Abstract
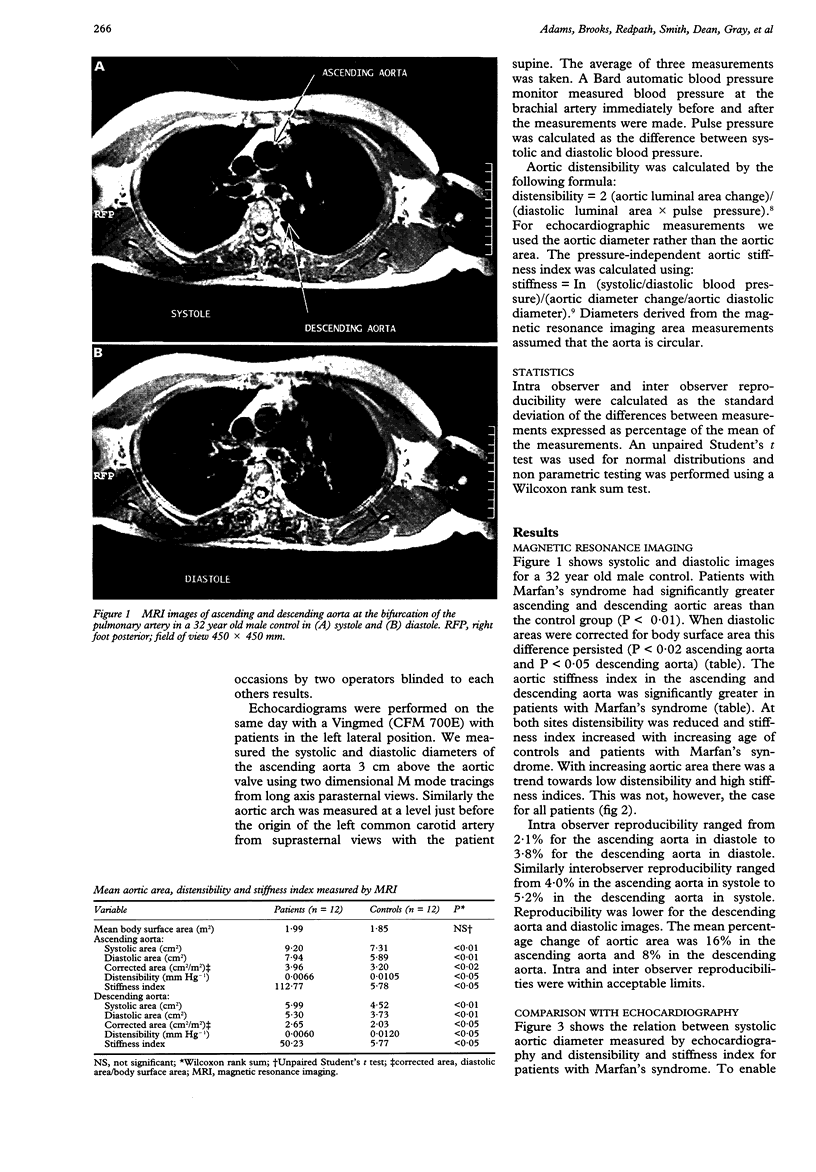
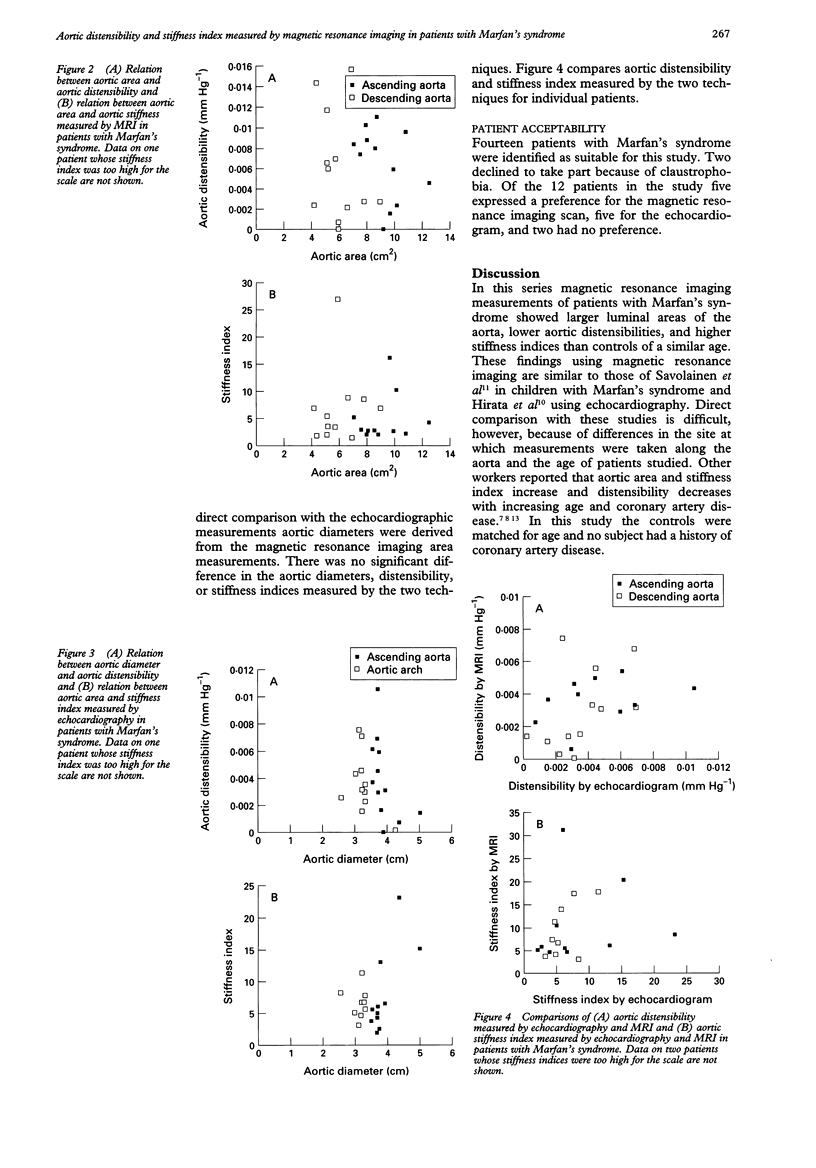
OBJECTIVES--To use magnetic resonance imaging to measure the elastic properties of the aorta of adults with Marfan's syndrome and to compare these results with those obtained by echocardiography. PATIENTS AND METHODS--12 patients with Marfan's syndrome and 12 controls matched for age. Transverse luminal areas of the ascending and descending aorta were measured using electrocardiographic gated magnetic resonance imaging. Echocardiography was used to measure the diameter of the ascending aorta and aortic arch in patients with Marfan's syndrome. Blood pressure was measured during both scans. RESULTS--In diastole, transverse luminal areas of the ascending and descending aorta were significantly greater in patients with Marfan's syndrome when measured by magnetic resonance imaging and corrected for body surface area; P < 0.02 and P < 0.05 respectively. Patients with Marfan's syndrome had a higher stiffness index (112.77 v 5.78, P < 0.05) and a lower distensibility (0.0066 v 0.0105, P < 0.05) than controls. Results produced by MRI and echocardiography were not significantly different. CONCLUSIONS--Magnetic resonance imaging gives good quality reproducible images of the ascending and descending aorta. In patients with Marfan's syndrome, aortic distensibility and stiffness index measured by magnetic resonance imaging were abnormal (but did not always relate directly to the size of the aorta.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beighton P., de Paepe A., Danks D., Finidori G., Gedde-Dahl T., Goodman R., Hall J. G., Hollister D. W., Horton W., McKusick V. A. International Nosology of Heritable Disorders of Connective Tissue, Berlin, 1986. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;29(3):581–594. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno L., Tredici S., Mangiavacchi M., Colombo V., Mazzotta G. F., Sirtori C. R. Cardiac, skeletal, and ocular abnormalities in patients with Marfan's syndrome and in their relatives. Comparison with the cardiac abnormalities in patients with kyphoscoliosis. Br Heart J. 1984 Feb;51(2):220–230. doi: 10.1136/hrt.51.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford E. S. Marfan's syndrome. Broad spectral surgical treatment cardiovascular manifestations. Ann Surg. 1983 Oct;198(4):487–505. