Figure 27.
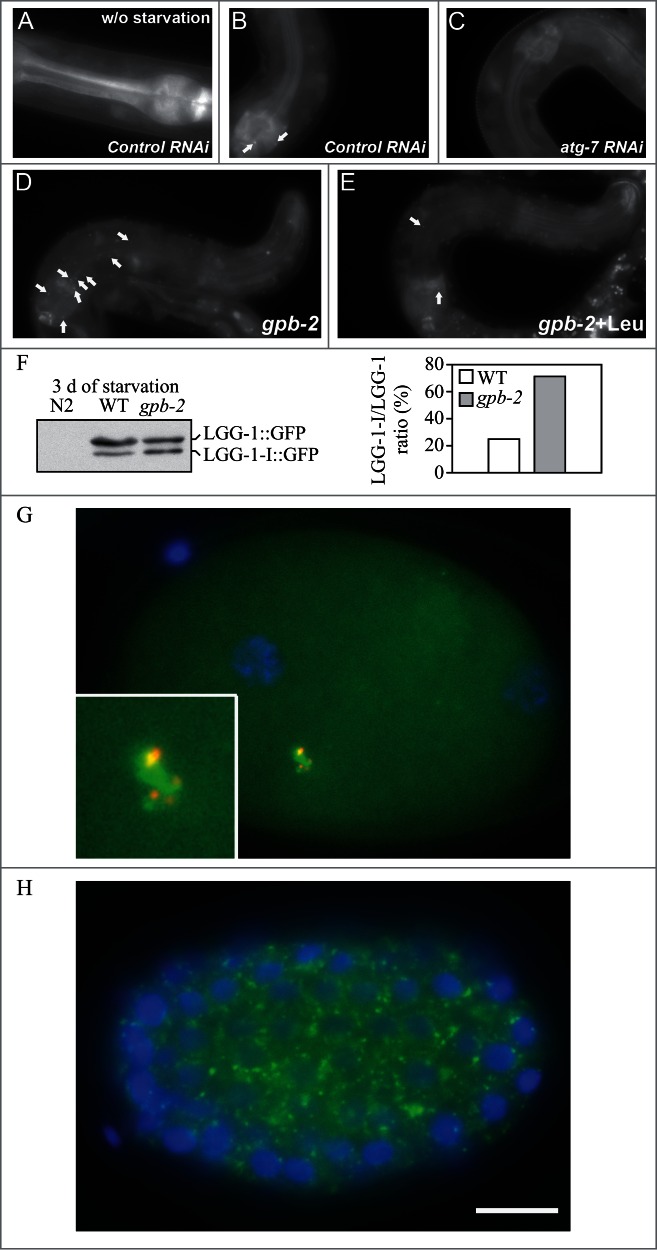
GFP::LGG-1 and GFP::LGG-2 are autophagy markers in C. elegans. (A–F) Animals were generated that carry an integrated transgene expressing a GFP-tagged version of lgg-1, the C. elegans ortholog of mammalian MAP1LC3. Representative green fluorescence images in the pharyngeal muscles of (A) control RNAi animals without starvation, (B) control RNAi animals after 9 d of starvation, (C) atg-7 RNAi animals after 9 d of starvation, (D) starvation-hypersensitive gpb-2 mutants without leucine after 3 d of starvation, and (E) gpb-2 mutants with leucine after 3 d of starvation. The arrows show representative GFP::LGG-1-positive punctate areas that label pre-autophagosomal and autophagosomal structures. (F) The relative levels of PE-conjugated and unconjugated GFP::LGG-1 were determined by western blotting. These figures were modified from data previously published in ref. 1267, Kang, C., Y.J. You, and L. Avery. 2007. Dual roles of autophagy in the survival of Caenorhabditis elegans during starvation. Genes & Development. 21:2161–2171, Copyright © 2007, Genes & Development by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press and Kang, C., and L. Avery. 2009. Systemic regulation of starvation response in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes & Development. 23:12–17, Copyright © 2011, Genes & Development by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, www.genesdev.org. (G–H) GFP:LGG-2 serves as a marker for autophagosomes in early C. elegans embryos. (G) GFP::LGG-2 expressed in the germline from an integrated transgene reveals the formation of autophagosomes (green) around sperm-inherited membranous organelles (red). DNA of the 2 pronuclei is stained (blue). (H) Later during development, GFP::LGG-2-positive structures are present in all cells of the embryo. Scale bar: 10 µm. Images provided by V. Galy.
