Abstract
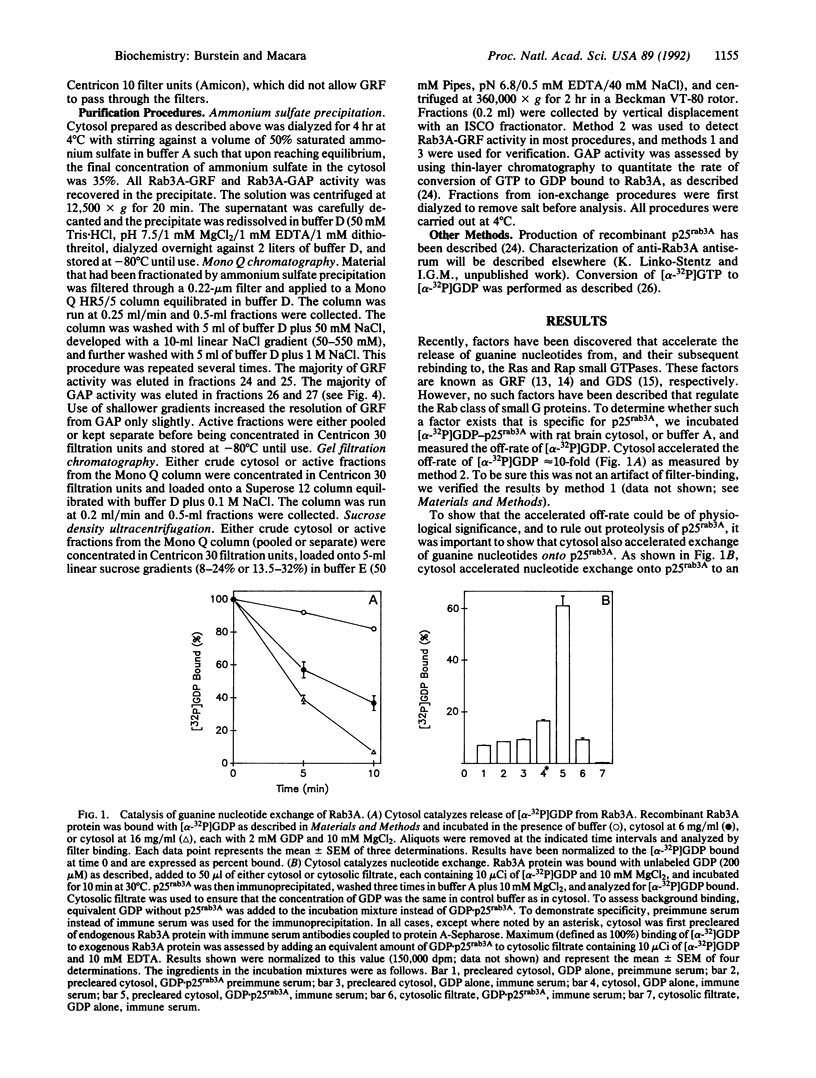
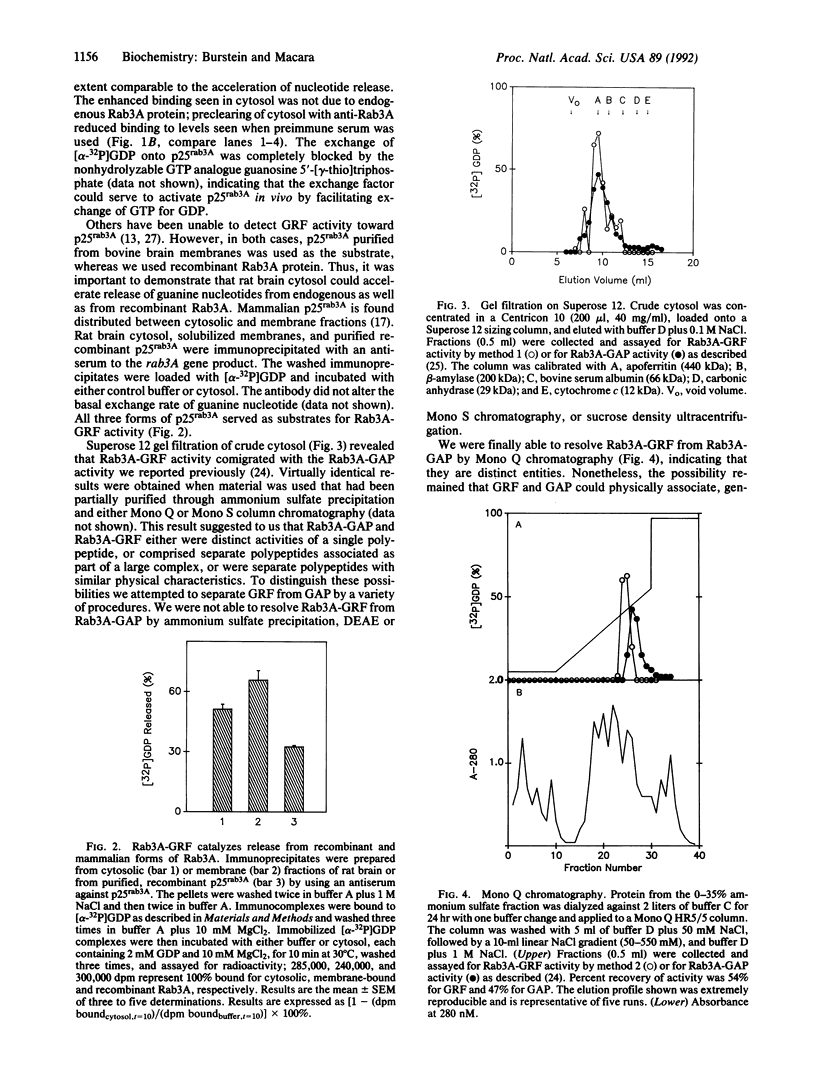
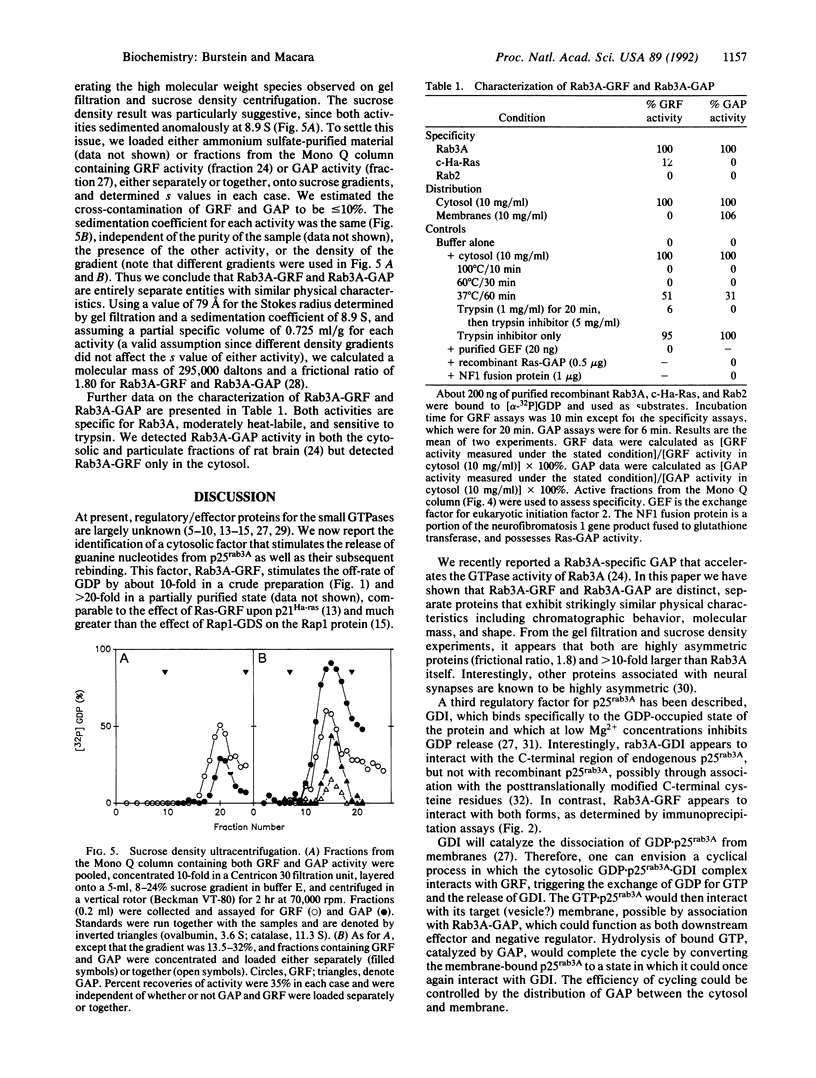
The rab3A gene product is a 25-kilodalton guanine nucleotide-binding protein that is expressed at high levels in neural tissue and has about 30% homology to the ras gene product. Recombinant Rab3A protein and p25rab3A purified from bovine brain membranes have been used as substrates to look for factors that regulate its biochemical activity. A factor in rat brain cytosol exists that accelerates, by approximately 10-fold, the release and subsequent rebinding of guanine nucleotides to both native and recombinant p25rab3A. We have partially purified this activity, termed Rab3A-GRF, and a GTPase-activating protein (Rab3A-GAP) reported previously. The two activities copurified through a variety of procedures but were separated by Mono Q anion-exchange chromatography, indicating that the activities arise from distinct polypeptides. Both factors were thermolabile, sensitive to trypsin, and specific for Rab3A, exhibiting little or no activity toward c-Ha-Ras or Rab2 proteins. By gel filtration chromatography and sucrose density ultracentrifugation, both Rab3A-GRF and Rab3A-GAP have Stokes radii of 79 A and sedimentation coefficients of 8.9 S. We calculate a molecular mass of 295,000 daltons and a frictional ratio of 1.80 for each factor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki S., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Hata Y., Takai Y. Role of the C-terminal region of smg p25A in its interaction with membranes and the GDP/GTP exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1438–1447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki S., Kikuchi A., Hata Y., Isomura M., Takai Y. Regulation of reversible binding of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, to synaptic plasma membranes and vesicles by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13007–13015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester R., Marchuk D., Boguski M., Saulino A., Letcher R., Wigler M., Collins F. The NF1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E. S., Linko-Stentz K., Lu Z. J., Macara I. G. Regulation of the GTPase activity of the ras-like protein p25rab3A. Evidence for a rab3A-specific GAP. