-sufficient conditions (625 μM KH2PO4; Figure 3C), suggesting that a beneficial interaction with plants is established under Pi deficiency.
We also tested the plant growth promotion ability of a closely related Colletotrichum species pathogenic on Raphanus sativus that was previously reported as C. dematium (Sato et al., 2005), but now identified as C. incanum (Ci) (Hacquard et al., 2016). Remarkably, inoculation of Arabidopsis roots with Ci significantly inhibited plant growth under low Pi conditions (Figure 3C).
The improved shoot growth provided by Ct under Pi-deficient conditions correlated with a significantly higher P concentration in shoot tissues, as measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (Figure S3D), suggesting Ct enhances plant growth by improving Pi uptake from media. The hyphae of AM fungi are known to capture Pi from the soil outside the rhizosphere and translocate it into the plant (Bucher, 2007). To study phosphate transport by Ct to distant plant roots and subsequent allocation to the shoot, we used a two-compartment system with the radioactive tracer 33P-phosphate added to one compartment (Figures 3D and S3E). To prevent 33P diffusion through the medium, plants and 33P were separated by a plastic barrier, which could only be bridged by fungal hyphae. 33P accumulation in shoots under Pi-starvation was analyzed in mock-inoculated plants and plants colonized by beneficial Ct or pathogenic Ci at 17 days after 33P addition to the inner compartment. Mock-inoculated plants (with 33P, but without fungus) accumulated <5 kBq/g dry weight (DW) 33P in their shoots (Figure 3D, mock). By contrast, 29 out of 37 plants colonized by Ct accumulated 33P in their shoots to higher levels than mock-inoculated plants (Figure 3D, Ct). 33P accumulation differed markedly between replicate Ct-inoculated plants, ranging from moderate (>5 to <40 kBq/g DW) to high levels (>40 up to 160 kBq/g DW). In contrast, although most shoots of plants colonized by the pathogenic Ci accumulated more 33P than mock-inoculated controls, the translocated 33P levels were dramatically lower (<10 kBq/g DW in 30 of 36 plants) compared to Ct-infected plants (Figure 3D, Ci). Remarkably, most plants colonized by Ct under Pi-replete conditions also did not accumulate more 33P than the corresponding mock control plants (Figure 3D), which might explain why Ct-mediated plant growth promotion was detectable only under Pi-deficient conditions (Figure 3C). Collectively, these results indicate that the transfer of 33P from Ct hyphae to the shoots of host plants is strictly regulated by Pi availability.
Ct Colonization Activates the Expression of Several A. thaliana Pht1 Pi Transporters
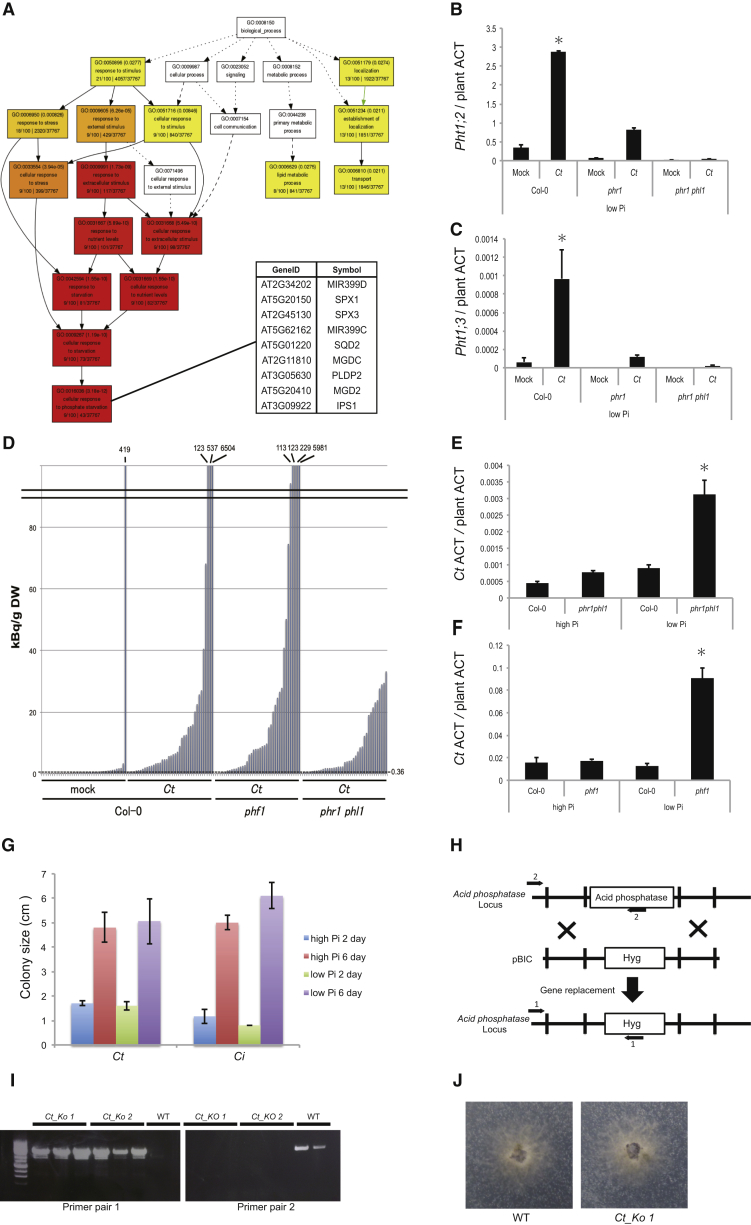
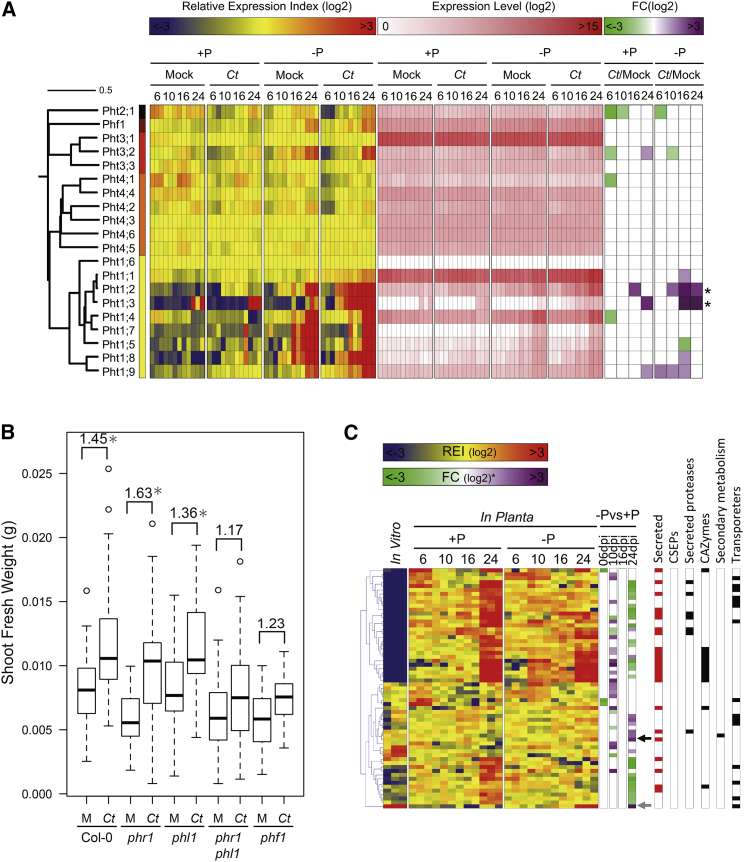
