Abstract
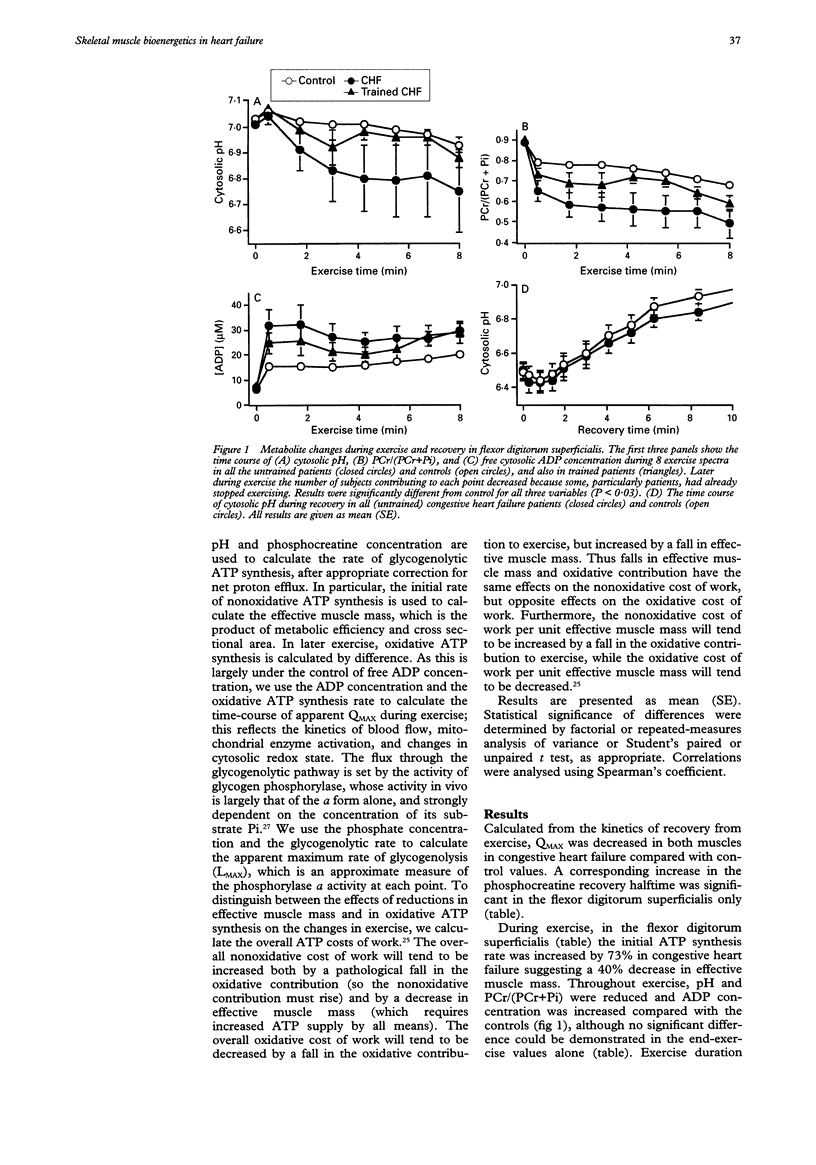
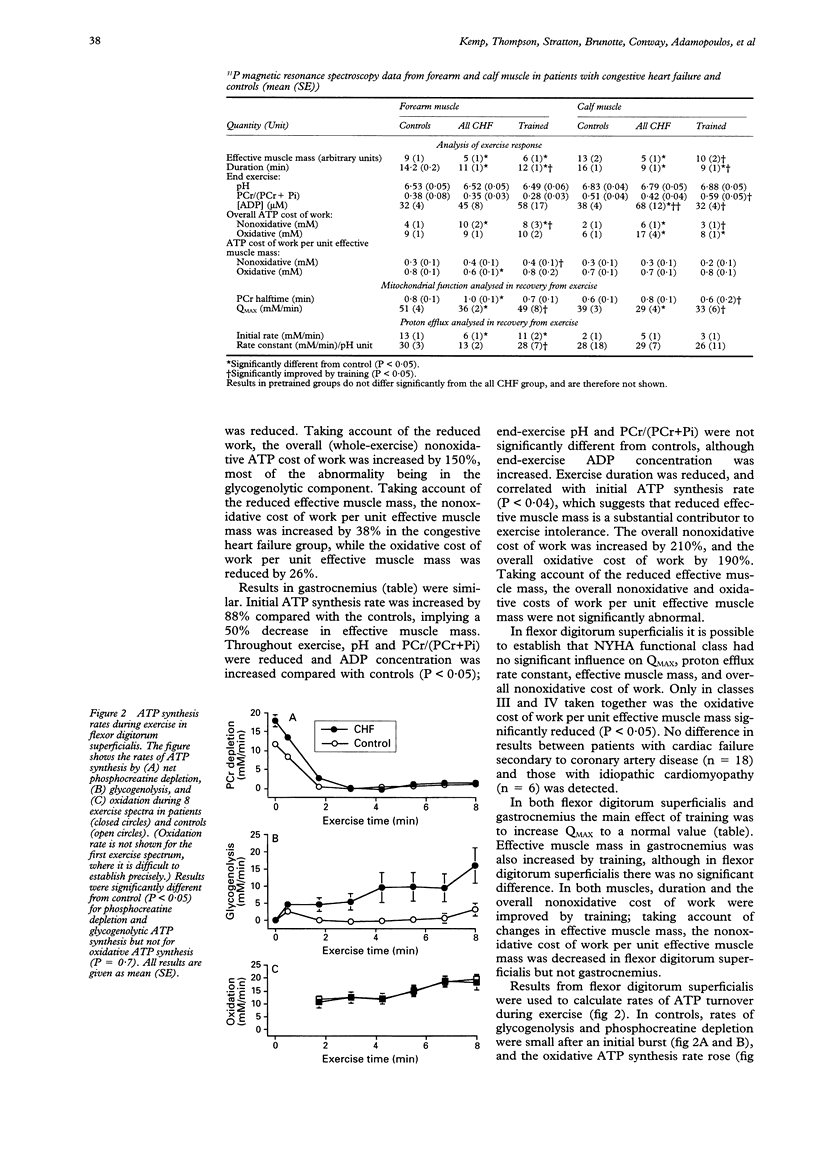
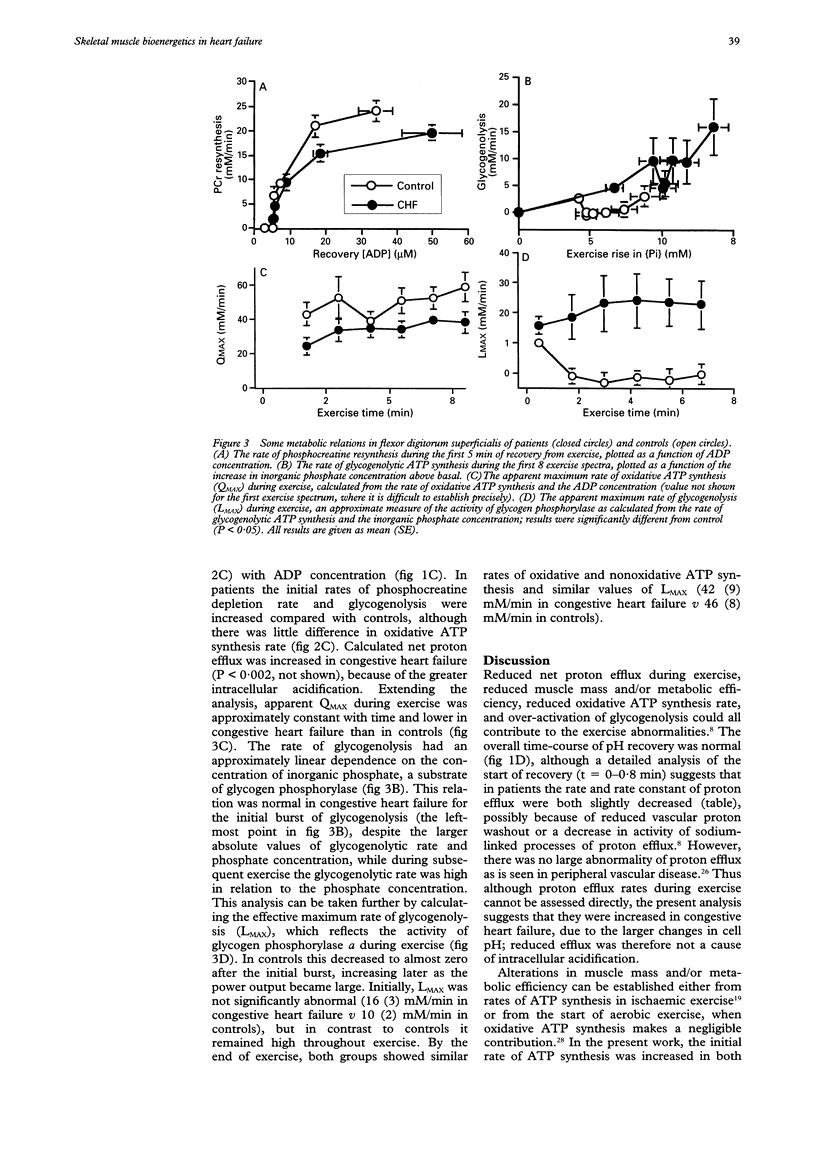
OBJECTIVE: To distinguish between the effects of reduced oxidative capacity and reduced metabolic efficiency on skeletal muscle bioenergetics during exercise in patients with congestive heart failure. DESIGN AND PATIENTS: Patients were studied by 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy during aerobic exercise and recovery, and results compared with controls. RESULTS: In flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (26 patients) there was a 30% decrease in oxidative capacity compared with control (mean (SE) 36 (2) v 51 (4) mM/min) and also a 40% decrease in "effective muscle mass" (5 (1) v 9 (1) arbitrary units), probably at least partly the result of reduced metabolic efficiency. Both contribute to increased phosphocreatine depletion and intracellular acidosis during exercise. However, an increased concentration of ADP (an important mitochondrial regulator) during exercise permitted near-normal rates of oxidative ATP synthesis. Results were similar in gastrocnemius muscle (20 patients), with a 30% decrease in maximum oxidative capacity (29 (4) v 39 (3) mM/min) and a 65% decrease in effective muscle mass (5 (1) v 13 (2) arbitrary units). Exercise training improved maximum oxidative capacity in both muscles, and in gastrocnemius effective muscle mass also. CONCLUSIONS: Skeletal muscle exercise abnormalities in patients with congestive heart failure results more from decreased metabolic efficiency than from the abnormalities in mitochondrial oxidation. Both decreased efficiency and defective mitochondrial oxidation result in an increased activation of glycogen phosphorylase, and may be improved by exercise training.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold D. L., Matthews P. M., Radda G. K. Metabolic recovery after exercise and the assessment of mitochondrial function in vivo in human skeletal muscle by means of 31P NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1984 Sep;1(3):307–315. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnolda L., Brosnan J., Rajagopalan B., Radda G. K. Skeletal muscle metabolism in heart failure in rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):H434–H442. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.2.H434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnolda L., Conway M., Dolecki M., Sharif H., Rajagopalan B., Ledingham J. G., Sleight P., Radda G. K. Skeletal muscle metabolism in heart failure: a 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of leg muscle. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Dec;79(6):583–589. doi: 10.1042/cs0790583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasiotis D. The regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen breakdown in human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1983;518:1–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chati Z., Zannad F., Robin-Lherbier B., Escanye J. M., Jeandel C., Robert J., Aliot E. Contribution of specific skeletal muscle metabolic abnormalities to limitation of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure: a phosphorus 31 nuclear magnetic resonance study. Am Heart J. 1994 Oct;128(4):781–792. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy J. O. Adaptations of muscular tissue to training. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1976 May-Jun;18(6):445–458. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(76)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. J., Hands L. J., Ramaswami G., Taylor D. J., Nicolaides A., Amato A., Radda G. K. Calf muscle mitochondrial and glycogenolytic ATP synthesis in patients with claudication due to peripheral vascular disease analysed using 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Sci (Lond) 1995 Dec;89(6):581–590. doi: 10.1042/cs0890581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. J., Radda G. K. Quantitative interpretation of bioenergetic data from 31P and 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of skeletal muscle: an analytical review. Magn Reson Q. 1994 Mar;10(1):43–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. J., Taylor D. J., Styles P., Radda G. K. The production, buffering and efflux of protons in human skeletal muscle during exercise and recovery. NMR Biomed. 1993 Jan-Feb;6(1):73–83. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940060112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. J., Thompson C. H., Barnes P. R., Radda G. K. Comparisons of ATP turnover in human muscle during ischemic and aerobic exercise using 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1994 Mar;31(3):248–258. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. J., Thompson C. H., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K. ATP production and mechanical work in exercising skeletal muscle: a theoretical analysis applied to 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of dialyzed uremic patients. Magn Reson Med. 1995 May;33(5):601–609. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910330504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini D. M., Coyle E., Coggan A., Beltz J., Ferraro N., Montain S., Wilson J. R. Contribution of intrinsic skeletal muscle changes to 31P NMR skeletal muscle metabolic abnormalities in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1338–1346. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini D. M., Ferraro N., Tuchler M., Chance B., Wilson J. R. Detection of abnormal calf muscle metabolism in patients with heart failure using phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Dec 1;62(17):1234–1240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini D. M., Walter G., Reichek N., Lenkinski R., McCully K. K., