Abstract
Background
Primary stability after implant placement is essential for osseointegration. It is important to understand the bone/implant interface for analyzing the influence of implant design on primary stability. In this study rigid polyurethane foam is used as artificial bone to evaluate the bone–implant interface and to identify where the torque is being generated during placement.
Methods
Five implant systems—Straumann-Standard (ST), Straumann-Bone Level (BL), Straumann-Tapered Effect (TE), Nobel Biocare-Brånemark MKIII (MK3), and Nobel Biocare-Brånemark MKIV (MK4)—were used for this experiment. Artificial bone blocks were prepared and the implant was installed. After placement, a metal jig and one side artificial bone block were removed and then the implant embedded in the artificial bone was exposed for observing the bone–implant interface. A digital micro-analyzer was used for observing the contact interface.
Results
The insertion torque values were 39.35, 23.78, 12.53, 26.35, and 17.79 N cm for MK4, BL, ST, TE, and MK3, respectively. In ST, MK3, TE, MK4, and BL the white layer areas were 61 × 103 μm2, 37 × 103 μm2, 103 × 103 μm2 in the tapered portion and 84 × 03 μm2 in the parallel portion, 134 × 103 μm2, and 98 × 103 μm2 in the tapered portion and 87 × 103 μm2 in the parallel portion, respectively.
Conclusions
The direct observation method of the implant/artificial bone interface is a simple and useful method that enables the identification of the area where implant retention occurs. A white layer at the site of stress concentration during implant placement was identified and the magnitude of the stress was quantitatively estimated. The site where the highest torque occurred was the area from the thread crest to the thread root and the under and lateral aspect of the platform. The artificial bone debris created by the self-tapping blade accumulated in both the cutting chamber and in the space between the threads and artificial bone.
Keywords: Primary stability, Implant design, Artificial bone, Implant/bone interface
Background
Primary stability after implant placement is essential for osseointegration. Aside from the patient’s bone quantity and density, primary stability may also be affected by the implant design, including surface topography, and by the technique used to prepare the insertion socket (Friberg et al. 1995; Chiapasco et al. 1997; Javed and Romanos 2010). To analyze the influence of implant design on primary stability, it is also important to understand the bone/implant interface. Conventionally, microscopy of animal tissue samples (Orsini et al. 2010; Ericsson et al. 1994; Duyck et al. 2001; Shalabi et al. 2006; Marin et al. 2008) or radiographic analyses have been used (Akkocaoglu et al. 2005). The former focused on the morphology of the interface only after osseointegration had occurred, whereas the latter displayed low resolution, making it difficult to standardize (Meredith 1998) and provide an accurate evaluation. In an attempt to solve these issues, a novel method was developed to observe the implant/simulated bone interface using an artificial bone.
There are a number of reports investigating the properties of rigid polyurethane foam (PUF) for use as artificial bone (Thompson et al. 2003; Palissery et al. 2004; Szivek et al. 1993; Patel et al. 2008; Calvert et al. 2010). PUF is currently used as a standard orthopedic mechanical test material by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (ASTM 2008). For mechanical testing of bone screws, the Japanese Industrial Standards recommend PUF to simulated bone, as it reproduces the dynamic characteristics of both cortical and cancellous bone (Doe 2009). The Solid Rigid Polyurethane and Cellular Rigid Polyurethane comply with the ASTM standard F1839, indicating that the materials are suitable for simulating bone to test orthopedic devices and instruments. In recent years, PUF has been used to simulated bone in dentistry for the retention of dental implants (Tabassum et al. 2009; Chong et al. 2009; Kim and Lim 2011; Kim et al. 2011; Ahn et al. 2012; Yamaguchi et al. 2015), as well as to investigate the retention of mini-implants (Lim et al. 2008; Kim et al. 2008). In this study, PUF was used evaluate the implant/simulated bone interface and to identify where the torque values is being generated during implant placement.