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198310000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detrano R., Moodie D. S., Gill C. C., Markovich D., Simpfendorfer C. Intravenous digital subtraction aortography in the preoperative and postoperative evaluation of Marfan's aortic disease. Chest. 1985 Aug;88(2):249–253. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Furthmayr H. Marfan's syndrome and other disorders of fibrillin. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1384–1385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gott V. L., Pyeritz R. E., Cameron D. E., Greene P. S., McKusick V. A. Composite graft repair of Marfan aneurysm of the ascending aorta: results in 100 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991 Jul;52(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(91)91414-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Triposkiadis F., Sparks E., Bowen J., Boudoulas H., Wooley C. F. The Marfan syndrome: cardiovascular physical findings and diagnostic correlates. Am Heart J. 1992 Mar;123(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90515-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Triposkiadis F., Sparks E., Bowen J., Wooley C. F., Boudoulas H. The Marfan syndrome: abnormal aortic elastic properties. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Jul;18(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Sasayama S., Yagi S., Asakawa T., Hirai T. Non-invasive assessment of the age related changes in stiffness of major branches of the human arteries. Cardiovasc Res. 1987 Sep;21(9):678–687. doi: 10.1093/cvr/21.9.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohiaddin R. H., Underwood S. R., Bogren H. G., Firmin D. N., Klipstein R. H., Rees R. S., Longmore D. B. Regional aortic compliance studied by magnetic resonance imaging: the effects of age, training, and coronary artery disease. Br Heart J. 1989 Aug;62(2):90–96. doi: 10.1136/hrt.62.2.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch J. L., Walker B. A., Halpern B. L., Kuzma J. W., McKusick V. A. Life expectancy and causes of death in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 13;286(15):804–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204132861502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C. Aortic dissection: anatomy, consequences, and causes. Am Heart J. 1981 Feb;101(2):195–214. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90666-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C., Honig H. S. The spectrum of cardiovascular disease in the Marfan syndrome: a clinico-morphologic study of 18 necropsy patients and comparison to 151 previously reported necropsy patients. Am Heart J. 1982 Jul;104(1):115–135. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90650-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen A., Keto P., Hekali P., Nisula L., Kaitila I., Viitasalo M., Poutanen V. P., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Kupari M. Aortic distensibility in children with the Marfan syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1992 Sep 1;70(6):691–693. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)90215-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer S., Peshock R. M., Malloy C. R., Katz J., Parkey R. W., Willerson J. T. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging in Marfan's syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Jan;9(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlatmann T. J., Becker A. E. Pathogenesis of dissecting aneurysm of aorta. Comparative histopathologic study of significance of medial changes. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Jan;39(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(77)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shores J., Berger K. R., Murphy E. A., Pyeritz R. E. Progression of aortic dilatation and the benefit of long-term beta-adrenergic blockade in Marfan's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1335–1341. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanadis C., Stratos C., Boudoulas H., Kourouklis C., Toutouzas P. Distensibility of the ascending aorta: comparison of invasive and non-invasive techniques in healthy men and in men with coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 1990 Nov;11(11):990–996. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treasure T. Elective replacement of the aortic root in Marfan's syndrome. Br Heart J. 1993 Feb;69(2):101–103. doi: 10.1136/hrt.69.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]