Abstract
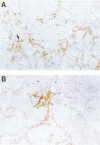
OBJECTIVE: To examine the hypothesis that tenascin, an extracellular matrix glycoprotein, contributes to fibrotic changes in dilated cardiomyopathy. METHODS: The localisation of tenascin in biopsy specimens of the hearts obtained from eight patients with dilated cardiomyopathy was examined using staining by the avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex method. RESULTS: (1) Perimysium and endomysium. Although positive staining for tenascin was observed in the enlarged perimysium and endomysium in all patients, moderately intense staining was characteristically observed near the replacement fibrotic lesions. In the narrow perimysium and endomysium of the myocardium not containing replacement fibrotic lesions, tenascin was not present, as in the control specimens. (2) Replacement fibrotic lesions. Non-homogeneous positive staining for tenascin was detected in all replacement fibrotic lesions examined. Intense tenascin deposition was observed in the peripheral portion of the replacement fibrotic lesions. The tenascin staining observed in the small replacement fibrotic lesions was more intense than that in the large lesions. CONCLUSIONS: Tenascin contributes to the development of the fibrotic changes seen in the dilated cardiomyopathic heart. Its characteristic location, specifically the distribution along the margin of the fibrosis, suggests that fibrotic change is a continuous process in hearts with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufderheide E., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Ekblom P. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the developing kidney lead to expression of tenascin in the mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):599–608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Wikstrand C. J., Furthmayr H., Matthews T. J., Bigner D. D. Human glioma-mesenchymal extracellular matrix antigen defined by monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2796–2805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. J., Pearson C. A., Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Fambrough D. M. Chick myotendinous antigen. I. A monoclonal antibody as a marker for tendon and muscle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1926–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. E., Rosing D. R. Verapamil: its potential for causing serious complications in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1981 Sep;64(3):437–441. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulcher J. R., Nies D. E., Marton L. S., Stefansson K. An alternatively spliced region of the human hexabrachion contains a repeat of potential N-glycosylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Halfter W., Liverani D. Induction of tenascin in healing wounds. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2757–2767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Thesleff I., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Tenascin is associated with chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation in vivo and promotes chondrogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2569–2579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. J., Tucker R. P., Halfter W., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Epperlein H. H. The distribution of tenascin coincides with pathways of neural crest cell migration. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):237–250. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami R., Yamaoka I., Sakakura T. Appearance of tenascin in healing skin of the mouse: possible involvement in seaming of wounded tissues. Int J Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;33(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike Y., Hiraiwa H., Kawakatsu H., Nishikai M., Okinaka T., Suzuki T., Okada A., Yatani R., Sakakura T. Isolation and characterization of human fibroblast tenascin. An extracellular matrix glycoprotein of interest for developmental studies. Int J Dev Biol. 1990 Jun;34(2):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz F., Mall G., Zebe H., Blickle J., Derks H., Manthey J., Kübler W. Quantitative morphologic findings of the myocardium in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Feb;51(3):501–506. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(83)80088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Mackie E., Vainio S., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Changes in the distribution of tenascin during tooth development. Development. 1987 Oct;101(2):289–296. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Jalkanen M., Thesleff I. Syndecan and tenascin expression is induced by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in embryonic tooth mesenchyme. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1945–1953. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrle B., Chiquet M. Tenascin is accumulated along developing peripheral nerves and allows neurite outgrowth in vitro. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby D. J., Ferguson M. W. The extracellular matrix of lip wounds in fetal, neonatal and adult mice. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):651–668. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Ichida T., Matsuda Y., Miyazaki Y., Hatano T., Hata K., Asakura H., Hirota N., Geerts A., Wisse E. Tenascin expression in human chronic liver disease and in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver. 1992 Feb;12(1):10–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1992.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]