Abstract.
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has become one of the fastest growing fields in biomedical optics. Unlike pure optical imaging, such as confocal microscopy and two-photon microscopy, PAT employs acoustic detection to image optical absorption contrast with high-resolution deep into scattering tissue. So far, PAT has been widely used for multiscale anatomical, functional, and molecular imaging of biological tissues. We focus on PAT’s basic principles, major implementations, imaging contrasts, and recent applications.
Keywords: Photoacoustic tomography, photoacoustic computed tomography, photoacoustic microscopy, optical absorption contrast
1. Introduction
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT), also called optoacoustic tomography, is a three-dimensional (3-D) imaging modality based on the photoacoustic (PA) effect. Although the PA effect was discovered more than a century ago by Alexander Graham Bell, it has found applications in biomedical imaging only in the last decade or so. Nowadays, PAT is one of the largest research areas in biomedical optics and is still growing rapidly.1
Harnessing both rich optical absorption contrast and high ultrasonic resolution, PAT is a hybrid imaging modality that can image deep tissues. While pure optical imaging modalities can also detect optical absorption by monitoring intensity variations in transmitted or reflected light, their sensitivities are usually two orders of magnitude lower than that of PAT.2 In addition, because acoustic waves scatter much more weakly than light in biological tissues, they can propagate a greater distance than photons without losing their original propagation directions, providing PAT with high spatial resolution at depths. While pure ultrasonic imaging can also achieve high spatial resolution in deep tissues, its mechanical contrast is incapable of providing certain physiological parameters, such as the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin and the metabolic rate of oxygen.
Several comprehensive reviews of PAT can be found in the literature;1,3–21 some are general,1,3–5,11,21 and some focus on specific areas, such as PAT’s application in imaging molecules,9 microvasculature,6 tumors,17 the brain,16 and small animals.15 Here, we will review the fundaments of PAT, including its principles, major implementations, system characteristics, main contrast agents, and recent applications.
2. Principles
2.1. Initial Pressure Rise
In PAT, a short-pulsed light source is typically used to irradiate the tissue, resulting in broadband PA waves with a frequency content extending to several tens or even hundreds of megahertz for acoustic detection. Following absorption of the light, an initial temperature rise induces a pressure rise, which propagates as a photoacoustic wave and finally is detected by a single-element ultrasonic transducer or a transducer array. There are two important time scales in the generation of PA waves,2 the thermal relaxation time () and the stress relaxation time (). denotes the thermal relaxation (thermal diffusion) time of the desired voxel, and is given by
| (1) |
where is the desired spatial resolution and is the thermal diffusivity (). , which characterizes the stress relaxation time of the desired voxel, is given by
| (2) |
where is the speed of sound (m/s).
Upon laser excitation, the fractional volume expansion of the heated region can be expressed as
| (3) |
where denotes the isothermal compressibility (), denotes the change in pressure (Pa), denotes the thermal coefficient of volume expansion (), and denotes the change in temperature (K).
If the laser pulse duration is shorter than and , the excitation satisfies both thermal and stress confinements. In this situation, the fractional volume change is negligible. Thus, the initial pressure rise can be derived from
| (4) |
Further, the local temperature rise can be expressed as
| (5) |
where is the percentage of absorbed light converted into heat, and is the specific optical energy deposition (). Substituting Eq. (5) into Eq. (4), we have
| (6) |
By defining the Gruneisen parameter (dimensionless) as
| (7) |
Equation (6) becomes
| (8) |
For single-photon optical absorption, is proportional to the local optical fluence (). In this case, Eq. (8) becomes
| (9) |
where is the optical absorption coefficient (). Based on Eq. (9), the initial pressure rise is proportional to and . and are usually approximated as constants, although they have been found to depend on the tissue type;22,23 thus, if can be measured and is known, can be recovered. After the generation of the initial pressure , an acoustic wave starts to propagate at the speed of sound in the material. The propagation in an inviscid medium can be described by general photoacoustic equations in the time-domain, as discussed in Sec. 2.2.
2.2. Photoacoustic Wave Propagation
The propagation and generation of acoustic pressure at position and time t is governed by the following wave equation:
| (10) |
Note that represents the temperature rise instead of the temperature, i.e., the temperature rise above its initial value. Under the condition of thermal confinement, where heat conduction is negligible, the heat diffusion equation becomes
| (11) |
where is the heating function, defined as the thermal energy deposited per unit volume and per unit time. Note that the heating function is related to the specific optical energy deposition by the following equation:
| (12) |
Substituting Eq. (11) into Eq. (10), we have
| (13) |
where is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure.
Solving Eq. (13) with the Green function approach, we have the following delta heating response:
| (14) |
where is the initial pressure rise at location . If the heating pulse has a finite duration, the response can be computed by convolution
| (15) |
where is the temporal profile of the excitation pulse.
3. Photoacoustic Image Formation
The goal of PA imaging is to retrieve the local pressure rise inside the tissue. Based on Eq. (9), if we know the local optical fluence , the absorption coefficient can then be calculated. In practice, the adjacent fluence in the tissue is usually comparable, but the absorption coefficient differs considerably. For example, blood in the visible light region has much stronger absorption than other components in tissue.14 Thus, if is assumed to be regionally homogeneous in anatomic PA imaging, then can be used to directly map the relative absorption coefficient . There are two basic methods to recover the original distribution inside the target once the pressures at the observation points are measured:11 reconstruction-based image formation and focused-scanning image formation. While the former is the basis of photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT), the latter is commonly used for photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) and occasionally for photoacoustic macroscopy (PAMac). Because PAM and PAMac mainly differ in their spatial resolution, i.e., PAM has a spatial resolution less than while PAMac does not, we will only discuss PAM in this review paper.
3.1. Image Formation in Photoacoustic Computed Tomography
For PACT, the light is expanded to illuminate the whole object to be imaged. PA signals are acquired at multiple locations around the object, either by using a transducer array or by scanning a single-element transducer to simulate an array. Next, back-projecting all the PA data, similar to traditional computed tomography or positron emission tomography imaging, generates PA images of the object. Note that in order to detect PA signals from the same object at multiple locations, a transducer or transducer array with a large acceptance angle is desirable. Several methods are widely used for PA image formation,24,25–30 such as universal back-projection (UBP)25 and time reversal.26
Demonstrated in spherical, cylindrical, and planar detection geometries, the UBP algorithm has the following formula:
| (16) |
where is the solid angle of the entire detection surface with respect to a source point at . The factor weighs the contribution from each element on the detection surface . The term is the direct back-projection of the detected PA signals onto a spherical surface centered at . The first derivative with respect to time represents a ramp filter, which suppresses low frequency signals. In the UBP algorithm, the medium is assumed to be acoustically lossless and homogeneous.
The time-reversal method has recently been recognized as the least restrictive reconstruction algorithm: it can work for any closed geometry and can incorporate acoustic heterogeneities. In the time-reversal method, the measured acoustic pressure is retransmitted into the medium in time reversed order. The same wave equation is solved from to , where is the maximum time for the acoustic wave to traverse the detection region. The measured pressure data are treated either as boundary conditions or as a source. To solve the wave equation, numerical methods are employed, such as time-domain finite-difference techniques or k-space pseudospectral methods. Thus, the time-reversal method is more computationally intensive than the UBP method, especially for 3-D image reconstruction.
3.2. Image Formation in Photoacoustic Microscopy
Different from reconstruction-based methods, the focused-scanning scheme of PAM usually focuses both the optical excitation and acoustic detection. If the optical focus is tighter than the acoustic focus, the technique is called optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM);31,32 otherwise, it is called acoustic resolution photoacoustic microscopy (AR-PAM).33–35 In both cases, each laser pulse generates a one-dimensional (1-D) photoacoustic image (A-line) along the axial direction. Raster-scanning laterally and then piecing together all the A-lines provides a 3-D PA image. Because each signal acquired by the transducer directly represents a 1-D image of a single line inside the object after minimal signal processing, there is no need for image reconstruction. Although raster-scanning is used in most cases, there are alternative scanning methods, such as circumferential-section-scanning for endoscopic imaging,36,37–40 3-D arbitrary scanning for blood vessel monitoring,41 and random access scanning for cell tracking.42
4. Photoacoustic Systems and Their Characteristics
As mentioned earlier, based on their different image formation mechanism, PA systems can be classified as either reconstruction-based PACT or focused-scanning-based PAM. In this section, we discuss typical PA systems and their characteristics, including spatial resolution, imaging speed, and penetration depth.
4.1. Photoacoustic Computed Tomography
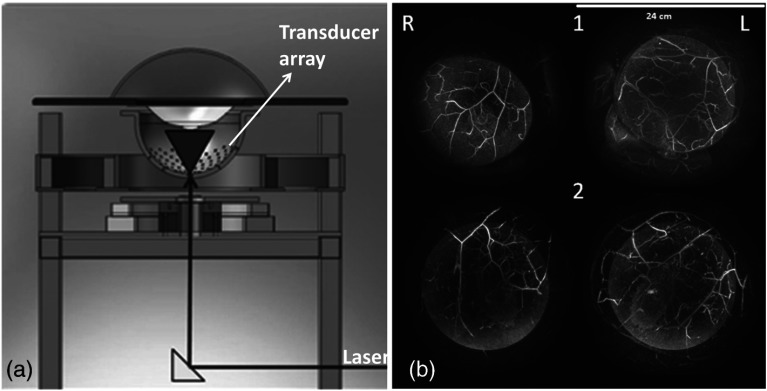
Current PACT systems use spherical,43,44–46 cylindrical,15,47–52 or planar detection geometry.53–60 Each geometry has several implementations. For spherical-view systems, either an arc-shaped transducer array44 or a hemispherical array with a spiral pattern45,46 is used. In both cases, mechanical scanning is required for dense spatial sampling, and 3-D reconstruction is performed. Figure 1(a) shows a hemispherical array based PACT system,46 with 512 ultrasonic transducer elements distributed in a hemispherical shell with a radius of 127 mm. The diameter of each transducer element is 3 mm, and the center frequency is 2 MHz, with a 70% bandwidth. The transducer array is scanned spirally to achieve dense spatial sampling for image reconstruction. As shown in Fig. 1(a), the bottom of the hemispherical shell contains an aperture for light delivery. In this case, pulses from an Alexandrite laser at 756 nm are used to excite the target. Depending on the spiral scanning pattern, total data acquisition time varies from 12 s for the smallest spiral (24-mm radius) to 3.2 min for the largest spiral (96-mm radius). Using a thin graphite fiber phantom ( diameter), the resolution of this system was quantified to be 0.42 mm. Because spherical-view detection was implemented, this resolution was constant at different graphite fiber orientations. A 5.3-cm penetration was achieved in the phantom. As shown in Fig. 1(b), blood vessels in the breasts of two healthy volunteers were clearly imaged although their depths are not shown.
