Abstract
Tumour-specific mutations are ideal targets for cancer immunotherapy as they lack expression in healthy tissues and can potentially be recognized as neo-antigens by the mature T-cell repertoire. Their systematic targeting by vaccine approaches, however, has been hampered by the fact that every patient’s tumour possesses a unique set of mutations (‘the mutanome’) that must first be identified. Recently, we proposed a personalized immunotherapy approach to target the full spectrum of a patient’s individual tumour-specific mutations1. Here we show in three independent murine tumour models that a considerable fraction of non-synonymous cancer mutations is immunogenic and that, unexpectedly, the majority of the immunogenic mutanome is recognized by CD4+ T cells. Vaccination with such CD4+ immunogenic mutations confers strong antitumour activity. Encouraged by these findings, we established a process by which mutations identified by exome sequencing could be selected as vaccine targets solely through bioinformatic prioritization on the basis of their expression levels and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-binding capacity for rapid production as synthetic poly-neo-epitope messenger RNA vaccines. We show that vaccination with such polytope mRNA vaccines induces potent tumour control and complete rejection of established aggressively growing tumours in mice. Moreover, we demonstrate that CD4+ T cell neo-epitope vaccination reshapes the tumour microenvironment and induces cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against an independent immunodominant antigen in mice, indicating orchestration of antigen spread. Finally, we demonstrate an abundance of mutations predicted to bind to MHC class II in human cancers as well by employing the same predictive algorithm on corresponding human cancer types. Thus, the tailored immunotherapy approach introduced here may be regarded as a universally applicable blueprint for comprehensive exploitation of the substantial neo-epitope target repertoire of cancers, enabling the effective targeting of every patient’s tumour with vaccines produced ‘just in time’.
We recently reported comprehensive mapping of non-synonymous mutations of the B16F10 tumour by next-generation sequencing (Fig. 1a)1. Tumour-bearing C57BL/6 mice were immunized with synthetic 27mer peptides encoding the mutated epitope (mutation in position 14), resulting in T-cell responses which conferred in vivo tumour control. In continuation of that work, we now characterized the T-cell responses against the neo-epitopes, starting with those with a high likelihood of MHC I binding. Mice were vaccinated with synthetic 27mer peptides (Fig. 1b). Immunogenic mutations were identified by IFN-γ ELISpot of splenocytes and T-cell subtype was determined by cytokine release assay (Fig. 1a). About 30% of neo-epitopes were found to induce mutation-reactive cytokine-secreting T cells. Surprisingly, responses against nearly all mutated epitopes (16/17, 95%) were CD4+ (Fig. 1b, Extended Data Table 1).
Figure 1. Cancer-associated mutations are frequently immunogenic and pre-dominantly recognized by CD4+ T cells.
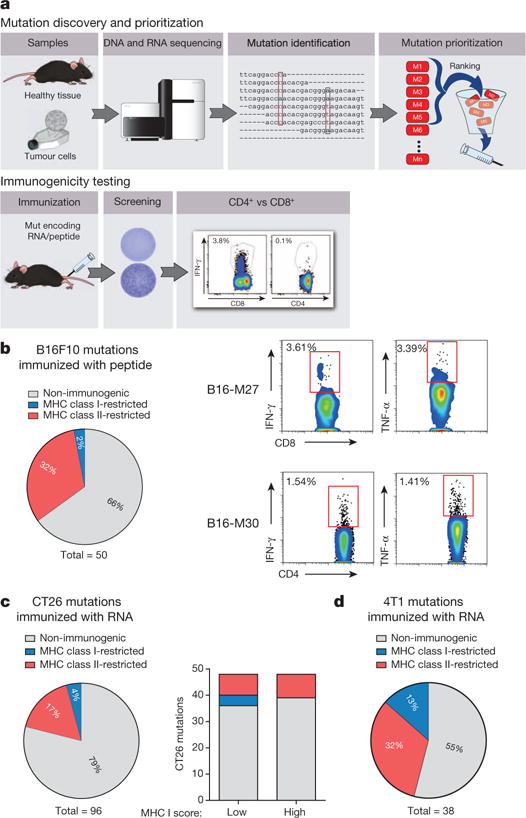
a, Schematic describing mutation discovery and immunogenicity testing. b–d, Splenocytes of mice vaccinated with peptides and polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (polyI:C) (b, B16F10, n = 5) or immunized with antigen-encoding RNA (c, CT26, n = 5; d, 4T1, n = 3) were tested for recognition of mutated peptides by ELISpot. Subsequent subtyping was performed via MHC II blockade or intracellular cytokine and CD4/CD8 surface staining. Pie charts represent the prevalence of non-immunogenic, MHC class I- or II-restricted mutated epitopes. b, Right, subtyping of mutation-specific T cells. c, Right, MHC restriction of neo-epitopes prioritized based on either good (0.1–2.1) or poor (>3.9) MHC I binding scores.
To exclude bias associated with the peptide format, this experiment was repeated using in vitro transcribed (IVT) mRNA encoding the neo-epitopes. Also in this setting the majority of mutation-specific immune responses (10/12, ~80%) were conferred by CD4+ T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1, Extended Data Table 1).
Recently, we identified over 1,680 non-synonymous mutations2 in the colon carcinoma model CT26 in BALB/c mice. We selected 48 of these mutations in analogy to the B16F10 study based on good MHC class I binding (‘low score’ 0.1–2.1). The other half was deliberately chosen for poor binding (‘high score’ >3.9). In total, about 20% of mutated epitopes were found to be immunogenic in mice immunized with the respective RNA monotopes (Fig. 1c, Extended Data Table 2). In the ‘low’ MHC I score subgroup, but not in the ‘high’ score subgroup, several epitopes inducing CD8+ T cells were identified (Fig. 1c right). MHC class II-restricted epitopes were represented in similar frequency in both subgroups, constituting the majority of CT26 immunogenic mutations (16/21, 80%).
Similarly, in the 4T1 mammary carcinoma model about 70% of the immunogenic epitopes determined by RNA monotope vaccines representing all 38 mutations of this model were recognized by CD4+ T cells (Fig. 1d, Extended Data Table 3). In summary, we showed that in three independent mouse tumour models with different MHC backgrounds, a considerable fraction of non-synonymous cancer mutations is immunogenic and quite unexpectedly, the immunogenic mutanome is predominantly recognized by CD4+ T cells.
To investigate whether MHC class II-restricted cancer mutations are good vaccine targets in vivo, we engineered pharmacologically optimized RNA (stabilizing elements in RNA sequence and liposomal formulation)3–5 encoding B16-M30, one of the epitopes that elicited strong CD4+ T-cell responses in the B16F10 tumour model. The mutated amino acid was essential for T-cell recognition, hence the wild type peptide was not recognized (Extended Data Fig. 2a). When B16F10 tumour-bearing C57BL/6 mice were repeatedly vaccinated with the B16-M30 RNA monotope, tumour growth was profoundly retarded (Fig. 2a). About two thirds of the neo-epitope RNA treated mice were still alive at day 100, while all the control RNA treated mice had died by 65 days. Depletion experiments in B16-M30 RNA treated mice revealed involvement of CD4+ but not CD8+ T-cells for therapeutic antitumour efficacy of the neo-epitope (Fig. 2a right).
Figure 2. Efficient tumour control and survival benefit in B16F10 melanoma with an RNA vaccine encoding a single mutated CD4+ T-cell epitope.

a, Tumour growth (mean + s.e.m.) and survival (±CD4- or CD8-depleting antibodies) in untreated (control) or B16-M30 immunized C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) inoculated subcutaneously (s.c.) with B16F10. b, B6 albino mice (n = 8) developing lung metastases upon intravenous (i.v.) injection of B16F10-Luc were treated with B16-M30 or irrelevant RNA (control). Median tumour growth was determined by BLI as photons per second. c, Single-cell suspensions of B16F10 tumours of irrelevant (control) or B16-M30 RNA immunized mice (n = 4) were restimulated with B16-M30 or irrelevant peptide (vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein, VSV-NP52–59) and tested by ELISpot (mean + s.e.m.). Data pooled from two experiments. d, Frequency of infiltrating cells in s.c. B16F10 tumours (n = 3) left untreated (control) or vaccinated with B16-M30 RNA.