Methods
Implants
The types of implants used for this experiment and their design characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Standard RN (ST) and Brånemark MKIII (MK3) implants are parallel design. The outer profile of the Bone Level RC (BL) implant is entirely parallel, although the inner profile is tapered only in the neck region and the thread height is reduced. For the Tapered Effect RN (TE) implant, the apical portion is parallel and the inner and outer profiles display the same taper in the neck region. The Brånemark MKIV (MK4) implant has a gentle taper along the entire inner and outer profile, with a cutting chamber. ST, BL, and TE are considered non-self-tapping implants, whereas MK3 and MK4 are self-tapping implants with double-threaded.
Table 1.
Implants used in this study
| Implant system | Length (mm) | Diameter (mm) | Pitch (mm) | Lead (mm) | Code | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard RN | 10 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | ST | Straumann |
| Bone level RC | 10 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | TE | Straumann |
| Tapered effect RN | 10 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | TE | Straumann |
| Brånemark MKIII | 10 | 3.75 | 0.6 | 1.2 | MK3 | Nobel Biocare |
| Brånemark MKIV | 10 | 4.0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | MK4 | Nobel Biocare |
Direct observation method
The mean bone mineral density for the posterior maxilla is 0.31 g/cm3 ( 2015). The densities of used PUF (0.32 g/cm3) were density of similar in type 4 bone density, and the following physical properties: 8.4 MPa compressive strength, 5.6 MPa tensile strength, 4.3 MPa shear strength, and a coefficient of elasticity of 284 GPa (Solid Rigid polyurethane Form 20 pcf; Sawbone; pacific Research Laboratories Inc., USA) (Doe 2015).
A divided block specimen is assembled by following procedures. Four pieces of prismatic simulated bone of 1 cm × 1 cm × 3 cm were prepared, they were fixed with tape beforehand, and their circumference was fixed with metal jigs. The insertion socket was prepared in the center of the column using manufacture protocol (ASD-360, Ashina, Hiroshima, Japan), avoiding movement. Each implant was installed with a load of 500 g and a speed of 15 rpm (Fig. 1). The maximum insertion torque-time curve during placemen was recorded using a torque analyzer (TRQ-5DRU, PC Torque Analyzer, Vectrix, Tokyo, Japan).
Fig. 1.
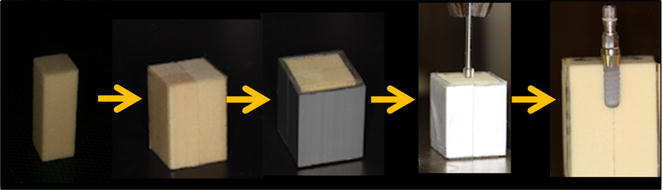
Flow of a divided block specimen. Four divided block specimen was assembled by tape. Their circumference was fixed with metal jigs and the implant was inserted according to the manufacturer instructions. After the placement, the metal jigs and two of the divided block were removed carefully
After implant placement, the metal jigs and two of the simulated bone were removed carefully, the implant body was exposed. A digital micro analyzer (VHX-1000, Keyence, Osaka, Japan) and image analysis software (PopImaging, Digital Being Kids, Kanagawa, Japan) were used for observation of the implant/simulated bone interface and for image analysis, respectively. The observation of the white layer was carried out only at representative specimen that closes to average value of IT. Regression analysis examining the correlation between the area of the white layer and Torque raise rate (JMP, SAS Institute Japan, Tokyo, Japan).
Results
The insertion torque-time curves for each implant are illustrated in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
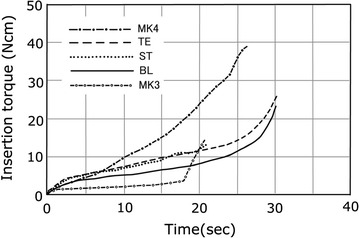
Torque-time curves for average insertion value of MK4, TE, ST, BL, MK3 implant
Implant/simulated bone interface. In ST (Fig. 3a, b), a compressed channel was observed in the implant neck. The compressed channel had smaller morphology when compared with the threads, and a subtle circular-shaped white layer could be observed around the channel. Figure 3c shows a white layer around the thread crests. The upper surface of the threads engaged the artificial bone, although a gap could be seen between the under thread and the thread root. The area of the white layer was approximately 61 × 103 μm2.
