Abstract
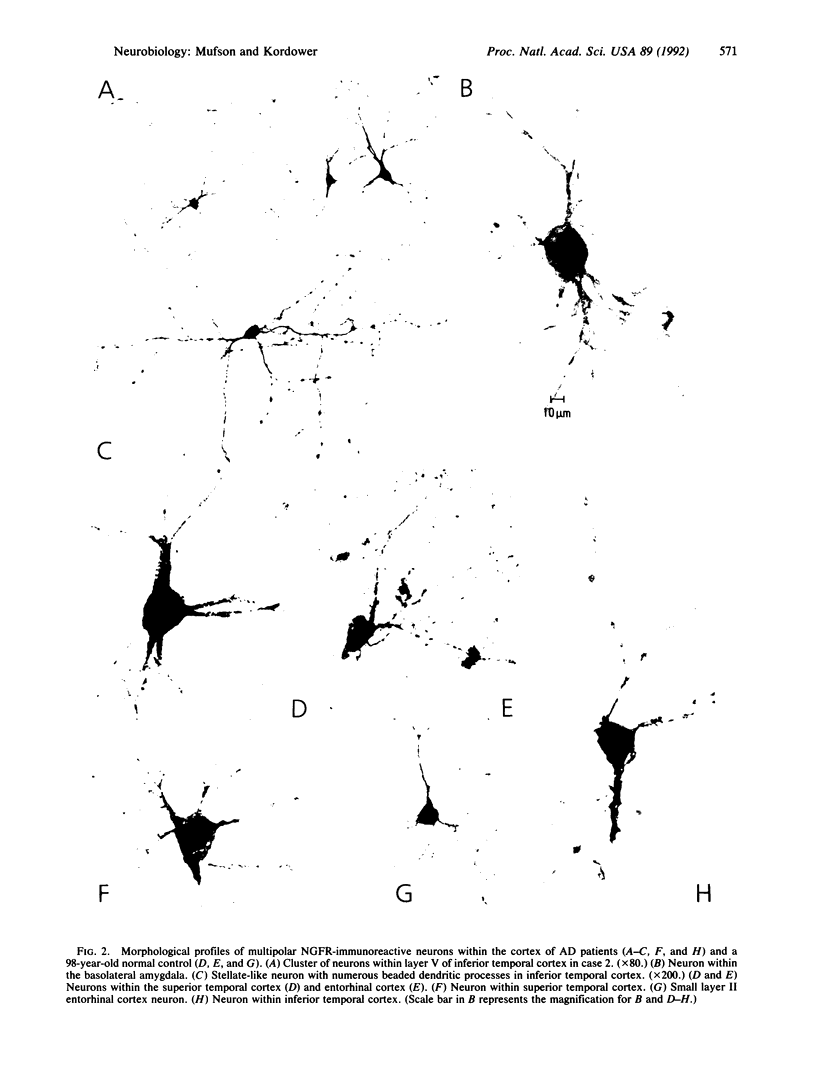
Using a monoclonal antibody directed against the primate nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor, we examined the expression of NGF receptors within neuronal perikarya of normal adult human cerebral cortex (27-98 years old) and individuals with Alzheimer disease (AD). This expression of cortical NGF receptors was compared with that seen in other neurological diseases and normal human development as well as in young and aged nonhuman primates. NGF receptor-containing cortical neurons were not observed in young adults (less than 50 years old) and were observed only infrequently in non-demented elderly individuals (50-80 years old). In contrast, numerous NGF receptor-containing cortical neurons were seen in AD patients of all ages and in one 98-year-old nondemented patient. In advanced age and AD, numerous NGF receptor-positive neurons were located within laminae II-VI of temporal association cortices whereas only a few were seen in the subicular complex, entorhinal cortex, parahippocampal gyrus, and amygdaloid complex. These perikarya appeared healthy, with bipolar, fusiform, or multipolar morphologies and extended varicose dendritic arbors. These neurons failed to express neurofibrillary tangle-bearing material. In contrast to AD, NGF receptor-containing cortical neurons were not observed in Parkinson disease, Pick disease, or Shy-Drager syndrome. The NGF receptor-containing cortical neurons seen in advanced age and AD were similar in morphology to those observed in human fetal cortex. No NGF receptor-containing cortical neurons were observed in young or aged nonhuman primates. These findings suggest that neurons within the human cerebral cortex exhibit plasticity in their expression of NGF receptors in AD and extreme advanced aging.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Ghoul W. M., Miller M. W. Transient expression of Alz-50 immunoreactivity in developing rat neocortex: a marker for naturally occurring neuronal death? Brain Res. 1989 Mar 6;481(2):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allendoerfer K. L., Shelton D. L., Shooter E. M., Shatz C. J. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity is transiently associated with the subplate neurons of the mammalian cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):187–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. M., Brady R., Hersh L. B., Hayes R. C., Wiley R. G. Expression of choline acetyltransferase and nerve growth factor receptor within hypoglossal motoneurons following nerve injury. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Feb 22;304(4):596–607. doi: 10.1002/cne.903040407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. P., Snyder S. H., Cuatrecasas P., Greene L. A. Binding of nerve growth factor receptor in sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell S. J., Coleman P. D. Dendritic growth in the aged human brain and failure of growth in senile dementia. Science. 1979 Nov 16;206(4420):854–856. doi: 10.1126/science.493989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Galanin hyperinnervates surviving neurons of the human basal nucleus of Meynert in dementias of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: a hypothesis for the role of galanin in accentuating cholinergic dysfunction in dementia. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 22;273(4):543–557. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emory C. R., Ala T. A., Frey W. H., 2nd Ganglioside monoclonal antibody (A2B5) labels Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Neurology. 1987 May;37(5):768–772. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.5.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Busciglio J., Cáceres A. An immunocytochemical analysis of the ontogeny of the microtubule-associated proteins MAP-2 and Tau in the nervous system of the rat. Brain Res. 1987 Jul;431(1):9–31. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Batchelor P., Chen K. S., Chin D., Higgins G. A., Koh S., Deputy S., Rosenberg M. B., Fischer W., Bjorklund A. NGF receptor reexpression and NGF-mediated cholinergic neuronal hypertrophy in the damaged adult neostriatum. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1177–1184. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. W., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Lott I. T., Kim R. C., Chui H. C. Plasticity of hippocampal circuitry in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.4071042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamre K. M., Hyman B. T., Goodlett C. R., West J. R., Van Hoesen G. W. Alz-50 immunoreactivity in the neonatal rat: changes in development and co-distribution with MAP-2 immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Apr 10;98(3):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Knusel B. Function of neurotrophic factors in the adult and aging brain and their possible use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):515–533. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F. Is Alzheimer disease caused by lack of nerve growth factor? Ann Neurol. 1983 Jan;13(1):109–110. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Mash D. C. Localization of nerve growth factor receptors in the normal human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(89)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Koh S., Chen K. S., Gage F. H. NGF induction of NGF receptor gene expression and cholinergic neuronal hypertrophy within the basal forebrain of the adult rat. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Mufson E. J. NGF receptor gene expression is decreased in the nucleus basalis in Alzheimer's disease. Exp Neurol. 1989 Dec;106(3):222–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn A., Leibrock J., Bailey K., Barde Y. A. Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):339–341. doi: 10.1038/344339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr Regulation of nerve growth factor receptor expression on Schwann cells. Prog Brain Res. 1988;78:327–331. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, Taniuchi M., Clark H. B., Springer J. E., Koh S., Tayrien M. W., Loy R. Demonstration of the retrograde transport of nerve growth factor receptor in the peripheral and central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):923–929. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00923.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Loy R. Localization and development of nerve growth factor-sensitive rat basal forebrain neurons and their afferent projections to hippocampus and neocortex. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):2999–0318. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-02999.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koliatsos V. E., Shelton D. L., Mobley W. C., Price D. L. A novel group of nerve growth factor receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the ventral horn of the lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91084-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Bartus R. T., Bothwell M., Schatteman G., Gash D. M. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in the nonhuman primate (Cebus apella): distribution, morphology, and colocalization with cholinergic enzymes. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Nov 22;277(4):465–486. doi: 10.1002/cne.902770402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Gash D. M., Bothwell M., Hersh L., Mufson E. J. Nerve growth factor receptor and choline acetyltransferase remain colocalized in the nucleus basalis (Ch4) of Alzheimer's patients. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(89)80013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Mufson E. J. Galanin-like immunoreactivity within the primate basal forebrain: differential staining patterns between humans and monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):281–292. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez H. J., Dreyfus C. F., Jonakait G. M., Black I. B. Nerve growth factor promotes cholinergic development in brain striatal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7777–7781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Rutkowski J. L., Tennekoon G. I., Buchanan K., Johnston M. V. Choline acetyltransferase activity in striatum of neonatal rats increased by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):284–287. doi: 10.1126/science.2861660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Rutkowski J. L., Tennekoon G. I., Gemski J., Buchanan K., Johnston M. V. Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase activity in developing basal forebrain neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Jul;387(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Bothwell M., Hersh L. B., Kordower J. H. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactive profiles in the normal, aged human basal forebrain: colocalization with cholinergic neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):196–217. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Bothwell M., Kordower J. H. Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain. Exp Neurol. 1989 Sep;105(3):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Higgins G. A., Kordower J. H. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in the new world monkey (Cebus apella) and human cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jun 22;308(4):555–575. doi: 10.1002/cne.903080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Presley L. N., Kordower J. H. Nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity within the nucleus basalis (Ch4) in Parkinson's disease: reduced cell numbers and co-localization with cholinergic neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 18;539(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90682-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Issa V. M., Riopelle R. J. Distribution of neuronal receptors for nerve growth factor in the rat. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2312–2321. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02312.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosene D. L., Roy N. J., Davis B. J. A cryoprotection method that facilitates cutting frozen sections of whole monkey brains for histological and histochemical processing without freezing artifact. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Oct;34(10):1301–1315. doi: 10.1177/34.10.3745909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strahler J. R., Rosenbloom B. B., Hanash S. M. A silent, neutral substitution detected by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: hemoglobin Beirut. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6879181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Clark H. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Induction of nerve growth factor receptor in Schwann cells after axotomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Schweitzer J. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor receptor molecules in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore S. R., Seiger A. The expression, localization and functional significance of beta-nerve growth factor in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1987 Nov;434(4):439–464. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(87)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Clark H. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor receptor in neural lobe of rat pituitary gland: immunohistochemical localization, biochemical characterization and regulation. J Neurocytol. 1990 Jun;19(3):302–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01188400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Johnson E. M., Jr An immunohistochemical study of the nerve growth factor receptor in developing rats. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3481–3498. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03481.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]