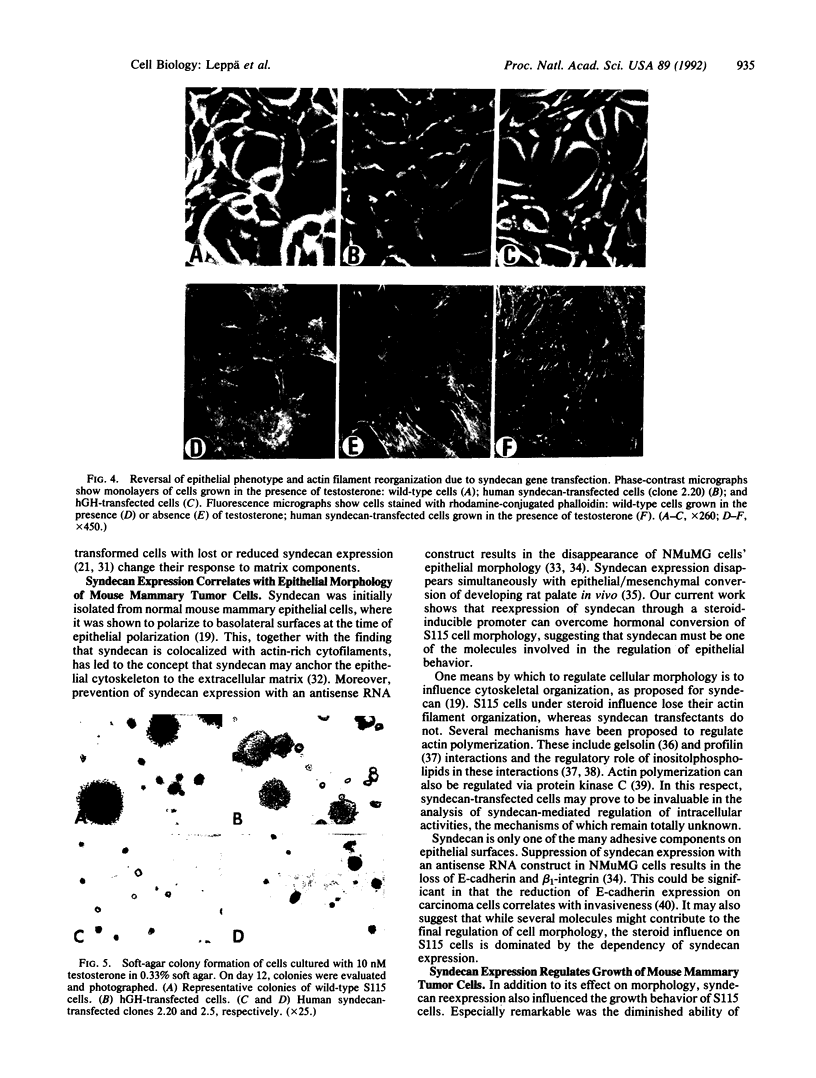
Abstract
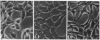
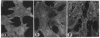
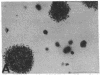
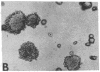
S115 mouse mammary epithelial cells lose their epithelial morphology and become tumorigenic when exposed to steroids. We have recently reported that testosterone exposure results in the suppression of syndecan expression, suggesting that this cell surface proteoglycan may influence S115 cell phenotype. We now report that a similar suppression and morphological response of S115 cells can be achieved by glucocorticoid exposure. We introduced into S115 cells an exogenous gene construct containing the full-length human syndecan cDNA under the control of a glucocorticoid-inducible retroviral promoter, in order to study the effect of syndecan expression on S115 cell behavior. Glucocorticoid-induced re-expression of syndecan in S115 cells restored an epithelial phenotype, while control transfectants and parental S115 cells exhibited an altered, nonepithelial phenotype. Moreover, the S115 cells expressing exogenous syndecan revealed a reduced ability to form colonies in soft agar. Therefore, the maintenance of epithelial morphology and normal growth of S115 cells are dependent on syndecan expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apgar J. R. Regulation of the antigen-induced F-actin response in rat basophilic leukemia cells by protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1157–1163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J. The first intron of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene contains several transcriptional regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1603–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Yates J., King R. J., Badley R. A. Changes in microfilament and focal adhesion distribution with loss of androgen responsiveness in cultured mammary tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Salmivirta M., Inki P., Mali M., Jalkanen M. Binding of human syndecan to extracellular matrix proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17837–17843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Vainio S., Laato M., Salmivirta M., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Induced expression of syndecan in healing wounds. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):585–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frixen U. H., Behrens J., Sachs M., Eberle G., Voss B., Warda A., Löchner D., Birchmeier W. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):173–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen M., Rapraeger A., Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan of mouse mammary epithelial cells is shed by cleavage of its matrix-binding ectodomain from its membrane-associated domain. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3087–3096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):362–364. doi: 10.1038/325362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Stephans J. C., Crawford K., Okino K., Barr P. J. Ligand-affinity cloning and structure of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan that binds basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda J. E., Rapraeger A., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. Cell surface proteoglycan as a receptor for interstitial collagens. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8157–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and profilactin. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):472–474. doi: 10.1038/314472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppä S., Härkönen P., Jalkanen M. Steroid-induced epithelial-fibroblastic conversion associated with syndecan suppression in S115 mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Jan;2(1):1–11. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mali M., Jaakkola P., Arvilommi A. M., Jalkanen M. Sequence of human syndecan indicates a novel gene family of integral membrane proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6884–6889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A. C., Krufka A., Olwin B. B. Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1705–1708. doi: 10.1126/science.1646484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan associates with the cytoskeleton at the basolateral cell surface of mouse mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2683–2696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapraeger A., Jalkanen M., Endo E., Koda J., Bernfield M. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11046–11052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Yamaguchi Y. Proteoglycans as modulators of growth factor activities. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90308-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Elenius K., Vainio S., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Syndecan from embryonic tooth mesenchyme binds tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Bernfield M. Molecular polymorphism of a cell surface proteoglycan: distinct structures on simple and stratified epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9562–9566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Lalor P., Bernfield M. B lymphocytes express and lose syndecan at specific stages of differentiation. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):27–35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan binds mouse mammary epithelial cells to fibronectin and behaves as a receptor for interstitial matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):423–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Streuli C. H., Martins-Green M., Bissell M. J. Designer microenvironments for the analysis of cell and tissue function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;2(5):864–874. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90085-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Jalkanen M., Vainio S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Thesleff I. Syndecan and tenascin expression is induced by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in embryonic tooth mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1945–1953. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Vaahtokari A., Sahlberg C., Mali M., Bernfield M., Thesleff I. Expression of syndecan gene is induced early, is transient, and correlates with changes in mesenchymal cell proliferation during tooth organogenesis. Dev Biol. 1991 Oct;147(2):322–333. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90290-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Lehtonen E., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M., Saxén L. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions regulate the stage-specific expression of a cell surface proteoglycan, syndecan, in the developing kidney. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., King R. J. Correlation of growth properties and morphology with hormone responsiveness of mammary tumor cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., King R. J. Multiple sensitivities of mammary tumor cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4135–4137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayon A., Klagsbrun M., Esko J. D., Leder P., Ornitz D. M. Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90512-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]