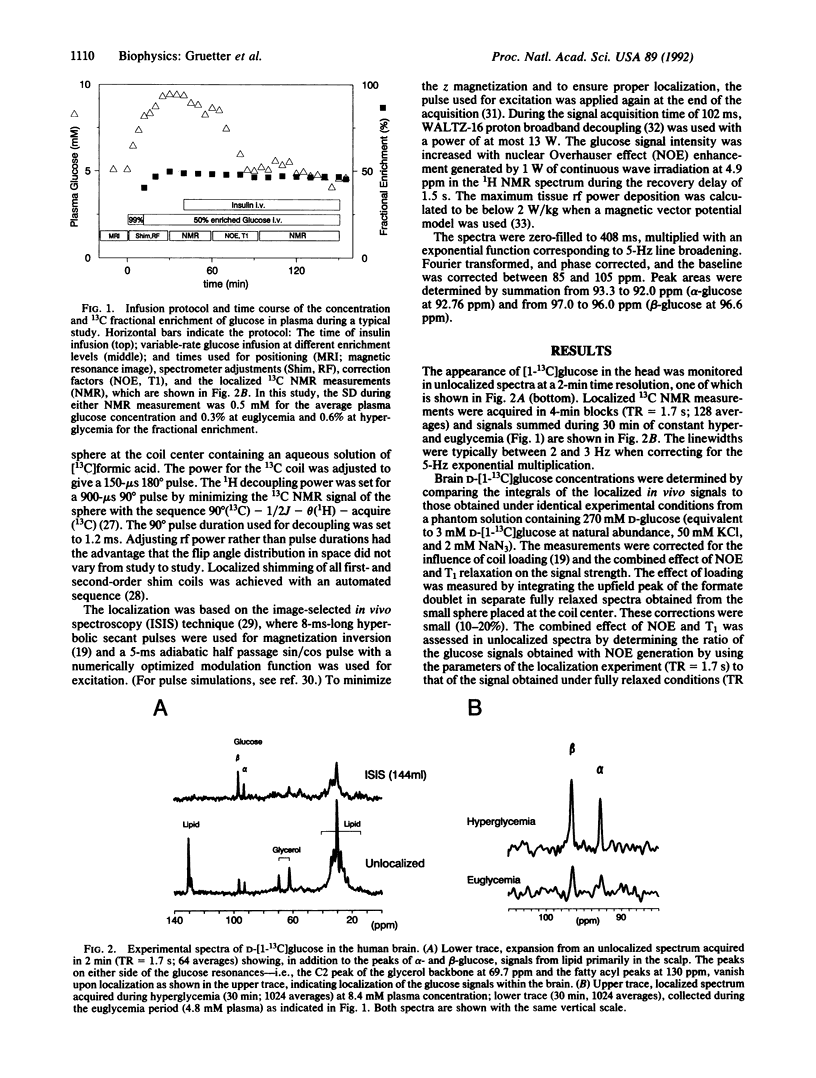
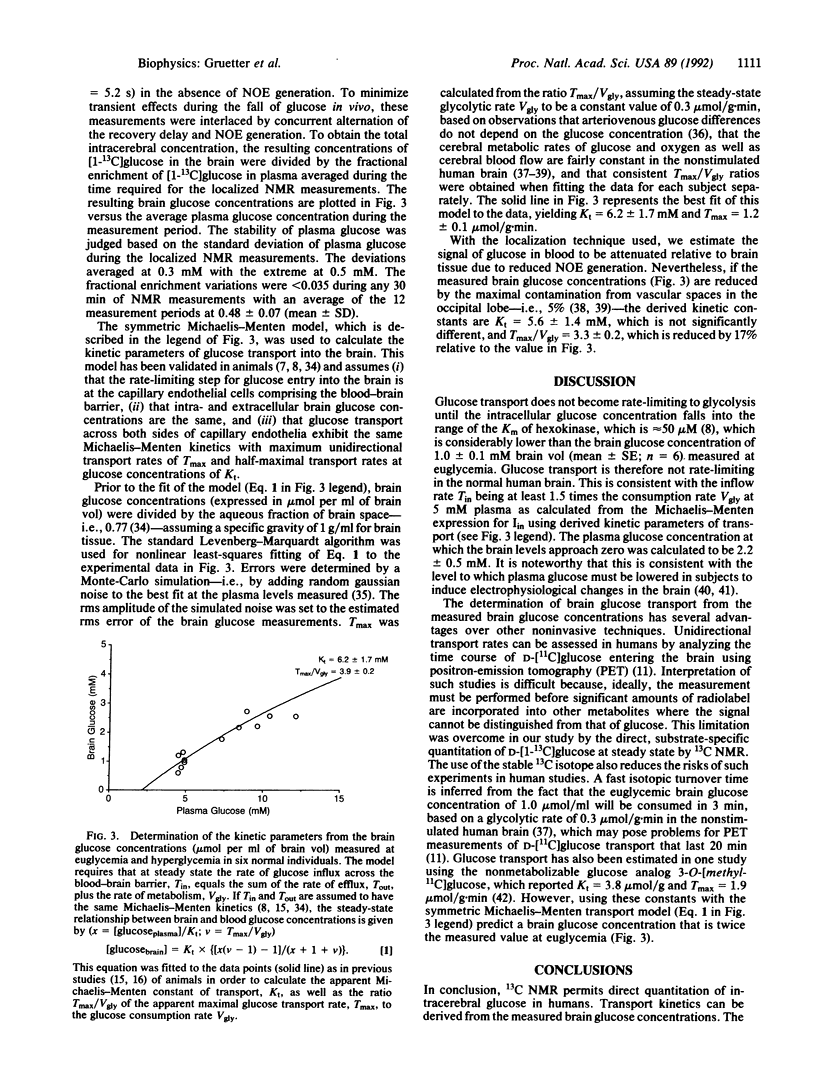
Abstract
Glucose is the main fuel for energy metabolism in the normal human brain. It is generally assumed that glucose transport into the brain is not rate-limiting for metabolism. Since brain glucose concentrations cannot be determined directly by radiotracer techniques, we used 13C NMR spectroscopy after infusing enriched D-[1-13C]glucose to measure brain glucose concentrations at euglycemia and at hyperglycemia (range, 4.5-12.1 mM) in six healthy children (13-16 years old). Brain glucose concentrations averaged 1.0 +/- 0.1 mumol/ml at euglycemia (4.7 +/- 0.3 mM plasma) and 1.8-2.7 mumol/ml at hyperglycemia (7.3-12.1 mM plasma). Michaelis-Menten parameters of transport were calculated to be Kt = 6.2 +/- 1.7 mM and Tmax = 1.2 +/- 0.1 mumol/g.min from the relationship between plasma and brain glucose concentrations. The brain glucose concentrations and transport constants are consistent with transport not being rate-limiting for resting brain metabolism at plasma levels greater than 3 mM.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agardh C. D., Kalimo H., Olsson Y., Siesjö B. K. Hypoglycemic brain injury: metabolic and structural findings in rat cerebellar cortex during profound insulin-induced hypoglycemia and in the recovery period following glucose administration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):71–84. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H. S., Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. The transport of glucose into the brain of the rat in vivo. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):71–82. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar K. L., Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W., Alger J. R., Shulman R. G. Detection of metabolites in rabbit brain by 13C NMR spectroscopy following administration of [1-13C]glucose. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Dec;3(6):911–920. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Hardy C. J., Roemer P. B., Mueller O. M. Proton-decoupled, Overhauser-enhanced, spatially localized carbon-13 spectroscopy in humans. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Dec;12(3):348–363. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910120307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vivo D. C., Trifiletti R. R., Jacobson R. I., Ronen G. M., Behmand R. A., Harik S. I. Defective glucose transport across the blood-brain barrier as a cause of persistent hypoglycorrhachia, seizures, and developmental delay. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 5;325(10):703–709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109053251006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinendegen L. E., Herzog H., Wieler H., Patton D. D., Schmid A. Glucose transport and utilization in the human brain: model using carbon-11 methylglucose and positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med. 1986 Dec;27(12):1867–1877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E., Mintun