Abstract
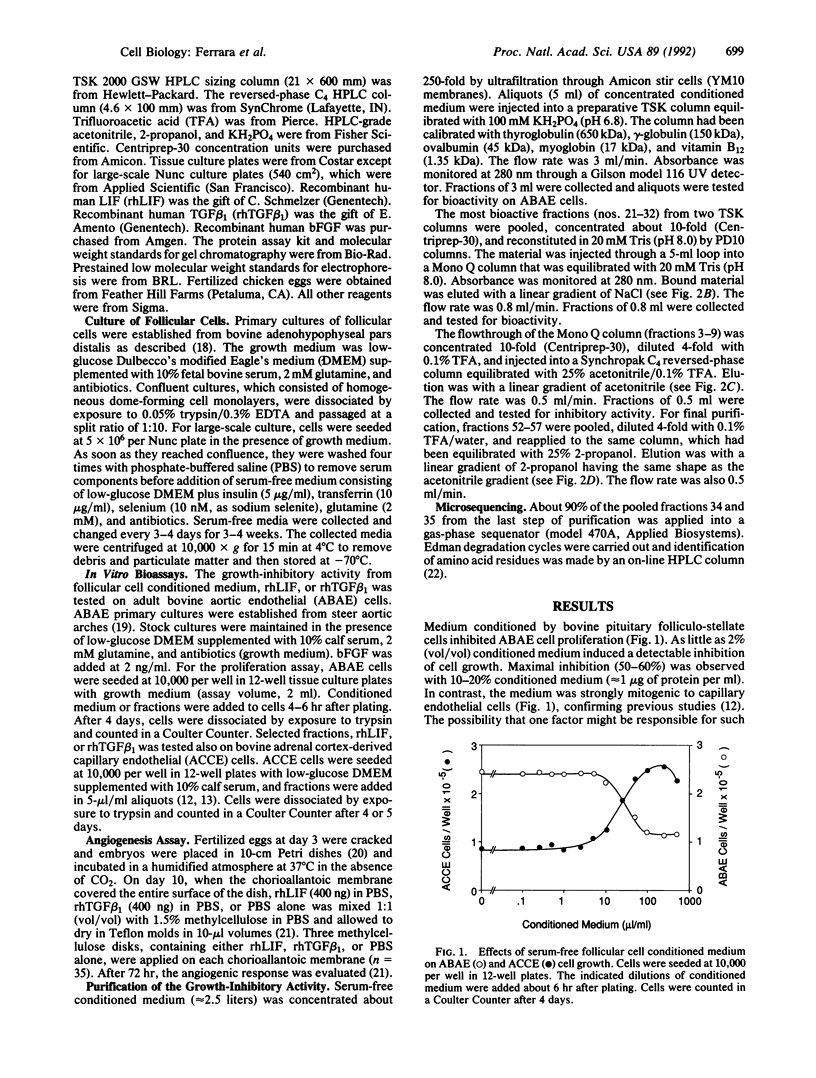
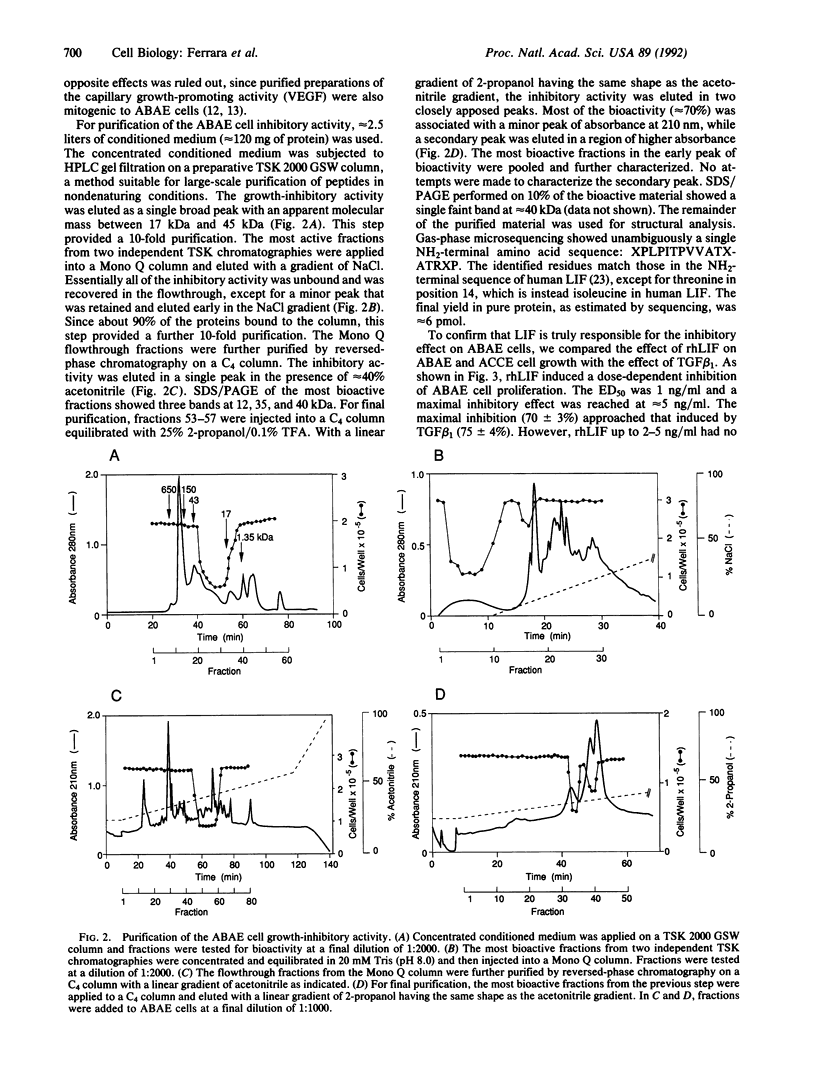
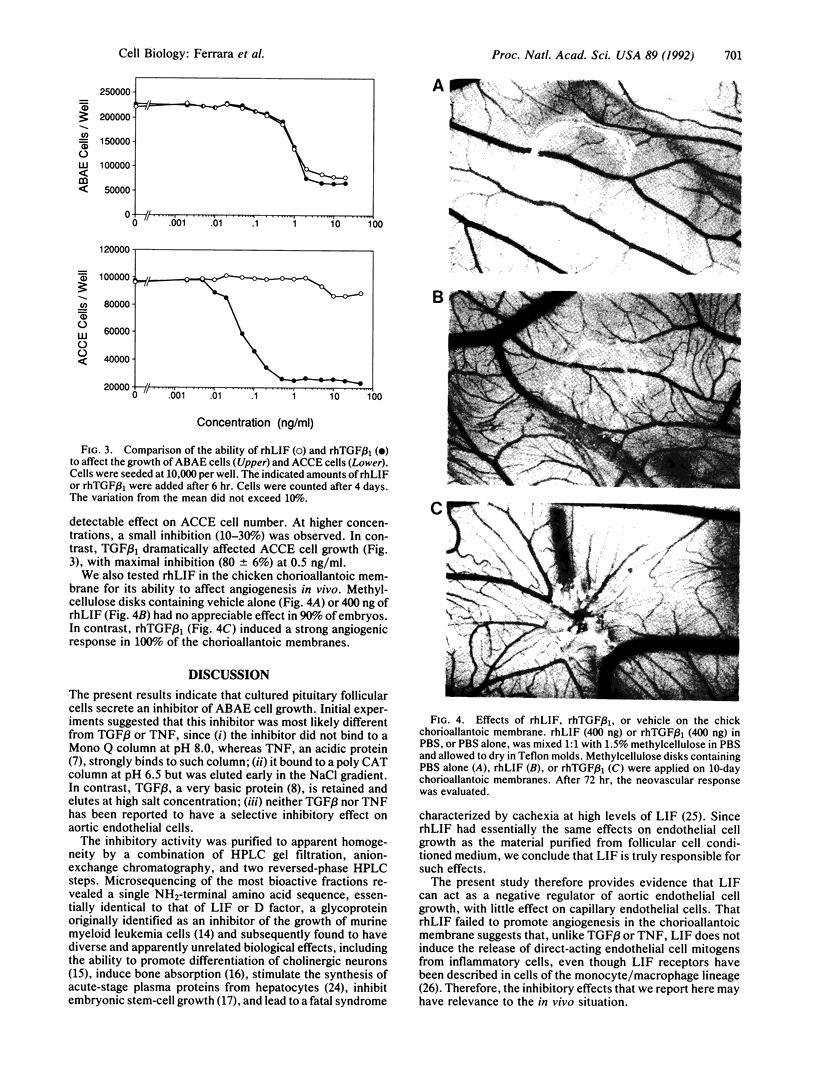
Medium conditioned by bovine pituitary follicular cells paradoxically inhibits the growth of adult bovine aortic endothelial (ABAE) cells at dilutions that are instead mitogenic to adrenal cortex capillary endothelial (ACCE) cells, suggesting that follicular cells secrete a growth inhibitor with a selectivity for ABAE cells. The ABAE cell inhibitory activity was purified to apparent homogeneity by a combination of size-exclusion chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, and two reversed-phase steps on a C4 column. Microsequencing of the purified material revealed a single NH2-terminal amino acid sequence, identical to that of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a glycoprotein originally identified by its ability to inhibit the growth of MT1 mouse leukemia cells and subsequently found to have numerous effects. Recombinant human LIF inhibited the growth of ABAE cells as effectively as transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta 1). However, it failed to inhibit markedly the growth of ACCE cells, whereas TGF beta 1 dramatically inhibited their growth. Recombinant human LIF also failed to induce a significant angiogenic response in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane, indicating that, unlike TGF beta, LIF probably does not induce the release of direct-acting angiogenic factors from inflammatory cells. The presence of LIF in follicular cells may relate to the peculiar vascular organization of the pituitary gland, where no arteries reach the pars distalis and all of the blood supply to this area is by capillaries.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach R., Kubai L., Knighton D., Folkman J. A simple procedure for the long-term cultivation of chicken embryos. Dev Biol. 1974 Dec;41(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Durkin T. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by type beta-transforming growth factor: interactions with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger A. C., Beeuwkes R., 3rd, Lainey L. L., Silverman K. J. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of human coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):175–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Wong G. G. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor III shares structural and functional identity with leukemia-inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1163–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergland R. M., Page R. B. Pituitary-brain vascular relations: a new paradigm. Science. 