Fig. 3.

Representative photographs of ST/simulated bone interface. Photographs of a and b were taken from the neck of the implant, showing the tapped channel (a: magnification, ×30, b: magnification, ×40). A photograph of c was taken from the middle of the implants, showing the white layer (dotted line) (magnification, ×40)
In MK3, a gap between the tapped channel and the threads was also observed (Fig. 4a, b). The debris regarded as artificial bone chips were scattered along the implant surface and observed abundantly in the cutting chamber. A white layer could be observed around the threads, and debris could easily be removed by air-blowing. The thread crests closely engaged the artificial bone, although a gap could be seen under to the threads extending to the thread root. The white layer on the thread crest was 37 × 103 μm2 (Fig. 4c).
Fig. 4.
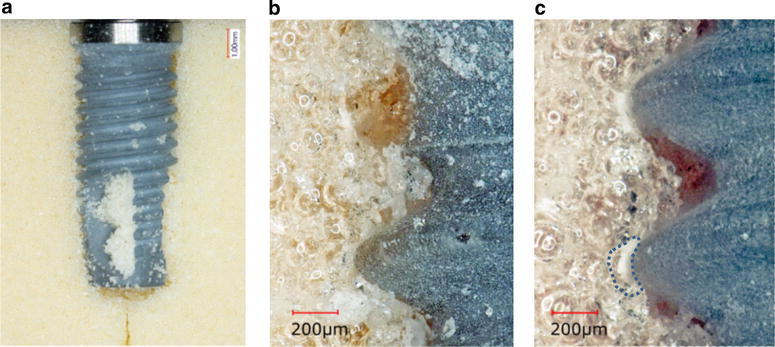
Representative photographs of MK3/simulated bone interface. Debris was scattered overall implant body and the cutting chamber (a: magnification, ×3). A photograph of b was taken from the neck of the implant, showing the tapped channel (magnification, ×30). A photograph of c was taken from the middle of the implant, showing the space between the under implant threads to the root (magnification, ×30)
In TE, a gap was observed between the inner profile of the implant and the artificial bone (Fig. 5a). In the tapered portion, approximately half of the thread height engaged the artificial bone and a circular-shaped white layer were observed around the thread ridge (Fig. 5b, c). The upper threads closely engaged the artificial bone, although a gap could be seen between the under surface of the threads and the threads root. The white layer was 103 × 103 μm2 in the tapered portion (B) and 84 × 103 μm2 in the parallel portion (C).
Fig. 5.
Representative photographs of TE/simulated bone interface. A photograph of a was showing the space between threads (magnification, ×5). A photograph of b was taken from the neck of the implants (tapered portion) (magnification, ×40) and c was taken from the middle of the implant, both showing the white layer (dotted line) and the space between the under implant threads to the root (magnification, ×40)
In MK4, slight gaps were observed along the entire implant and artificial bone interface (Fig. 6a). The cutting debris on the implant surface and thread root (Fig. 6b). The debris was removed and a gap was then observed around the thread root, and white layers were observed around both the thread crest and root. The white layer was 134 × 103 μm2 (Fig. 6c).
Fig. 6.
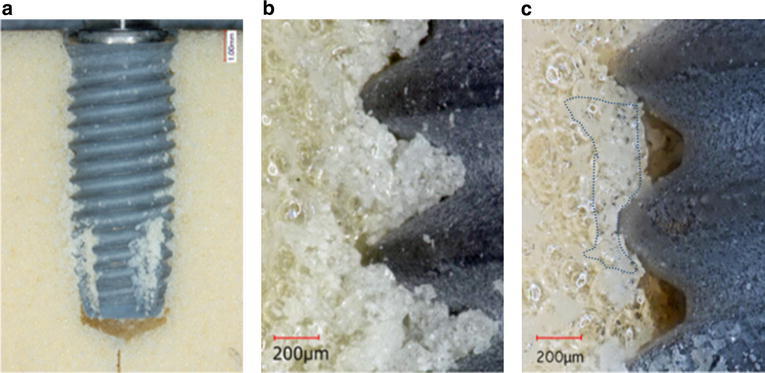
Representative photographs of MK4/simulated bone interface. Debris was scattered overall implant body and the cutting chamber (a: magnification, ×4). A photograph of b and c was taken from the middle of the implant (magnification, ×40), and b was showing debris in the threads root, and after air-blowing of c was showing the white layer (dotted line), the space realized thread root (magnification, ×40)
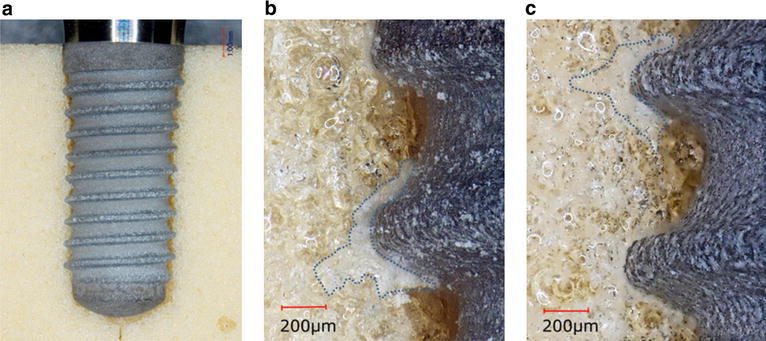
In BL, the upper thread surface closely engaged the artificial bone, and a gap was observed the thread root (Fig. 7a, b). The white layer surrounding the threads was 98 × 103 μm2 in the tapered portion (B) and 87 × 103 μm2 in the parallel portion (C).
Fig. 7.
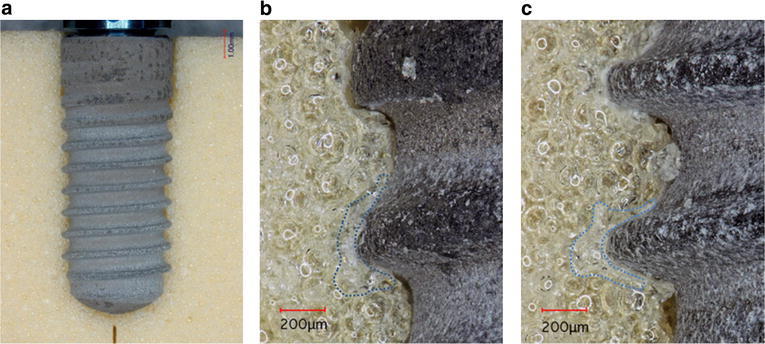
Representative photographs of BL/simulated bone interface. A photograph of a was showing the tapered portion engaged the simulated bone (magnification, ×5). A photograph of b was taken from the neck of the implant, showing the white layer (dotted line) (magnification, ×40). A photograph of c was taken from the middle of the implants, showing the white layer (dotted line) (magnification, ×40)
Table 2 shows the white layer corresponds with the torque value. Regression analysis examining the correlation between the white layer area and torque raise rate, the correlation coefficient is 0.617566, slope 0.019372, intercept 0.60584 is obtained, a positive correlation was observed.
Table 2.
Area of white layer and torque rise rate of each implant
| Implant | Portion | Area of white layer (×103 μm2) | Torque rise rate (N cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST | Parallel | 61 | 0.45 |
| MK3 | Parallel | 37 | 0.13 |
| TE | Parallel | 84 | 0.45 |
| BL | Parallel | 87 | 0.35 |
| TE | Taper | 103 | 2.31 |
| MK4 | Taper | 134 | 1.32 |
| BL | Taper | 98 | 2.45 |
Discussion
The bone density of used PUF was similar to other reports (Tabassum et al. 2009; Bayarchimeg et al. 2013), and the PUF is homogeneous consistency and eliminate anatomical or structural differences of biological samples to IT evaluate better the effects of the implant design (Tabassum et al. 2009). Furthermore, PUF exhibit stress–strain behaviors similar to trabecular bone (Calvert et al. 2010). The novel direct observation method devised for this study enables the center of the implant to be exposed without becoming destruction of the specimen; therefore, the implant/artificial bone interface could be observed successfully.
