Abstract
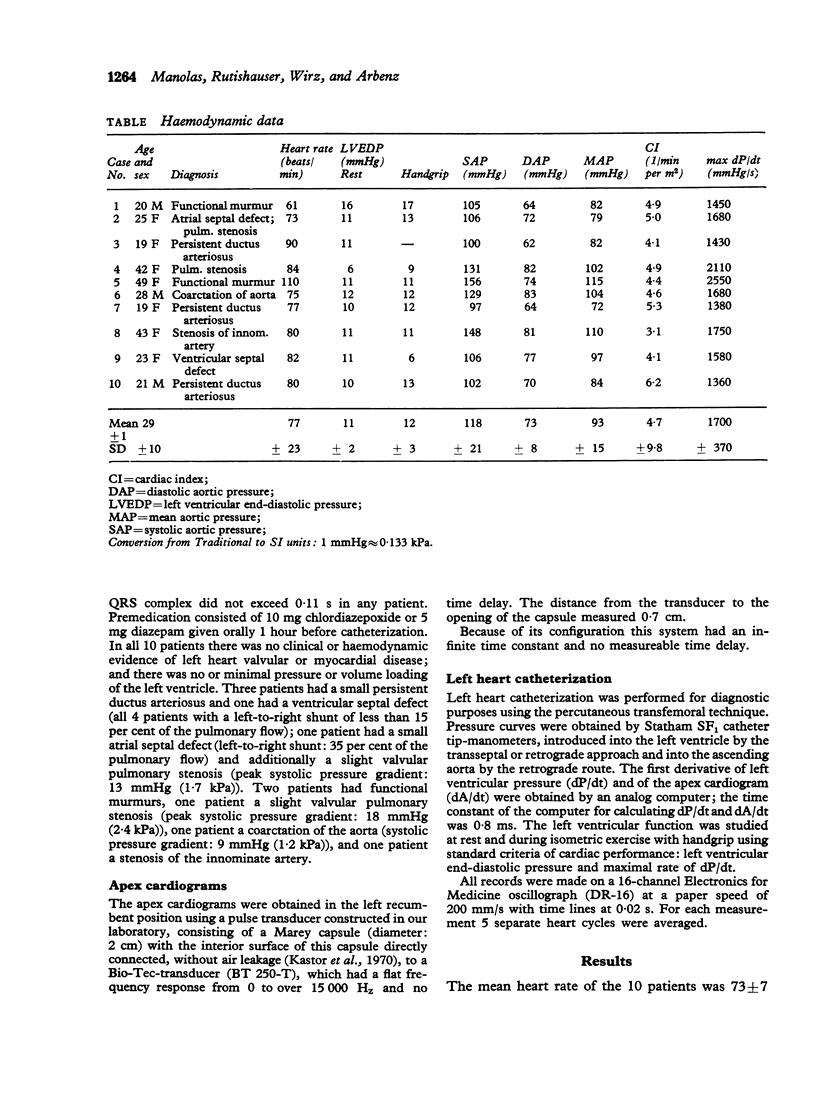
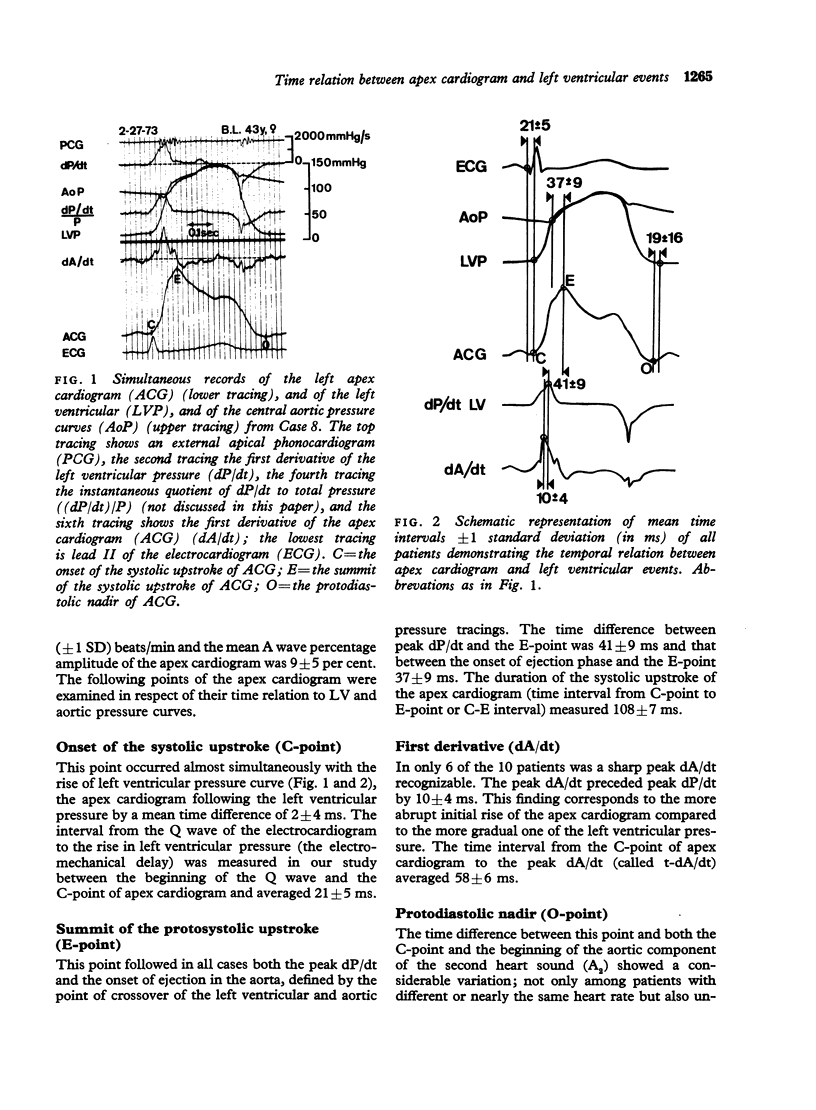
In 10 patients without left heart valvular disease and having normal function of the left ventricle, the left ventricular apex cardiogram with its first derivative (dA/dt), left ventricular pressure with its first derivative (dP/dt), aortic pressure, electrocardiogram, and phonocardiogram were reocrded simultaneously during cardiac catheterization. The apex cardiographic tracings were obtained by means of a transducer with infinite time constant and very high resonant frequency and the LV and aortic pressures with catheter tip-manometers. The onset of the systolic rise of apex cardiographic and LV pressures were found to occur almost simultaneously with the upstroke of LV pressure, preceding that of the apex cardiogram by only 2 +/- 4 ms (mean +/- 1 SD). The summit of the systolic upstroke of the apex cardiogram (called E-point) occurred 37 +/- 9 ms after opening of the aortic valve and 41 +/- 9 ms after peak dP/dt. The peak of dA/dt preceded peak dP/dt by 10 +/- 4 ms. The protodiastolic nadir of the apex cardiogram (called-O-point) occurred slightly earlier (19 +/- 16 ms) than the nadir of the LV pressure curve, with considerable variation. In conclusion, this study using external and internal transducers with similar characteristics gives a new definition of the time relation between the externally recorded apex cardiogram and the haemodynamic events within the left heart in human subjects with normal left ventricular function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurelio Perosio A. M., Cuesta Silva M. A., Jorge Ricci G. The first heart sound: its relation with the apex cardiogram. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Sep 7;32(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(73)80134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENCHIMOL A., DIMOND E. G. THE NORMAL AND ABNORMAL APEXCARDIOGRAM. ITS PHYSIOLOGIC VARIATION AND ITS RELATION TO INTRACARDIAC EVENTS. Am J Cardiol. 1963 Sep;12:368–381. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(63)90232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft W. H., Jr, Eddleman E. E., Jr Methods and physical characteristics of the kinetocardiographic and apexcardiographic systems for recording low-frequency precordial motion. Am Heart J. 1967 Jun;73(6):756–764. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(67)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian J., Epstein E. J., Coulshed N. Duration of phases of left ventricular systole using indirect methods. I. Normal subjects. Br Heart J. 1972 Sep;34(9):874–881. doi: 10.1136/hrt.34.9.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman J., Fouchard J., Delzant J. F., Varin G., Dupérier C. Apexocardiogramme et courbes de pression. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1967 Sep;60(9):1250–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadient A., Manolas J., Arbenz U., Mehmel H., Wirz P., Rutishauser W. Zeitwerte im Apexkardiogramm bei Koronarsklerose. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1973 Feb 24;103(8):315–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Young G. M., Grierson A. L., Smulyan H., Eich R. H. Isometric contraction period of the left ventricle in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1970 Jul;42(1):79–90. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.42.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastor J. A., Aronow S., Nagle R. E., Garber T., Walker H. Air leaks as a source of distortion in apexcardiography. Chest. 1970 Feb;57(2):163–171. doi: 10.1378/chest.57.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot H., Willems J., van Vollenhoven E. On the physical principles and methodology of mechanocardiography. Acta Cardiol. 1969;24(2):147–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolas J., Wirz P., Krayenbühl H. P., Rutishauser W. Kontraktilitätskriterien am simultan mit dem linksventrikulären Druck registrierten, frequenz- und amplitudengetreuen Apexkardiogramm. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1974 Nov 2;104(44):1590–1592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreshkov V. Indirect measurement of isovolumetric contraction time on the basis of polygraphic tracing. (Apexcardiogram, carotid tracing and phonocardiogram). Cardiologia. 1965;47(5):315–322. doi: 10.1159/000168399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEMME T. E. Pressure measurement: electrical pressure transducers. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1963 May;5:574–594. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(63)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E., Craige E., Hood W. P., Jr The Austin Flint murmur and the a wave of the apexcardiogram in aortic regurgitation. Circulation. 