Abstract
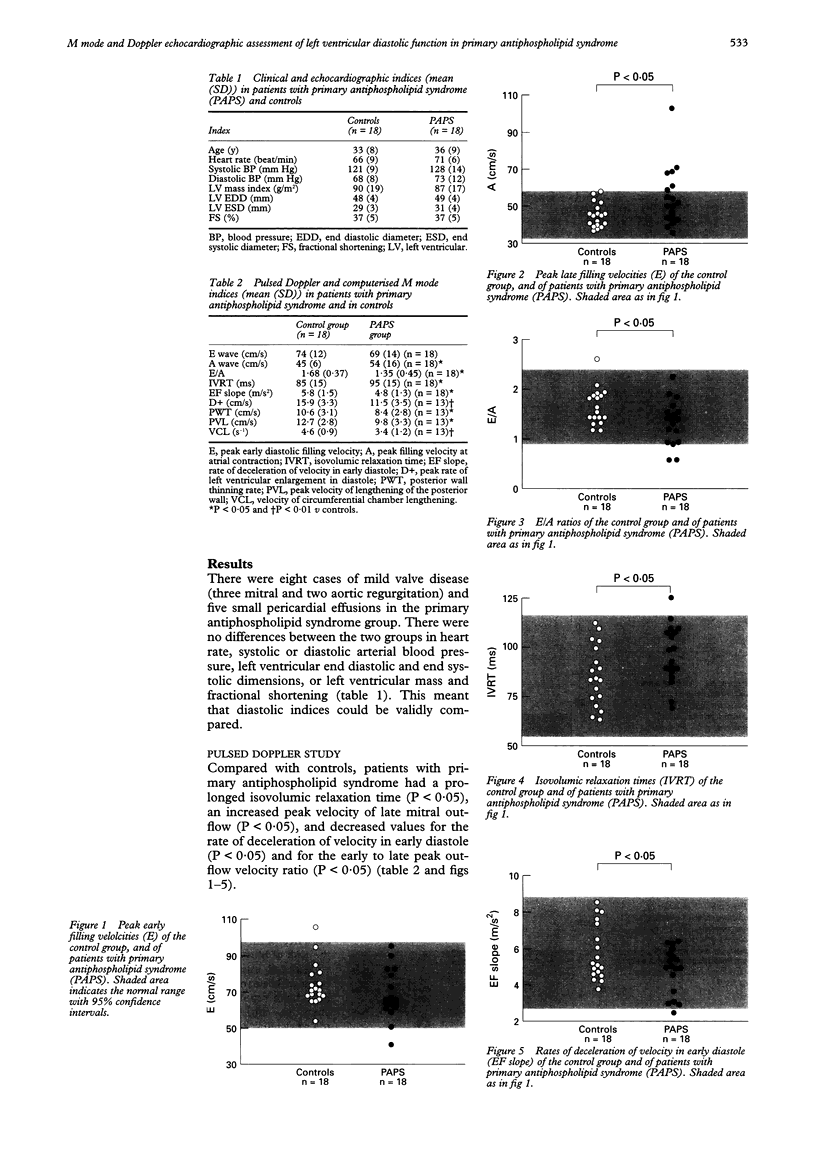
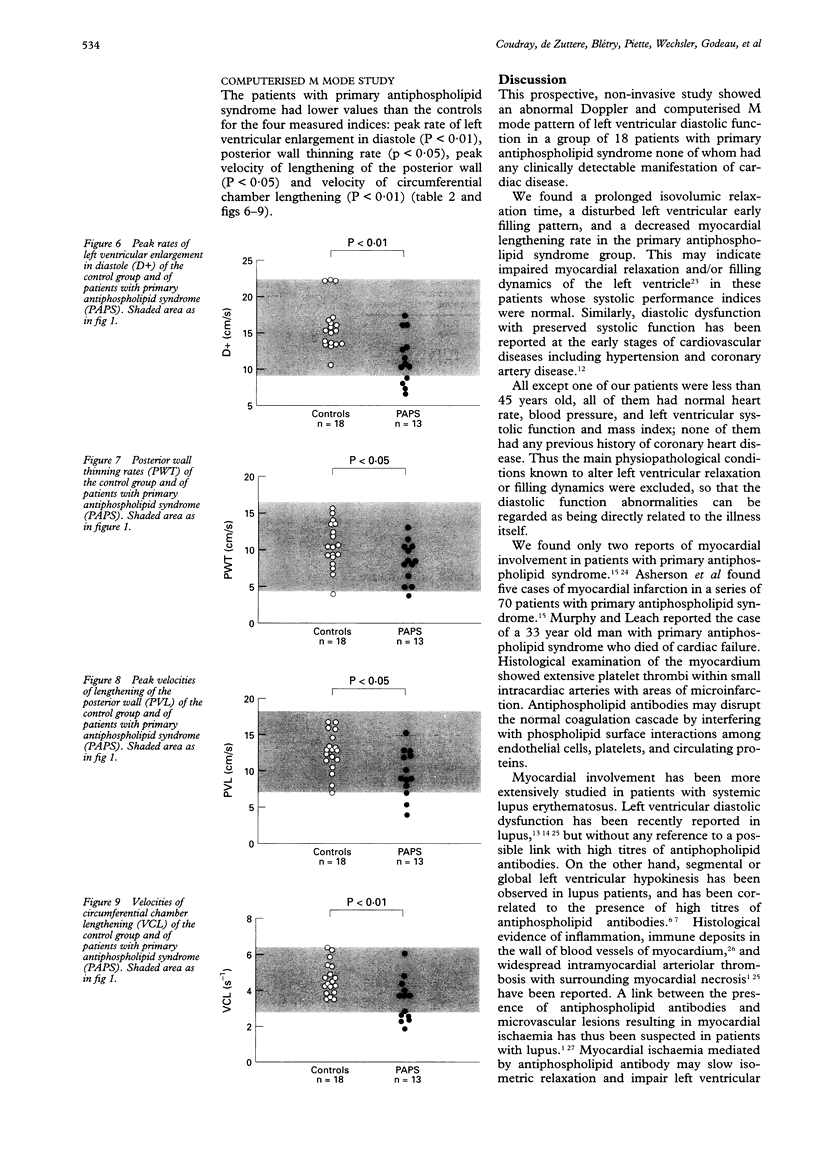
BACKGROUND--High titres of serum antiphospholipid antibodies are a possible pathogenic factor for cardiac lesions in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. OBJECTIVE--To test the hypothesis of a causal link between high titres of antiphospholipid antibodies in the serum and myocardial involvement in patients without systemic lupus erythematosus. PATIENTS AND DESIGN--18 patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (recurrent fetal loss, arterial and/or venous thrombosis, high titres of antiphospholipid antibodies, and no criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus) were prospectively studied by cross sectional, M mode, and pulsed Doppler echocardiography, and compared with 18 healthy controls. The pulsed Doppler indices of left ventricular diastolic function included isovolumic relaxation time and four mitral outflow indices: peak velocity of early flow, peak velocity of late flow, early to late peak flow velocity ratio, and rate of deceleration of early flow. Four computerised M mode indices were also measured: peak rate of left ventricular enlargement in diastole, peak rate of posterior wall thinning, peak velocity of lengthening of the posterior wall, and velocity of circumferential chamber lengthening. RESULTS--Compared with controls, patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome had higher values for isovolumic relaxation time and peak velocity of late mitral outflow and lower values for early to late mitral peak outflow velocity ratio, rate of deceleration of early mitral outflow, peak rate of left ventricular enlargement in diastole, peak rate of posterior wall thinning, peak velocity of lengthening of the posterior wall and velocity of circumferential chamber lengthening. CONCLUSION--This abnormal pattern reflects an impairment of myocardial relaxation and filling dynamics of the left ventricle in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome who were free of any clinically detectable heart disease. These data suggest that high serum titres of antiphospholipid antibodies may be associated with subclinical myocardial damage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson R. A., Khamashta M. A., Ordi-Ros J., Derksen R. H., Machin S. J., Barquinero J., Outt H. H., Harris E. N., Vilardell-Torres M., Hughes G. R. The "primary" antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Nov;68(6):366–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidani A. K., Roberts J. L., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Immunopathology of cardiac lesions in fatal systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1980 Dec;69(6):849–858. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(80)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Blumenfeld Z., Markiewicz W., Reisner S. A. Cardiac involvement in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Oct;18(4):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90749-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Doherty C. C., Allen D. C., Morton P. Fatal cardiac failure due to myocardial microthrombi in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 May 28;296(6635):1505–1505. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6635.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia B. L., Mah E. P., Feng P. H. Cardiovascular abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Ultrasound. 1981 May-Jun;9(5):237–243. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870090507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux R. B., Alonso D. R., Lutas E. M., Gottlieb G. J., Campo E., Sachs I., Reichek N. Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy: comparison to necropsy findings. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Feb 15;57(6):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galve E., Candell-Riera J., Pigrau C., Permanyer-Miralda G., Garcia-Del-Castillo H., Soler-Soler J. Prevalence, morphologic types, and evolution of cardiac valvular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 29;319(13):817–823. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809293191302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galve E., Ordi J., Barquinero J., Evangelista A., Vilardell M., Soler-Soler J. Valvular heart disease in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Feb 15;116(4):293–298. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-4-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason C. B., Stoddard M. F., Wagner S. G., Longaker R. A., Pierangeli S., Harris E. N. A comparison of cardiac valvular involvement in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome versus anticardiolipin-negative systemic lupus erythematosus. Am Heart J. 1993 Apr;125(4):1123–1129. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(93)90124-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman W. Diastolic dysfunction in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 28;325(22):1557–1564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111283252206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. D., Chartash E. K., Pizzarello R. A., Furie R. A. Cardiac manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Am Heart J. 1992 Nov;124(5):1331–1338. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(92)90420-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khamashta M. A., Cervera R., Asherson R. A., Font J., Gil A., Coltart D. J., Vázquez J. J., Paré C., Ingelmo M., Oliver J. Association of antibodies against phospholipids with heart valve disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1541–1544. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91373-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. H., Wong K. L., Lau C. P., Wong C. K., Cheng C. H., Tai Y. T. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am Heart J. 1990 Jul;120(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(90)90163-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. H., Wong K. L., Lau C. P., Wong C. K., Liu H. W. Association between antiphospholipid antibodies and cardiac abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1990 Oct;89(4):411–419. doi: 10.1007/BF01453668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E. K., Crozier I. G., Milne M. J., Nicholls M. G., Cohen M. G. Lack of association between anticardiolipin antibodies and heart valve disease in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):504–505. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92052-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Mead L. A., Kwiterovich P. O., Jr, Pearson T. A. Dyslipidemias with desirable plasma total cholesterol levels and angiographically demonstrated coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Jan 1;65(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90017-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. J., Leach I. H. Findings at necropsy in the heart of a patient with anticardiolipin syndrome. Br Heart J. 1989 Jul;62(1):61–64. doi: 10.1136/hrt.62.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nihoyannopoulos P., Gomez P. M., Joshi J., Loizou S., Walport M. J., Oakley C. M. Cardiac abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Association with raised anticardiolipin antibodies. Circulation. 1990 Aug;82(2):369–375. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R. A., Housmans P. R., Hatle L. K., Tajik A. J. Assessment of diastolic function of the heart: background and current applications of Doppler echocardiography. Part I. Physiologic and pathophysiologic features. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 Jan;64(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollick C., Fitzgerald P. J., Popp R. L. Variability of digitized echocardiography: size, source, and means of reduction. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Feb;51(3):576–582. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(83)80100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan C. A., Shively B. K., Lau C. C., Gurule F. T., Smith E. A., Crawford M. H. Systemic lupus erythematosus valve disease by transesophageal echocardiography and the role of antiphospholipid antibodies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Nov 1;20(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90368-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahn D. J., DeMaria A., Kisslo J., Weyman A. Recommendations regarding quantitation in M-mode echocardiography: results of a survey of echocardiographic measurements. Circulation. 1978 Dec;58(6):1072–1083. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.6.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasson Z., Rasooly Y., Chow C. W., Marshall S., Urowitz M. B. Impairment of left ventricular diastolic function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Cardiol. 1992 Jun 15;69(19):1629–1634. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)90715-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John Sutton M. G., Reichek N., Kastor J. A., Giuliani E. R. Computerized M-mode echocardiographic analysis of left ventricular dysfunction in cardiac amyloid. Circulation. 1982 Oct;66(4):790–799. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zuttere D., Touche T., Saumon G., Nitenberg A., Prasquier R. Doppler echocardiographic measurement of mitral flow volume: validation of a new method in adult patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Feb;11(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