Similarly, lung metastases of luciferase transduced B16F10 cells were efficiently eradicated with B16-M30 RNA but not control RNA in the vast majority of mice as shown by bioluminescence imaging (BLI) (Fig. 2b). Tumour infiltrating leukocytes purified from tumours of B16-M30 RNA immunized mice strongly reacted against B16-M30 (Fig. 2c). In tumours from neo-epitope-encoding RNA treated versus control mice, CD4+ as well as CD8+ T-cell infiltrates were significantly more abundant, whereas MDSCs and FoxP3+ T cells were significantly reduced (Fig. 2d). To benchmark antitumour efficacy, we tested immunogenic B16F10 neo-epitopes and a non-mutated TRP2-derived immunodominant epitope6. Whereas with TRP2 RNA, the two class I and three of the mutated class II neo-epitopes conferred a modest non-significant antitumour activity, three class II neo-epitopes mediated a significant inhibition of tumour growth (Extended Data Fig. 2d). Taken together, these data establish that a significant proportion of class II neo-epitopes have antitumour vaccine potency. Establishing B16-M30 as a novel rejection antigen in B16F10 our findings show that RNA encoding a single neo-epitope may give rise to functional T cells capable of targeting into the cancer lesion, controlling and even curing murine tumours. Our findings are in agreement with recent reports of the pivotal role of CD4+ T-cell immunity in the control of cancer7,8.
The vast majority of mutations are unique to the individual patient. Hence, mutanome vaccines need to be individually tailored9 and rapidly manufactured on-demand. This challenge can be viably addressed by RNA vaccine technology (Fig. 3a). At present, GMP-grade RNA is release-ready within 3 weeks. On another note, though we achieved tumour eradication in mice with a single mutation, to combine several mutations would be preferable to address tumour heterogeneity and immune editing, which mediate clinical failure of vaccines in humans10,11. We sought to integrate our insights into a concept which we call ‘mutanome engineered RNA immunotherapy’ (MERIT) (Fig. 3a).
Figure 3. RNA pentatope immunization confers disease control and survival benefit in murine tumours.
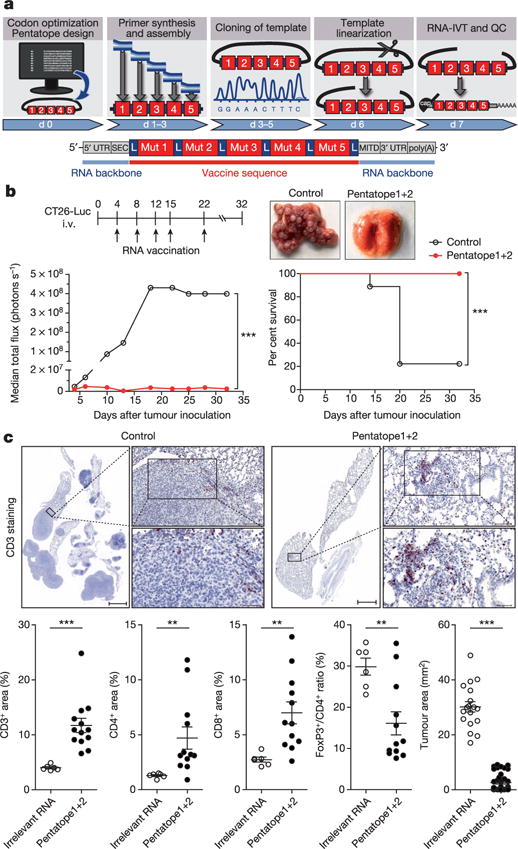
a, Engineering of a poly-neo-epitope RNA. b, BALB/c mice (n = 10) developing lung metastases upon i.v. injection of CT26-Luc were treated with a mixture of two pentatopes or left untreated (control). The median tumour growth by BLI, survival data and lungs from treated animals are shown. c, Upper panel, CD3 stained lung tissue sections. Scale bars: 1,000 μm (scan), 100 μm (top), 50 μm (bottom). Lower panel, proportional lymphocyte areas in lung tumour tissue of control (n = 6) or pentatope-treated (CD3: n = 14; CD4, CD8, FoxP3: n = 12) animals. Lower panel right, tumour area (mean ± s.e.m.) in sections of control (n = 18) and pentatope112-treated (n = 39) mice.
To test this concept, we engineered RNA monotopes encoding four MHC class II (CT26-M03, CT26-M20, CT26-M27, CT26-M68) and one MHC class I (CT26-M19) restricted mutation from the CT26 model (see Extended Data Table 2) and a synthetic RNA pentatope encoding all five neo-epitopes connected by 10mer non-immunogenic glycine/serine linkers (Fig. 3a). In naive BALB/c mice the quantity of IFN-γ-producing T cells elicited by the pentatope was comparable (3 of 5) or even higher than that evoked by the respective monotope (Extended Data Fig. 3a).
In BALB/c mice with CT26 luciferase-transfected (CT26-Luc) lung metastases vaccinated repeatedly with a mixture of two RNA pentatopes (3 MHC class I- and 7 class II-restricted epitopes, Extended Data Table 4) including the mutations tested in the previous experiment, tumour growth was significantly inhibited (Fig. 3b). At day 32 all mice in the RNA pentatope group were alive whereas 80% of the control mice had already died. Dissection of the antitumour activity of single RNA pentatopes in the CT26 model revealed that RNA pentatope 2 has a very strong antitumour activity, whereas pentatope 1 is modestly active (Extended Data Fig. 3b). A subsequent study confirmed the antitumour activity of pentatope 2, and showed its significant decrease upon CD40L blockade and complete loss by CD8+ T-cell depletion (Extended Data Fig. 3c). Tumour load in the vaccinated as compared to untreated mice was significantly lower as shown by post mortem macroscopic (Fig. 3b), histological (Fig. 3c upper panel) and computerized image analysis (Fig. 3c lower panel right) of tissue sections. CD3+ T-cell infiltrates in tumour lesions of pentatope RNA vaccinated mice, in contrast to findings in controls, were significantly brisker as compared to the surrounding lung tissues (Fig. 3c lower panel left). Moreover, in independent experiments we found a significant increase of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in tumour lesions of RNA pentatope immunized mice but a lower FoxP3/CD4 ratio as compared to tumours of mice treated with irrelevant RNA (Fig. 3c lower panel, Extended Data Fig. 3d).
Taken together our data indicate that with a poly-neo-epitope encoding RNA vaccine T cells against each single epitope are elicited. These T cells target tumour lesions, recognize their mutated targets, reshape the cellular composition of the tumour microenvironment and result in efficient tumour control in vivo.
The current paradigm for selecting mutations for immunization is to employ MHC class I binding scores for enrichment of mutated epitope candidates12–14 which can elicit CD8+ responses and tumour rejection. Our findings indicate that MHC class II presented neo-epitopes may be of higher interest for a MERIT approach. In fact, a correlation analysis revealed that immunogenic mutations have a significantly better MHC class II binding score as compared to non-immunogenic ones (Fig. 4a). As most cancers lack MHC class II expression, effective recognition of neo-epitopes by CD4+ T cells should depend on presentation of released tumour antigens by antigen presenting cells (APCs). This is most efficient for highly expressed antigens15. Thus, we implemented an algorithm combining good MHC class II binding with abundant expression of the mRNA encoding the neo-epitope based on confirmed mutated RNA sequencing reads normalized to the overall read count (NVRC: normalized variant read counts). To test the impact of predicted MHC class II binding affinity, we ranked CT26 mutanome data with this algorithm and selected the top ten mutations (‘ME’ mutations in Extended Data Table 5) predicted to be the best MHC class II binders among the most abundant candidate epitopes (NVRC ≥ 60). The control comprised ten mutations with abundant expression only (‘E’ mutations in Extended Data Table 5). These neo-epitopes were used without any further pre-validation or immunogenicity testing to engineer two RNA pentatopes for each group (PME and PE pentatopes). In mice with established CT26-Luc lung tumours, PME induced a much stronger T-cell response as compared to PE pentatopes (Fig. 4c). Analysis of immune responses proved the presence of multiple immunogenic MHC class II neo-epitopes in the PME RNA pentatopes (Extended Data Fig. 4). Established lung metastases were completely rejected in almost all PME mice whereas PE pentatopes were not able to control tumour growth (Fig. 4b). An independent study confirmed the strong antitumour activity of the pentatope PME and showed loss of the anti-tumour effect upon anti-CD40L and anti-CD8 treatments (Fig. 4d).