To investigate the mechanism(s) by which Ct promotes plant growth, we collected samples for RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis from infected A. thaliana roots grown under Pi-sufficient and Pi-deficient conditions at four time points (6, 10, 16, and 24 dpi) and also Ct hyphae grown in vitro. We focused our analysis on fungal and A. thaliana genes that were differentially expressed in Pi-deficient versus Pi-sufficient conditions (log2FC >1, false discovery rate [FDR] <0.05). Among the top 100 A. thaliana genes that were differentially expressed at 24 dpi under Pi-starvation, nine were related to “cellular response to phosphate starvation,” validating that the host reprograms its transcriptome in response to Pi deficiency (Figure S4A). These included genes belonging to the Pht1 family of plasma membrane phosphate:H+ symporters, some of which were shown to be required for Pi uptake from the rhizosphere (Shin et al., 2004). Nine of these transporter genes were significantly upregulated in phosphate-starved roots in the absence of Ct while two, Pht1;2 and Pht1;3, were induced at higher levels only in the presence of Ct under Pi-limiting conditions at later time points (16 and 24 dpi; Figure 4A). This result indicates that Ct enhances phosphate uptake in the host under Pi-deficient conditions, similar to mycorrhizal associations (Bonfante and Genre, 2010).
Figure S4.
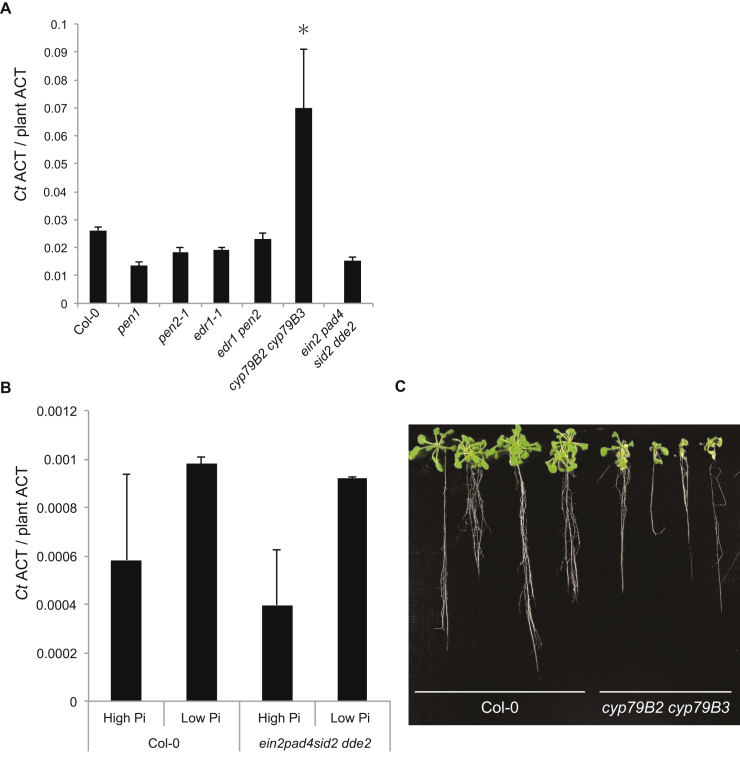
GO-Term Enrichment Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Genes Induced after 24 Days Growth in Low Pi Conditions, Related to Figure 4
(A) GO-term enrichment analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana genes induced after 24 days growth in low Pi conditions. Based on RNA-Seq analysis of A. thaliana genes that were differentially expressed in Pi-deficient versus Pi-sufficient conditions (log2FC > 1, fdr < 0.05), Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that among the top 100 A. thaliana genes that were upregulated at 24 dpi under Pi-starvation conditions, nine were related to ‘cellular response to phosphate starvation’ (GO: 0016036). The color coding visually represents p value in each Go term box (Red box shows lower p value than yellow.).
(B) Analysis of regulatory mutants of the A. thaliana phosphate starvation response (PSR). Ct-mediated and phosphate starvation-dependent activation of both Pht1;2 and Pht1;3 was abrogated in phr1 phl1 plants. q-RT-PCR analysis revealed the reduction of Pht1;2 expression in phr1 phl1 mutant plants relative to Col-0 wild-type plants grown in low Pi media at 24 dpi. Expression levels are shown relative to the mean expression of plant actin. (Col-0 with Ct versus phr1 phl1 with Ct, two-tailed t test, p < 0.01).
(C) q-RT-PCR analysis revealed the reduction of Pht1;3 expression in phr1 phl1 mutant plants grown in low Pi media at 24 dpi. Expression levels are shown relative to the mean expression of plant actin. (Col-0 with Ct versus phr1 phl1 with Ct, two-tailed t test, p < 0.01).
(D) Translocation of 33P-labeled orthophosphate from Ct to A. thaliana shoots. Col-0 plants were grown on low Pi medium without (mock, n = 39) or with Ct (n = 40), phf1 mutants with Ct (n = 40), and phr1 phl1 double mutants with Ct (n = 40) in a two-compartment system. 33P was added to the hyphal compartment and after 17 days 33P -incorporation into shoots was measured by scintillation counting. Columns represent counting results in kBq 33P /g dry weight (DW) of individual plants. The dotted line shows the median level of 33P background counts from mock inoculations.