Fig. 1.
Hemispherical array based photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) system and its representative images. (a) Schematic of a spherical-view photoacoustic system. (b) Representative human breast images from two healthy volunteers (1) and (2). R, right breast and L, left breast. Reproduced with permission from Refs. 45 and 46.
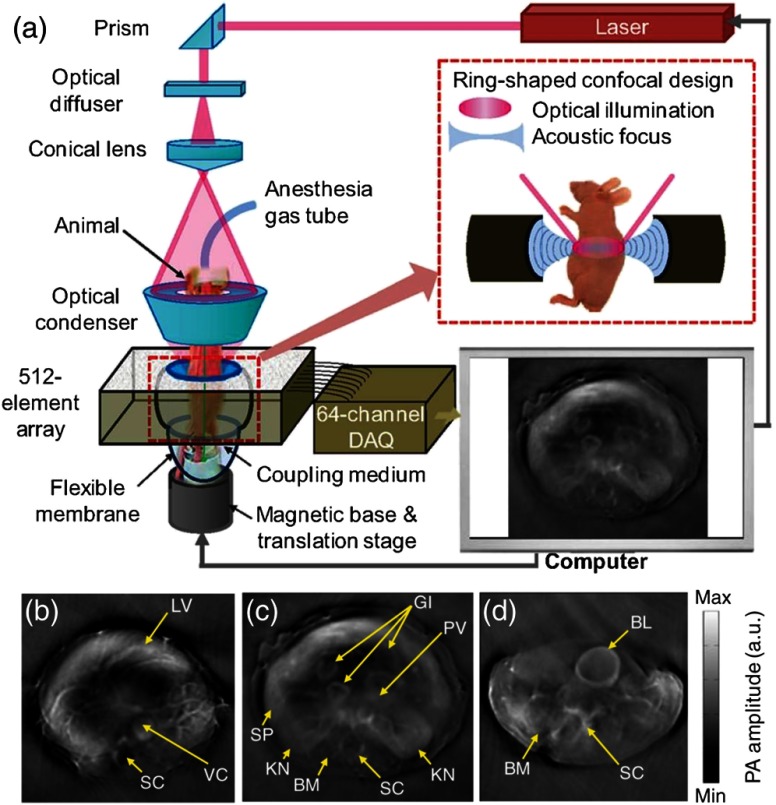
A representative cylindrical-view PACT system48 is shown in Fig. 2. The system contains a 512-element full ring transducer array with a ring diameter of 5 cm. Each transducer element has a center frequency of 5 MHz and an 80% (one-way) detection bandwidth.61 To improve the cross-sectional imaging ability, each element is cylindrically focused to reject out-of-plane signals. The combined foci from all elements provide a central imaging region with a diameter and thickness. Strictly speaking, such a system is a circular-view system, since only a ring is used to reconstruct the image instead of a cylinder. However, by taking advantage of its cylindrical focusing capability, high-quality two-dimensional (2-D) cross-sectional images are attainable. In addition, by scanning the sample or the array along the elevational direction, 3-D images can be acquired. Within the imaging region, the system provides 100- to transverse resolution in the circumferential direction and axial resolution in the radial direction. Limited by its 64-channel data acquisition and 10-Hz laser, the system acquires one . However, by employing a 512-channel real-time data acquisition system and a faster laser, higher rate imaging can be realized. Because of the fixed ring diameter, only 1-cm penetration depth was reported. As shown in Figs. 2(b) and 2(c), blood-rich organs, such as the liver, kidneys, spleen, spine, and GI tracts can be clearly visualized. In addition, blood-poor organs, such as the bladder, can also be imaged with the help of a near-infrared contrast agent (IRDye800, LI-COR, Inc.), as shown in Fig. 2(d).
Fig. 2.
Cylindrical-view PACT system and its representative images. (a) Schematic of the system, showing the confocal design of both the optics and acoustics. (b)–(d) In vivo images of athymic mice acquired by the system at different anatomical locations: (b) liver, (c) kidneys, and (d) bladder. BL, bladder; BM, backbone muscle; GI, GI tract; KN, kidney; LV, liver; PV, portal vein; SC, spinal cord; SP, spleen; and VC, vena cava. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 48.
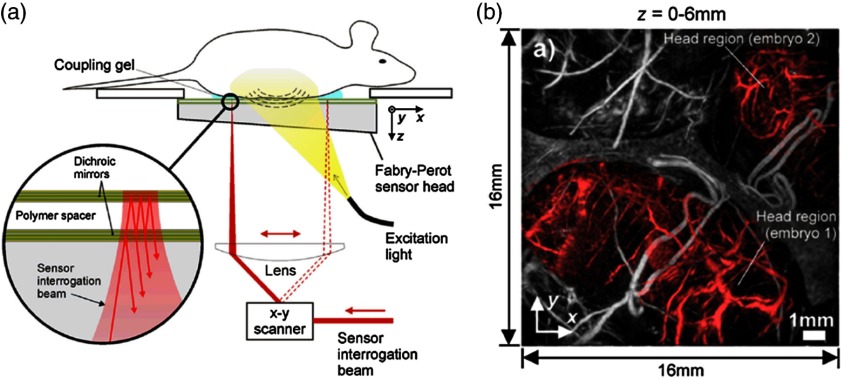
There are different implementations for planar-view PACT, using either a 2-D ultrasound transducer array44,53 or a Fabry–Perot interferometer (FPI).55,60 Generally, the 2-D transducer array based PACT system has a higher frame rate, while the FPI-based system has higher sensitivity and a larger receiving angle. Figure 3(a) is a schematic of the FPI-based PACT system.62 In this type of PA imaging, the deformation of pressure-sensitive materials (e.g., polymer) is measured by optical resonance. The PA excitation beam was at 640 nm, and the PA probing beam was at 1550 nm. By raster scanning the probe beam across the FPI surface, photoacoustic waves can be mapped in 2-D. Depending on the detector bandwidth (22 MHz in this work), the axial resolution of this system was . The lateral resolution was about , which was determined by primarily the detection bandwidth and angular range. To scan an area of , the image acquisition time was about 8 min, which was limited by the 50-Hz pulse repetition rate of the excitation laser. The in vivo penetration depth of this system was demonstrated to be more than 10 mm. As shown in Fig. 3(b), two embryos (shaded in red) with detailed structures, such as the liver, ribs, pulmonary vein, and right atrium, can be clearly imaged.
Fig. 3.
Fabry–Perot interferometer (FBI) based PACT system. (a) Schematic and (b) a representative image of a FBI based PACT system. The red parts in (b) indicate the location of embryos. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 62.
4.2. Photoacoustic Microscopy
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of PAM: OR-PAM and AR-PAM. In OR-PAM, although the optical focus determines its lateral resolution, the detection transducer is also placed confocally with the optical focus to maximize the system’s detection sensitivity. Similarly, in AR-PAM, the excitation beam fills the entire acoustic focus to maximize the system’s sensitivity. The axial resolution in both OR-PAM and AR-PAM is determined by the detection bandwidth of the transducer. Due to the frequency dependence of acoustic attenuation, the bandwidth is chosen according to the desired imaging depth.
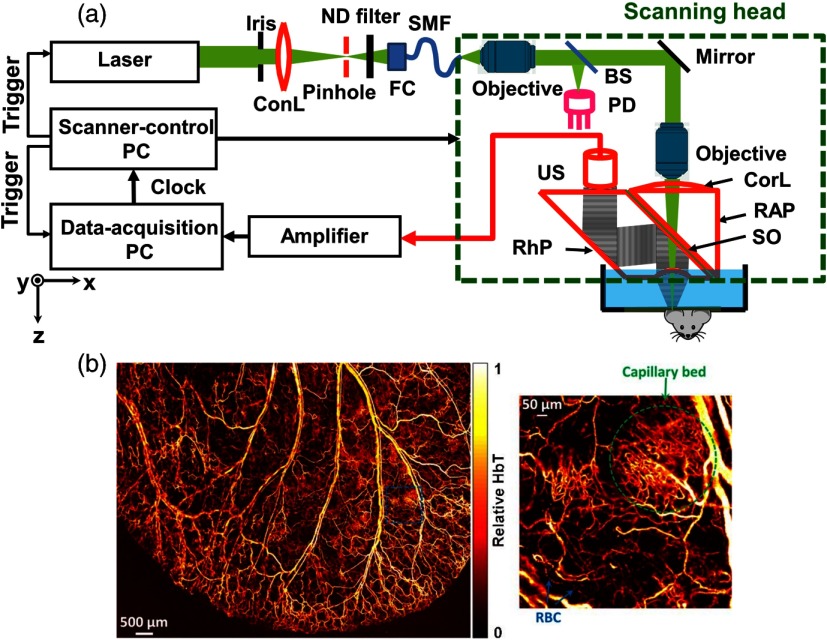
As shown in Fig. 4(a), a typical OR-PAM system employs an optical lens to focus light into the sample. A light-sound combiner transmits the light and reflects the sound. The combiner is composed of a right-angled prism, a thin layer of silicone oil, and a rhomboid prism for acoustic-optical coaxial alignment. Usually the laser beam is tightly focused, whose diameter can range from several hundred nanometers to several micrometers, depending on the numerical aperture (NA) of the optical focusing lens, the wavelength of the excitation beam, and the desired imaging depth. Relying on the tight optical focus, the penetration of an OR-PAM system is limited to about one transport mean free path in tissue ().12,63,64 However, by using longer wavelength laser pulses, which have longer transport mean free paths, the penetration limit can be increased.65 OR-PAM can image vasculature in a mouse ear,31 eye,66–69 and brain31,70,71 clearly. Figure 4(b) shows a representative mouse ear image acquired with OR-PAM, where both a capillary bed and flowing red blood cells can be clearly visualized.
Fig. 4.
Typical optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) system. (a) Schematic and (b) a representative image of OR-PAM. BS, beam splitter; ConL, condenser lens; CorL, correction lens; FC, fiber collimator; HbT, total hemoglobin concentration; ND, neutral density; PD, photodiode; RAP, right-angle prism; RBC, red blood cell; RhP, rhomboid prism; SMF, single-mode fiber; SO, silicone oil; and US, ultrasonic transducer. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 31.