Figure 4. RNA pentatope vaccines with mutations selected for in silico predicted favourable MHC class II binding and abundant expression confer potent antitumour control.
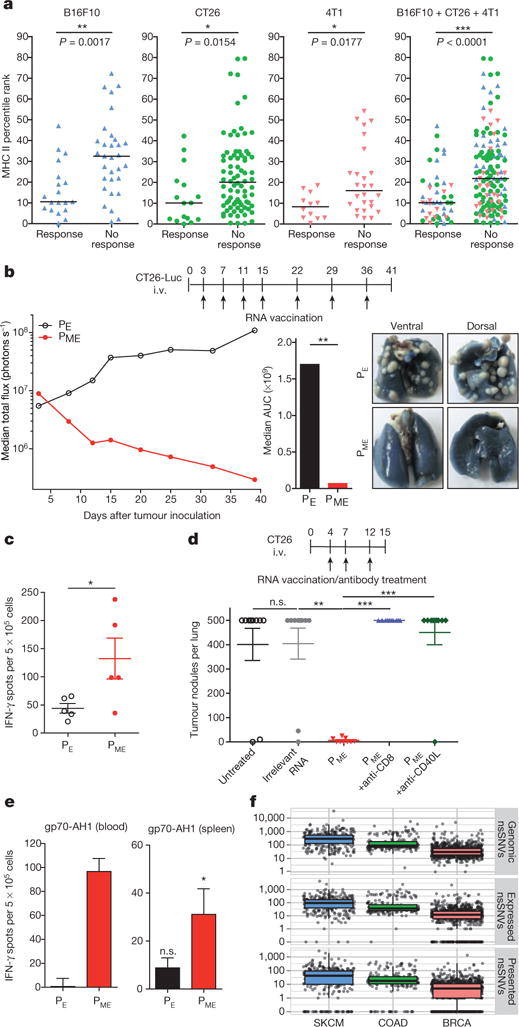
a, Comparison of median MHC II binding scores of immunogenic (Response) and non-immunogenic (No response) mutated 27mers. b, Highly expressed mutations were selected with (‘ME’) or without (‘E’) considering MHC class II binding score. Ten mutations (two pentatopes) per category were used for vaccination of CT26-Luc tumour-bearing mice (n = 10). Tumour growth, area under the curve (AUC) at day 40 and ink-treated lungs are shown. c, Mice (n = 5) were analysed for T-cell responses against the RNA pentatopes via ELISpot (mean ± s.e.m. subtracted by an irrelevant RNA control). d, CT26 tumour nodules per lung of untreated mice or mice (n = 10) injected with irrelevant or PME (±CD8 depletion or CD40L blocking) RNA. e, T-cell responses against gp70423–431 (gp70-AH1) determined via ELISpot in blood (pooled from 5 mice at day 20) and spleen (n = 5). Background (medium control) subtracted mean ± s.e.m. shown. f, Genomic, expressed and predictively presented (HLA-DRB1, IEDB rank <10) non-synonymous single nucleotide variations (nsSNVs) derived from human cancer samples (TCGA). SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma; COAD, colon adenocarcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma.
Antigen-specific TH cells promote the cross-priming of tumour-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses by CD40 ligand-mediated activation of dendritic cells. If TH cells recognize their antigen on the same APC (cross-)presenting an CTL epitope, a diversified CTL response may result16. In support of this notion, we detected strong CD8+ T-cell responses against gp70-AH1, a well characterized immunodominant CTL epitope of the endogenous murine leukaemia virus-related cell surface antigen in the blood and spleen of mice immunized with PME but not PE pentatopes (Fig. 4e). This indicates that cancer neo-epitope specific TH cells, in analogy to viral neo-antigen specific T cells, may exert their antitumour function by augmentation of CTL responses through epitope spreading.
In summary, we show that MHC class II-restricted T-cell epitopes are more abundant than previously appreciated in the cancer mutanome and can be targeted by customized RNA-based poly-neo-epitope vaccines with substantial therapeutic effect in mouse tumour models. A recent study reports that about 0.5% of mutations induce spontaneous CD4+ T-cell immune responses in human tumours17. Even by the most conservative estimate, our findings indicate that the proportion of relevant neo-epitope vaccine targets recognized by CD4+ T-cells is a full log higher than that reported to induce spontaneous CD4+ T-cell responses. The reason might be that spontaneous immunogenicity is not driven by antigenicity alone, but is a function of many factors including tumour biology and local immunosuppression. Both B16 (Extended Data Fig. 2e) and CT26 are tumours with strong immunosuppressive properties, such that they are not able to induce protective immunity unless transfected with immunomodulators such as GM-CSF. As our study shows that vaccination with CD4+ T-cell neo-epitopes identified by exome sequencing counteracts the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment in these models resulting in rejection of established tumours, one key prediction from our work is that such ‘poorly immunogenic’ tumours can be successfully targeted through induction of mutation-specific CD4+ T-cell responses.
A simple explanation for this remarkable frequency of CD4+ T-cell recognition of mutations may be less stringent length and sequence requirement for peptides binding to MHC class II molecules as compared to MHC class I epitopes increasing the likelihood that a given mutation is found within a presented peptide18.
The first evidence of spontaneous CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses directed against mutated gene-products in cancer patients was generated in the 1990s19,20. Recent publications have renewed enthusiasm for the enormous potential of mutation-specific T cells to confer anti-tumour activity in cancer patients7,8,21. As elegantly proven in a murine carcinogen-induced sarcoma model22 there is evidence for a direct link between T-cell recognition of mutant neo-epitopes and clinical response to checkpoint blockade treatment14,23.
To assess whether the principles unraveled in the mouse models for melanoma, colon and breast cancer are true in the human setting, we analysed mutation and RNA-Seq data in the same human cancer types provided by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). For all three human cancers we confirmed the abundance of mutations predicted to bind to MHC class II (Fig. 4f).
The MERIT approach we presented here by integrating advances in the field of next-generation sequencing, computational immunology and synthetic genomics provides the technology for comprehensive exploitation of the neo-epitope target repertoire. The approach might be particularly useful to reshape the tumour microenvironment in patients who lack T-cell infiltration in their tumours and applicable as a standalone or combination therapy to increase the clinical success rate of checkpoint blockade therapy that depends on pre-existing immunity24–26. Targeting multiple mutations at once may in theory pave the way to solve critical problems in current cancer drug development such as clonal heterogeneity and antigen escape10,12.
Based on the findings of this study and of our prior work, a first-in-concept trial in melanoma patients1,27,28 has been initiated and is recruiting (NCT02035956), confirming that ‘just in time’ production of a poly-neo-epitope mRNA cancer vaccine is in fact feasible.
METHODS
Cell lines and mice
Female 8–12 weeks old C57BL/6, BALB/c mice (Janvier Labs) and C57BL/6BrdCrHsd-Tyrc mice (B6 albino, Harlan) were kept in accordance with federal policies on animal research at the University of Mainz. B16F10 melanoma cell line, CT26 colon carcinoma cell line and 4T1-luc2-tdtomato (4T1-Luc) cells were purchased in 2010, 2011 and 2011, respectively (ATCC CRL-6475 lot no. 58078645, ATCC CRL-2638 lot no. 58494154, Caliper 125669 lot no. 101648). Firefly-luciferase-expressing CT26-Luc and B16F10-Luc cells were lentivirally transduced. Master and working cell banks were generated immediately upon receipt, of which third and fourth passages were used for tumour experiments. Cells were tested for mycoplasma every 3 months. Reauthentification of cells was not performed since receipt.
Next-generation sequencing and data processing
As described previously1, exome capture from mouse tumour cells and tail tissue samples of BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice were sequenced in triplicate (except 4T1-Luc in duplicate). Oligo (dT)-based RNA sequencing libraries for gene expression profiling were prepared in triplicate. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq2000 to generate 50 nucleotide single-end (B16F10) or 100 nucleotide paired-end (CT26, 4T1-Luc) reads, respectively. Gene expression values were determined by counting reads overlapping transcript exons and junctions, and normalizing to RPKM expression units (reads which map per kilobase of transcript length per million mapped reads). Mutation expression was determined by normalization of mutated RNA reads to the total mapped read counts multiplied by 100 million (normalized variant read counts, NVRC).