1971 Mar;43(3):349–359. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.43.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIOS J. C., MASSUMI R. A. CORRELATION BETWEEN THE APEX CARDIOGRAM AND LEFT VENTRICULAR PRESSURE. Am J Cardiol. 1965 May;15:647–655. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(65)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale A. Evaluation of the contractile state of the human heart from the first derivative of the apexcardiogram. Circulation. 1967 Dec;36(6):933–941. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.36.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer W. H., 3rd, Behar V. S., Orgain E. S. Apex cardiogram in patients with prolapsing mitral valve. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Sep 7;32(3):276–282. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(73)80133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spodick D. H., Kumar S. Isovolumetric contraction period of the left ventricle. Results in a normal series and comparison of methods of calculation by atraumatic techniques. Am Heart J. 1968 Oct;76(4):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(68)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAFUR E., COHEN L. S., LEVINE H. D. THE NORMAL APEX CARDIOGRAM: ITS TEMPORAL RELATIONSHIP TO ELECTRICAL, ACOUSTIC, AND MECHANICAL CARDIAC EVENTS. Circulation. 1964 Sep;30:381–391. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.30.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavel M. E., Campbell R. W., Feigenbaum H., Steinmetz E. F. The apex cardiogram and its relationship to haemodynamic events within the left heart. Br Heart J. 1965 Nov;27(6):829–839. doi: 10.1136/hrt.27.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt G. C., Friesinger G. C. The use of apexcardiography in the assessment of left ventricular diastolic pressure. Circulation. 1970 Jun;41(6):1015–1024. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.41.6.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems J. L., De Geest H., Kesteloot H. On the value of apex cardiography for timing intracardiac events. Am J Cardiol. 1971 Jul;28(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(71)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