(E) At 4 days after roots were inoculated with Ct (4 dpi), Ct biomass in phr1 phl1 mutant plants was significantly higher than in Col-0 wild-type plants grown under low Pi conditions (Col-0 versus phr1 phl1, two-tailed t test, p < 0.05). To measure fungal biomass by qPCR, 500 ng RNA from infected plants was used to amplify the Ct actin fragment (CtACT) and RNA amounts were normalized to plant actin (AT3G18780).
(F) At 4 dpi, Ct biomass in mutant phf1 plants was significantly higher than in Col-0 plants grown under low Pi conditions (Col-0 versus phf1, two-tailed t test, p < 0.05).
(G) Histogram showing the diameter of Ct and Ci colonies at 2 and 6 days after mycelial plugs of these fungi were transferred to MS medium containing 50 μM (low) or 625 μM (high) KH2PO4. Colony sizes of Ct or Ci were not significantly different between high (+) and low Pi (-) conditions. Bars = SE.
(H) Schematic representation of the targeted replacement of secreted acid phosphatase gene CT04_08450 by homologous recombination. Flanking sequences upstream and downstream of the acid phosphatase gene were cloned into the T-DNA of binary vector pBIG4MRHrev adjoining the hygromycin (HYG) resistance cassette. The upstream and downstream flanking sequences of the incoming T-DNA undergo double cross-over homologous recombination with the target sequences, resulting in hygromycin-resistant mutants lacking the target gene.
(I) Confirmation of the gene replacement event in fungal transformants Ct_KO1 and Ct_KO2 by PCR analysis using primer pairs 1 and 2.
(J) Fungal growth in agar medium in which hydroxyapatite was the only P source. Both WT and the knockout strain Ct_KO1 were incubated for 3 days. Growth of the mutant was not significantly different to that of wild-type C. tofieldiae.
Figure 4.
C. tofieldiae Colonization Induces Expression of A. thaliana Pht1 Pi Transporter Genes
(A) Transcript profiling of 19 A. thaliana phosphate transporter genes and PHF1 in colonized and mock-treated roots under Pi-limiting (low P: [50 μM]) or Pi-sufficient (high P: [625 μM]) conditions at 6, 10, 16, and 24 dpi. Overrepresented (yellow to red) and underrepresented transcripts (yellow to blue) are shown as log2 fold changes relative to the mean expression measured across all stages. Log2-transformed expression levels (white to red) are also depicted for each sample. Significantly regulated genes (|log2FC| >1, FDR <0.05) are highlighted in purple (upregulated) to green (downregulated). Note that two Pht transporter genes were strongly induced at late stages of C. tofieldiae (Ct) colonization (asterisks).
(B) Quantitative analysis of shoot fresh weight (SFW) of PSR regulatory mutants under Pi-deficient conditions. SFW was measured at 30 dpi from at least 15 plants per treatment, per experiment. Results of three independent experiments were combined. An ANOVA and subsequent Tukey HSD test were conducted to evaluate whether the fold-change in SFW between Ct- and mock-inoculated (M) plants (calculated as SFW Ct/SFW Mock) was significantly different (∗p < 0.01) between genotypes (Col-0: 1.45-fold versus phf1: 1.23-fold).
(C) Transcript profiling of 61 Ct genes significantly regulated between Ct- and mock-inoculated roots under Pi-deficient (low Pi: [50 μM]) or Pi-sufficient (high Pi: [625 μM]) conditions at 6, 10, 16, and 24 dpi. Overrepresented (yellow to red) and underrepresented transcripts (yellow to blue) are shown as log2 fold changes relative to the mean expression measured across all stages. Significantly regulated genes (|log2FC| >1, FDR <0.05) are highlighted in purple (upregulated) to green (downregulated). Arrows indicate the two most highly upregulated genes: phosphate H+symporter (CT04_05366, gray) and acid phosphatase (CT04_08450, black). The right part of the heatmap depicts the functional categories to which genes belong. CSEPs, candidate secreted effector proteins; CAZymes, carbohydrate active enzymes.
See also Figure S4.
Ct-Mediated PGP under Pi Starvation Requires an Intact A. thaliana PSR
We tested plants lacking regulatory components of the A. thaliana PSR, encoding functionally overlapping transcription factors PHR1 and PHL1, or the phosphate transporter traffic facilitator PHF1 (Rubio et al., 2001, González et al., 2005, Bustos et al., 2010). Due to the inherent plant-to-plant variation in 33P translocation to the host (see above), we collected data for each host genotype from three independent experiments, each including at least 15 Ct-infected plants grown on at least three agar plates, for statistical analysis. Ct-mediated PGP under Pi-starvation was significantly impaired (p < 0.01) in phf1 mutants (Col-0: 1.45-fold versus phf1: 1.23-fold) (Figure 4B). The PHF1 membrane protein exerts a specific role in subcellular targeting of phosphate transporters from the Golgi to the plasma membrane and phf1 mutants display plant growth and Pi accumulation defects under Pi-limiting but not Pi-sufficient conditions (González et al., 2005). Similarly, phr1 phl1 double mutants lacking the transcriptional regulators of the PSR exhibited significantly reduced (p < 0.01) Ct-mediated PGP (Col-0: 1.45-fold versus phr1 phl1: 1.17-fold); Figure 4B) (Bustos et al., 2010). Ct-mediated and phosphate starvation-dependent activation of both Pht1;2 and Pht1;3 was abrogated in phr1 phl1 plants (Figures 4B, S4B, and S4C). Moreover, Ct-mediated translocation of high-levels of 33P to the shoot (>40 kBq/g DW) under Pi-limiting conditions is compromised in the phr1 phl1 double mutant (Figure S4D). Together, this indicates a functional engagement of the PSR in (1) Ct-dependent activation of phosphate transporter genes, (2) 33Pi translocation to the shoot, and (3) PGP. However, translocation of high-levels of 33P (>40 kBq/g DW) under Pi-limiting conditions was retained in phf1 plants (Figure S4D), indicating Ct-mediated 33P translocation is uncoupled from PGP in this PSR mutant. We speculate that in phf1 plants Ct-mediated bulk Pi translocation to the shoot is retained whereas fine allocation between tissues needed for PGP might be impaired. Strikingly, Ct biomass was increased in phf1 single and phr1 phl1 double mutants compared to wild-type at 4 dpi (Figures S4E and S4F), revealing that PSR regulatory components limit fungal colonization.