1979 Apr 6;204(4388):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.373118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias K. A., Weiner R. I. Direct arterial vascularization of estrogen-induced prolactin-secreting anterior pituitary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Clapp C., Weiner R. The 16K fragment of prolactin specifically inhibits basal or fibroblast growth factor stimulated growth of capillary endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):896–900. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Goldsmith P., Fujii D., Weiner R. Culture and characterization of follicular cells of the bovine anterior pituitary and pars tuberalis. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:245–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Winer J., Henzel W. J. Purification and cloning of vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by pituitary folliculostellate cells. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:391–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98040-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fràter-Schröder M., Risau W., Hallmann R., Gautschi P., Böhlen P. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Gough N. M., King J. A., Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Simpson R. J., Nice E. C., Kelso A., Metcalf D. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a murine myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF). EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3995–4002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. J., Polverini P. J., Rastinejad F., Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Frazier W. A., Bouck N. P. A tumor suppressor-dependent inhibitor of angiogenesis is immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from a fragment of thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ferrara N., Schweigerer L., Neufeld G. Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):95–114. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henzel W. J., Rodriguez H., Watanabe C. Computer analysis of automated Edman degradation and amino acid analysis data. J Chromatogr. 1987 Aug 28;404(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86835-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Specific binding of murine leukemia inhibitory factor to normal and leukemic monocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5971–5975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings J. C., Mohan S., Linkhart T. A., Widstrom R., Baylink D. J. Comparison of the biological actions of TGF beta-1 and TGF beta-2: differential activity in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):167–172. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Nunes W., Bombara M., McCabe S., Ranges G. E., Henzel W., Tomida M., Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y., Hozumi M., Goeddel D. V. Genomic cloning and heterologous expression of human differentiation-stimulating factor. DNA. 1989 Jun;8(5):351–359. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Gearing D. P. Fatal syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of the leukemia inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5948–5952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. R., Lowe C., Cornish J., Skinner S. J., Hilton D. J., Willson T. A., Gearing D. P., Martin T. J. Leukemia inhibitory factor: a novel bone-active cytokine. Endocrinology. 1990 Mar;126(3):1416–1420. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-3-1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A. Endothelial regeneration. VIII. Interaction of smooth muscle cells with endothelial regrowth. Lab Invest. 1988 Jul;59(1):36–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Heimark R. L., Majesky M. W. Developmental mechanisms underlying pathology of arteries. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1177–1209. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Malerstein B., Gospodarowicz D. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits the proliferation of cultured capillary endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Heath J. K., Donaldson D. D., Wong G. G., Moreau J., Stahl M., Rogers D. Inhibition of pluripotential embryonic stem cell differentiation by purified polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):688–690. doi: 10.1038/336688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankelecom H., Carmeliet P., Van Damme J., Billiau A., Denef C. Production of interleukin-6 by folliculo-stellate cells of the anterior pituitary gland in a histiotypic cell aggregate culture system. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Jan;49(1):102–106. doi: 10.1159/000125097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilette D., Setiadi H., Wautier M. P., Caen J., Wautier J. L. Identification of an endothelial cell growth-inhibitory activity produced by human monocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Jun;188(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Fukada K., Aebersold R., Korsching S., Fann M. J., Patterson P. H. The cholinergic neuronal differentiation factor from heart cells is identical to leukemia inhibitory factor. Science. 1989 Dec 15;246(4936):1412–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.2512641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]