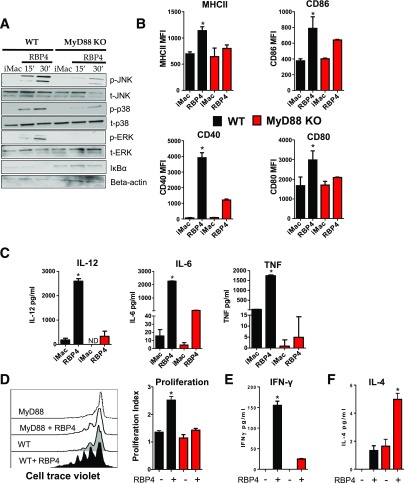
Figure 5.
RBP4-induced activation of macrophages and the resulting activation of CD4 T cells are dependent on the MyD88 pathway. A: BMDMs from WT and MyD88−/− mice were stimulated with RBP4 for 15 or 30 min, and phosphorylation of JNK, p38, and Erk and IκBα disappearance were evaluated by Western blot. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. B: MHCII and costimulatory molecule (CD80, CD86, and CD40) levels. C: TNF, IL-6, and IL-12 levels. D: BMDMs from WT and MyD88−/− were stimulated with RBP4 and cocultured with cell trace–labeled WT CD4 T cells, and proliferation of CD4 T cells was evaluated by cell trace dilution. Representative histograms indicating CD4 T-cell proliferation (left panel) and proliferation index (right panel). E: IFN-γ secretion in the coculture assay. F: IL-4 secretion in the coculture assay. n = 4 mice/group. Values are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. all other groups. #P < 0.05 vs. nonstimulated control group. iMAC, not activated, immature macrophage; MFI, median fluorescence intensity.