In contrast to the dramatic transcriptional reprograming observed in A. thaliana roots in response to phosphate starvation (>2,000 genes regulated across all conditions, log2FC >1, FDR <0.05), the fungal transcriptome remained very stable with only 61 genes significantly regulated (log2FC >1, FDR < 0.05, Figure 4C). This result suggests that the Pi concentration used in our study (50 μM) does not provoke a major PSR in Ct. Consistent with this, Ct grew similarly in media containing either 50 μM or 625 μM Pi, as measured by mycelial radial growth (Figure S4G). Nevertheless, the two genes (out of 61) showing strongest induction at 24 dpi encode an acid phosphatase and a phosphate symporter (Figure 4C), suggesting that under low Pi conditions these are important for fungal solubilization and uptake of Pi, respectively. The capacity for growth in hydroxyapatite media was retained in mutant Ct strains in which this acid phosphatase gene (CT04_08450) was inactivated by targeted gene disruption, indicating that additional fungal genes are engaged in mobilization of this insoluble Pi source (Figures S4H, S4I, and S4J).
Trp-Derived Metabolites Are Required for Restricting Ct Colonization
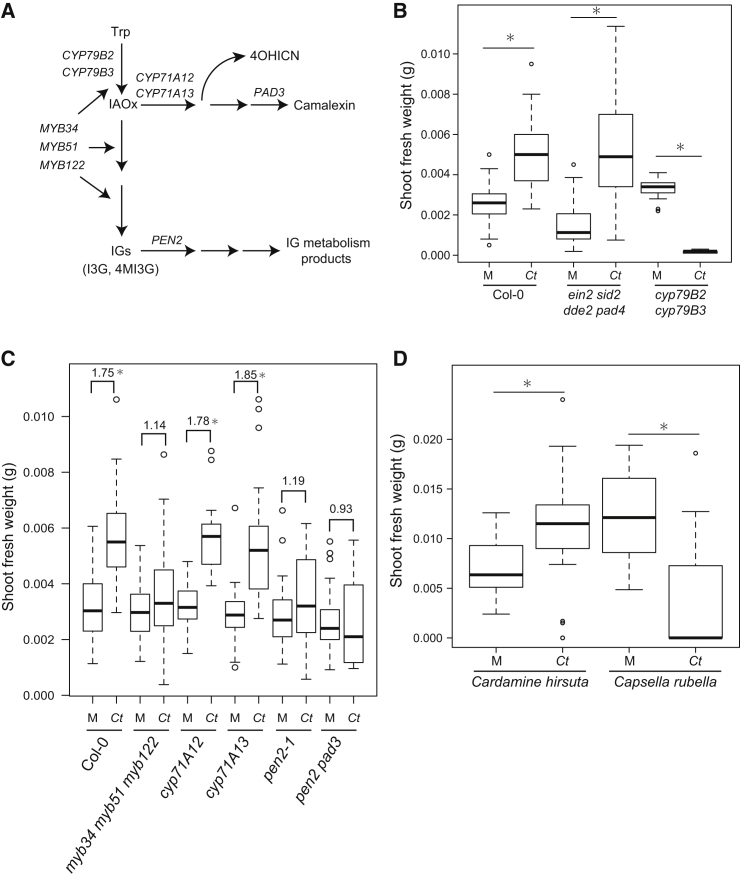
We tested whether the colonization of A. thaliana roots by Ct is restricted by innate immunity components (Figure 5A). We inoculated Ct onto roots of immunocompromised plants and then measured fungal biomass by qRT-PCR at 4 dpi. Neither fungal colonization nor Ct-mediated PGP were significantly different between Col-0 wild-type and the ein2 pad4 sid2 dde2 quadruple mutant even at late time points of infection (24 dpi; Figures 5B, S5A, and S5B), although this mutant is simultaneously defective in all three major phytohormone-dependent defense signaling pathways involving ethylene, salicylic acid, and jasmonic acid (Tsuda et al., 2009). Thus, either the combined action of these defense pathways does not restrict Ct colonization or their activity in roots is fundamentally different from leaves. Due to the apparent metabolic link between the PSR system and glucosinolate biosynthesis and the known role of secondary metabolite biosynthesis pathways derived from Trp for innate immune responses (Bednarek et al., 2009, Clay et al., 2009, Pant et al., 2015, Rajniak et al., 2015), we also tested cyp79B2 cyp79B3 double mutant plants, which are depleted of all Trp-derived secondary metabolites, including the antimicrobials camalexin and indole glucosinolates (Figure 5A). Ct fungal biomass was significantly increased in this double mutant (Figure S5A). Furthermore, Ct had a severe negative effect on the growth of this mutant and eventually killed the plants under both high and low Pi conditions, indicating that in the absence of these two cytochrome P450 enzymes Ct becomes a pathogenic fungus (Figures 5B and S5C).
Figure 5.
Trp-Derived Secondary Metabolites Are Required for Beneficial Ct Interactions
(A) Scheme of Trp-derived metabolite pathways in A. thaliana.
(B) Shoot fresh weight (SFW) of cyp79B2 cyp79B3 and ein2 pad4 sid2 dde2 mutant plants grown with and without Ct in low Pi conditions. SFW was measured 24 days after inoculation of sterilized seeds with C. tofieldiae (Ct). The boxplot shows combined data from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significantly different means between mock and Ct-treated plants for each genotype (t test, p < 0.01).
(C) SFW of A. thaliana mutants defective in the biosynthesis of camalexin and/or indole glucosinolates at 24 dpi in low Pi conditions.
(D) SFW of Cardamine hirusuta and Capsella rubella plants grown with and without Ct in low Pi conditions (24 dpi). Asterisks indicate significantly different means between mock (M) and Ct-treated plants for each species (t test, p < 0.01).
See also Figure S5.
Figure S5.
Tryptophan-Derived Metabolites Restrict Root Colonization by C. tofieldiae, Related to Figure 5
To measure fungal biomass by qPCR, 500 ng RNA from infected plants was used to amplify the C. tofieldiae (Ct) actin fragment (CtACT) and RNA amounts were normalized to plant actin (AT3G18780).