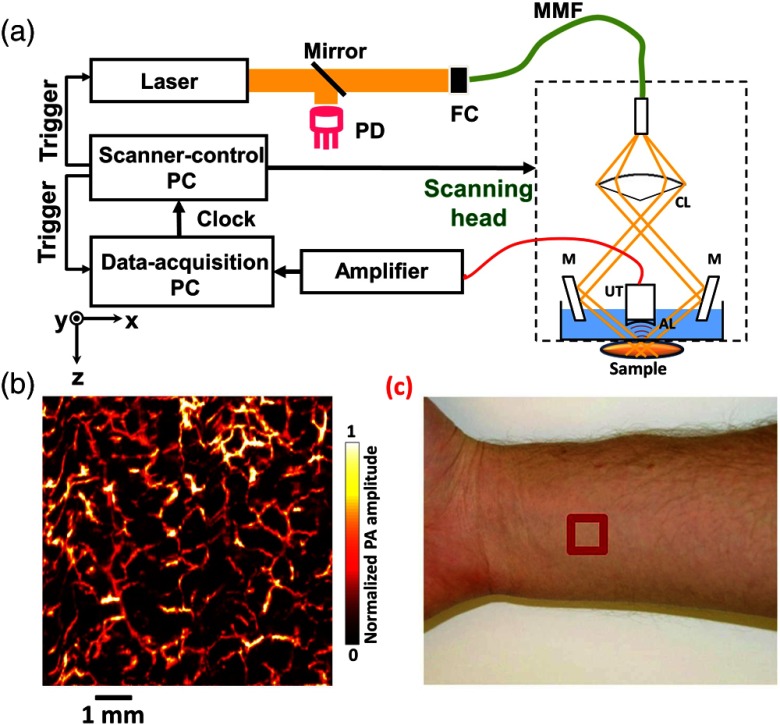
As shown in Fig. 5(a), in a typical AR-PAM system, the laser beam passes through a conical lens to form a ring-shaped illumination pattern.34,72,73–75 The beam is then focused into the target by custom-made mirrors. The optical illumination on the skin surface has a donut shape with a dark center to minimize strong surface signals. Since acoustic scattering is much weaker than optical scattering in tissue, tight acoustic focusing can be maintained at depths. For example, using a 50-MHz center frequency transducer with an NA of 0.44, a lateral resolution of was achieved with an imaging depth of more than 3 mm. By choosing transducers with different center frequencies and NAs, the lateral resolutions can be scaled. Note that although acoustic scattering is weak in tissue, high frequency ultrasound signals suffer strong attenuation. In the end, the attenuation becomes the limiting factor for deep high-resolution AR-PAM imaging. Figure 5(b) shows a representative AR-PAM image of a human forearm, where detailed vasculatures can be clearly discerned. Figure 5(c) is a photo of the forearm, where the red box indicates the image area of .
Fig. 5.
Typical acoustic resolution photoacoustic microscopy (AR-PAM) system. (a) Schematic and (b) a representative image of AR-PAM. AL, acoustic lens; CL, conical lens; FC, fiber coupler; M, mirror; MMF, multimode fiber; PD, photodiode; and UT, ultrasonic transducer. (c) Red box is the image area. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 74.
The lateral and axial resolutions as well as imaging depth are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Summary of typical PA system characteristics.
| Modality | Lateral resolution () | Axial resolution () | Imaging depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subwavelength OR-PAM76 | 0.22 | 15 | 0.1a |
| Second generation OR-PAM31 | 2.5 | 15 | 1.2a |
| Dark-field AR-PAM34 | 45 | 15 | 3a |
| Bright-field AR-PAM77 | 44 | 15 | 4.8a |
| Spherical-view PACT46 | 420 | 420 | 53b |
| Cylindrical-view PACT48 | 100–250 | 100 | 10a |
| FPI PACT62 | 120 | 27 | 10a |
| Clinical linear array PACT11,78 | 720 | 640 | 70b |
Note: FPI: Fabry–Perot interferometer.
Based on in vivo data.
Based on phantom data.
5. Photoacoustic Contrast Agents
Theoretically speaking, any material with sufficiently high optical absorption can be detected by PAT. Thus, by choosing the right wavelengths, PAT potentially can be used to image all materials. Specifically, in biological applications, absorbers are usually divided into endogenous and exogenous categories. We will discuss these two categories in Secs. 5.1 and 5.2.
5.1. Endogenous Contrast Agents
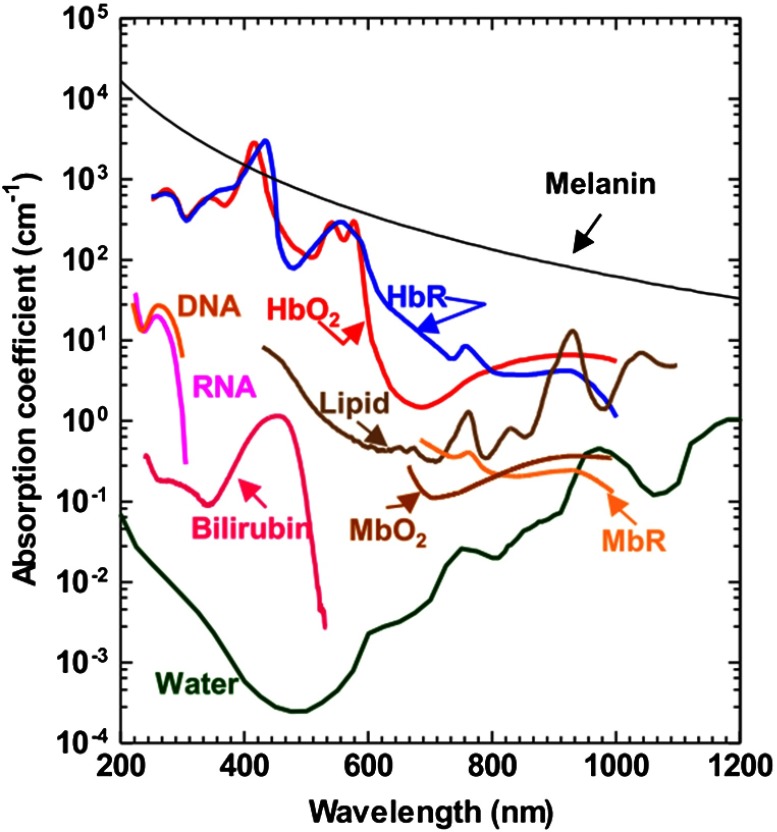
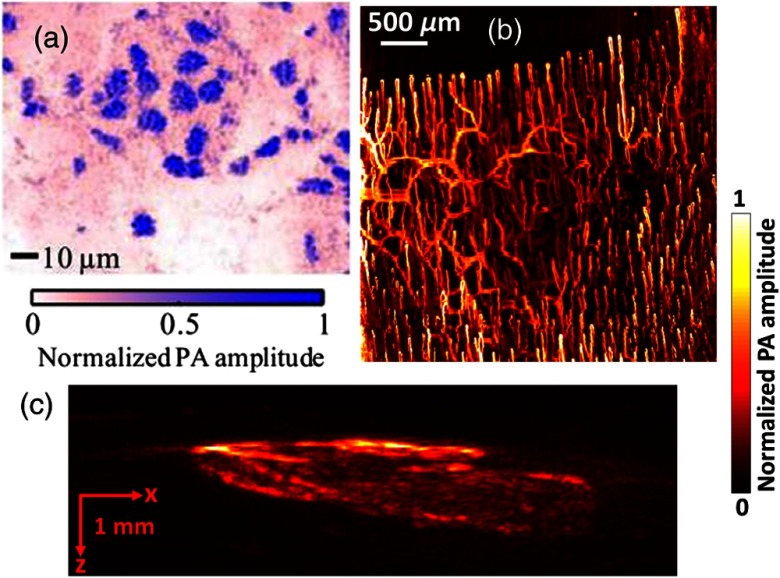
The primary advantage of endogenous contrast agents is that they allow label-free imaging, so they do not affect the original biological environment. In biological tissue, there are varieties of optical absorbers,14 such as DNA/RNA,79,80 cytochromes,81 bilirubin,82 myoglobin,83,84 hemoglobin,85,86 methemoglobin,87 carboxyhemoglobin,88 melanin,54,89,90 lipid,91–93 water,94,95 and glucose.96,97 Among all these agents, DNA/RNA is commonly used for cell nuclear imaging in the ultraviolet region [Fig. 6(a)],79 hemoglobin is widely used for vascular imaging in the visible and the near-infrared spectral regions [Fig. 6(b)],19 and melanin is employed for melanoma tumor imaging in the near-infrared region [Fig. 6(c)].54 In addition, in the near-infrared region, lipids and water are used for atherosclerotic plaque98,99 and injury94 imaging, respectively. As shown in Fig. 7, different endogenous contrast agents have different absorption spectra. Thus, PAT can separate them with spectral measurement, when the local optical fluence is known.
Fig. 6.
PAT imaging of endogenous contrast agents: DNA/RNA (a), hemoglobin (b), and melanin (c). Reproduced with permission from Ref. 14.
Fig. 7.
Absorption spectra of the main endogenous pigments in tissue at normal concentrations. , oxygenated hemoglobin; HbR, deoxygenated hemoglobin; , oxygenated myoglobin; and MbR, deoxygenated myoglobin. Reproduced with permission from Refs. 79, 19, and 54.