Mutation selection, validation and prioritization
As described previously1,2,28, mutations were selected based on following criteria: (1) present in the respective tumour cell line sequencing triplicates and absent in the corresponding healthy tissue sample triplicates, (2) occur in a RefSeq transcript, (3) cause non-synonymous changes, and (4) occurrence in expressed genes of tumour cell lines (median RPKM across replicates). For validation, mutations were amplified from DNA from the respective cell lines of mice tail tissue and subjected to Sanger sequencing. DNA-derived mutations were classified as validated if confirmed by either Sanger sequencing or the RNA-Seq reads. No confirmation via Sanger sequencing and immunogenicity testing was performed for experiments in Fig. 4. For experiments shown in Fig. 1 mutated epitopes were prioritized according to their MHC class I binding predicted by the consensus method (version 2.5) of the Immune Epitope Database (http://www.iedb.org). Mutations shown in Fig. 4b–e were selected based on either their expression (NVRC) alone or together with their predicted MHC class II peptide binding capability (IEDB consensus method version 2.5). Retrospective analysis of MHC II binding prediction shown in Fig. 4a was determined with IEDB consensus method version 2.12. For analysis of mutations in human tumours, DNA sequencing data of skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM, n = 308), colon adenocarcinoma (COAD, n = 192) or breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA, n = 872) retrieved from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (August 2014) was filtered to obtain genomic non-synonymous point mutations (nsSNVs). RNA-Seq data (TCGA) of tumour samples with identified genomic mutations was used to define expressed nsSNVs (STAR aligner, reference genome: GRCh37/hg19, max. mismatch ratio of 2%). The reads mapping to the reference genome were intersected with the UCSC gene model database. To predict MHC II binding of expressed neo-epitopes, seq2HLA29 was employed to identify the patients’ 4-digit HLA class II (HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1) type. The IEDB consensus binding prediction (version 2.12) was used to predict MHC class II binding from a 27mer peptide and the patients HLA-DRB1 alleles. As recommended from IEDB, neo-epitopes with a percentile rank below 10% were considered as binders.
Synthetic RNA and synthetic peptides
Non-synonymous mutations were studied in the context of the respective 27mer amino acid epitope with the mutated amino acid in the centre (position 14). Mutated peptides were synthesized together with gp70-AH1 (gp70423–431) and control peptides (vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein (VSV-NP52–59), tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP2180–188) by JPT Peptide Technologies GmbH. Alternatively, sequences encoding mutated 27mer peptides were cloned into the pST1-Sp-MITD-2hBgUTR-A120 backbone3 featuring sequence elements for pharmacologically optimized synthetic RNA in terms of translation efficiency and MHC class I/II processing of epitopes either as mono-topes or fused to each other by sequences encoding 10 amino acid long glycine-serine linker in between resulting in pentatopes. Linearization of these plasmid constructs, in vitro translation (IVT) and purification are described in detail elsewhere3.
Mouse models
For immunogenicity studies of mutated epitopes age-matched female C57BL/6 or BALB/c mice were vaccinated on day 0, 3, 7 and 14 (RNA immunization) or day 0 and 7 (peptide immunization). The read out was performed five to six days after the last immunization (see also Enzyme-linked ImmunoSpot and Flow cytometric analysis method sections). Vaccination was performed either by i.v. injection of 200 μl (20 μg per mutation for B16F10, 40 μg per mutation for CT26) RNA complexed with cationic lipids (manuscript in preparation) or subcutaneous (s.c.) injection of 100 μg synthetic peptide and 50 μg poly(I:C) formulated in PBS (200 μl total volume) into the lateral flank. Two mutations per mouse were tested (n = 5 for B16F10, n = 3 for CT26). For confirmation of immunogenic mutations and subtyping, mice were vaccinated against a single mutation (n = 5).
For therapeutic tumour experiments C57BL/6 mice were inoculated s.c. with 1 × 105 B16F10 melanoma cells into the flank and randomly distributed into treatment groups. Tumour volume was measured unblinded with a caliper and calculated using the formula (A × B2)/2 (A as the largest and B the smallest diameter of the tumour). Tumour growth was documented as mean tumour size with standard error disregarding single distant outliers.
In lung metastasis experiments 5 × 105 CT26-Luc or 2× 105 CT26 cells were injected into the tail vein of BALB/c mice or 1.5 × 105 B16F10-Luc tumour cells into B6 albino mice. Tumour growth of luciferase transgenic cells was traced unblinded by bioluminescence imaging after i.p. injection of an aqueous solution of D-luciferin (250 μl, 1.6 mg, BD Bioscience) on an IVIS Lumina (Caliper Life Sciences). Five minutes after injection emitted photons were quantified. In vivo bioluminescence in regions of interest (ROI) were quantified as total flux (photons s−1) (IVIS Living Image 4.0). Mice were randomized based on their total flux values (ANOVA-P method, Daniel’s XL Toolbox V6.53). CT26 lung tumour burden was quantified unblinded after tracheal ink (1:10 diluted in PBS) injection and fixation with Fekete’s solution (5 ml 70% ethanol, 0.5 ml formalin, and 0.25 ml glacial acetic acid). In therapeutic experiments mice were administered repeated doses of either monotope (40 μg), pentatope RNA (in total 40 μg) or equimolar amounts of irrelevant RNA. In some experiments repeated doses (200 μg per mouse i.p.) of CD8-depleting (clone YTS191, BioXcell), CD4-depleting (clone YTS169.1, BioXcell) or CD40L-blocking (clone MR1) antibodies were administered. The experimental group sizes were approved by the regulatory authorities for animal welfare after being defined to balance statistical power, feasibility and ethical aspects.
Enzyme-linked ImmunoSpot (ELISpot)
As previously described30, 5 × 105 splenocytes were cultured over night at 37 °C in anti-INF-γ (10 μg ml−1, clone AN18, Mabtech) coated Multiscreen 96-well plates (Millipore) and cytokine secretion was detected with an anti-IFN-γ antibody (1 μg ml−1, clone R4-6A2, Mabtech). For stimulation either 2 μg ml−1 peptide was added or spleen cells were coincubated with 5 × 104 syngeneic bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) transfected with RNA. For analysis of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, single-cell suspensions of lung metastasis were rested overnight to get rid of living tumour cells via plastic adherence. Viable cells were separated via density gradient centrifugation and added to the ELISpot plate. For analysis of T-cell responses in peripheral blood, PBMC were isolated via density gradient centrifugation, counted and restimulated by addition of peptide and syngeneic BMDC. Subtyping of T-cell responses was performed with an MHC class II blocking antibody (20 μg ml−1, clone M5/114, BioXcell). All samples were tested in duplicates or triplicates.
Flow cytometric analysis
In the presence of Brefeldin A (Sigma-Aldrich) 2 × 106 splenocytes were stimulated with 2 × 105 RNA-transfected BMDC or 2 μg ml−1 peptide. Splenocytes treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, 0.5 μg ml−1, Sigma-Aldrich) and Ionomycin (1 μg ml−1, Sigma-Aldrich) served as a positive control. Cells were incubated for 5 h at 37 °C, stained for CD4+ and CD8+ cell surface markers, permeabilized and fixed using BD Cytofix/Cytoperm according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Thereafter cells were stained for INF-γ, TNF-α and IL-2 cytokines (BD Biosciences). Cytokine secretion among CD4+ or CD8+ T cells in stimulated samples was compared to control samples (medium, irrelevant RNA or irrelevant peptide) in order to determine the responding T-cell subtype (n = 5). Tumour infiltrating leucocytes were prepared from subcutaneous B16F10 tumours fifteen to twenty days after inoculation. Tumours were harvested and minced into pieces of 1–2 mm diameter. The resulting cell suspension was harvested, filtered through a 70-μm cell strainer, washed two times and stained for CD4, CD8, Gr-1 and CD11b surface marker. Intracellular FoxP3 staining was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Mouse Foxp3 Buffer Set, BD). Samples were acquired on a BD FACSCanto II.
