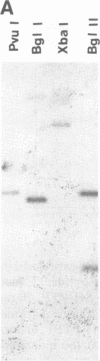
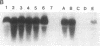
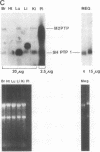
Abstract
Tyrosine phosphorylation is controlled by the opposing actions of tyrosine kinases and phosphotyrosine phosphatases (PTPs). src homology 2 domains (SH2) are found in several types of signaling proteins, including some tyrosine kinases. These domains bind phosphotyrosyl proteins and thus help promote signal transduction. Using mixed oligonucleotide-directed polymerase chain reactions, two previously undescribed rat PTP cDNA fragments were generated. Through subsequent screening of rat megakaryocyte and human erythroleukemia libraries, we obtained a full-length coding sequence for one of these fragments. This cDNA, SH-PTP1, encodes a tyrosine phosphatase containing two highly conserved SH2 domains. SH-PTP1, with a 2.4-kilobase mRNA, a predicted open reading frame of 595 amino acids, and a structure suggesting a nontransmembrane protein, is expressed primarily in hematopoietic and epithelial cells. When expressed in Escherichia coli, SH-PTP1 possesses PTP activity. The structure of SH-PTP1 establishes an additional branch of the tyrosine phosphatase family and suggests mechanisms through which tyrosine phosphatases might participate in signal transduction pathways.
Full text
PDF

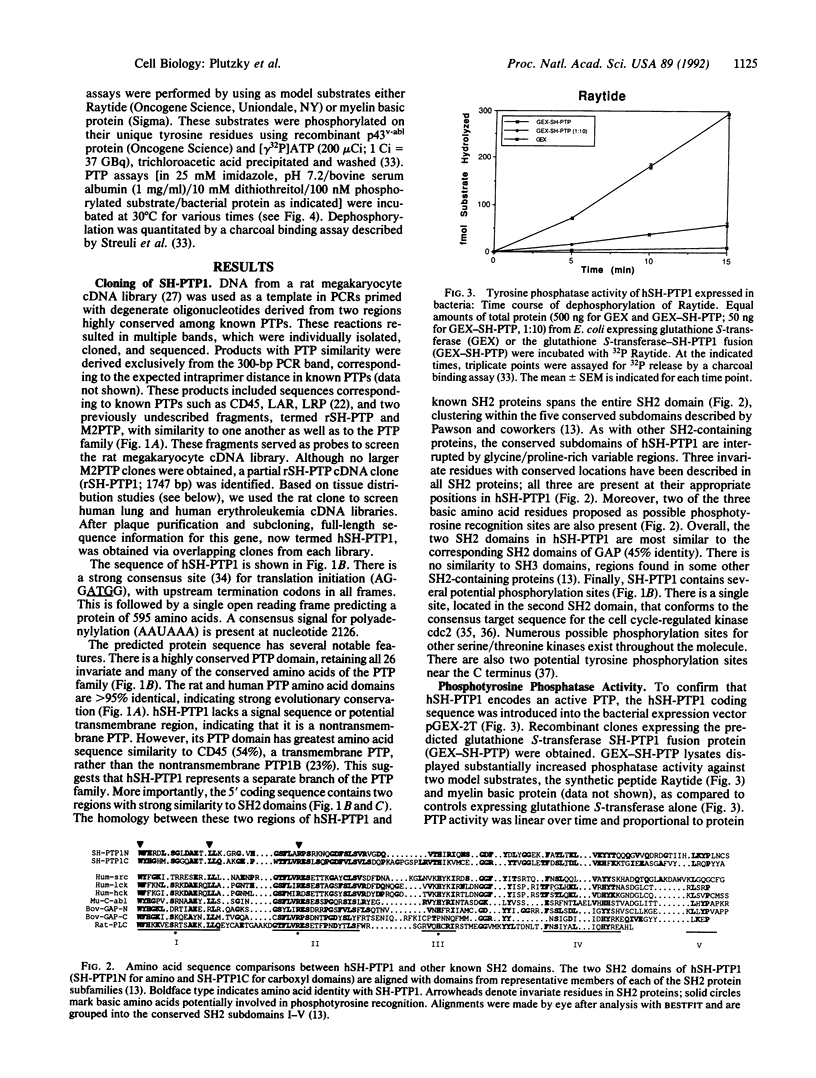

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown-Shimer S., Johnson K. A., Lawrence J. B., Johnson C., Bruskin A., Green N. R., Hill D. E. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of the human gene encoding protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5148–5152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Schievella A. R., Jost C. A., Erikson R. L., Neel B. G. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Expression of a human T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7280–7284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Lu M. L., Lo S. H., Lin S., Butler J. A., Druker B. J., Roberts T. M., An Q., Chen L. B. Presence of an SH2 domain in the actin-binding protein tensin. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.1708917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Greenberg S. M., Rosenberg R. D. Structure of the rat platelet factor 4 gene: a marker for megakaryocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):898–904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M. Human megakaryocytopoiesis. Semin Hematol. 1986 Jan;23(1):27–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger N. X., Streuli M., Saito H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3241–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Xenopus oocytes and the biochemistry of cell division. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3157–3166. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. l., Gautier J., Langan T. A., Lohka M. J., Shenoy S., Shalloway D., Nurse P. Maturation-promoting factor and the regulation of the cell cycle. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:53–63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S. M., Brugge J. S. Investigation of factors that influence phosphorylation of pp60c-src on tyrosine 527. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2465–2471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Hall L. R., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that has a cytoplasmic region homologous to the leukocyte common antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1523–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Thai T., Tang M., Saito H. Distinct functional roles of the two intracellular phosphatase like domains of the receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases LCA and LAR. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2399–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]