A representative application of spectral decomposition is to quantify the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin () in blood vessels by differentiating signals from oxy-hemoglobin () and deoxy-hemoglobin (HbR). As derived above, the measured PA amplitude of blood is proportional to the local fluence and the absorption coefficient of blood
| (17) |
where is the measured PA amplitude at wavelength , is a system constant, is the blood absorption coefficient, is the optical fluence. and are the molar extinction coefficients of HbR and , respectively, and and are the concentrations of HbR and , respectively. For a given system, is a constant. In OR-PAM, which works within the optical ballistic regime, can be corrected for by measuring the surface optical fluence. Thus, by performing measurements at two wavelengths, the relative concentrations of HbR and can be quantified
| (18) |
and
| (19) |
where stands for the second wavelength. By definition, the value can be calculated as
| (20) |
However, in AR-PAM and PACT, which work in the optical (quasi)diffusive regime, it is challenging to correct for . So far, several methods have been proposed to address this issue and achieve more accurate measurement in the optical (quasi)diffusive regime,100–103 such as directly fitting the temporal profiles of PA signals,100,103 analyzing their acoustic spectra,101 and measuring their dynamics.102
5.2. Exogenous Contrast Agents
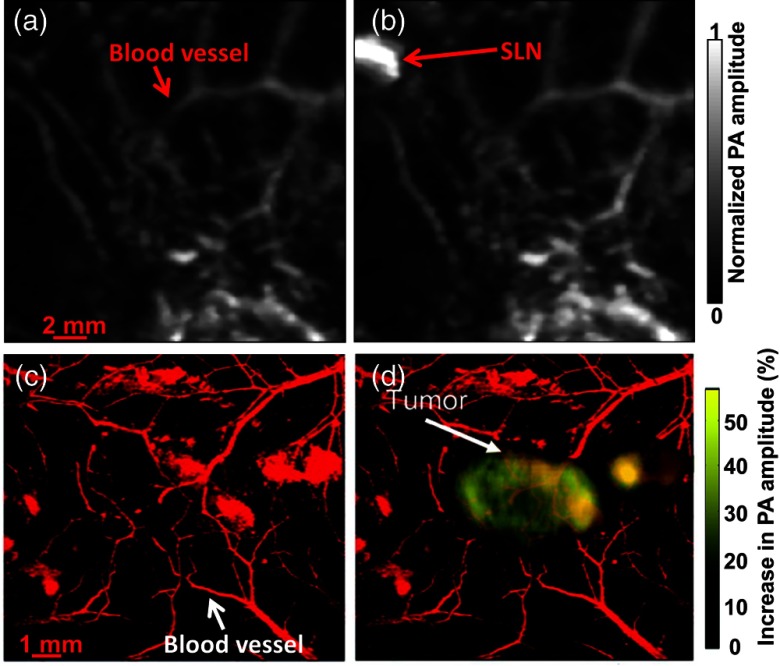
Compared with endogenous contrast agents, exogenous ones can be engineered to absorb at specific wavelengths to maximize their detection sensitivities. In addition, exogenous agents can be made to bind to only certain molecules; thus, these molecules can be selectively imaged by PAT. So far, a variety of exogenous agents have been developed,9,104,105 including nanoparticles,106–109 organic dyes,110–115 and proteins.116,117 Recently, for PA imaging, agents with specially designed functions have been developed, such as photosensitizing,118,119 activatable,120 and switchable agents.121–123 Note that since hemoglobin and water have strong absorption in the visible and midinfrared regions, respectively, most of these exogenous agents are designed to work in the near-infrared window, i.e., from 700 to 1350 nm. Usually, to enable more accurate spectral decomposition, two or more wavelengths are chosen to image blood and exogenous contrasts separately. Figure 8 shows two examples of using exogenous contrast agents in PA imaging: methylene blue115 and gold nanoparticles.108 Before the contrasts were injected, only blood vessels could be detected, as shown in Figs. 8(a) and 8(c). However, after injecting the contrasts, a sentinel lymph node and tumor appeared with high contrast, as seen in Figs. 8(b) and 8(d), respectively.
Fig. 8.
PAT imaging aided by exogenous contrast agents. PA images acquired before (a) and after (b) methylene blue injection, showing a dramatic PA signal increase in a sentinel lymph node (SLN). PA images acquired (c) before and (d) 6 h after gold nanoparticle injection, showing a significant PA signal increase in a melanoma tumor. Reproduced with permission from Refs. 115 (a) and (b) and 108 (c) and (d).
6. Recent Applications
With its multiparameter and multiscale imaging capability, PAT has been applied in many different disciplines, including cardiology,77,124,125 dermatology,126–129 oncology,130–133 ophthalmology,67,69,134–136 gastroenterology,36–38,40,137–140 hematology,141–143 and neurology.144–147 In terms of imaging locations, PAT can be used for human breast imaging148–150 and small-animal imaging of the brain,70,151,152 ear,153–155 eye,134–136 liver,15 intestine,156 and skin.54,90 In terms of functionality, PAT has been widely used for anatomical,157,158 functional,159–161 molecular,9,82 and metabolic imaging.162,163 As for object size, PAT can detect objects ranging from organelles to human organs or whole-body small animals.11 PAT has been used for both small animal imaging (such as zebrafish,164 mice,165 rats,151 and rabbits166) and human imaging.72 In this review paper, rather than cover details of all the applications, we will simply list the most recent advances and significant applications of PAT.
6.1. High Speed Imaging of Mouse Brain Functions
PAT has been extensively applied for brain studies. Wang et al.47 reported the first in vivo mouse brain function study with PAT. Using a circular-view PACT system, they imaged rat brain responses to vibrational stimulations to whiskers. Because a single-element ultrasonic transducer with a center frequency of 3.5 MHz was used, both the frame rate and spatial resolution were limited. With newer techniques, both the frame rate and spatial resolution have been significantly improved. For example, using an ultrasonic transducer array with 512 elements, mouse brain imaging at one frame per 1.25 s has been achieved.48 Using OR-PAM, optical resolution mouse brain images, i.e., at micrometer or submicrometer level resolution, were obtained.167
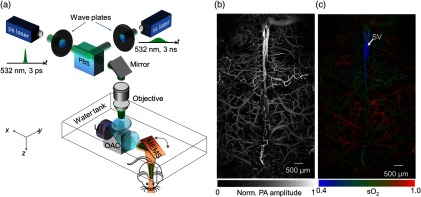
Recently, Yao et al.70 reported fast functional PAM (ffPAM) for mouse brain function imaging in action. Working as OR-PAM, this system has a lateral resolution of and an axial resolution of . Using a water-immersed microelectromechanical system (MEMS) scanning mirror along with a 500 kHz repetition rate laser, ffPAM has a 2-D frame rate of 400 Hz over a 3-mm scanning range. With a field of view, a 3-D volumetric rate of 1 Hz can be achieved. By using a single-wavelength pulse-width-based method (PW-), ffPAM can perform high speed imaging of up to a 1-D rate of 100 kHz. As shown in Fig. 9(a), to implement the PW- method, lasers with different pulse widths are used, i.e., 3 ps and 3 ns. Figure 9(b) shows a representative PA image of the mouse brain with the skull intact, where the cortex vasculature can be visualized in detail. With the PW- method, only 40 s were required to acquire the map shown in Fig. 9(c).
Fig. 9.
Fast functional PAM (ffPAM) of the mouse brain. (a) Schematic of the ffPAM system. MEMS, microelectromechanical system; OAC, optical-acoustic combiner; PBS, polarizing beam splitter; and UT, ultrasonic transducer. Anatomical (b) and (c) functional images of the mouse brain. , oxygen saturation of hemoglobin; and SV, skull vessel. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 70.
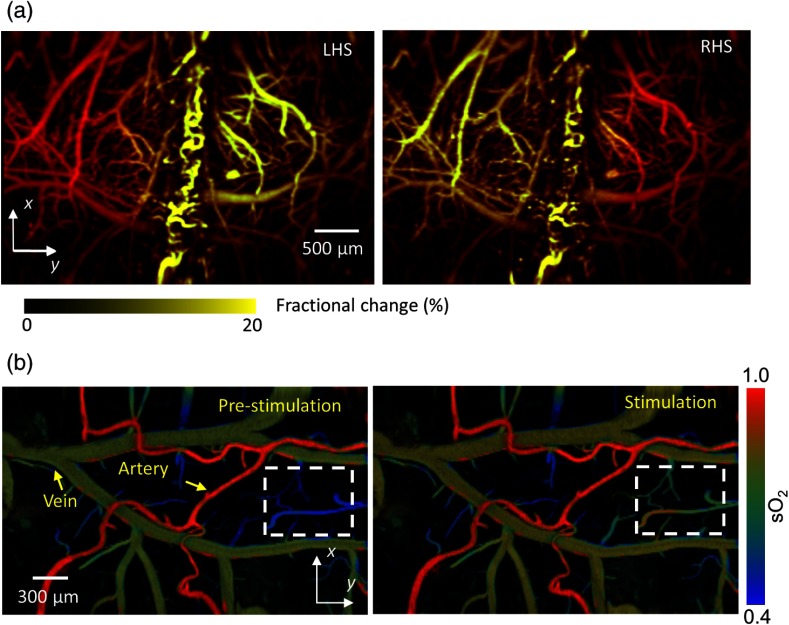
To further demonstrate the fast functional imaging capability, the authors studied mouse cortical responses to electrical stimulations of the hindlimbs. As shown in Fig. 10(a), upon stimulations, PA signals in the corresponding regions increased. In addition, levels increased in veins and deep capillary beds upon stimulation, as shown in Fig. 10(b). However, there was no arterial response, which is consistent with the fact that arterial blood had not reached the capillaries for oxygen exchange and thus maintained a high oxygenation level.
Fig. 10.
ffPAM of brain responses to electrical stimulations of the hindlimbs of mice. (a) Fractional PA amplitude changes during left hindlimb stimulation (LHS) and right hindlimb stimulation (RHS). (b) imaging (marked by the dashed box) before and during stimulations of the left hindlimb. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 70.
6.2. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Guidance in Patients with Breast Cancer
Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy is a standard of care in diagnosing cancer, including breast and melanoma cancers. Because the SLN is the first node in the lymphatic system that drains a tumor site, metastasis can be diagnosed by SLN biopsy. A positive biopsy result suggests that cancer has spread to the node and probably to distant organs. Recently, a handheld dual-modality ultrasound (US) and PAT system was used to accurately identify an SLN and thus to precisely guide SLN biopsy.168
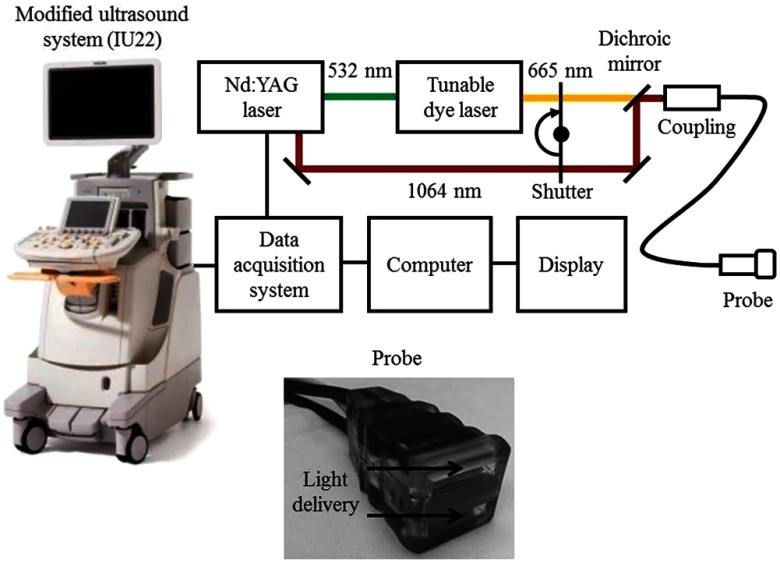
The dual-modality system was modified from a clinical US scanner (iU22, Philips Healthcare). To highlight SLNs in patients, a very common clinical contrast agent, methylene blue, was used. As shown in Fig. 11, laser pulses at two wavelengths of 665 and 1064 nm spectrally differentiated methylene blue from other major absorbers, such as blood. The pulse width was around 6.5 ns, and the pulse repetition rate was 10 Hz. With a custom-built data acquisition computer, this system could achieve a frame rate of 5 Hz for coregistered US and PA imaging. To improve the detection sensitivity and operation convenience, the light delivery fiber bundles and ultrasonic transducer array were integrated into a single probe, as shown in Fig. 11. Because the probe is handheld, it is convenient for physicians to operate for SLN biopsy guidance.