(A) Under high Pi conditions at 4 dpi, Ct biomass was significantly higher in cyp79B2 cyp79B3 double mutants compared with Col-0 wild-type plants and the other tested plant defense mutants (Col-0 versus cyp79B2 cyp79B3, two-tailed t test, p < 0.05).
(B) Quantification of Ct biomass in roots of Col-0 and ein2 pad4 sid2 dde2 quadruple mutant plants grown under high and low Pi conditions at 24 dpi. Under both conditions, fungal biomass in ein2 pad4 sid2 dde2 plants was not significantly higher than in Col-0 wild-type plants.
(C) Inoculation of Ct onto the roots of cyp79B2 cyp79B3 mutant plants severely inhibited plant growth under high Pi conditions. The photograph was taken at 10 dpi.
To investigate which host metabolites are required for maintaining beneficial interactions with Ct, we tested A. thaliana mutant lines impaired in the production of particular classes of Trp-derived compounds (Figure 5A). We found that Ct-mediated PGP was significantly reduced in pen2 mutants, which cannot activate 4-methoxyindol-3-ylmethylglucosinolate (4MI3G) for antifungal defense by means of the PEN2 myrosinase in leaves (Bednarek et al., 2009) (Figure 5A). However, PGP was not reduced in cyp71A12 or cyp71A13 plants, which lack sequence-related P450 monooxygenases required for camalexin biosynthesis in roots (Nafisi et al., 2007, Millet et al., 2010, Müller et al., 2015). As CYP71A12 was recently shown to have an additional function in the biosynthesis of the antimicrobial 4-hydroxyindole-3-carbonyl nitrile (4OHICN; Figure 5A) (Rajniak et al., 2015), both camalexin and the short-lived nitrile are dispensable for the initiation and maintenance of the beneficial interaction. Ct-mediated PGP was similarly impaired in both pen2 single and pen2 pad3 double mutants (Figure 5C), excluding the possibility that simultaneous depletion of camalexin and PEN2-initiated indole glucosinolate metabolism in the latter genotype accounts for the detrimental plant growth phenotype seen in the cyp79B2 cyp79B3 double mutant. The transcription factors MYB34, MYB51, and MYB122 act together to control biosynthesis of indol-3-ylmethylglucosinolate (the direct precursor of the PEN2 substrate 4MI3G) in shoots and roots and myb34 myb51 myb122 triple mutant plants are highly depleted of indole glucosinolates (Figure 5A) (Frerigmann and Gigolashvili, 2014). Under Pi-starvation, Ct-mediated PGP was significantly impaired in this triple mutant (Figure 5C), suggesting that transcriptional control of indole glucosinolate biosynthesis genes is needed to maintain a beneficial interaction with the host. Interestingly however, despite the impairment of Ct-mediated PGP in pen2 plants, fungal biomass in roots of this genotype was not significantly different to wild-type plants (Figures 5C and S5A). This indicates either that the assay for fungal biomass quantification fails to detect slightly elevated fungal growth or implies a previously unsuspected positive role of indole glucosinolates in plant growth. Irrespective of this, the impairment of Ct-mediated PGP is a shared phenotype of pen2, pen2 pad3, and myb34 myb51 myb122 triple mutant plants and contrasts with the strongly detrimental plant growth phenotype of cyp79B2/B3 double mutants as well as enhanced fungal biomass only in the latter genotype (Figures 5C and S5A). This is reminiscent of the enhanced colonization shown by the endophytes Piriformospora indica or Sebacina vermifera on roots of cyp79B2/B3 double and myb34/51/122 triple mutants (Lahrmann et al., 2015, Nongbri et al., 2012). Taken together, these data strongly suggest that (1) more than one Trp-derived branch pathway is needed for establishing a beneficial interaction with Ct, and (2) simultaneous depletion of all Trp-derived metabolites not only abolishes the beneficial interaction, but also allows excessive Ct colonization that ultimately kills host roots.
Finally, we examined whether natural genetic variation in the spectrum of Trp-derived metabolites in A. thaliana relatives can affect the establishment of a beneficial interaction with Ct. For example, the A. thaliana relatives Cardamine hirsuta and Capsella rubella are unable to produce camalexin and indole glucosinolates, respectively (Bednarek et al., 2011). We found that Ct colonization promoted the growth of Cardamine hirsuta under low Pi conditions (Figure 5D), whereas it strongly inhibited the growth of Capsella rubella, similar to A. thaliana cyp79B2 cyp79B3 mutants under low Pi conditions (Figure 5B). Our findings from these close relatives of A. thaliana support our conclusions from A. thaliana mutants that the production of indole glucosinolates, but not camalexin, is critical for establishing a beneficial interaction with the fungus. Moreover, since the absence of indole glucosinolates seems to be rare within the Brassicaceae (Windsor et al., 2005, Bednarek et al., 2011) and A. thaliana and C. rubella are both found in central-southern Europe including Spain, the evolutionarily conserved capacity for indole glucosinolate metabolism within this plant family conceivably serves as a host range determinant for Ct.
Discussion
Here, we have shown that an endophyte previously identified in A. thaliana leaves, C. tofieldiae, is prevalent in four tested populations within an ∼300 km north–south transect in the Central Plateau of Spain, but not in three other populations in Germany and France, suggesting habitat-specific determinants constrain the geographical distribution of this fungus in A. thaliana. Ct strains have been isolated from many other plant species, including monocots, and from diverse habitats across Eurasia, suggesting a very broad host range and geographic distribution for this fungal species (Damm et al., 2009, Tao et al., 2013), but it remains to be determined whether the occurrence of Ct in these habitats and plants across Eurasia reflects stochastic associations or has physiological relevance. By analogy to Koch’s postulates for pathogenic microorganisms, we showed that Ct reproducibly colonizes germ-free A. thaliana plants under laboratory conditions via roots, but not leaves, without apparent disease symptoms. Although Ct was originally identified as an endophyte from surface-sterilized A. thaliana leaves (García et al., 2013), our data reveal this fungus to be a root endophyte, which can also infect shoots systemically via the root central cylinder.