Immune histochemistry
Lungs of CT26 tumour bearing mice were fixed overnight in 4% phosphate buffered formaldehyde solution (Carl Roth) and embedded in paraffin. 50-μm consecutive sections (3 per mouse) were stained for CD3 (clone SP7, Abcam), CD4 (clone 1, catalogue no. 50134-M08H, Sino Biologinal) and FoxP3 (polyclonal, catalogue no. NB100-39002, Novus Biologicals) following detection by a HRP-conjugated antibody (Poly-HRP-anti-rabbit IgG, ImmunoLogic) and the corresponding peroxidase substrate (Vector Nova Red, Vector Laboratories) and counterstained with hematoxylin. CD3+, CD4+, FoxP3+ and tumour areas were captured on an Axio Scan.Z1 (Zeiss) and manually pre-defined tumour and lung regions were quantified via computerized image analysis software (Tissue Studio 3.6.1, Definiens). CD8+ area was calculated by subtracting CD4 stained area from CD3+ area. For comparison of tumour areas between control and pentatope1 +2-treated animals, tumour-free sections were excluded.
Immunofluorescence staining
8-μm sections of cryo-conserved organs were attached on Superfrost slides, dried overnight at room temperature and fixed in 4% para-formaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min at room temperature in the dark. Sections were washed 3 times with PBS and blocked using PBS supplemented with 1% BSA, 5% mouse serum, 5% rat serum and 0.02% Nonident for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. Fluorescent labelled antibodies (FoxP3, clone FJK-16 s, eBioscience; CD8, clone 53-6.7, BD; CD4, clone RM4-5, BD) were diluted in staining buffer (PBS supplemented with 1% BSA, 5% mouse serum and 0.02% Nonident) and sections were stained overnight at 4 °C. After washing twice with washing buffer (PBS supplemented with 1% BSA and 0. 02% Nonident) and once with PBS, slides were stained for 3 min with Hoechst (Sigma), washed 3 times with PBS, once with distilled water and mounted using Mounting Medium Flouromount G (eBioscience). Immunofluorescence images were acquired using an epifluorescence microscope (ApoTome, Zeiss). Tumour, CD4, CD8 and FoxP3 stained areas were quantified within manually pre-defined tumour regions via computerized image analysis software (Tissue Studio 3.6.1., Definiens). The proportion of marker positive cells in comparison to DAPI positive cells was calculated.
Statistics
Means were compared by using Student’s t-test for hypothesis testing to compare individual treatment and corresponding control groups. In case of significantly different variances (F-test, alpha = 0.05) Welch’s correction was used. Mann–Whitney U test was applied if data sets failed the Pearson omnibus normality test (alpha = 0.05). Tumour growth was compared by calculating the area under the tumour growth curve (AUC) for single mice. Statistical differences in medians between two groups were calculated with a nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. Survival benefit was determined with the log-rank test. All analyses were two-tailed (except Fig. 4c, e) and carried out using GraphPad Prism 5.03. n.s.: P > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. Grubb’s test was used for identification of outliers (alpha = 0.05). No statistical methods were used to predetermine sample size.
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1. Non synonymous cancer-associated mutations are frequently immunogenic and pre-dominantly recognized by CD4+ T cells.
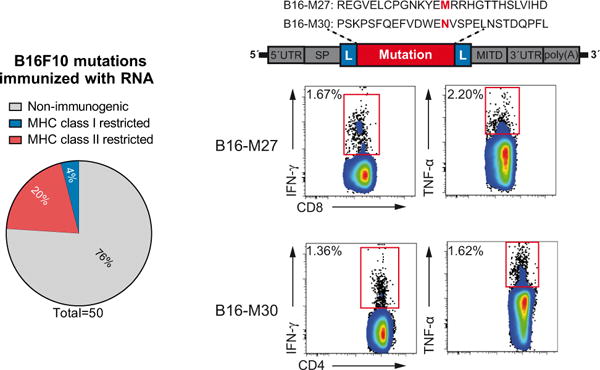
T-cell responses obtained by vaccinating C57BL/6 mice with antigen-encoding RNA in the B16F10 tumour model (n = 5). Left, prevalence of non-immunogenic, MHC-class-I- or class-II-restricted mutated epitopes. Right, detection and typing of mutation-specific T cells (individual epitopes shown in Extended Data Table 1).
Extended Data Figure 2. Mutant epitope-specific T cells induced by RNA vaccination control tumour growth.
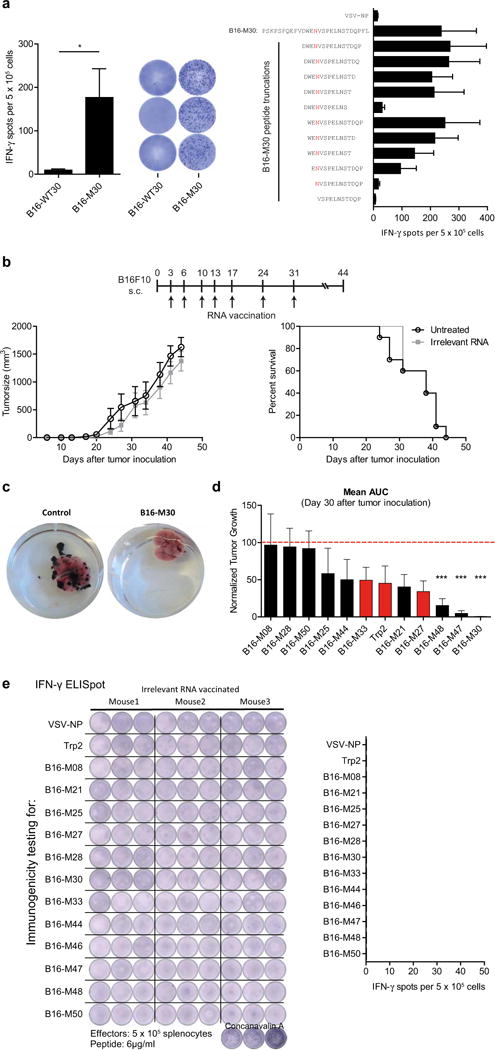
a, Splenocytes of mice (n = 5) vaccinated with B16-M30 RNA were tested by ELISpot for recognition of mutated peptides as compared to the corresponding wild-type (B16-WT30) sequence. Right, testing of truncated variants of B16-M30 (mean + s.e.m.). b, Mean ± s.e.m. tumour growth (left) and survival (right) of C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) inoculated s.c. with B16F10 and left untreated (control) or injected i.v. with irrelevant RNA. c, Lungs of B16F10-Luc tumour bearing mice shown in Fig. 2b (day 27 after tumour inoculation). d, Therapeutic antitumour activity against B16F10 tumours in mice (B16-M27, Trp2 n = 8; B16-M30 n = 7; others n = 10) conferred by immunization with epitopes encoding immunogenic B16F10 mutations or an immunodominant wild type Trp2 epitope6. The area under the tumour growth curve at day 30 after tumour inoculation was normalized to untreated control mice and depicted as mean ± s.e.m. Red and black columns represent mutations recognized by CD8+ or CD4+ T cells, respectively. e, Spontaneous immune responses in splenocytes of irrelevant RNA treated B16F10 tumour bearing C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) were tested by ELISpot for recognition of peptides (mean + s.e.m.).
Extended Data Figure 3. Mechanism of antitumour activity of mutation specific poly-epitope vaccines in CT26 tumour-bearing mice.