Fig. 11.
Schematic of the dual-modality ultrasound and photoacoustic system for SLN detection. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 168.
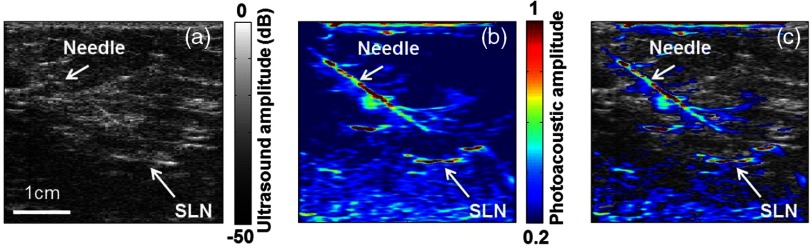
As shown in Fig. 12, by combining both US and PA, the SLN in a patient with breast cancer can be clearly detected. In addition, taking advantage of its high frame rate, this system can provide guidance for fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) with minimal invasiveness. Because both the SLN and the needle can be imaged with high contrast, FNAB can be performed with high accuracy.
Fig. 12.
In vivo images of a human axilla acquired by US (a), PA (b), and both (c). Reproduced with permission from Ref. 168.
6.3. Multiscale Photoacoustic Tomography with Photo-Switchable Protein Contrast
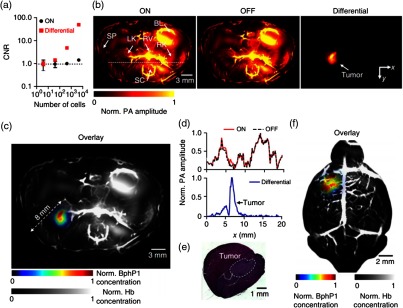
A reversibly switchable bacterial phytochrome, Rhodopseudomonas palustris (BphP1), has been recently combined with PAT for deep molecular imaging with improved detection sensitivity and spatial resolution.121 BphP1 has two states: Pfr and Pr. Upon 730- to 790-nm light illumination, it undergoes a Pfr→Pr photoconversion; while upon 630- to 690-nm light illumination, Pr→Pfr photoconversion happens. For simplicity, the Pfr state of BphP1 was denoted as the ON state and the Pr state as the OFF state. In the reported work, 780 nm light was used for Pfr→Pr photoconversion, and 630-nm light was used for Pr→Pfr photoconversion. Because the background absorbers, primarily blood, did not have the same switchable properties as BphP1, taking differential images largely suppressed the background signals and thus increased the detection sensitivity for BphP1-expressing tumors in deep tissue.
First implementing BphP1 with a circular-view PACT system, the authors observed a noise-equivalent detection sensitivity of U87 human glioblastoma cells expressing BphP1, as shown in Fig. 13(a). With the single-wavelength differential method, the CNR was about 34-fold higher than the two-wavelength spectral unmixing method. In the in vivo experiment, a mouse was imaged 1 week after injection of BphP1-expressing U87 cells into its left kidney. As shown in Fig. 13(b), although major organs, such as the skin, kidneys, spleen, and bladder, can all be clearly imaged, the tumor in the left kidney could not be detected because of the overwhelming blood signals. However, after 20 cycles of photoswitching, the differential image showed the tumor at depths up to 8 mm with high contrast, as seen in Figs. 13(b) and 13(c). The line profiles in Fig. 13(b) show that while the background blood signals remained unchanged, the photoswitchable tumor had clearly different signals in the ON- and OFF-state images [Fig. 13(d)]. A histological examination taken after PA imaging confirmed the tumor, as shown in Fig. 13(e). Another tumor detection experiment, in a mouse brain, also showed the superior sensitivity of the BphP1-enhanced PACT system, as shown in Fig. 13(f).
Fig. 13.
Circular-view PACT system combined with reversely switchable BphP1 for deep imaging. (a) Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of U87 cells imaged by PACT at 10-mm depth. (b) Whole-body mouse images acquired with BphP1 at different state. The differential image clearly shows that the tumor is at the left kidney. (c) An overlay of the differential image (in color) and the blood-dominated OFF-state image (in grayscale). (d) Normalized PA amplitude along the dashed line in (b), showing the contrast enhancement of the tumor in the differential image. (e) A histology image of the left kidney showing the tumor region. (f) PACT image of a mouse brain with a U87 tumor expressing BphP1. The tumor was beneath the scalp. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 121.
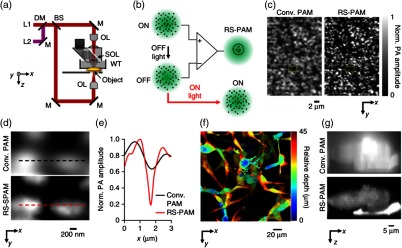
Combined with a high NA (1.4 in this work) OR-PAM system [Fig. 14(a)], this reversely switchable protein can also be used for super-resolution PA imaging (RS-SPAM). As shown in Fig. 14(b), because the switching-off rate is proportional to the local excitation intensity, PA signals from the center of the excitation spot will decay faster than those from the periphery. By fitting the nonlinear signal-decay process, a high-order coefficient can be extracted and thus subdiffraction resolution can be achieved. As shown in Figs. 14(c)–14(g), RS-SPAM showed much finer lateral and axial resolutions. The lateral resolution was quantified to be , which is about twofold better than that of conventional PAM, and the axial resolution was around 400 nm in RS-SPAM, which was around 75 times better than that of conventional PAM.
Fig. 14.
Reversely switchable BphP1-enhanced super-resolution PAM (RS-SPAM). (a) Schematic of the RS-SPAM system. (b) Subdiffraction-resolution principle. In the diffraction-limited excitation volume (green), part of the ON-state BphP1 molecules (black dots) are switched to the OFF state, where the switching rate is proportional to the local optical intensity. The differential signals generate super-resolution images. (c) Conventional (Conv.) PAM and RS-SPAM images of BphP1-expressing bacteria, showing the superior lateral resolution of RS-SPAM. (d) Zoomed-in images of the dashed box areas in (c). (e) Normalized PA amplitude along the dashed line in (d). (f) Depth-encoded RS-SPAM image of BphP1-expressing U87 cells. (g) x-z cross images of two stacked U87 cells, showing the finer axial resolution of RS-SPAM. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 121.
7. Summary
In summary, PAT is a highly scalable imaging modality with major implementations of PAM and PACT. In PAM, light is focused into the target and a focused transducer is typically used for the signal detection. Thus, its lateral resolution is determined by either the optical focus (OR-PAM) or acoustic focus (AR-PAM), depending on which one is tighter. In OR-PAM, the lateral resolution is given by , where is the light wavelength, and is the NA of the optical focusing lens. In AR-PAM, the lateral resolution is given by , where is the central acoustic wavelength of the ultrasonic transducer, and is the NA of the acoustic lens. The difference in the scaling factors arises because optical excitation is based on light intensity, while ultrasonic detection is based on acoustic amplitude. In both cases, the axial resolution is given by , where is the speed of sound in soft tissue, and is the bandwidth of the ultrasonic transducer. This axial resolution formula also applies to PACT systems. However, unlike PAM, lateral resolutions in PACT are usually not a constant. Thus, we can see that by choosing different optical focusing lenses or ultrasonic transducers, both lateral and axial resolution can be changed. Super optical resolution has been achieved in OR-PAM.169 In addition, because acoustic attenuation in tissues increases with the acoustic frequency, ultrasonic transducers with different center frequencies should be chosen according to the desired imaging penetration limit. The maximum penetration achieved in PA images is with a lateral resolution about .11
PAT is also a multiparameter imaging modality. In most of the cases, because hemoglobin provides the highest contrast in biological imaging, most studies focus on extracting and studying blood-related parameters, such as blood vessel diameter,31 blood flow speed,170,171 hemoglobin oxygen concentration,19,31 blood pulse wave velocity,172 and the metabolic rate of oxygen.162 PAT has provided valuable information for studying vasculature-related diseases, such as stroke,173 diabetes,174 and atherosclerosis.98,175,176 In addition, because neural activities are closely related to hemodynamics, measuring these hemodynamic parameters is also useful for neurological studies, such as studies on epilepsy,177 resting state functional connectivity,152 and stimulation responses.147 Because of its high contrast in comparison to other absorbers, such as melanin54 and DNA/RNA,79 PAT can also image other important biological parameters. Imaging melanin can provide the depth of melanoma, as well as its rate of growth and metastatic rate,54 which are all very important parameters in diagnosing and treating melanoma patients. Imaging DNA/RNA provides a tool for label-free measurement of cell nuclear density, which potentially can be used for tumor demarcation.
PAT has become one of the fastest growing fields in biomedical imaging. So far, PAT has translated several important applications into clinics, which may help solve existing problems in health care. For example, noninvasive detection of SLNs168 in patients can potentially provide minimally invasive cancer staging, and quantification of melanoma depth54 can potentially guide more accurate surgeries, both reducing morbidity and costs. With advances in new techniques, we anticipate that PAT will provide valuable information for disease diagnosis as well as treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Professor James Ballard for manuscript editing. This work was sponsored in part by National Institutes of Health Grant Nos. DP1 EB016986 (NIH Director’s Pioneer Award), R01 CA186567 (NIH Director’s Transformative Research Award), and S10 RR026922. L. V. W. has a financial interest in Microphotoacoustics, Inc., which, however, did not support this work.
Biographies
Yong Zhou is currently a graduate student in biomedical engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, under the supervision of Dr. Lihong V. Wang, Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor. His research focuses on the development of photoacoustic imaging systems.
Junjie Yao received his BE and ME degrees in biomedical engineering from Tsinghua University, Beijing, in 2006 and 2008, respectively, under the tutelage of Prof. Jing Bai. He received his PhD in biomedical engineering at Washington University in St. Louis (WUSTL), in 2013, under the tutelage of Prof. Lihong V. Wang. He is currently a postdoctoral research associate at WUSTL. His research interest is in photoacoustic, optical, and ultrasound imaging technologies in biomedicine.
