Abstract
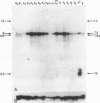
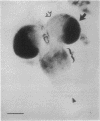
The X-chromosomal complementation unit lethal(1)optomotor-blind [l(1)omb] is defined by lack of complementation among over a dozen recessive lethal mutations that map to the omb gene locus. Mutations in l(1)omb also fail to complement viable mutations of three seemingly unrelated functions in this region: bifid (bi), manifesting defective wings, Quadroon (Qd), a semi-dominant mutation expressing abnormal tergite pigmentation, and In(1)ombH31, giving rise to a normal external morphology but with discrete defects in the optic lobes and behavior. The locus encodes a 70-kilobase primary transcript that is spliced into a 6-kilobase mature RNA. cDNAs for this transcript were isolated and sequenced and the derived amino acid sequence was analyzed. Certain features of this sequence suggest that the l(1)omb gene product is a nuclear regulatory protein. The lethal phase of various apparent null mutants was determined and found to occur mainly in the pupal stage. A large proportion of all hemizygous mutant males develop to pharate adults that eclose only rarely but can be rescued from the pupal case. These animals show a severe maldevelopment of the optic lobes. In addition they have only rudimentary wings as well as a Quadroon-like abdominal pigmentation. Thus, in the lethal mutants those parts of the body are affected for which independent viable mutations have been previously described in the omb locus, such as optomotor-blind, bifid, and Quadroon.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banga S. S., Bloomquist B. T., Brodberg R. K., Pye Q. N., Larrivee D. C., Mason J. M., Boyd J. B., Pak W. L. Cytogenetic characterization of the 4BC region on the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: localization of the mei-9, norpA and omb genes. Chromosoma. 1986;93(4):341–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00327593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausenwein B., Wolf R., Heisenberg M. Genetic dissection of optomotor behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Studies on wild-type and the mutant optomotor-blindH31. J Neurogenet. 1986 Mar;3(2):87–109. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan S., Falkenburg D., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Characterization and developmental expression of beta tubulin genes in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2543–2548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman R. K., Sanicola M., Raftery L. A., Gillevet T., Gelbart W. M. An extensive 3' cis-regulatory region directs the imaginal disk expression of decapentaplegic, a member of the TGF-beta family in Drosophila. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):657–666. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. R., Grossman D., White K. Mutant alleles at the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster lead to nervous system defects. A developmental-genetic analysis. J Neurogenet. 1985 Jun;2(3):197–218. doi: 10.3109/01677068509100150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronmiller C., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Molecular characterization of daughterless, a Drosophila sex determination gene with multiple roles in development. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1666–1676. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberledge S., Zaratzian A., Sakonju S. Characterization of two RNAs transcribed from the cis-regulatory region of the abd-A domain within the Drosophila bithorax complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach K. F., Technau G. Cell degeneration in the developing optic lobes of the sine oculis and small-optic-lobes mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):219–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio G., Burri M., Bopp D., Baumgartner S., Noll M. Structure of the segmentation gene paired and the Drosophila PRD gene set as part of a gene network. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogness D. S., Lipshitz H. D., Beachy P. A., Peattie D. A., Saint R. B., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Harte P. J., Gavis E. R., Helfand S. L. Regulation and products of the Ubx domain of the bithorax complex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:181–194. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irish V. F., Martinez-Arias A., Akam M. Spatial regulation of the Antennapedia and Ultrabithorax homeotic genes during Drosophila early development. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1527–1537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshitz H. D., Kankel D. R. Specificity of gene action during central nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster: analysis of the lethal (1) optic ganglion reduced locus. Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;108(1):56–77. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshitz H. D., Peattie D. A., Hogness D. S. Novel transcripts from the Ultrabithorax domain of the bithorax complex. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):307–322. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., McLeod E., Jack J. Four distinct regulatory regions of the cut locus and their effect on cell type specification in Drosophila. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):151–159. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Kankel D. R. A genetic analysis of visual system development in Drosophilia melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1978 Jan;62(1):112–142. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pflugfelder G. O., Schwarz H., Roth H., Poeck B., Sigl A., Kerscher S., Jonschker B., Pak W. L., Heisenberg M. Genetic and molecular characterization of the optomotor-blind gene locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):91–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoller D., Friedel C., Schmid A., Bettler D., Lam L., Yedvobnick B. The Drosophila neurogenic locus mastermind encodes a nuclear protein unusually rich in amino acid homopolymers. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1688–1700. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann-Zwicky M. Sex determination in Drosophila: the X-chromosomal gene liz is required for Sxl activity. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3889–3898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Fischbach K. F., Rubin G. M. Disconnected: a locus required for neuronal pathway formation in the visual system of Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1139–1153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. SPXX, a frequent sequence motif in gene regulatory proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):61–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Herrero E., Akam M. Spatially ordered transcription of regulatory DNA in the bithorax complex of Drosophila. Development. 1989 Oct;107(2):321–329. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Kankel D. R. Molecular cloning and analysis of l(1)ogre, a locus of Drosophila melanogaster with prominent effects on the postembryonic development of the central nervous system. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):1033–1044. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Kankel D. R. Patterns of cell division and cell movement in the formation of the imaginal nervous system in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):296–321. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]