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2689–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E., Macara I. G. The ras-like protein p25rab3A is partially cytosolic and is expressed only in neural tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4807–4811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darchen F., Zahraoui A., Hammel F., Monteils M. P., Tavitian A., Scherman D. Association of the GTP-binding protein Rab3A with bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5692–5696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. A small GTP-binding protein dissociates from synaptic vesicles during exocytosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):79–81. doi: 10.1038/349079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Self A. J., van Oers C., Hall A. Identification of distinct cytoplasmic targets for ras/R-ras and rho regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A., Self A. J. The effect of Mg2+ on the guanine nucleotide exchange rate of p21N-ras. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10963–10965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. ras and GAP--who's controlling whom? Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90054-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. K., Kung H. F., Kamata T. Purification of a factor capable of stimulating the guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins and its effect on ras-related small molecular mass G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8008–8012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Neurobiology. A system for synapse control. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):650–651. doi: 10.1038/349650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Araki S., Hata Y., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of two GTPase-activating proteins specific for smg p21, a GTP-binding protein having the same effector domain as c-ras p21s. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9133–9136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. ras GTPase activating protein: signal transmitter and signal terminator. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi A., Kim S., Ueda T., Takai Y. Tissue distribution of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, studied by use of a specific monoclonal antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1438–1445. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90835-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Prange R., Gallwitz D. A carboxyl-terminal cysteine residue is required for palmitic acid binding and biological activity of the ras-related yeast YPT1 protein. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):971–976. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Kikuchi A., Matsui Y., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Tissue-specific expression of a novel GTP-binding protein (smg p25A) mRNA and its increase by nerve growth factor and cyclic AMP in rat pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kikuchi A., Araki S., Hata Y., Isomura M., Kuroda S., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a protein that inhibits the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2333–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Goud B., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J. Mutational analysis of SEC4 suggests a cyclical mechanism for the regulation of vesicular traffic. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1685–1693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M., Kung H. F., Kamata T. A novel membrane factor stimulates guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80019-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. A cytosolic protein catalyzes the release of GDP from p21ras. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2181667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Moscucci A., Macara I. G. Evidence for multiple, ras-like, guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in Swiss 3T3 plasma membranes. Stimulation of GTPase activity by cytosolic factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10820–10827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., Lin B., Tanaka K., Dunn D., Wood D., Gesteland R., White R., Weiss R., Tamanoi F. The catalytic domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product stimulates ras GTPase and complements ira mutants of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Hiroyoshi M., Shirataki H., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of proteins that regulate the GDP/GTP exchange reaction of smg p21s, ras p21-like GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16626–16634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