Lihong V. Wang is the Beare distinguished professor at Washington University, has published 425 journal articles (h-index = 96, citations >36,000) and delivered 420 keynote/plenary/invited talks. His laboratory published the first functional photoacoustic CT and 3-D photoacoustic microscopy. He received the Goodman Award for his Biomedical Optics textbook, NIH Director’s Pioneer Award, OSA Mees Medal, IEEE Technical Achievement and Biomedical Engineering Awards, SPIE Britton Chance Biomedical Optics Award, and an honorary doctorate from Lund University, Sweden.
References
- 1.Wang L. V., Gao L., “Photoacoustic microscopy and computed tomography: from bench to bedside,” Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 16, 155–185 (2014). 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-104553 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang L. V., “Tutorial on photoacoustic microscopy and computed tomography,” IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 14(1), 171–179 (2008). 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.913398 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beard P., “Biomedical photoacoustic imaging,” Interface Focus 1(4), 602–631 (2011). 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yao J., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic tomography: fundamentals, advances and prospects,” Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 6(5), 332–345 (2011). 10.1002/cmmi.443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ntziachristos V., “Going deeper than microscopy: the optical imaging frontier in biology,” Nat. Methods 7(8), 603–614 (2010). 10.1038/nmeth.1483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hu S., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic imaging and characterization of the microvasculature,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(1), 011101 (2010). 10.1117/1.3281673 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li C., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic tomography and sensing in biomedicine,” Phys. Med. Biol. 54(19), R59–R97 (2009). 10.1088/0031-9155/54/19/R01 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang L. V., “Multiscale photoacoustic microscopy and computed tomography,” Nat. Photonics 3(9), 503–509 (2009). 10.1038/nphoton.2009.157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim C., Favazza C., Wang L. V., “In vivo photoacoustic tomography of chemicals: high-resolution functional and molecular optical imaging at new depths,” Chem. Rev. 110(5), 2756–2782 (2010). 10.1021/cr900266s [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cai X., et al. , “Photoacoustic microscopy in tissue engineering,” Mater. Today 16(3), 67–77 (2013). 10.1016/j.mattod.2013.03.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang L. V., Hu S., “Photoacoustic tomography: in vivo imaging from organelles to organs,” Science 335(6075), 1458–1462 (2012). 10.1126/science.1216210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yao J., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic microscopy,” Laser Photon. Rev. 7(5), 758–778 (2013). 10.1002/lpor.2013.7.issue-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yao J., Song L., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic microscopy superdepth, superresolution, and superb contrast,” IEEE Pulse 6(3), 34–37 (2015). 10.1109/MPUL.2015.2409100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yao J., Wang L. V., “Sensitivity of photoacoustic microscopy,” Photoacoustics 2(2), 87–101 (2014). 10.1016/j.pacs.2014.04.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xia J., Wang L. V., “Small-animal whole-body photoacoustic tomography: a review,” IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 61(5), 1380–1389 (2014). 10.1109/TBME.2013.2283507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yao J., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic brain imaging: from microscopic to macroscopic scales,” Neurophotonics 1(1), 011003 (2014). 10.1117/1.NPh.1.1.011003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mallidi S., Luke G. P., Emelianov S., “Photoacoustic imaging in cancer detection, diagnosis, and treatment guidance,” Trends Biotechnol. 29(5), 213–221 (2011). 10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.01.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cox B., et al. , “Quantitative spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging: a review,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 061202 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.061202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu S., Wang L. V., “Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy: auscultation of biological systems at the cellular level,” Biophys. J. 105(4), 841–847 (2013). 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.07.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang L. V., “Prospects of photoacoustic tomography,” Med. Phys. 35(12), 5758–5767 (2008). 10.1118/1.3013698 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang L. V., “Multiscale photoacoustic microscopy and computed tomography,” Nat. Photonics 3(9), 503–509 (2009). 10.1038/nphoton.2009.157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yao D. K., et al. , “Photoacoustic measurement of the Gruneisen parameter of tissue,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(1), 017007 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.1.017007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gao L., et al. , “Intracellular temperature mapping with fluorescence-assisted photoacoustic-thermometry,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(19) (2013). 10.1063/1.4807140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xu M. H., Wang L. H. V., “Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77(4), 041101 (2006). 10.1063/1.2195024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu M. H., Wang L. H. V., “Universal back-projection algorithm for photoacoustic computed tomography,” Phys. Rev. E 71(1), 016706 (2005). 10.1117/12.589146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Treeby B. E., Cox B. T., “k-Wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(2), 021314 (2010). 10.1117/1.3360308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xu M., Wang L. V., “Analytic explanation of spatial resolution related to bandwidth and detector aperture size in thermoacoustic or photoacoustic reconstruction,” Phys. Rev. E 67(5 Pt 2), 056605 (2003). 10.1103/PhysRevE.67.056605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang K., et al. , “Investigation of iterative image reconstruction in three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography,” Phys. Med. Biol. 57(17), 5399–5423 (2012). 10.1088/0031-9155/57/17/5399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang K., et al. , “Discrete imaging models for three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography using radially symmetric expansion functions,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(5), 1180–1193 (2014). 10.1109/TMI.2014.2308478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang K., et al. , “An imaging model incorporating ultrasonic transducer properties for three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(2), 203–214 (2011). 10.1109/TMI.2010.2072514 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hu S., Maslov K., Wang L. V., “Second-generation optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy with improved sensitivity and speed,” Opt. Lett. 36(7), 1134–1136 (2011). 10.1364/OL.36.001134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Maslov K., et al. , “Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for in vivo imaging of single capillaries,” Opt. Lett. 33(9), 929–931 (2008). 10.1364/OL.33.000929 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang H. F., Maslov K., Wang L. H. V., “In vivo imaging of subcutaneous structures using functional photoacoustic microscopy,” Nat. Protoc. 2(4), 797–804 (2007). 10.1038/nprot.2007.108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang H. F., et al. , “Functional photoacoustic microscopy for high-resolution and noninvasive in vivo imaging,” Nat. Biotechnol. 24(7), 848–851 (2006). 10.1038/nbt1220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maslov K., Stoica G., Wang L. H. V., “In vivo dark-field reflection-mode photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 30(6), 625–627 (2005). 10.1364/OL.30.000625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yang J. M., et al. , “Photoacoustic endoscopy,” Opt. Lett. 34(10), 1591–1593 (2009). 10.1364/OL.34.001591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yang J. M., et al. , “Catheter-based photoacoustic endoscope,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(6), 066001 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.6.066001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yang J. M., et al. , “Optical-resolution photoacoustic endomicroscopy in vivo,” Biomed. Opt. Express. 6(3), 918–932 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.000918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yang J. M., et al. , “Simultaneous functional photoacoustic and ultrasonic endoscopy of internal organs in vivo,” Nat. Med. 18(8), 1297–1302 (2012). 10.1038/nm.2823 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li C. Y., et al. , “Urogenital photoacoustic endoscope,” Opt. Lett. 39(6), 1473–1476 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.001473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yeh C., et al. , “Three-dimensional arbitrary trajectory scanning photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biophotonics 8(4), 303–308 (2015). 10.1002/jbio.v8.4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liang J. Y., et al. , “Random-access optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy using a digital micromirror device,” Opt. Lett. 38(15), 2683–2686 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.002683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kruger R. A., et al. , “Thermoacoustic molecular imaging of small animals,” Mol. Imaging 2(2), 113–123 (2003). 10.1162/153535003322331993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Brecht H. P., et al. , “Whole-body three-dimensional optoacoustic tomography system for small animals,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(6), 064007 (2009). 10.1117/1.3259361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kruger R. A., et al. , “Photoacoustic angiography of the breast,” Med. Phys. 37(11), 6096–6100 (2010). 10.1118/1.3497677 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kruger R. A., et al. , “Dedicated 3D photoacoustic breast imaging,” Med. Phys. 40(11), 113301 (2013). 10.1118/1.4824317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang X. D., et al. , “Noninvasive laser-induced photoacoustic tomography for structural and functional in vivo imaging of the brain,” Nat. Biotechnol. 21(7), 803–806 (2003). 10.1038/nbt839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xia J., et al. , “Whole-body ring-shaped confocal photoacoustic computed tomography of small animals in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(5), 050506 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.5.050506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Li C. H., Wang L. H. V., “Photoacoustic tomography of the mouse cerebral cortex with a high-numerical-aperture-based virtual point detector,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(2), 024047 (2009). 10.1117/1.3122365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li C. H., et al. , “Real-time photoacoustic tomography of cortical hemodynamics in small animals,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(1), 010509 (2010). 10.1117/1.3302807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Buehler A., et al. , “Video rate optoacoustic tomography of mouse kidney perfusion,” Opt. Lett. 35(14), 2475–2477 (2010). 10.1364/OL.35.002475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nie L. M., et al. , “Photoacoustic tomography through a whole adult human skull with a photon recycler,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(11), 110506 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.11.110506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang Y., et al. , “In vivo three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging based on a clinical matrix array ultrasound probe,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 061208 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.061208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhou Y., et al. , “Handheld photoacoustic probe to detect both melanoma depth and volume at high speed in vivo,” J. Biophotonics 1(7) (2015). 10.1002/jbio.201400143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang E., Laufer J., Beard P., “Backward-mode multiwavelength photoacoustic scanner using a planar Fabry-Perot polymer film ultrasound sensor for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of biological tissues,” Appl. Opt. 47(4), 561–577 (2008). 10.1364/AO.47.000561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Piras D., et al. , “Photoacoustic imaging of the breast using the twente photoacoustic mammoscope: present status and future perspectives,” IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electronics 16(4), 730–739 (2010). 10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2034870 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Heijblom M., et al. , “Visualizing breast cancer using the Twente photoacoustic mammoscope: What do we learn from twelve new patient measurements?” Opt. Express. 20(11), 11582–11597 (2012). 10.1364/OE.20.011582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Heijblom M., et al. , “Appearance of breast cysts in planar geometry photoacoustic mammography using 1064-nm excitation,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(12), 126009 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.12.126009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Laufer J., et al. , “Three-dimensional noninvasive imaging of the vasculature in the mouse brain using a high resolution photoacoustic scanner,” Appl. Optics 48(10), D299–D306 (2009). 