Abstract
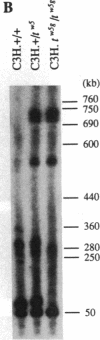
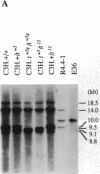
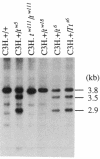
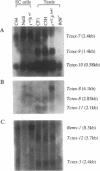
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) of the mouse is located on chromosome 17 in the distal inversion of the t complex. In addition to genes playing major roles in the immune response, it contains a diversity of genes. In humans, numerous diseases are known to be associated with the MHC loci. Moreover, at least three recessive embryonic t-lethal mutations have been mapped to the MHC. Here a molecular genetic approach was used to study the detailed genomic structure of 240 kilobases (kb) surrounding the H-2K gene and 150 kb of a partly homologous region located in the distal inversion of the t complex. Combined with previous findings, the H-2K region was found to contain an impressively high density of genes--12 transcription units in 240 kb. Surprisingly, virtually all of these genes are expressed in testis and/or embryos. The genomic organization of this region is contrasted with the 150 kb of the homologous area where only three genes and an endogenous retrovirus reside.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Wei J. F., Wei F. S., Hsu Y. C., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: the H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3441–3449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artzt K., Abe K., Uehara H., Bennett D. Intra-H-2 recombination in t haplotypes shows a hot spot and close linkage of 1tw5 to H-2K. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(1):30–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00372526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S., Attaya M., Brown M. G., Monaco J. J. A cluster of transcribed sequences between the Pb and Ob genes of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5197–5201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deverson E. V., Gow I. R., Coadwell W. J., Monaco J. J., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. MHC class II region encoding proteins related to the multidrug resistance family of transmembrane transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):738–741. doi: 10.1038/348738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fronek Z., Timmerman L. A., Alper C. A., Hahn B. H., Kalunian K., Peterlin B. M., McDevitt H. O. Major histocompatibility complex genes and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Oct;33(10):1542–1553. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha H., Howard C. A., Yeom Y. I., Abe K., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Several testis-expressed genes in the mouse t-complex have expression differences between wild-type and t-mutant mice. Dev Genet. 1991;12(4):318–332. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Poustka A., Trowsdale J. New genes in the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90327-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. Colinearity of novel genes in the class II regions of the MHC in mouse and human. Immunogenetics. 1991;34(1):5–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00212306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson T., Epstein C. J., Silver L. M., Martin G. R. Pluripotent embryonic stem cell lines can be derived from tw5/tw5 blastocysts. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):750–753. doi: 10.1038/298750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Evans M. J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner C. M., Campbell R. D. Structure and expression of the three MHC-linked HSP70 genes. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(4):242–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00187095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzo M., Andres X., Ruano-Gil D. Etude morphologique d'une population homogène de cellules de térato-carcinome. Bull Assoc Anat (Nancy) 1983 Sep;67(198):315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata M. M., Khan A. S. Structure, distribution, and expression of an ancient murine endogenous retroviruslike DNA family. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4381–4386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4381-4386.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Murialdo H., Delius H., Chai J. H., Poustka A., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. Analysis of cosmids using linearization by phage lambda terminase. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Steege D. A., Juricek D. K., Summers W. P., Ruddle F. H. A herpes simplex virus 1 integration site in the mouse genome defined by somatic cell genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):455–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Arnold D., Blanck G., Mellins E., Pious D., DeMars R. A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region controlling the class I antigen presentation pathway. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):744–747. doi: 10.1038/348744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuscher C., Gasser D. L., Woodward S. R., Hickey W. F. Experimental allergic orchitis in mice. VI. Recombinations within the H-2S/H-2D interval define the map position of the H-2-associated locus controlling disease susceptibility. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(5):337–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00211648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara H., Abe K., Park C. H., Shin H. S., Bennett D., Artzt K. The molecular organization of the H-2K region of two t-haplotypes: implications for the evolution of genetic diversity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):83–90. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. (1). N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 11;316(24):1519–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706113162406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]