The insertion torque values provides more accurate data for the retention of an implant (Friberg et al. 1995; Homolka et al. 2002; Sakoh et al. 2006; Atsumi et al. 2007). The implant design affects the insertion torque values (O’Sullivan and Sennerby 2000). This study revealed that the white layer corresponds with the insertion torque to some degree. Differences in insertion torque value were related to differences in the morphology of the white layer. The relationship between the white layer area of the parallel and tapered sections with torque raise rate. The white layer area remains small when the implant design is parallel and torque increases gradually. The white layer area remains wide when a tapered design is used and the torque increases suddenly. A limitation of the direct method used to observe the implant/artificial bone interface is disturbance and spreading of the blocks when the insertion torques becomes large. Therefore, it is necessary to securely fix the blocks assembly using metal jigs and to ensure that the specimen is correctly placed by measuring the insertion torque values.
The white layers were observed around the implant threads in all specimens. The area of the white layers varied, and included the thread crests, circular-shaped sites around the thread ridges, and thread roots. Some areas were belt-shaped with a constant width and in other areas, the white layer spread deeply from the crest of the threads.
The comparing the IT of self-tapping and non-self-tapping implants were resulted the self-tapping implant higher insertion values than with non-self-tapping implants in a clinical study (Marković et al. 2013). The conical Implant compared with cylindric screw-type implant resulted in higher primary stability in soft bone (Sakoh et al. 2006). The primary stability of five implant designs was compared in fresh human cadavers. In type 4 bones, the MkIV Brånemark implant maintained a high primary stability in compare with all other types tested (O’Sullivan and Sennerby 2000). However, when measuring the area of these white layers, it was found that self-tapping straight implant of MK3 had the smallest, followed by ST, BL, TE, and self-tapping tapered implant of MK4. Therefore, this result could be the implant macro-design (e.g. tapered and straight) effect to IT than cutting chamber. This order correlates with the implant torque values, suggesting that the size of the white layer is closely related to insertion torque values. It is presumed that the white layer occurs when the cell structure of the artificial bone is damaged by an external force, with variations in reflection factor and refractive index causing the area to become cloudy. Therefore, the location of the white layer is thought to correspond with the site of stress concentration. In addition, if the size of the white layer does indeed correspond with stress, it could be used to indicate the location, direction, and magnitude of force acting on the artificial bone. The present study showed that the IT and white layer increased according to the tapered portion, resulting in a positive correlation. In other words, the primary stability was shown to be highly dependent on the implant design.
Observing the interface between the threads and artificial bone in detail, the upper threads closely engaged the artificial bone, whereas the under did not contact the artificial bone closely, resulting in the presence of a gap. Based on this observation, it is believed that primary stability of the implants was mainly dependent on the friction between the upper surface of the threads and the bone. Potential causes for the gap under to the threads are as follows. During insertion, a rotational force is used to extend the implant into the artificial bone, resulting in slight expansion of the implant as the under thread surfaces rotate and compress the artificial bone upon contact. However, once the rotational force disappears, the implant shrinks by elastic recovery. This shrinkage results in a separation between the under thread surfaces and the bone. In ST and MK3, the parallel implant groups, the threads contacted the artificial bone at the neck. This was a characteristic finding of the parallel implants as it was not observed with tapered implants. This gap was slightly smaller than that noted between the artificial bone and the threads positioned further apically. It is suggested that the elastic recovery force holed the threads and enhanced retention of the implant. The implant platform in MK3 and MK4 engaged the artificial bone closely and no gap was seen. However, white layers such as those around the threads were not observed. The insertion torque-time curves showed that a greater torque values was generated when the platform contacted the bone. This is presumably because the surface where the platform contacted the bone was large and flat, and therefore the force was dispersed and did not create sufficient plastic deformation to destroy the foam. For self-tapping implant of MK3 and MK4, it was confirmed that the bone debris, which occurred during tapping, were distributed over the contacting interface. This study revealed that most of the bone debris was accumulated in the chamber, although some were simultaneously accumulated in the gap between the threads and artificial bone. Therefore, it is thought that a greater decrease in reverse torque occurred because of the bone debris on the contact interface being gradually fragmented and flattened. One of the causes early lost might flattening of the irregularities of the contact area.