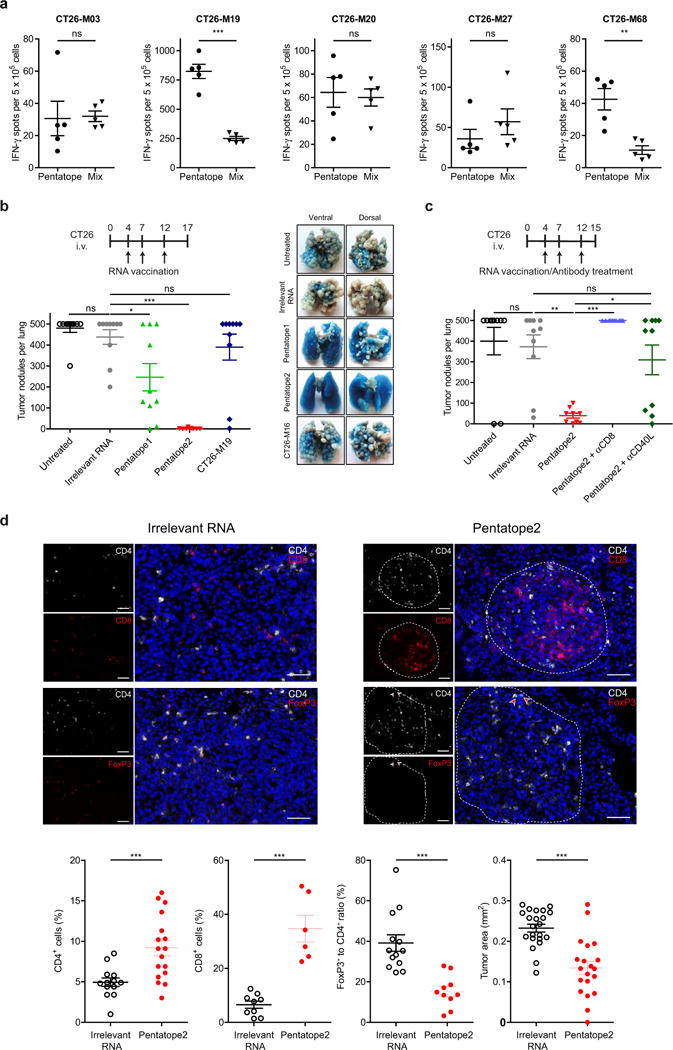
a, BALB/c mice (n = 5) were vaccinated either with pentatope (35 μg) or the corresponding mixture of five RNA monotopes (7 μg each). T-cell responses in peptide-stimulated splenocytes of mice were measured ex vivo via ELISpot (medium control subtracted mean ± s.e.m.). b, c, BALB/c mice (n = 10) were inoculated i.v. with CT26 tumour cells and left untreated or injected with irrelevant, CT26-M19 or pentatope1 or 2 RNA in absence (b) or presence of a CD8 T cell depleting antibody or a CD40L blocking antibody (c). Mean ± s.e.m. of tumour nodules per lung are shown. d, Immunofluorescence analyses of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in pentatope2-vaccinated mice. Upper panel, lung tumour tissue stained for CD4 and CD8 or CD4 and FoxP3. Scale bar, 50 μm. Lower panel left, proportion of infiltrating cells in sections of irrelevant (CD4: n = 13; CD8 = 9; FoxP3: n = 13) or pentatope (CD4: n = 17; CD8: n = 6; FoxP3: n = 10) RNA-treated animals. Lower panel right, tumour area in sections of control (n = 22) and pentatope2-treated (n = 20) animals (mean ± s.e.m.).
Extended Data Figure 4. Immunogenicity testing of PME pentatope-encoded mutations.
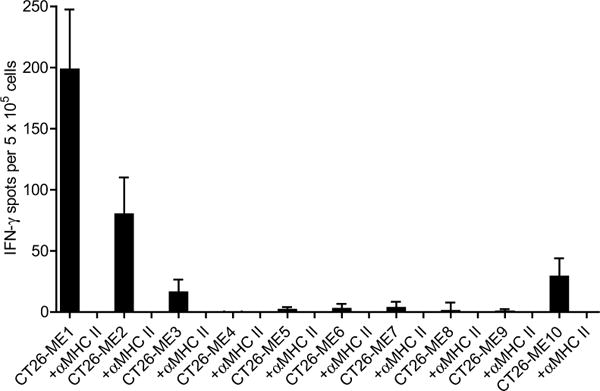
Splenocytes of PME RNA vaccinated BALB/c mice (n = 6) were tested ex vivo for recognition of peptides representing the mutated 27mer sequences represented in PME pentatopes with or without addition of an MHC class II-blocking antibody. Mean + s.e.m. of background (medium control) subtracted responses are shown.
Extended Data Table 1.
Immunogenic B16F10 mutations
| Mutation | Gene | Mutated sequence used for vaccination | Substitution (WT, AA#, Mut) | Reactive T cell subtype | MHC I score (best prediction) | Response after vaccination with | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide | RNA | ||||||
| B16-M05 | Eef2 | FVVKAYLPVNESFAFTADLRSNTGGQA | G795A | CD4+ | 1.1 | x | |
| B16-M08 | Ddx23 | ANFESGKHKYRQTAMFTATMPPAVERL | V602A | CD4+ | 1.3 | x | |
| B16-M12 | Gnas | TPPPEEAMPFEFNGPAQGDHSQPPLQV | S111G | CD4+ | 1.2 | x | |
| B16-M17 | Tnpo3 | VVDRNPQFLDPVLAYLMKGLCEKPLAS | G504A | CD4+ | 1.0 | x | |
| B16-M20 | Tubb3 | FRRKAFLHWYTGEAMDEMEFTEAESNM | G402A | CD4+ | 1.9 | x | |
| B16-M21 | Atp11a | SSPDEVALVEGVQSLGFTYLRLKDNYM | R552S | CD4+ | 0.1 | x | |
| B16-M22 | Asf1b | PKPDFSQLQRNILPSNPRVTRFHINWD | A141P | CD4+ | 1.7 | x | |
| B16-M24 | Dag1 | TAVITPPTTTTKKARVSTPKPATPSTD | P425A | CD4+ | 2.2 | x | |
| B16-M25 | Plod1 | STANYNTSHLNNDVWQIFENPVDWKEK | F530V | CD4+ | 0.1 | x | x |
| B16-M27 | Obsl1 | REGVELCPGNKYEMRRHGTTHSLVIHD | T1764M | CD8+ | 2.3 | x | x |
| B16-M28 | Ppp1r7 | NIEGIDKLTQLKKPFLVNNKINKIENI | L170P | CD4+ | 3.2 | x | x |
| B16-M29 | Mthfd1l | IPSGTTILNCFHDVLSGKLSGGSPGVP | F294V | CD4+ | 1.7 | x | |
| B16-M30 | Kif18b | PSKPSFQEFVDWENVSPELNSTDQPFL | K739N | CD4+ | 1.2 | x | x |
| B16-M33 | Pbk | DSGSPFPAAVILRDALHMARGLKYLHQ | V145D | CD8+ | 0.1 | x | |
| B16-M36 | Tm9sf3 | CGTAFFINFIAIYHHASRAIPFGTMVA | Y382H | CD4+ | 0.2 | x | |
| B16-M44 | Cpsf3l | EFKHIKAFDRTFANNPGPMVVFATPGM | D314N | CD4+ | 0.5 | x | x |
| B16-M45 | Mkrn1 | ECRITSNFVIPSEYWVEEKEEKQKLIQ | N346Y | CD4+ | 1.4 | x | |
| B16-M46 | Actn4 | NHSGLVTFQAFIDVMSRETTDTDTADQ | F835V | CD4+ | 0.2 | x | x |
| B16-M47 | Rpl13a | GRGHLLGRLAAIVGKQVLLGRKVVVVR | A24G | CD4+ | 0.5 | x | |
| B16-M48 | Def8 | SHCHWNDLAVIPAGVVHNWDFEPRKVS | R255G | CD4+ | 3.8 | x | x |
| B16-M50 | Sema3b | GFSQPLRRLVLHVVSAAQAERLARAEE | L663V | CD4+ | 2.9 | x | x |
B16F10 mutations determined to be immunogenic upon peptide or RNA immunization (see Fig. 1 and Extended Data Fig. 1). WT, wild type; AA#, position of mutated amino acid; Mut, mutation.
Extended Data Table 2.
