Abstract
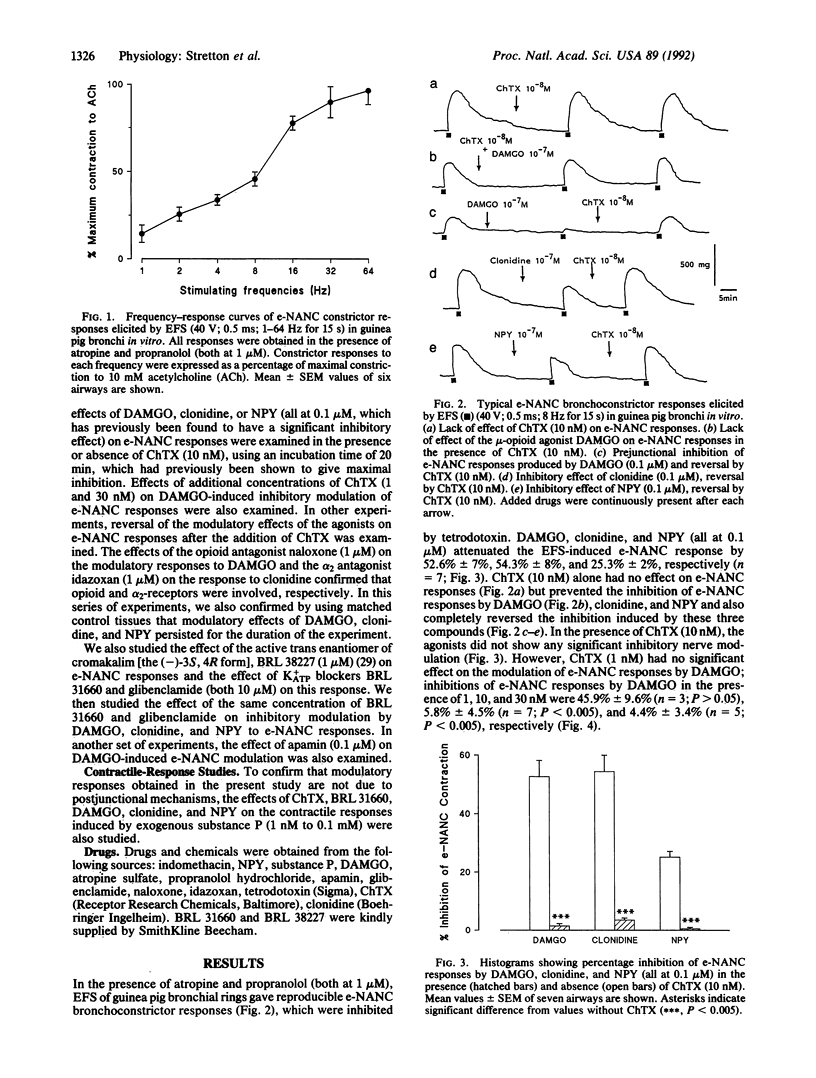
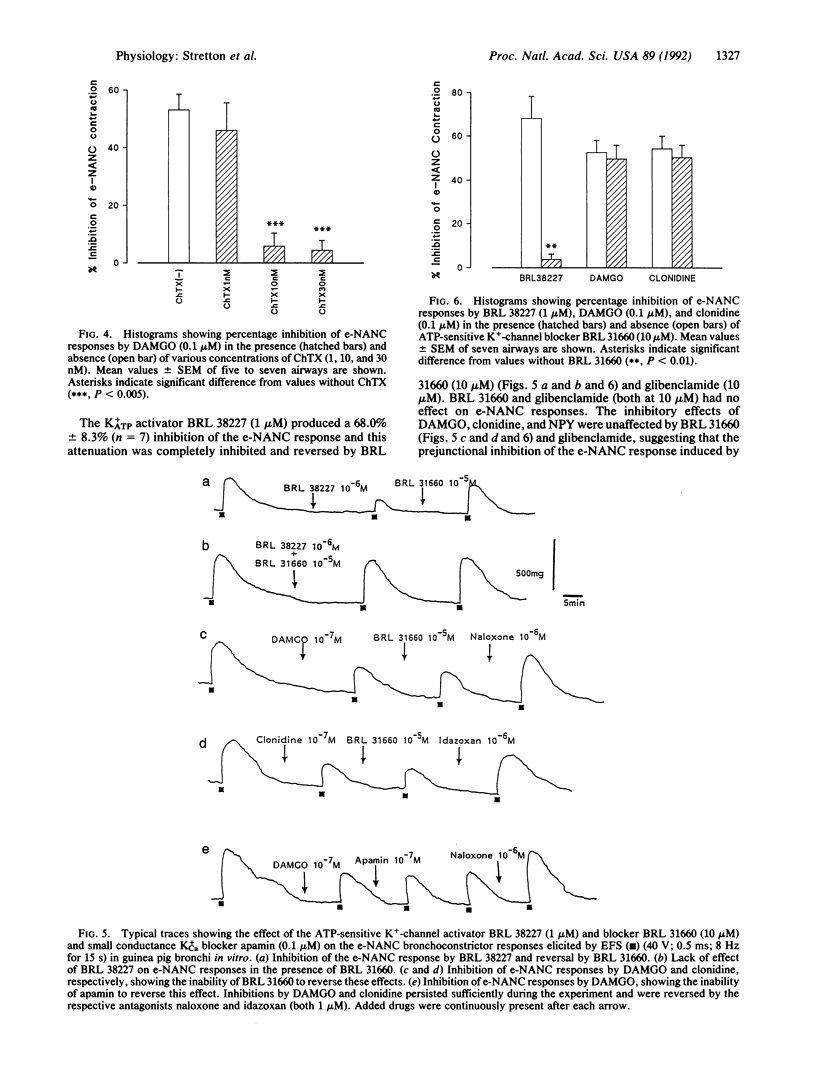
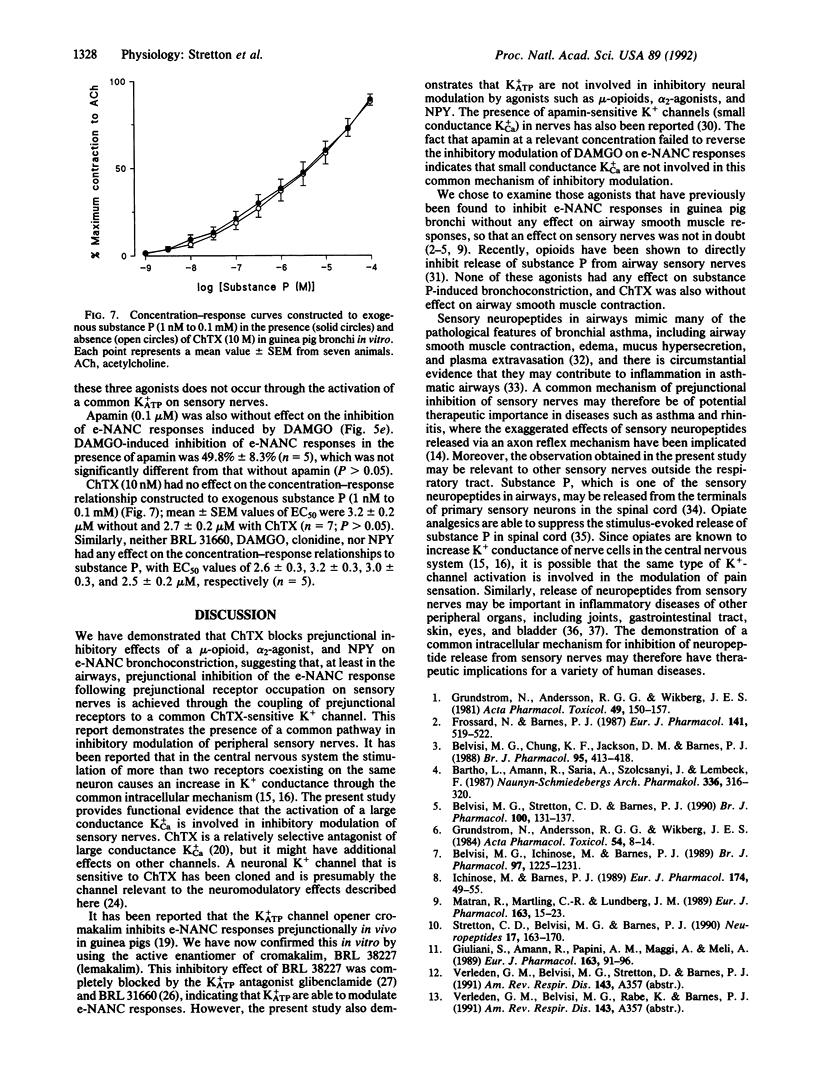
Activation of several receptors, including mu-opioid, alpha 2-adrenergic, and neuropeptide Y receptors, inhibits excitatory nonadrenergic noncholinergic (NANC) neural responses in airways, which were mediated by the release of peptides from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. This raises the possibility of a common inhibitory mechanism, which may be related to an increase in K+ conductance in sensory nerves. To examine this hypothesis, we have studied whether K(+)-channel blockers inhibit the effects of neuromodulators of sensory nerves in guinea pig bronchi by using selective K(+)-channel blockers. Charybdotoxin (ChTX; 10 nM), which blocks large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+)-channel function, completely blocked and reversed the inhibitory effects of a mu-opioid agonist, neuropeptide Y, and an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist on excitatory NANC responses. Neither inhibitors of ATP-sensitive K+ channels (BRL 31660 or glibenclamide, both at 10 microM) nor an inhibitor of small conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels (apamin; 0.1 microM) were effective. This suggests that ChTX-sensitive K(+)-channel activation may be a common mechanism for the prejunctional modulation of sensory nerves in airways. This may have important implications for the control of neurogenic inflammation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R., Buckle D. R., Bumstead J., Clarke G. D., Taylor J. F., Taylor S. G. Evaluation of the potassium channel activator cromakalim (BRL 34915) as a bronchodilator in the guinea-pig: comparison with nifedipine. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):763–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Asthma as an axon reflex. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Belvisi M. G., Rogers D. F. Modulation of neurogenic inflammation: novel approaches to inflammatory disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90112-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Neuropeptides and asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3 Pt 2):S28–S32. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3_Pt_2.S28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Amann R., Saria A., Szolcsányi J., Lembeck F. Peripheral effects of opioid drugs on capsaicin-sensitive neurones of the guinea-pig bronchus and rabbit ear. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;336(3):316–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00172684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Chung K. F., Jackson D. M., Barnes P. J. Opioid modulation of non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Modulation of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig airways via GABAB-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1225–1231. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways by opioids. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. L., Armour C. L., Johnson P. R., Alouan L. A., Barnes P. J. The action of a potassium channel activator, BRL 38227 (lemakalim), on human airway smooth muscle. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1384–1389. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard N., Barnes P. J. Mu-opioid receptors modulate non-cholinergic constrictor nerves in guinea-pig airways. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90578-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Navia M. A., Reuben J. P., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani S., Amann R., Papini A. M., Maggi C. A., Meli A. Modulatory action of galanin on responses due to antidromic activation of peripheral terminals of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 12;163(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Inhibition of the excitatory non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurotransmission in the guinea pig tracheo-bronchial tree mediated by alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1984 Jan;54(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström N., Andersson R. G., Wikberg J. E. Pharmacological characterization of the autonomous innervation of the guinea pig tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1981 Aug;49(2):150–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1981.tb00884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Erxleben C. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels in Aplysia neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):27–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):739–768. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. A potassium channel activator modulates both excitatory noncholinergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig airways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Histamine H3-receptors modulate nonadrenergic noncholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in guinea-pig in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90872-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Tsunoo A., Otsuka M. Enkephalin as a transmitter for presynaptic inhibition in sympathetic ganglia. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):80–82. doi: 10.1038/294080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Brodin E., Saria A. Effects and distribution of vagal capsaicin-sensitive substance P neurons with special reference to the trachea and lungs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Nov;119(3):243–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(1):1–43. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matran R., Martling C. R., Lundberg J. M. Inhibition of cholinergic and non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig mediated by neuropeptide Y and alpha 2-adrenoceptors and opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 12;163(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray N. J., Jones A. J., Keen P. Morphine, but not sodium cromoglycate, modulates the release of substance P from capsaicin-sensitive neurones in the rat trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):797–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Levitan I. B. A family of calcium-dependent potassium channels from rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1031–1041. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton C. D., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Neuropeptide Y modulates non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neural bronchoconstriction in vivo and in vitro. Neuropeptides. 1990 Dec;17(4):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(90)90031-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Jessell T. M., Gamse R., Mudge A. W., Leeman S. E. Intrathecal morphine inhibits substance P release from mammalian spinal cord in vivo. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):155–157. doi: 10.1038/286155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