Plant growth promotion (PGP) by Ct was shown to be tightly regulated by Pi availability, suggesting that beneficial activities of the fungus are conditional upon particular environmental conditions, e.g., the amount of bioavailable soil phosphate. This stands in striking contrast to the fungal root endophyte Piriformospora indica, which promotes plant growth under both low and high phosphate conditions (10 μM and 1 mM, respectively) (Yadav et al., 2010). In central Spain, the levels of soil phosphorus are generally lower compared to central North Europe (Tóth et al., 2013) and phosphate levels are very low (ranging from 0 to 16 mg/kg soil) within a 5 km radius of the Las Rozas sampling site, potentially providing a fitness advantage for local A. thaliana populations colonized by Ct. The ability of Ct to promote A. thaliana growth when inorganic hydroxyapatite (Ca10 (PO4)6 (OH)2) was the sole phosphorus source (Figure S3C) suggests that a part of the beneficial activity of Ct involves solubilization of Pi from plant-inaccessible hydroxyapatite. Plant growth promotion by Ct was also observed with limiting amounts of bioavailable Pi in agar plates (50 μM; Figure 3), likely reflecting an expanded capacity of host roots to access Pi by means of long-distance transport via extraradical hyphal networks. Thus, the combined effects of extended soil exploration by infected roots and solubilization of plant-inaccessible Pi by Ct might contribute to the beneficial activity of the fungus in natural soils containing low levels of bioavailable phosphorus.
Our radioactive 33P tracer experiments provide direct evidence for translocation of Pi from Ct, via roots, to A. thaliana shoots. This beneficial function is reminiscent of associations between plants and mycorrhizal fungi, which interact with roots and translocate Pi from soil via fungal hyphae to the plant shoot to promote plant growth (Bonfante and Genre, 2010). Pi translocation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is known to take place under Pi-limiting conditions at the fungus-plant interface inside root cells. Mycorrhiza-specific phosphate transporter genes and their regulation are conserved across phylogenetically distant plant species (Bonfante and Genre, 2010). In Medicago truncatula, the mycorrhiza-induced Pi:H+ symporter MtPT4 is essential for efficient Pi uptake from the fungus and symbiosis establishment (Javot et al., 2007). Among 19 A. thaliana Pi:H+ symporter genes we identified, two belonging to the PHT1 subfamily, Pht1;2 and Pht1;3, that are more strongly activated in roots in the presence of Ct under Pi-starvation conditions. Our findings provide indirect genetic evidence for a functional engagement of Pi starvation-inducible high-affinity Pi:H+ symporter genes in A. thaliana during Ct colonization because phr1 phl1 mutant plants, in which transcriptional activation of the AtPHT1 family is blocked (Bustos et al., 2010), are impaired in Ct-mediated PGP and translocation of high-levels of 33P to the shoot. Functional homologs of AtPHR1 and AtPHF1 have been described in rice, designated OsPHR2 and OsPHF1 (Zhou et al., 2008, Chen et al., 2011). Thus, it is conceivable that the evolutionarily conserved machinery for phosphate starvation-induced Pi uptake (Chiou and Lin, 2011) has been independently recruited for beneficial interactions with Ct in A. thaliana and mycorrhizal fungi in other flowering plants and that in the Brassicaceae lineage Ct compensates the loss of mycorrhizal symbiosis in low phosphate soils.
Both Ct-mediated PGP and 33P translocation to the shoot are tightly regulated by Pi availability. Analysis of regulatory mutants of the A. thaliana PSR revealed an unexpected link between phosphate starvation and Ct root colonization: roots of phf1 single and phr1 phl1 double mutants supported higher levels of colonization, indicating that an intact PSR system limits Ct root colonization. Elsewhere, we show that transcriptional outputs of Ct-colonized roots depend on their nutritional status, with mutualistic responses favored during phosphate starvation and defense responses under phosphate-sufficient conditions (Hacquard et al., 2016). Metabolic profiling of A. thaliana wild-type and phr1 mutants has revealed a metabolic link between the PSR system and indole glucosinolate metabolism (Pant et al., 2015). Our systematic genetic depletion of the corresponding immune response pathways encoding these Trp-derived secondary metabolites revealed that more than one branch pathway is needed for the establishment of a beneficial interaction with Ct. Taken together, our data provide genetic evidence for a specific coordination between the PSR, the plant immune system and invasive fungal growth during beneficial interactions with Ct. Thus, the innate immune system has wider physiological roles than restricting only pathogen growth.
Endophytic fungi comprise a major fraction of the root microbiota of wild and cultivated plants as well as forest ecosystems, where they outnumber mycorrhizal taxa (Hacquard and Schadt, 2015). Despite their diversity and potential contributions to plant growth and productivity, the physiological significance of these fungal endophytes is largely unknown. The C. tofieldiae-A. thaliana interaction offers a model for dissecting these poorly understood associations where the fungal partner is amenable to molecular genetic manipulation, including targeted gene disruption, and abundant genetic tools and resources are available for the plant host.
Experimental Procedures
A detailed description of protocols can be found in the Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Detection of C. tofieldiae from Natural A. thaliana Populations
Healthy A. thaliana leaves and roots were collected from natural populations at four sites in Spain as described previously (García et al., 2013). DNA extracted from the samples was used for qPCR amplification of the Ct tubulin 2 sequence.
Cytological Observations
Roots or leaves of 2-week-old A. thaliana plants expressing PIP2A-mCherry were inoculated with Ct-GFP spores (2–5 × 105/ml) and imaged by confocal microscopy after 1 to 14 days.
Plant Growth Promotion Assay
A. thaliana plants were grown in MS agarose medium containing defined Pi concentrations or a low-nutrient vermiculite matrix, with or without Ct. Plant growth promotion (PGP) was evaluated by measuring shoot fresh weight, root length, or number of siliques from ∼15 plants per experiment.
33P Translocation Experiments
A small Petri plate (hyphal compartment [HC]) was inserted into a larger square plate (root/hyphal compartment [RHC]), and both plates were filled with MS-medium (Figure 3D). Fungal mycelium was added to the HC and the system was incubated for 7 days. Two 10-day-old A. thaliana Col-0 seedlings were then added to each RHC and cultivated vertically for a further 7 days. When mycelium reached the plant roots, carrier-free 33P-labeled H3PO4 (270 kBq) was added to the HC and plants were harvested 17 days later.
