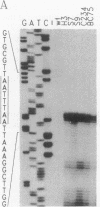
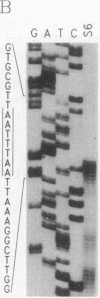
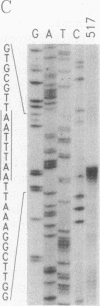
Abstract
The cryptic bgl operon of Escherichia coli is activated by the spontaneous insertion of mobile DNA elements. Screening of a collection of such mutations revealed insertion of the 1195-base-pair element IS5 into various positions both upstream and downstream of the bgl promoter P0. Activation of the operon was in all cases attributable to enhancement of P0 activity. Introduction of internal deletions into IS5 almost completely abolished P0 enhancement, demonstrating that enhancement is not simply the result of mutational inactivation of some inhibitory sequences. Intact copies of IS5 in trans restored the enhancing activity of the deletion derivatives. The trans-activator is encoded by IS5 gene ins5A, an essential transposition function. Activation of gene expression by means of interaction of a defective mobile element in cis with functions encoded by a nondefective element in trans has so far been described only for a maize controlling element.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Claverie-Martín F., Díaz-Torres M. R., Kushner S. R. Transcript mapping using [35S]DNA probes, trichloroacetate solvent and dideoxy sequencing ladders: a rapid method for identification of transcriptional start points. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amster O., Zamir A. Sequence rearrangements may alter the in vivo superhelicity of recombinant plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding specificity of cyclic AMP receptor protein to recognition sites. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenbihl R. P., Vielmetter W. Complete maps of IS1, IS2, IS3, IS4, IS5, IS30 and IS150 locations in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Dec;220(1):147–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00260869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. M., Jackson M. S., Kidwell M. G., Dover G. A. KP elements repress P-induced hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4125–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler J. A., van Bree M. P. The nucleotide sequence and protein-coding capability of the transposable element IS5. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Company M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Ty1 sequence with enhancer and mating-type-dependent regulatory activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):258–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A. How maize transposable elements escape negative selection. Trends Genet. 1990 May;6(5):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Saedler H., Peterson P. A. Maize transposable elements. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:71–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. R., Gierl A., Saedler H. En/Spm encoded tnpA protein requires a specific target sequence for suppression. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2029–2035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger M., Hobom G. Structural analysis of insertion sequence IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):159–162. doi: 10.1038/297159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P., Surosky R., Kingsbury J. A., Fedoroff N. V. Genetic and molecular analysis of the Spm-dependent a-m2 alleles of the maize a locus. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):117–137. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., Lusky M., Hable M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):124–128. doi: 10.1038/297124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., von Reutern M. Insertion element IS5 contains a third gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):807–811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Felton J., Wright A. Insertion of DNA activates the cryptic bgl operon in E. coli K12. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):625–629. doi: 10.1038/293625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Mahadevan S., LeGrice S. F., Wright A. Enhancement of bacterial gene expression by insertion elements or by mutation in a CAP-cAMP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Rak B. Beta-glucoside permease represses the bgl operon of Escherichia coli by phosphorylation of the antiterminator protein and also interacts with glucose-specific enzyme III, the key element in catabolite control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5074–5078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Rak B. Regulation of the bgl operon of Escherichia coli by transcriptional antitermination. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3271–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Kahn M. The nucleotide sequence of IS5 from Escherichia coli. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Schoner R. G. Distribution of IS5 in bacteria. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Shepherd N., Tacke E., Gierl A., Rohde W., Leclercq L., Mattes M., Berndtgen R., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Influence of transposable elements on the structure and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):287–294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda M., Ohtsubo E. Mapping of insertion element IS5 in the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Chromosomal rearrangements mediated by IS5. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 20;213(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80186-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vögele K., Schwartz E., Welz C., Schiltz E., Rak B. High-level ribosomal frameshifting directs the synthesis of IS150 gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4377–4385. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sauerbier W. Flanking AT-rich sequences may lower the activation energy of cruciform extrusion in supercoiled DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R. The splicing of maize transposable elements from pre-mRNA--a minireview. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]