10.1364/AO.48.00D299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Laufer J., et al. , “In vivo preclinical photoacoustic imaging of tumor vasculature development and therapy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(5), 056016 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.5.056016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Xia J., et al. , “Wide-field two-dimensional multifocal optical-resolution photoacoustic-computed microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 38(24), 5236–5239 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.005236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Laufer J., et al. , “In vivo photoacoustic imaging of mouse embryos,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 061220 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.061220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zhou Y., Yao J. J., Wang L. H. V., “Optical clearing-aided photoacoustic microscopy with enhanced resolution and imaging depth,” Opt. Lett. 38(14), 2592–2595 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.002592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Liu Y., Zhang C., Wang L. H. V., “Effects of light scattering on optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(12), 126014 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.12.126014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hai P. F., et al. , “Near-infrared optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 39(17), 5192–5195 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.005192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hu S., et al. , “Label-free photoacoustic ophthalmic angiography,” Opt. Lett. 35(1), 1–3 (2010). 10.1364/OL.35.000001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wu N., et al. , “High-resolution dual-modality photoacoustic ocular imaging,” Opt. Lett. 39(8), 2451–2454 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.002451 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Song W., et al. , “Integrating photoacoustic ophthalmoscopy with scanning laser ophthalmoscopy, optical coherence tomography, and fluorescein angiography for a multimodal retinal imaging platform,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 061206 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.061206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu X. J., et al. , “Optical coherence photoacoustic microscopy for in vivo multimodal retinal imaging,” Opt. Lett. 40(7), 1370–1373 (2015). 10.1364/OL.40.001370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yao J. J., et al. , “High-speed label-free functional photoacoustic microscopy of mouse brain in action,” Nat. Methods 12(5), 407–410 (2015). 10.1038/nmeth.3336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hu S., et al. , “Functional transcranial brain imaging by optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(4), 040503 (2009). 10.1117/1.3194136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhou Y., et al. , “Microcirculatory changes identified by photoacoustic microscopy in patients with complex regional pain syndrome type I after stellate ganglion blocks,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(8), 086017 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.8.086017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zhang H. F., et al. , “In vivo volumetric imaging of subcutaneous microvasculature by photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Express. 14(20), 9317–9323 (2006). 10.1364/OE.14.009317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Favazza C. P., Cornelius L. A., Wang L. H. V., “In vivo functional photoacoustic microscopy of cutaneous microvasculature in human skin,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(2), 026004 (2011). 10.1117/1.3536522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Favazza C. P., et al. , “In vivo photoacoustic microscopy of human cutaneous microvasculature and a nevus,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(1), 016015 (2011). 10.1117/1.3528661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zhang C., Maslov K., Wang L. H. V., “Subwavelength-resolution label-free photoacoustic microscopy of optical absorption in vivo,” Opt. Lett. 35(19), 3195–3197 (2010). 10.1364/OL.35.003195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Wang L. D., et al. , “Video-rate functional photoacoustic microscopy at depths,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(10), 106007 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.10.106007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ke H. X., et al. , “Performance characterization of an integrated ultrasound, photoacoustic, and thermoacoustic imaging system,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(5), 056010 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.5.056010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yao D. K., et al. , “In vivo label-free photoacoustic microscopy of cell nuclei by excitation of DNA and RNA,” Opt. Lett. 35(24), 4139–4141 (2010). 10.1364/OL.35.004139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Yao D. K., et al. , “Optimal ultraviolet wavelength for in vivo photoacoustic imaging of cell nuclei,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(5), 056004 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.5.056004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhang C., et al. , “Label-free photoacoustic microscopy of cytochromes,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(2), 020504 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.2.020504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Zhou Y., et al. , “Photoacoustic microscopy of bilirubin in tissue phantoms,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(12), 126019 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.12.126019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhang C., et al. , “Label-free photoacoustic microscopy of myocardial sheet architecture,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 060506 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.060506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Goldschmidt B. S., et al. , “Photoacoustic measurement of refractive index of dye solutions and myoglobin for biosensing applications,” Biomed. Opt. Express. 4(11), 2463–2476 (2013). 10.1364/BOE.4.002463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Zhang H. F., et al. , “Imaging of hemoglobin oxygen saturation variations in single vessels in vivo using photoacoustic microscopy,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(5), 053901 (2007). 10.1063/1.2435697 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhou Y., et al. , “Calibration-free absolute quantification of particle concentration by statistical analyses of photoacoustic signals in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(3), 037001 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.3.037001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Tang M., et al. , “Noninvasive photoacoustic microscopy of methemoglobin in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 20(3), 036007 (2015). 10.1117/1.JBO.20.3.036007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chen Z. J., Yang S. H., Xing D., “In vivo detection of hemoglobin oxygen saturation and carboxyhemoglobin saturation with multiwavelength photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 37(16), 3414–3416 (2012). 10.1364/OL.37.003414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Staley J., et al. , “Growth of melanoma brain tumors monitored by photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(4), 040510 (2010). 10.1117/1.3478309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Zhou Y., et al. , “Handheld photoacoustic microscopy to detect melanoma depth in vivo,” Opt. Lett. 39(16), 4731–4734 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.004731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wang H. W., et al. , “Label-free bond-selective imaging by listening to vibrationally excited molecules,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 106(23), 238106 (2011). 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.238106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yakovlev V. V., et al. , “Stimulated Raman photoacoustic imaging,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107(47), 20335–20339 (2010). 10.1073/pnas.1012432107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yakovlev V. V., et al. , “Monitoring stimulated Raman scattering with photoacoustic detection,” Opt. Lett. 36(7), 1233–1235 (2011). 10.1364/OL.36.001233 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Xu Z., Zhu Q. I., Wang L. H. V., “In vivo photoacoustic tomography of mouse cerebral edema induced by cold injury,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(6), 066020 (2011). 10.1117/1.3584847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Xu Z., Li C. H., Wang L. V., “Photoacoustic tomography of water in phantoms and tissue,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(3), 036019 (2010). 10.1117/1.3443793 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kottmann J., et al. , “Glucose sensing in human epidermis using mid-infrared photoacoustic detection,” Biomed. Opt. Express 3(4), 667–680 (2012). 10.1364/BOE.3.000667 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Pleitez M. A., et al. , “In vivo noninvasive monitoring of glucose concentration in human epidermis by mid-infrared pulsed photoacoustic spectroscopy,” Anal. Chem. 85(2), 1013–1020 (2013). 10.1021/ac302841f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Wang P., et al. , “High-speed intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipid-laden atherosclerotic plaque enabled by a 2-kHz barium nitrite Raman laser,” Sci. Rep. 4 (2014). 10.1038/srep06889 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wang B., et al. , “Detection of lipid in atherosclerotic vessels using ultrasound-guided spectroscopic intravascular photoacoustic imaging,” Opt. Express. 18(5), 4889–4897 (2010). 10.1364/OE.18.004889 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wang Y., Wang R. K., “Photoacoustic recovery of an absolute optical absorption coefficient with an exact solution of a wave equation,” Phys. Med. Biol. 53(21), 6167–6177 (2008). 10.1088/0031-9155/53/21/018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Guo Z. J., et al. , “Quantitative photoacoustic microscopy of optical absorption coefficients from acoustic spectra in the optical diffusive regime,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 066011 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.066011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Xia J., et al. , “Calibration-free quantification of absolute oxygen saturation based on the dynamics of photoacoustic signals,” Opt. Lett. 38(15), 2800–2803 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.002800 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Petrov Y. Y., et al. , “Multiwavelength optoacoustic system for noninvasive monitoring of cerebral venous oxygenation: a pilot clinical test in the internal jugular vein,” Opt. Lett. 31(12), 1827–1829 (2006). 10.1364/OL.31.001827 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Zackrisson S., van de Ven S. M. W. Y., Gambhir S. S., “Light in and sound out: emerging translational strategies for photoacoustic imaging,” Cancer Res. 74(4), 979–1004 (2014). 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Luke G. P., Yeager D., Emelianov S. Y., “Biomedical applications of photoacoustic imaging with exogenous contrast agents,” Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40(2), 422–437 (2012). 10.1007/s10439-011-0449-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.De La Zerda A., et al. , “Carbon nanotubes as photoacoustic molecular imaging agents in living mice,” Nat. Nanotechnol. 3(9), 557–562 (2008). 10.1038/nnano.2008.231 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kim C., et al. , “In vivo photoacoustic mapping of lymphatic systems with plasmon-resonant nanostars,” J. Mater. Chem. 21(9), 2841–2844 (2011). 10.1039/c0jm04194g [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kim C., et al. , “In vivo molecular photoacoustic tomography of melanomas targeted by bioconjugated gold nanocages,” ACS Nano 4(8), 4559–4564 (2010). 10.1021/nn100736c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Pan D. P. J., et al. , “Photoacoustic sentinel lymph node imaging with self-assembled copper neodecanoate nanoparticles,” ACS Nano 6(2), 1260–1267 (2012). 10.1021/nn203895n [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Yao J. J., et al. , “Evans blue dye-enhanced capillary-resolution photoacoustic microscopy in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(5), 054049 (2009). 10.1117/1.3251044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Ashkenazi S., “Photoacoustic lifetime imaging of dissolved oxygen using methylene blue,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(4), 040501 (2010). 10.1117/1.3465548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Wang X. D., et al. , “Noninvasive photoacoustic angiography of animal brains in vivo with near-infrared light and an optical contrast agent,” Opt. Lett. 29(7), 730–732 (2004). 10.1364/OL.29.000730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ku G., Wang L. H. V., “Deeply penetrating photoacoustic tomography in biological tissues enhanced with an optical contrast agent,” Opt. Lett. 30(5), 507–509 (2005). 10.1364/OL.30.000507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Chatni M. R., et al. , “Functional photoacoustic microscopy of pH,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(10), 100503 (2011). 10.1117/1.3644495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Song K. H., et al. , “Noninvasive photoacoustic identification of sentinel lymph nodes containing methylene blue in vivo in a rat model,” J. Biomed. Opt. 13(5), 054033 (2008). 10.1117/1.2976427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Li L., et al. , “Photoacoustic imaging of lacZ gene expression in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 12(2), 020504 (2007). 