RNA-Seq
Sterilized A. thaliana Col-0 seeds were inoculated with Ct (5 × 104 spores/ml) and grown on half-strength MS agarose medium containing either 50 or 625 μM KH2PO4 as Pi source. RNA was collected from infected roots at 6, 10, 16, and 24 dpi and Ct hyphae grown in liquid Mathur’s medium for 2 days. Plant and fungal transcriptomes were then sequenced for differential gene expression analysis. For further details, see Hacquard et al. (2016) and the Supplemental Experimental Procedures. The RNA-seq data used in this study are available from the NCBI GEO database: GSE70094.
qRT-PCR
cDNA was synthesized from 500 ng total RNA. Five microliters of cDNA (10 ng/μL) was amplified using the Thermal Cycle Dice Real Time System (TaKaRa). Primers used in this study are listed in Table S1.
Author Contributions
P.S.-L., R.J.O., S.S., and K.H. initiated the project. P.S.-L., R.J.O., and K.H. initiated, conceived, and coordinated all experiments except those described in Figures 1 and S1A. K.H. performed inoculation experiments, quantified fungal colonization and plant biomass on all host genotypes, isolated DNA/RNA, generated transgenic Ct strains, and analyzed the data. R.T.N. and U.N. performed confocal, epifluorescence, and electron microscopy. S.H., B.K., and K.H. analyzed RNA-seq data. N.G. designed and conducted 33P translocation experiments, supervised by M.B. S.S., together with D.R. and S.H., quantified Ct associations with A. thaliana populations. K.H., N.G., S.H., R.T.N., S.S., and U.N. prepared tables and figures. P.S.-L., R.J.O., and K.H. wrote and edited the paper.
Acknowledgments
K.H. was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) grant 15K18645. This work was supported by funding from the Max Planck Society (P.S.-L. and R.J.O.), European Research Council advanced grant ROOTMICROBIOTA (P.S.-L.), the ‘‘Cluster of Excellence on Plant Sciences’’ program of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (P.S.-L.), Agence Nationale de la Recherche Chaire d’Excellence grant ANR-12-CHEX-0008-01 (R.J.O.), Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad grant BIO2012-32910 (S.S.), and COST action FA1103 Endophytes in Biotechnology and Agriculture (S.S.). We thank Kathrin Schlücking and Stefanie Junkermann for technical support; Kenichi Tsuda, Tamara Gigolashvili, and Javier Paz-Ares for providing Arabidopsis mutants; and Pawel Bednarek, Nina Dombrowski, and Yusuke Saijo for helpful discussions.
Published: March 17, 2016
Footnotes
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Supplemental Information includes Supplemental Experimental Procedures, five figures, and one table and can be found with this article online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.028.
Contributor Information
Richard J. O’Connell, Email: richard.oconnell@versailles.inra.fr.
Paul Schulze-Lefert, Email: schlef@mpipz.mpg.de.
Accession Numbers
The accession number for the RNA-seq data reported in this paper is GEO: GSE70094.
Supplemental Information
References
- Bednarek P., Pislewska-Bednarek M., Svatos A., Schneider B., Doubsky J., Mansurova M., Humphry M., Consonni C., Panstruga R., Sanchez-Vallet A. A glucosinolate metabolism pathway in living plant cells mediates broad-spectrum antifungal defense. Science. 2009;323:101–106. doi: 10.1126/science.1163732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarek P., Piślewska-Bednarek M., Ver Loren van Themaat E., Maddula R.K., Svatoš A., Schulze-Lefert P. Conservation and clade-specific diversification of pathogen-inducible tryptophan and indole glucosinolate metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. New Phytol. 2011;192:713–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeman J.P., Hornby D. The persistence of Colletotrichum coccodes and Mycosphaerella ligulicola in soil with special reference to sclerotia and conidia. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1966;49:227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfante P., Genre A. Mechanisms underlying beneficial plant-fungus interactions in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nat. Commun. 2010;1:48. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher M. Functional biology of plant phosphate uptake at root and mycorrhiza interfaces. New Phytol. 2007;173:11–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarelli D., Schlaeppi K., Spaepen S., Ver Loren van Themaat E., Schulze-Lefert P. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013;64:807–838. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustos R., Castrillo G., Linhares F., Puga M.I., Rubio V., Pérez-Pérez J., Solano R., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. A central regulatory system largely controls transcriptional activation and repression responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Liu Y., Ni J., Wang Y., Bai Y., Shi J., Gan J., Wu Z., Wu P. OsPHF1 regulates the plasma membrane localization of low- and high-affinity inorganic phosphate transporters and determines inorganic phosphate uptake and translocation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011;157:269–278. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.181669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou T.J., Lin S.I. Signaling network in sensing phosphate availability in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011;62:185–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay N.K., Adio A.M., Denoux C., Jander G., Ausubel F.M. Glucosinolate metabolites required for an Arabidopsis innate immune response. Science. 2009;323:95–101. doi: 10.1126/science.1164627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman-Derr D., Desgarennes D., Fonseca-Garcia C., Gross S., Clingenpeel S., Woyke T., North G., Visel A., Partida-Martinez L.P., Tringe S.G. Plant compartment and biogeography affect microbiome composition in cultivated and native Agave species. New Phytol. 2016;209:798–811. doi: 10.1111/nph.13697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm U., Woudenberg J.H.C., Cannon P.F., Crous P.W. Colletotrichum species with curved conidia from herbaceous hosts. Fungal Divers. 2009;39:45–87. [Google Scholar]
- Deising H.B., Werner S., Wernitz M. The role of fungal appressoria in plant infection. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:1631–1641. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)01319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R.A. Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature. 2001;411:843–847. doi: 10.1038/35081178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerigmann H., Gigolashvili T. MYB34, MYB51, and MYB122 distinctly regulate indolic glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant. 2014;7:814–828. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García E., Alonso A., Platas G., Sacristan S. The endophytic mycobiota of Arabidopsis thaliana. Fungal Divers. 2013;60:71–89. [Google Scholar]