Conclusions
The limitation of this study is that only the correlations of mechanical retention and implant design were evaluated, whereas in clinical situations many biological factors affect primary stability. However, the novel direct observation method of the implant/artificial bone interface is a simple and useful that enables the identification of the area where implant retention occurs. Artificial bone composed a white layer at the site of stress concentration during implant placement; therefore, sites loaded by stress were identified and the magnitude of the stress was quantitatively estimated.
Authors’ contributions
YY participated in the sequence alignment concept/design, data collection, data analysis, drafted manuscript. MS helped to concept/design and drafted manuscript. MF and MS helped to data collection. MO participated critical revision of article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Vectrix Corporation and Director Kazuhiro Konagai for the consultation of the torque analyzer.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
- PUF
polyurethane foam
- ST
standard RN
- BL
bone level RC
- TE
tapered effect RN
- MK4
Brånemark MKIV
- MK3
Brånemark MKIII
Contributor Information
Yoko Yamaguchi, Phone: 81-3-3787-1151, Email: blacklab87@gmail.com.
Makoto Shiota, Email: mshiota.impl@tmd.ac.jp.
Masaki FuJii, Email: fujii.irm@tmd.ac.jp.
Michi Sekiya, Email: sekiyami@dent.showa-u.ac.jp.
Masahiko Ozeki, Email: ozekishowa@dent.showa-u.ac.jp.
References
- Ahn SJ, Leesungbok R, Lee SW, Heo YK, Kang KL. Differences in implant stability associated with various methods of preparation of implant bed: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107(6):366–372. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(12)60092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akkocaoglu M, Uysal S, Tekdemir I, Akca K, Cehreli MC. Implant design and intraosseous stability of immediately placed implants: a human cadaver study. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2005;16:202–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2004.01099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTM (2008) F1839, standard specification for rigid polyurethane foam for use as a standard material for testing orthopaedic devices and instruments. American Society for Testing and Materials. West Conshohocken: ASTM. doi:10.1520/F1839-08
- Atsumi M, Park SH, Wang HL. Methods used to assess implant stability: current status. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007;22:743–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayarchimeg D, Namgoong H, Kim BK, Kim MD, Kim S, Kim TI, Seol YJ, Lee YM, Ku Y, Rhyu IC, Lee EH, Koo KT. Evaluation of the correlation between insertion torque and primary stability of dental implants using a block bone test. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013;43(1):30–36. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2013.43.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert KL, Trumble KP, Webster TJ, Kirkpatrick LA. Characterization of commercial rigid polyurethane foams used as bone analogs for implant testing. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(5):1453–1461. doi: 10.1007/s10856-010-4024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiapasco M, Gatti C, Rossi E, Haeflige W, Markwaldel TH. Implant-retained mandibular overdentures with immediate loading: a retrospective multicenter study on 226 consecutive cases. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997;8:48–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.1997.tb00007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L, Khocht A, Suzuki JB, Gaughan J. Effect of implant design on initial stability of tapered implants. J Oral Implantol. 2009;35(3):130–135. doi: 10.1563/1548-1336-35.3.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe J (2015) JIS T0311:2009. Mechanical testing methods for metallic bone screws. Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. https://www.jisc.go.jp. Accessed 16 Dec 2015
- Doe J (2015) Sawbone block 20 PCF. http://www.sawbones.com. Accessed 16 Dec 2015
- Duyck J, Renold HJ, Van Oosterwyck H, Naert I, Vander Sloten J, Ellingsen JE. The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: an animal experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12:207–218. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.2001.012003207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson I, Johansson CB, Bystedt H, Norton MR. A histomorphometric evaluation of bone-to-implant contact on machine-prepared and roughened titanium dental Implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994;5:202–206. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1994.050402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friberg B, Sennerby L, Roos J, Johansson P, Strid CG, Lekholm U. Evaluation of bone density using cutting resistance measurements and microradiography. An in vitro study in pig ribs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1995;6:164–171. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1995.060305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homolka P, Beer A, Birkfellner W, Nowotny R, Gahleitner A, Tschabitscher M, Bergmann H. Bone mineral density measurement with dental quantitative CT prior to dental implant placement in cadaver mandibles: pilot study. Radiology. 2002;224:247–252. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2241010948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javed F, Romanos GE. The role of primary stability for successful immediate loading of dental implants. A literature review. J Dent. 2010;38:612–620. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2010.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim YS, Lim YJ. Primary stability and self-tapping blades: biomechanical assessment of dental implants in medium-density bone. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(10):1179–1184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JW, Baek SH, Kim TW, Chang YI. Comparison of stability between cylindrical and conical type mini-implants. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(4):692–698. doi: 10.2319/0003-3219(2008)078[0692:COSBCA]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim DR, Lim YJ, Kim MJ, Kwon HB, Kim SH. Self-cutting blades and their influence on primary stability of tapered dental implants in a simulated low-density bone model: a laboratory study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol. 2011;112(5):573–580. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim SA, Cha JY, Hwang CJ. Insertion torque of orthodontic miniscrews according to changes in shape, diameter, and length. Angle Orthod. 2008;78(2):234–240. doi: 10.2319/121206-507.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin C, Granato R, Suzuki M, Gil JN, Piattelli A, Coelho G. Removal torque and histomorphometric evaluation of bioceramic grit-blasted/acid-etched and dual acid-etched implant surfaces: an experimental study in dogs. J Periodontol. 2008;79:1942–1949. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.080106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marković A, Calvo-Guirado JL, Lazić Z, Gómez-Moreno G, Ćalasan D, Guardia J, Čolic S, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Gačić B, Delgado-Ruiz R, Janjić B, Mišić T. Evaluation of primary stability of self-tapping and non-self-tapping dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013;15(3):341–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11:491–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsini E, Giavaresi G, Trire A, Ottani V, Salgarello S. Dental implant thread pitch and its influence on the osseointegration process: an in vivo comparison study. Int J Maxillofac Implants. 2010;2:383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Meredith N. Measurements comparing the initial stability of five designs of dental implants: a human cadaver study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2000;2:85–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2000.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palissery V, Tayler M, Browne M. Fatigue characterization of a polymer foam to use as a cancellous bone analog material in the assessment of orthopaedic devices. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15:61–67. doi: 10.1023/B:JMSM.0000010098.65572.3b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P, Shepherd D, Hukins D. Compressive properties of commercially available polyurethane foams as mechanical models for osteoporotic human cancellous bone. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakoh J, Wahlmann U, Stender E, Nat R, Al-Nawas B, Wagner W. Primary stability of a conical implant and a hybrid, cylindric screw-type implant in vitro. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21:560–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalabi MM, Wolke JGC, Jansen JA. The effects of implant surface roughness and surgical technique on implant fixation in an in vitro model. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17:172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2005.01202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szivek JA, Thomas M, Benjamin JB. Characterization of a synthetic foam as a model for human cancellous bone. J Apple Biomater. 1993;4:269–272. doi: 10.1002/jab.770040309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum A, Meijer GJ, Wolke JG, Jansen JA. Influence of the surgical technique and surface roughness on the primary stability of an implant in artificial bone with a density equivalent to maxillary bone: a laboratory study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(4):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson MS, McCarthy ID, Lidgren L, Ryd L. Compressive and shear properties of commercially available polyurethane foams. J Biomech. 2003;125:732–734. doi: 10.1115/1.1614820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y, Shiota M, Munakata M, Kasugai S, Ozeki M. Effect of implant design on primary stability using torque-time curves in artificial bone. Int J Implant Dent. 2015;1:21. doi: 10.1186/s40729-015-0024-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


