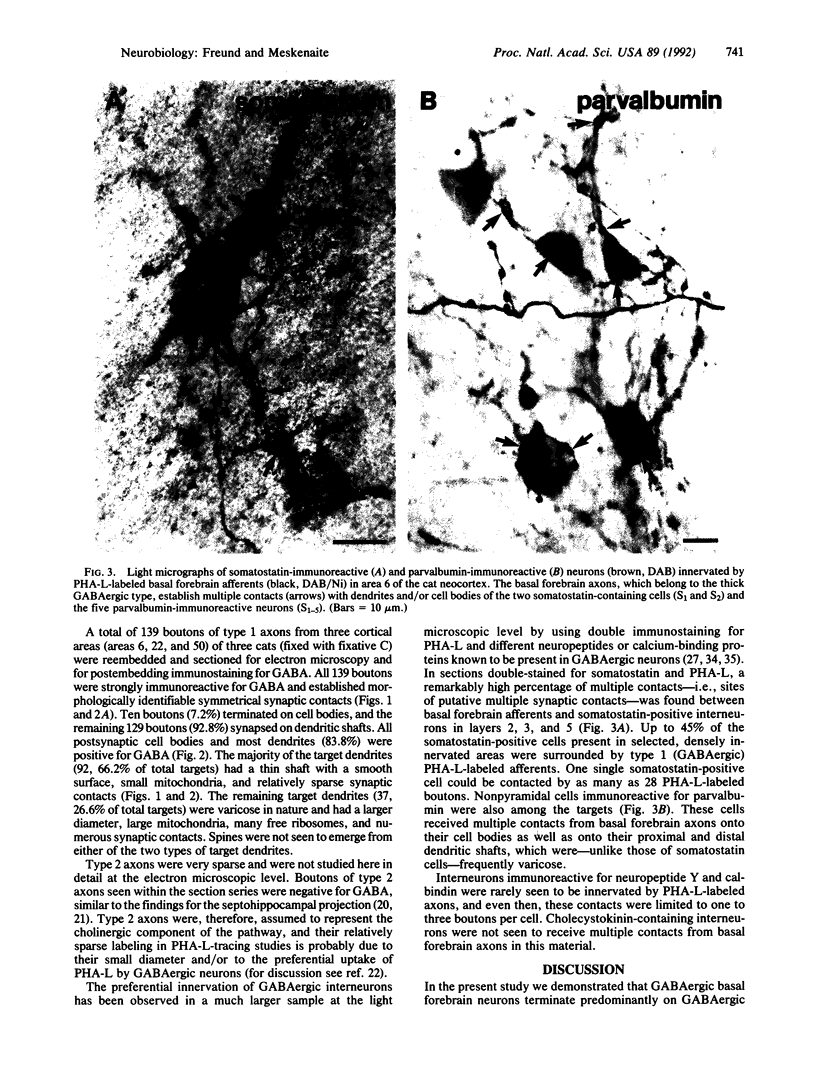
Abstract
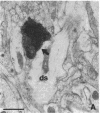
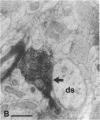
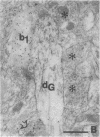
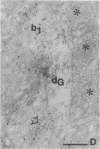
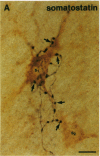
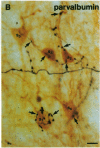
The basal forebrain-neocortex pathway--involved in higher cognitive processing, selective attention, and arousal--is considered one of the functionally most important ascending subcortical projections. The mechanism by which this relatively sparse subcortical pathway can control neuronal activity patterns in the entire cortical mantle is still unknown. The present study in the cat provides evidence that gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing basal forebrain neurons participate in the neocortical projection and establish multiple synaptic connections with gamma-aminobutyric acid-releasing interneurons containing somatostatin or parvalbumin. We propose that a mechanism by which the numerically small ascending pathways can exert a powerful global effect in the neocortex is by the selective innervation of gamma-aminobutyric acid-releasing interneurons, which, in turn, control the activity of large populations of pyramidal cells through their extensive axon arborizations. Finally, these results demonstrate a direct anatomical link between two cell populations implicated in Alzheimer disease pathology: basal forebrain neurons and cortical somatostatin cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artola A., Bröcher S., Singer W. Different voltage-dependent thresholds for inducing long-term depression and long-term potentiation in slices of rat visual cortex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):69–72. doi: 10.1038/347069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artola A., Singer W. Long-term potentiation and NMDA receptors in rat visual cortex. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):649–652. doi: 10.1038/330649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baimbridge K. G., Miller J. J., Parkes C. O. Calcium-binding protein distribution in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1982 May 13;239(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu C., Somogyi P. Enrichment of cholinergic synaptic terminals on GABAergic neurons and coexistence of immunoreactive GABA and choline acetyltransferase in the same synaptic terminals in the striate cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Feb 22;304(4):666–680. doi: 10.1002/cne.903040412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Baimbridge K. G. Distribution and co-localization of calbindin D28k with VIP and neuropeptide Y but not somatostatin, galanin and substance P in the enteric nervous system of the rat. Peptides. 1988 Mar-Apr;9(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Sikora L. K., Levy J. G., McIntosh C. H., Dyck I., Brown J. C. An immunocytochemical investigation with monoclonal antibodies to somatostatin. Histochemistry. 1985;83(2):175–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00495150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsaki G., Bickford R. G., Ponomareff G., Thal L. J., Mandel R., Gage F. H. Nucleus basalis and thalamic control of neocortical activity in the freely moving rat. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4007–4026. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csiffáry A., Görcs T. J., Palkovits M. Neuropeptide Y innervation of ACTH-immunoreactive neurons in the arcuate nucleus of rats: a correlated light and electron microscopic double immunolabeling study. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 8;506(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91253-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Katzman R., Terry R. D. Reduced somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex from cases of Alzheimer disease and Alzheimer senile dementa. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):279–280. doi: 10.1038/288279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divac I. Magnocellular nuclei of the basal forebrain project to neocortex, brain stem, and olfactory bulb. Review of some functional correlates. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 15;93(3):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett Stephen B., Rogers Derek C., Jones Graham H. Effects of Nucleus Basalis Magnocellularis Lesions in Rats on Delayed Matching and Non-Matching to Position Tasks. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Jul;1(4):395–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier I. N., Cross A. J., Johnson J. A., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Corsellis J. A., Lee Y. C., O'Shaughnessy D., Adrian T. E., McGregor G. P. Neuropeptides in Alzheimer type dementia. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. S., Buchwald N. A., Hull C. D., Levine M. S. GABAergic basal forebrain neurons project to the neocortex: the localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acetyltransferase in feline corticopetal neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 22;272(4):489–502. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Antal M. GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):170–173. doi: 10.1038/336170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Gulyás A. I., Acsády L., Görcs T., Tóth K. Serotonergic control of the hippocampus via local inhibitory interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8501–8505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Martin K. A., Smith A. D., Somogyi P. Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Dec 10;221(3):263–278. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar P., Duyckaerts C., Febvret A., Benoit R., Beck B., Berger B. Subpopulations of somatostatin 28-immunoreactive neurons display different vulnerability in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 19;490(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
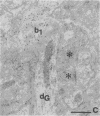
- Gerfen C. R., Sawchenko P. E. An anterograde neuroanatomical tracing method that shows the detailed morphology of neurons, their axons and terminals: immunohistochemical localization of an axonally transported plant lectin, Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L). Brain Res. 1984 Jan 9;290(2):219–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90940-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Görcs T. J., Freund T. F. Innervation of different peptide-containing neurons in the hippocampus by GABAergic septal afferents. Neuroscience. 1990;37(1):31–44. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90189-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Seress L., Tóth K., Acsády L., Antal M., Freund T. F. Septal GABAergic neurons innervate inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus of the macaque monkey. Neuroscience. 1991;41(2-3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90334-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Emson P. C., Lawson D. E., Heizmann C. W., Streit P. Two classes of cortical GABA neurons defined by differential calcium binding protein immunoreactivities. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(2):467–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00247904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. Immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat cerebral cortex: a study of cholinergic neurons and synapses. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Apr 1;234(1):17–34. doi: 10.1002/cne.902340103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irle E., Markowitsch H. J. Basal forebrain efferents reach the whole cerebral cortex of the cat. Brain Res Bull. 1984 May;12(5):493–512. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(84)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Schwartz S. The action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):320–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00237558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Chan-Palay V., Wu J. Y. Septal neurons containing glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactivity project to the hippocampal region in the rat brain. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1984;169(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00300585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Levey A. I., Wainer B. H. Cholinergic innervation of cortex by the basal forebrain: cytochemistry and cortical connections of the septal area, diagonal band nuclei, nucleus basalis (substantia innominata), and hypothalamus in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 20;214(2):170–197. doi: 10.1002/cne.902140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson D. D., Dykes R. W. Long-term enhancement of evoked potentials in cat somatosensory cortex produced by co-activation of the basal forebrain and cutaneous receptors. Exp Brain Res. 1988;70(2):276–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00248353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson R. T., DeLong M. R. A reappraisal of the functions of the nucleus basalis of Meynert. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):264–267. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins T. W., Everitt B. J., Marston H. M., Wilkinson J., Jones G. H., Page K. J. Comparative effects of ibotenic acid- and quisqualic acid-induced lesions of the substantia innominata on attentional function in the rat: further implications for the role of the cholinergic neurons of the nucleus basalis in cognitive processes. Behav Brain Res. 1989 Dec 1;35(3):221–240. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(89)80143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins T. W., Everitt B. J., Ryan C. N., Marston H. M., Jones G. H., Page K. J. Comparative effects of quisqualic and ibotenic acid-induced lesions of the substantia innominata and globus pallidus on the acquisition of a conditional visual discrimination: differential effects on cholinergic mechanisms. Neuroscience. 1989;28(2):337–352. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossor M. N., Emson P. C., Mountjoy C. Q., Roth M., Iversen L. L. Reduced amounts of immunoreactive somatostatin in the temporal cortex in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Dec;20(3):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye D. B., Wainer B. H., Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Saper C. B. Cortical projections arising from the basal forebrain: a study of cholinergic and noncholinergic components employing combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase. Neuroscience. 1984 Nov;13(3):627–643. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper C. B. Organization of cerebral cortical afferent systems in the rat. II. Magnocellular basal nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jan 20;222(3):313–342. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen H. S., Jolkkonen J. T., Reinikainen K. J., Halonen T. O., Riekkinen P. J. Reduced cholinesterase activity and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;63(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J. Antisera to gamma-aminobutyric acid. III. Demonstration of GABA in Golgi-impregnated neurons and in conventional electron microscopic sections of cat striate cortex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Mar;33(3):249–257. doi: 10.1177/33.3.2579124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., Smith A. D., Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Wu J. Y. Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin- or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2590–2603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Kisvárday Z. F., Martin K. A., Whitteridge D. Synaptic connections of morphologically identified and physiologically characterized large basket cells in the striate cortex of cat. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):261–294. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwolf C. H. Cerebral activity and behavior: control by central cholinergic and serotonergic systems. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1988;30:225–340. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle P., Sanides-Buchholtz C., Eckenstein F., Albus K. Concurrent visualization of choline acetyltransferase-like immunoreactivity and retrograde transport of neocortically injected markers in basal forebrain neurons of cat and rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Feb 24;44(3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainer B. H., Bolam J. P., Freund T. F., Henderson Z., Totterdell S., Smith A. D. Cholinergic synapses in the rat brain: a correlated light and electron microscopic immunohistochemical study employing a monoclonal antibody against choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 6;308(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouterlood F. G., Bol J. G., Steinbusch H. W. Double-label immunocytochemistry: combination of anterograde neuroanatomical tracing with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin and enzyme immunocytochemistry of target neurons. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Aug;35(8):817–823. doi: 10.1177/35.8.2439583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouterlood F. G., Groenewegen H. J. Neuroanatomical tracing by use of Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin (PHA-L): electron microscopy of PHA-L-filled neuronal somata, dendrites, axons and axon terminals. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 4;326(1):188–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]