- González E., Solano R., Rubio V., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. Phosphate transporter traffic facilitator1 is a plant-specific SEC12-related protein that enables the endoplasmic reticulum exit of a high-affinity phosphate transporter in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2005;17:3500–3512. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.036640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B.D., Giehl R.F., Friedel S., von Wirén N. Plasticity of the Arabidopsis root system under nutrient deficiencies. Plant Physiol. 2013;163:161–179. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.218453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacquard S., Schadt C.W. Towards a holistic understanding of the beneficial interactions across the Populus microbiome. New Phytol. 2015;205:1424–1430. doi: 10.1111/nph.13133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacquard S., Kracher B., Hiruma K., Münch P.C., Garrido-Oter R., Weimann A., Thon M.R., Damm U., Dallery J.F., Hainaut M. Survival trade-offs in plant roots during colonization by closely related beneficial and pathogenic fungi. Nat. Commun. 2016 doi: 10.1038/ncomms11362. Published online April 15, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkier B.A., Gershenzon J. Biology and biochemistry of glucosinolates. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006;57:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javot H., Penmetsa R.V., Terzaghi N., Cook D.R., Harrison M.J. A Medicago truncatula phosphate transporter indispensable for the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:1720–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608136104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovinich N., Kayanja G., Chanoca A., Riedl K., Otegui M.S., Grotewold E. Not all anthocyanins are born equal: distinct patterns induced by stress in Arabidopsis. Planta. 2014;240:931–940. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2079-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahrmann U., Strehmel N., Langen G., Frerigmann H., Leson L., Ding Y., Scheel D., Herklotz S., Hilbert M., Zuccaro A. Mutualistic root endophytism is not associated with the reduction of saprotrophic traits and requires a noncompromised plant innate immunity. New Phytol. 2015;207:841–857. doi: 10.1111/nph.13411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Arredondo D.L., Leyva-González M.A., González-Morales S.I., López-Bucio J., Herrera-Estrella L. Phosphate nutrition: improving low-phosphate tolerance in crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014;65:95–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-035949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg D.S., Lebeis S.L., Paredes S.H., Yourstone S., Gehring J., Malfatti S., Tremblay J., Engelbrektson A., Kunin V., del Rio T.G. Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature. 2012;488:86–90. doi: 10.1038/nature11237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millet Y.A., Danna C.H., Clay N.K., Songnuan W., Simon M.D., Werck-Reichhart D., Ausubel F.M. Innate immune responses activated in Arabidopsis roots by microbe-associated molecular patterns. Plant Cell. 2010;22:973–990. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.069658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T.M., Böttcher C., Morbitzer R., Götz C.C., Lehmann J., Lahaye T., Glawischnig E. Transcription activator-like effector nuclease-mediated generation and metabolic analysis of camalexin-deficient cyp71a12 cyp71a13 double knockout lines. Plant Physiol. 2015;168:849–858. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nafisi M., Goregaoker S., Botanga C.J., Glawischnig E., Olsen C.E., Halkier B.A., Glazebrook J. Arabidopsis cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 71A13 catalyzes the conversion of indole-3-acetaldoxime in camalexin synthesis. Plant Cell. 2007;19:2039–2052. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.051383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B.K., Cai X., Nebenführ A. A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J. 2007;51:1126–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nongbri P.L., Johnson J.M., Sherameti I., Glawischnig E., Halkier B.A., Oelmuller R. Indole-3-acetaldoxime-derived compounds restrict root colonization in the beneficial interaction between Arabidopsis roots and the endophyte Piriformospora indica. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012;25:1186–1197. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-12-0071-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pant B.D., Pant P., Erban A., Huhman D., Kopka J., Scheible W.R. Identification of primary and secondary metabolites with phosphorus status-dependent abundance in Arabidopsis, and of the transcription factor PHR1 as a major regulator of metabolic changes during phosphorus limitation. Plant Cell Environ. 2015;38:172–187. doi: 10.1111/pce.12378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Bucher M. Phosphate transport and homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis Book. 2002;1:e0024. doi: 10.1199/tab.0024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajniak J., Barco B., Clay N.K., Sattely E.S. A new cyanogenic metabolite in Arabidopsis required for inducible pathogen defence. Nature. 2015;525:376–379. doi: 10.1038/nature14907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R.J., White J.F., Jr., Arnold A.E., Redman R.S. Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol. 2009;182:314–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio V., Linhares F., Solano R., Martín A.C., Iglesias J., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2122–2133. doi: 10.1101/gad.204401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Muta T., Imamura Y., Nojima H., Moriwaki J., Yaguchi Y. Anthracnose of Japanese radish caused by Colletotrichum dematium. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2005;71:380–383. [Google Scholar]
- Sesma A., Osbourn A.E. The rice leaf blast pathogen undergoes developmental processes typical of root-infecting fungi. Nature. 2004;431:582–586. doi: 10.1038/nature02880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H., Shin H.S., Dewbre G.R., Harrison M.J. Phosphate transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1;1 and Pht1;4 play a major role in phosphate acquisition from both low- and high-phosphate environments. Plant J. 2004;39:629–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehmel N., Böttcher C., Schmidt S., Scheel D. Profiling of secondary metabolites in root exudates of Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry. 2014;108:35–46. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukno S.A., García V.M., Shaw B.D., Thon M.R. Root infection and systemic colonization of maize by Colletotrichum graminicola. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008;74:823–832. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01165-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao G., Liu Z., Liu F., Gao Y. Endophytic Colletotrichum species from Bletilla ochracea (Orchidaceae), with descriptions of seven new species. Fungal Divers. 2013;61:139–164. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth G., Jones A., Montanarella L., editors. LUCAS topsoil survey. Methodology, data and results. JRC Technical Reports. Publications Office of the European Union; Luxembourg: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda K., Sato M., Stoddard T., Glazebrook J., Katagiri F. Network properties of robust immunity in plants. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor A.J., Reichelt M., Figuth A., Svatos A., Kroymann J., Kliebenstein D.J., Gershenzon J., Mitchell-Olds T. Geographic and evolutionary diversification of glucosinolates among near relatives of Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae) Phytochemistry. 2005;66:1321–1333. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav V., Kumar M., Deep D.K., Kumar H., Sharma R., Tripathi T., Tuteja N., Saxena A.K., Johri A.K. A phosphate transporter from the root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica plays a role in phosphate transport to the host plant. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:26532–26544. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.111021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Zhou J., Jiao F., Wu Z., Li Y., Wang X., He X., Zhong W., Wu P. OsPHR2 is involved in phosphate-starvation signaling and excessive phosphate accumulation in shoots of plants. Plant Physiol. 2008;146:1673–1686. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.111443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.