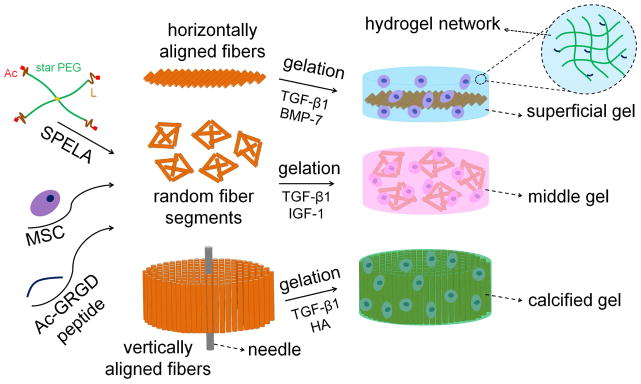
Figure 1.
Schematic representation for the synthesis of hydrogel constructs simulating the superficial, middle, and calcified zones of articular cartilage. SPELA was synthesized by chain-extension of the hydrophilic 4-arm star PEG macromer (green) with degradable, short lactide segments (brown) followed by functionalization with a crosslinkable acrylate group at each chain-end (red). For Superficial gel, aligned fiber microsheets were dip-coated in SPELA10 gel precursor solution (SPELA, hMSCs, Ac- GRGD peptide), the dipped microsheets were laminated, UV crosslinked, and cultured with TGF-β1 and BMP-7. For Middle gel, randomly-oriented fiber sheets were cut into small pieces, randomly dispersed in SPELA7.5 precursor solution, UV crosslinked, and cultured with TGF-β1 and IGF-1. For Calcified gel, aligned fiber sheets were dip-coated in SPELA5 precursor solution, wrapped around a needle to simulate the vertical orientation of the fibers with respect to the chondral surface, UV crosslinked, and cultured with TGF-β1 and HA.