M. A., Dence C. Nonoxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):462–464. doi: 10.1126/science.3260686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A. Calculation of cerebral glucose phosphorylation from brain uptake of glucose analogs in vivo: a re-examination. Brain Res. 1982 Jun;257(2):237–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(82)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A., Diemer N. H. Autoradiographic determination of regional brain glucose content. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1983 Sep;3(3):303–310. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1983.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruetter R., Boesch C., Martin E., Wüthrich K. A method for rapid evaluation of saturation factors in in vivo surface coil NMR spectroscopy using B1-insensitive pulse cycles. NMR Biomed. 1990 Dec;3(6):265–271. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940030605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutniak M., Blomqvist G., Widén L., Stone-Elander S., Hamberger B., Grill V. D-[U-11C]glucose uptake and metabolism in the brain of insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):E805–E812. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.5.E805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzen D. H., Müller U. Energiestoffwechsel und Funktion des Kaninchengehirns während Insulinhypoglykämie. Pflugers Arch. 1971;322(1):47–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00586664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. E., Mori K., Dienel G. A., Cruz N. F., Nelson T., Sokoloff L. Modeling the dependence of hexose distribution volumes in brain on plasma glucose concentration: implications for estimation of the local 2-deoxyglucose lumped constant. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Mar;11(2):171–182. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Gravina S. A., Schmidley J. W., Perry G., Harik S. I. The glucose transporter of the human brain and blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):757–764. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawry T. J., Karczmar G. S., Weiner M. W., Matson G. B. Computer simulation of MRS localization techniques: an analysis of ISIS. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Mar;9(3):299–314. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910090302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders K. L., Perani D., Lammertsma A. A., Heather J. D., Buckingham P., Healy M. J., Gibbs J. M., Wise R. J., Hatazawa J., Herold S. Cerebral blood flow, blood volume and oxygen utilization. Normal values and effect of age. Brain. 1990 Feb;113(Pt 1):27–47. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Andersen H. Transport of glucose from blood to brain. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):305–352. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyten P. R., Groen J. P., Vermeulen J. W., den Hollander J. A. Experimental approaches to image localized human 31P NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Jul;11(1):1–21. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mies G., Cruz N., Sokoloff L. Comparison of freeze-blowing and funnel-freezing of rat brain for the measurement of cerebral glucose concentration in vivo. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1673–1676. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Setchell B. P. Cerebral glucose transport and oxygen consumption in sheep and rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):529–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Boado R. J., Farrell C. R. Brain-type glucose transporter (GLUT-1) is selectively localized to the blood-brain barrier. Studies with quantitative western blotting and in situ hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18035–18040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M. Brain metabolism: a perspective from the blood-brain barrier. Physiol Rev. 1983 Oct;63(4):1481–1535. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.4.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén U., Ratcheson R. A., Salford L. G., Siesjö B. K. Optimal freezing conditions for cerebral metabolites in rats. J Neurochem. 1973 Nov;21(5):1127–1138. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pramming S., Thorsteinsson B., Theilgaard A., Pinner E. M., Binder C. Cognitive function during hypoglycaemia in type I diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 8;292(6521):647–650. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6521.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. NMR spectroscopy of brain metabolism in vivo. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:61–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radda G. K., Rajagopalan B., Taylor D. J. Biochemistry in vivo: an appraisal of clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Q. 1989 Apr;5(2):122–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Rothman D. L., Jue T., Stein P., DeFronzo R. A., Shulman R. G. Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):223–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofts P. S., Wray S. A critical assessment of methods of measuring metabolite concentrations by NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 1988 Feb;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. L., Strother S. C., Zatorre R. J., Alivisatos B., Worsley K. J., Diksic M., Yamamoto Y. L. Stability of regional cerebral glucose metabolism in the normal brain measured by positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med. 1988 May;29(5):631–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Gadian D. G. Tissue metabolism studied in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jul;71(3):335–360. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Kanno I., Uemura K., Shishido F., Inugami A., Ogawa T., Murakami M., Suzuki K. Reduction in regional cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen during human aging. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1220–1228. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