Immunogenic CT26 mutations
| Mutation | Gene | Mutated sequence used for vaccination | Substitution (WT, AA#, Mut) | Reactive T cell subtype | MHC I score (best prediction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT26-M03 | Slc20a1 | DKPLRRNNSYTSYIMAICGMPLDSFRA | T425I | CD4+ | 0,3 |
| CT26-M12 | Gpc1 | YRGANLHLEETLAGFWARLLERLFKQL | E165G | CD8+ | 1,9 |
| CT26-M13 | Nphp3 | AGTQCEYWASRALDSEHSIGSMIQLPQ | G234D | CD4+ | 0,1 |
| CT26-M19 | Tmem87a | QAIVRGCSMPGPWRSGRLLVSRRWSVE | G63R | CD8+ | 0,7 |
| CT26-M20 | Slc4a3 | PLLPFYPPDEALEIGLELNSSALPPTE | T373I | CD4+ | 0,9 |
| CT26-M24 | Cxcr7 | MKAFIFKYSAKTGFTKLIDASRVSETE | L340F | CD4+ | 1,8 |
| CT26-M26 | E2f8 | VILPQAPSGPSYATYLQPAQAQMLTPP | I522T | CD8+ | 0,1 |
| CT26-M27 | Agxt2l2 | EHIHRAGGLFVADAIQVGFGRIGKHFW | E247A | CD4+ | 0,2 |
| CT26-M35 | Nap1l4 | HTPSSYIETLPKAIKRRINALKQLQVR | V63I | CD4+ | 0,7 |
| CT26-M37 | Dhx35 | EVIQTSKYYMRDVIAIESAWLLELAPH | T646I | CD4+ | 0,1 |
| CT26-M39 | Als2 | GYISRVTAGKDSYIALVDKNIMGYIAS | L675I | CD8+ | 0,2 |
| CT26-M42 | Deptor | SHDSRKSTSFMSVNPSKEIKIVSAVRR | S253N | CD4+ | 0,3 |
| CT26-M43 | Tdg | AAYKGHHYPGPGNYFWKCLFMSGLSEV | H169Y | CD4+ | 0,3 |
| CT26-M55 | Dkk2 | EGDPCLRSSDCIDEFCCARHFWTKICK | G192E | CD4+ | 9,7 |
| CT26-M58 | Rpap2 | CGYPLCQKKLGVISKQKYRISTKTNKV | P113S | CD4+ | 11,3 |
| CT26-M68 | Steap2 | VTSIPSVSNALNWKEFSFIQSTLGYVA | R388K | CD4+ | 6,8 |
| CT26-M75 | Usp26 | KTTLSHTQDSSQSLQSSSDSSKSSRCS | S715L | n.d. | 5,8 |
| CT26-M78 | Nbea | PAPRAVLTGHDHEIVCVSVCAELGLVI | V576I | CD4+ | 6,3 |
| CT26-M90 | Aldh18a1 | LHSGQNHLKEMAISVLEARACAAAGQS | P154S | CD4+ | 8,3 |
| CT26-M91 | Zc3h14 | NCKYDTKCTKADCLFTHMSRRASILTP | P497L | CD4+ | 8,8 |
| CT26-M93 | Drosha | LRSSLVNNRTQAKIAEELGMQEYAITN | V1189I | CD4+ | 9,9 |
CT26 mutations determined to be immunogenic upon RNA immunization (see Fig. 1). WT, wild type; AA#, position of mutated amino acid; Mut, mutation.
Extended Data Table 3.
Immunogenic 4T1 mutations
| Mutation | Gene | Mutated sequence used for vaccination | Substitution (WT, AA#, Mut) | Reactive T cell subtype |
| 4T1-M2 | Gen1 | IPHNPRVAVKTTNNLVMKNSVCLERDS | K707N | CD4 |
| 4T1-M3 | Polr2a | LAAQSLGEPATQITLNTFHYAGVSAKN | M1102I | CD4 |
| 4T1-M8 | Tmtc2 | QGVTVLAVSAVYDIFVFHRLKMKQILP | V201I | CD8 |
| 4T1-M14 | Zfr | AHIRGAKHQKVVTLHTKLGKPIPSTEP | K411T | CD4 |
| 4T1-M16 | Cep120 | ELAWEIDRKVLHQNRLQRTPIKLQCFA | H68N | CD4 |
| 4T1-M17 | Malt1 | FLKDRLLEDKKIAVLLDEVAEDMGKCH | T534A | CD4 |
| 4T1-M20 | Wdr11 | NDEPDLDPVQELIYDLRSQCDAIRVTK | T340I | CD8 |
| 4T1-M22 | Kbtbd2 | DAAALQMIIAYAYRGNLAVNDSTVEQL | T91R | CD4 |
| 4T1-M25 | Adamts9 | KDYTAAGFSSFQKLRLDLTSMQIITTD | I623L | CD4 |
| 4T1-M26 | Pzp | AVKEEDSLHWQRPEDVQKVKALSFYQP | G1199E | CD8 |
| 4T1-M27 | Gprc5a | FAICFSCLLAHALNLIKLVRGRKPLSW | F119L | CD8 |
| 4T1-M30 | Enho | MGAAISQGAIIAIVCNGLVGFLL | L10I | CD4 |
| 4T1-M31 | Dmrta2 | EKYPRTPKCARCGNHGVVSALKGHKRY | R73G | CD4 |
| 4T1-M32 | Rragd | SHRSCSHQTSAPSPKALAHNGTPRNAI | L268P | CD4 |
| 4T1-M35 | Zzz3 | KELLQFKKLKKQNLQQMQAESGFVQHV | K311N | CD8 |
| 4T1-M39 | Ilkap | RKGEREEMQDAHVSLNDITQECNPPSS | 127S | CD4 |
| 4T1-M40 | Cenpf | RVEKLQLESELNESRTECITATSQMTA | D1327E | CD4 |
4T1 mutations determined to be immunogenic upon RNA immunization (see Fig. 1). WT, wild type; AA#, position of mutated amino acid; Mut, mutation.
Extended Data Table 4.
CT26 mutated epitopes encoded in pentatope 1+2
| Pentatope | Mutation | Gene | Mutated sequence used for vaccination | Substitution (WT, AA#, Mut) | Reactive T cell subtype |
| 1 | CT26-M19 | Tmem87a | QAIVRGCSMPGPWRSGRLLVSRRWSVE | G63R | CD8+ |
| 1 | CT26-M39 | Als2 | GYISRVTAGKDSYIALVDKNIMGYIAS | L675I | CD8+ |
| 1 | CT26-M13 | Nphp3 | AGTQCEYWASRALDSEHSIGSMIQLPQ | G234D | CD4+ |
| 1 | CT26-M55 | Dkk2 | EGDPCLRSSDCIDEFCCARHFWTKICK | G192E | CD4+ |
| 1 | CT26-M68 | Steap2 | VTSIPSVSNALNWKEFSFIQSTLGYVA | R388K | CD4+ |
| 2 | CT26-M20 | Slc4a3 | PLLPFYPPDEALEIGLELNSSALPPTE | T373I | CD4+ |
| 2 | CT26-M26 | E2f8 | VILPQAPSGPSYATYLQPAQAQMLTPP | I522T | CD8+ |
| 2 | CT26-M03 | Slc20a1 | DKPLRRNNSYTSYIMAICGMPLDSFRA | T425I | CD4+ |
| 2 | CT26-M37 | Dhx35 | EVIQTSKYYMRDVIAIESAWLLELAPH | T646I | CD4+ |
| 2 | CT26-M27 | Agxt2l2 | EHIHRAGGLFVADAIQVGFGRIGKHFW | E247A | CD4+ |
Ten immunogenic mutated epitopes were used for generation of two pentatopes used for therapeutic vaccination shown in Fig. 3b. WT, wild type; AA#, position of mutated amino acid; Mut, mutation.
Extended Data Table 5.