10.1117/1.2717531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Cai X., et al. , “Multi-scale molecular photoacoustic tomography of gene expression,” PLoS One 7(8), e43999 (2012). 10.1371/journal.pone.0043999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ho C. J. H., et al. , “Multifunctional photosensitizer-based contrast agents for photoacoustic imaging,” Sci. Rep. 4 (2014). 10.1038/srep05342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Attia A. B., et al. , “Phthalocyanine photosensitizers as contrast agents for in vivo photoacoustic tumor imaging,” Biomed. Opt. Express 6(2), 591–598 (2015). 10.1364/BOE.6.000591 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Morgounova E., et al. , “Photoacoustic lifetime contrast between methylene blue monomers and self-quenched dimers as a model for dual-labeled activatable probes,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(5), 056004 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.5.056004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yao J., et al. , “Multiscale photoacoustic tomography using reversibly switchable bacterial phytochrome as a near-infrared photochromic probe,” Nat Methods (2015). 10.1038/nmeth.3656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Stiel A. C., et al. , “High-contrast imaging of reversibly switchable fluorescent proteins via temporally unmixed multispectral optoacoustic tomography,” Opt. Lett. 40(3), 367–370 (2015). 10.1364/OL.40.000367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Galanzha E. I., et al. , “Photoacoustic and photothermal cytometry using photoswitchable proteins and nanoparticles with ultrasharp resonances,” J. Biophotonics 8(1–2), 81–93 (2015). 10.1002/jbio.201300140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Zemp R. J., et al. , “Realtime photoacoustic microscopy of murine cardiovascular dynamics,” Opt. Express. 16(22), 18551–18556 (2008). 10.1364/OE.16.018551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Taruttis A., et al. , “Real-time imaging of cardiovascular dynamics and circulating gold nanorods with multispectral optoacoustic tomography,” Opt. Express. 18(19), 19592–19602 (2010). 10.1364/OE.18.019592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Song L. A., et al. , “Ultrasound-array-based real-time photoacoustic microscopy of human pulsatile dynamics in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 15(2), 021303 (2010). 10.1117/1.3333545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Aizawa K., et al. , “Photoacoustic monitoring of burn healing process in rats,” J. Biomed. Opt. 13(6), 064020 (2008). 10.1117/1.3028005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Sato S., et al. , “Photoacoustic diagnosis of burns in rats,” J. Trauma 59(6), 1450–1455 (2005). 10.1097/01.ta.0000197389.94466.04 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Zhang H. F., et al. , “Imaging acute thermal burns by photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 11(5), 054033 (2006). 10.1117/1.2355667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.de la Zerda A., et al. , “Ultrahigh sensitivity carbon nanotube agents for photoacoustic molecular imaging in living mice,” Nano Lett. 10(6), 2168–2172 (2010). 10.1021/nl100890d [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Li M. L., et al. , “In-vivo photoacoustic microscopy of nanoshell extravasation from solid tumor vasculature,” J. Biomed. Opt. 14(1), 010507 (2009). 10.1117/1.3081556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Kang J., et al. , “Photoacoustic imaging of breast microcalcifications: a validation study with 3-dimensional ex vivo data and spectrophotometric measurement,” J. Biophotonics 8(1–2), 71–80 (2015). 10.1002/jbio.201300100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Sim C., et al. , “Photoacoustic-based nanomedicine for cancer diagnosis and therapy,” J. Control Release 203, 118-125 (2015). 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Nam S. Y., Emelianov S. Y., “Array-based real-time ultrasound and photoacoustic ocular imaging,” J. Opt. Soc. Korea 18(2), 151–155 (2014). 10.3807/JOSK.2014.18.2.151 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Song W., et al. , “Multimodal photoacoustic ophthalmoscopy in mouse,” J. Biophotonics 6(6–7), 505–512 (2013). 10.1002/jbio.v6.6/7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Liu T., et al. , “Fundus camera guided photoacoustic ophthalmoscopy,” Curr. Eye Res. 38(12), 1229–1234 (2013). 10.3109/02713683.2013.815219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Yang J. M., et al. , “Three-dimensional photoacoustic endoscopic imaging of the rabbit esophagus,” PLoS One 10(4) (2015). 10.1371/journal.pone.0120269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Hajireza P., Shi W., Zemp R., “Label-free in vivo GRIN-lens optical resolution photoacoustic micro-endoscopy,” Laser Phys. Lett. 10(5), 055603 (2013). 10.1088/1612-2011/10/5/055603 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Hajireza P., et al. , “Optical resolution photoacoustic microendoscopy with ultrasound-guided insertion and array system detection,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(9), 090502 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.9.090502 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Yang J. M., et al. , “A 2.5-mm diameter probe for photoacoustic and ultrasonic endoscopy,” Opt. Express 20(21), 23944–23953 (2012). 10.1364/OE.20.023944 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Kneipp M., et al. , “Functional real-time optoacoustic imaging of middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice,” PLoS One 9(4) (2014). 10.1371/journal.pone.0096118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Bai X. S., et al. , “Intravascular optical-resolution photoacoustic tomography with a 1.1 mm diameter catheter,” PLoS One 9(3) (2014). 10.1371/journal.pone.0092463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Galanzha E. I., et al. , “In vivo flow cytometry of circulating clots using negative photothermal and photoacoustic contrasts,” Cytom Part A 79A(10), 814–824 (2011). 10.1002/cyto.a.v79a.10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Liao L. D., et al. , “Transcranial imaging of functional cerebral hemodynamic changes in single blood vessels using in vivo photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 32(6), 938–951 (2012). 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Liao L. D., et al. , “Imaging brain hemodynamic changes during rat forepaw electrical stimulation using functional photoacoustic microscopy,” NeuroImage 52(2), 562–570 (2010). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Yao J. J., et al. , “Noninvasive photoacoustic computed tomography of mouse brain metabolism in vivo,” NeuroImage 64, 257-266 (2013). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.08.054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Tsytsarev V., et al. , “Photoacoustic microscopy of microvascular responses to cortical electrical stimulation,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(7), 076002 (2011). 10.1117/1.3594785 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Heijblom M., Steenbergen W., Manohar S., “Clinical photoacoustic breast imaging,” IEEE Pulse 6(3), 42–46 (2015). 10.1109/MPUL.2015.2409102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Gould T., Wang Q. Z., Pfefer T. J., “Optical-thermal light-tissue interactions during photoacoustic breast imaging,” Biomed. Opt. Express 5(3), 832–847 (2014). 10.1364/BOE.5.000832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Xia W. F., et al. , “An optimized ultrasound detector for photoacoustic breast tomography,” Med. Phys. 40(3), 032901 (2013). 10.1118/1.4792462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Lin L., et al. , “In vivo deep brain imaging of rats using oral-cavity illuminated photoacoustic computed tomography,” J. Biomed. Opt. 20(1), 016019 (2015). 10.1117/1.JBO.20.1.016019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Nasiriavanaki M., et al. , “High-resolution photoacoustic tomography of resting-state functional connectivity in the mouse brain,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(1), 21–26 (2014). 10.1073/pnas.1311868111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Zhang R. Y., et al. , “In vivo optically encoded photoacoustic flowgraphy,” Opt. Lett. 39(13), 3814–3817 (2014). 10.1364/OL.39.003814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Zhang C., et al. , “Slow-sound photoacoustic microscopy,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(16) (2013). 10.1063/1.4803444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Zhang C., et al. , “Reflection-mode submicron-resolution in vivo photoacoustic microscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(2), 020501 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.2.020501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Yao J. J., et al. , “Double-illumination photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 37(4), 659–661 (2012). 10.1364/OL.37.000659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Zou X. T., et al. , “Polydimethylsiloxane thin film characterization using all-optical photoacoustic mechanism,” Appl. Opt. 52(25), 6239–6244 (2013). 10.1364/AO.52.006239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Zhang E. Z., et al. , “In vivo high-resolution 3D photoacoustic imaging of superficial vascular anatomy,” Phys. Med. Biol. 54(4), 1035–1046 (2009). 10.1088/0031-9155/54/4/014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Zhou Y., et al. , “Calibration-free in vivo transverse blood flowmetry based on cross correlation of slow time profiles from photoacoustic microscopy,” Opt. Lett. 38(19), 3882–3885 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.003882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Yao J. J., et al. , “Absolute photoacoustic thermometry in deep tissue,” Opt. Lett. 38(24), 5228–5231 (2013). 10.1364/OL.38.005228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Liang J. Y., et al. , “Cross-correlation-based transverse flow measurements using optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy with a digital micromirror device,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(9), 096004 (2013). 10.1117/1.JBO.18.9.096004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Yao J. J., et al. , “Label-free oxygen-metabolic photoacoustic microscopy in vivo,” J. Biomed. Opt. 16(7), 076003 (2011). 10.1117/1.3594786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Ning B., et al. , “Ultrasound-aided multi-parametric photoacoustic microscopy of the mouse brain,” Sci. Rep. 5, 18775 (2015). 10.1038/srep18775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Li G., et al. , “Multiview Hilbert transformation for full-view photoacoustic computed tomography using a linear array,” J. Biomed. Opt. 20(6), 066010 (2015). 10.1117/1.JBO.20.6.066010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Xia J., et al. , “Retrospective respiration-gated whole-body photoacoustic computed tomography of mice,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(1), 016003 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.1.016003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hennen S. N., et al. , “Photoacoustic tomography imaging and estimation of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in ocular tissue of rabbits,” Exp. Eye Res. 138, 153–158 (2015). 10.1016/j.exer.2015.05.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Wang L. D., Maslov K., Wang L. H. V., “Single-cell label-free photoacoustic flowoxigraphy in vivo,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(15), 5759–5764 (2013). 10.1073/pnas.1215578110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Garcia-Uribe A., et al. , “Dual-modality photoacoustic and ultrasound imaging system for noninvasive sentinel lymph node detection in patients with breast cancer,” Sci. Rep. 5, 15748 (2015). 10.1038/srep15748 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Danielli A., et al. , “Label-free photoacoustic nanoscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 19(8), 086006 (2014). 10.1117/1.JBO.19.8.086006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Zhou Y., Liang J., Wang L. V., “Cuffing-based photoacoustic flowmetry in humans in the optical diffusive regime,” J. Biophotonics (2015). 10.1002/jbio.201500181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Zhou Y., et al. , “In vivo photoacoustic flowmetry at depths of the diffusive regime based on saline injection,” J. Biomed. Opt. 20(8), 087001 (2015). 10.1117/1.JBO.20.8.087001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Yeh C. H., et al. , “Photoacoustic microscopy of blood pulse wave,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(7), 070504 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.7.070504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Zhu X. H., et al. , “Simultaneous and noninvasive imaging of cerebral oxygen metabolic rate, blood flow and oxygen extraction fraction in stroke mice,” NeuroImage 64, 437–447 (2013). 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Krumholz A., et al. , “Functional photoacoustic microscopy of diabetic vasculature,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(6), 060502 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.6.060502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Yeager D., et al. , “Intravascular photoacoustic imaging of exogenously labeled atherosclerotic plaque through luminal blood,” J. Biomed. Opt. 17(10), 106016 (2012). 10.1117/1.JBO.17.10.106016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Wu M., et al. , “Impact of device geometry on the imaging characteristics of an intravascular photoacoustic catheter,” Appl. Opt. 53(34), 8131–8139 (2014). 10.1364/AO.53.008131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Wang B., et al. , “Photoacoustic tomography system for noninvasive real-time three-dimensional imaging of epilepsy,” Biomed. Opt. Express 3(6), 1427–1432 (2012). 10.1364/BOE.3.001427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]