In silico prediction of CT26 mutations with abundant expression and favourable MHC class II binding properties
| Mutation | Gene | Mutated sequence used for vaccination | Substitution (WT, AA#, Mut) | Expression (NVRC) | MHC II score (best prediciton) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT26-E1 | Asns | DSVVIFSGEGSDEFTQGYIYFHKAPSP | L370F | 1428,05 | 45,45 |
| CT26-E2 | Cd34 | PQTSPTGILPTTSNSISTSEMTWKSSL | D120N | 1150,85 | 23,76 |
| CT26-E3 | Actb | WIGGSILASLSTFHQMWISKQEYDESG | Q353H | 974,16 | 8,30 |
| CT26-E4 | Tmbim6 | SALGSLALMIWLMTTPHSHETEQKRLG | A73T | 825,51 | 2,96 |
| CT26-E5 | Glud1 | DLRTAAYVNAIEKIFKVYNEAGVTFT | V546I | 619,54 | 8,04 |
| CT26-E16 | Eif4g2 | KLCLELLNVGVESNLILKGVILLIVDK | K108N | 327,79 | 20,99 |
| CT26-E17 | Sept7 | NVHYENYRSRKLATVTYNGVDNNKNKG | A314T | 316,98 | 6,47 |
| CT26-E18 | Fn1 | YTVSVVALHDDMENQPLIGIQSTAIPA | S1710N | 303,62 | 17,41 |
| CT26-E19 | Brd2 | KPSTLRELERYVLACLRKKPRKPYTIR | S703A | 301,83 | 7,86 |
| CT26-E20 | Uchl3 | KFMERDPDELRFNTIALSAA | A224T | 301,78 | 9,75 |
| CT26-ME1 | Aldh18a1 | LHSGQNHLKEMAISVLEARACAAAGQS | P154S | 67,73 | 0,05 |
| CT26-ME2 | Ubqln1 | DTLSAMSNPRAMQVLLQIQQGLQTLAT | A62V | 84,08 | 0,24 |
| CT26-ME3 | Ppp6r1 | DGQLELLAQGALDNALSSMGALHALRP | D309N | 139,80 | 0,44 |
| CT26-ME4 | Trip12 | WKGGPVKIDPLALMQAIERYLVVRGYG | V1328M | 83,09 | 0,49 |
| CT26-ME5 | Pcdhgc3 | QDINDNNPSFPTGKMKLEISEALAPGT | E139K | 86,16 | 0,54 |
| CT26-ME6 | Cad | SDPRAAYFRQAENDMYIRMALLATVLG | G2139D | 152,86 | 0,55 |
| CT26-ME7 | Smarcd1 | MDLLAFERKLDQTVMRKRLDIQEALKR | I161V | 125,85 | 0,60 |
| CT26-ME8 | Ddx27 | ITTCLAVGGLDVKFQEAALRAAPDILI | S297F | 61,82 | 0,62 |
| CT26-ME9 | Snx5 | KARLKSKDVKLAEAHQQECCQKFEQLS | T341A | 120,27 | 0,73 |
| CT26-ME10 | Lin7c | GEVPPQKLQALQRALQSEFCNAVREVY | V41A | 71,24 | 1,09 |
CT26 mutations selected for high expression with (ME) or without (E) consideration of the MHC II percentile rank (IEDB consensus version 2.5). WT, wild type; AA#, position of mutated amino acid; Mut, mutation.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Holzmann, A. König, U. Schmitt, R. Roth, C. Worm and N. Krause for technical assistance; L. Ralla, J. Groß, A. Spruß, M. Erdeljan, S. Wöll and C. Rohde for immunohistochemical staining and analysis; C. Paret for sequence validation of mutations; M. Brkic for immunofluorescence staining; S. Witzel and Bodo Tillmann, S. Wurzel and Z. Yildiz for cloning of constructs; S. Kind, M. Mechler, F. Wille, B. Otte and S. Petri for RNA production as well as L. Kranz and colleagues involved in RNA formulation development. We are grateful to B. Kloke, S. Heesch, A. Kuhn, J. Buck, C. Britten and H. Haas for conceptual and technical discussions. Moreover, we would like to thank V. Bukur, J. de Graf and C. Albrecht who supported the next-generation sequencing of samples. Furthermore we like to acknowledge A. Kong for critical reading and A. Orlandini for help with graphic design. The results shown here are in part based on data generated by the TCGA Research Network http://cancergenome.nih.gov/. The study was supported by the CI3 excellence cluster program of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).
Footnotes
Online Content Methods, along with any additional Extended Data display items and Source Data, are available in the online version of the paper; references unique to these sections appear only in the online paper.
Author Contributions U.S. is principal investigator, conceptualized the study and experimental strategy. S.K., M.V., N.vdR., M.D., J.D., F.V. and U.S. planned and analysed experiments. M.V. and N.vdR. performed experiments. S.K., M.V., M.D., S.P.S., C.H., Ö.T. and U.S. interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. M.L., S.B., A.D.T. and J.C.C. processed next-generation sequencing data and identified mutations. M.V. and B.S. analysed murine MHC II binding predictions. S.B. analysed TCGA data and human MHC II binding predictions.
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
References
- 1.Castle JC, et al. Exploiting the mutanome for tumor vaccination. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1081–1091. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Castle JC, et al. Immunomic, genomic and transcriptomic characterization of CT26 colorectal carcinoma. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:190. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Holtkamp S, et al. Modification of antigen-encoding RNA increases stability, translational efficacy, and T-cell stimulatory capacity of dendritic cells. Blood. 2006;108:4009–4017. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-015024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kreiter S, et al. Increased antigen presentation efficiency by coupling antigens to MHC class I trafficking signals. J Immunol. 2008;180:309–318. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.1.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kuhn AN, et al. Phosphorothioate cap analogs increase stability and translational efficiency of RNA vaccines in immature dendritic cells and induce superior immune responses in vivo. Gene Ther. 2010;17:961–971. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bloom MB, et al. Identification of tyrosinase-related protein 2 as a tumor rejection antigen for the B16 melanoma. J Exp Med. 1997;185:453–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schumacher T, et al. A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity. Nature. 2014;512:324–327. doi: 10.1038/nature13387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tran E, et al. Cancer immunotherapy based on mutation-specific CD4+ T cells in a patient with epithelial cancer. Science. 2014;344:641–645. doi: 10.1126/science.1251102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Britten CM, et al. The regulatory landscape for actively personalized cancer immunotherapies. Nature Biotechnol. 2013;31:880–882. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gerlinger M, et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:883–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Koebel CM, et al. Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature. 2007;450:903–907. doi: 10.1038/nature06309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matsushita H, et al. Cancer exome analysis reveals a T-cell-dependent mechanism of cancer immunoediting. Nature. 2012;482:400–404. doi: 10.1038/nature10755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Robbins PF, et al. Mining exomic sequencing data to identify mutated antigens recognized by adoptively transferred tumor-reactive T cells. Nature Med. 2013;19:747–752. doi: 10.1038/nm.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van Rooij N, et al. Tumor exome analysis reveals neoantigen-specific T-cell reactivity in an ipilimumab-responsive melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:e439–e442. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shen Z, et al. Cloned dendritic cells can present exogenous antigens on both MHC class I and class II molecules. J Immunol. 1997;158:2723–2720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schoenberger SP, et al. T-cell help for cytotoxic T lymphocytes is mediated by CD40–CD40L interactions. Nature. 1998;393:480–483. doi: 10.1038/31002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Linnemann C, et al. High-throughput epitope discovery reveals frequent recognition of neo-antigens by CD4+ T cells in human melanoma. Nature Med. 2015;21:81–85. doi: 10.1038/nm.3773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arnold PY, et al. The majority of immunogenic epitopes generate CD4+ T cells that are dependent on MHC class II-bound peptide-flanking residues. J Immunol. 2002;169:739–749. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wolfel T, et al. A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma. Science. 1995;269:1281–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.7652577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang RF, et al. Cloning genes encoding MHC class II-restricted antigens: mutated CDC27 as a tumor antigen. Science. 1999;284:1351–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lu YC, et al. Mutated PPP1R3B is recognized by T cells used to treat a melanoma patient who experienced a durable complete tumor regression. J Immunol. 2013;190:6034–6042. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gubin MM, et al. Checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy targets tumour-specific mutant antigens. Nature. 2014;515:577–581. doi: 10.1038/nature13988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Snyder A, et al. Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2189–2199. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Herbst RS, et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 2014;515:563–567. doi: 10.1038/nature14011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tumeh PC, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014;515:568–571. doi: 10.1038/nature13954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rizvi NA, et al. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science. 2015;348:124–128. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Castle JC, et al. Mutated tumor alleles are expressed according to their DNA frequency. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4743. doi: 10.1038/srep04743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Löwer M, et al. Confidence-based somatic mutation evaluation and prioritization. PLOS Comput Biol. 2012;8:e1002714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boegel S, et al. A catalog of HLA type, HLA expression, and neo-epitope candidates in human cancer cell lines. OncoImmunology. 2014;3:e954893. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.954893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kreiter S, et al. Intranodal vaccination with naked antigen-encoding RNA elicits potent prophylactic and therapeutic antitumoral immunity. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9031–9040. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


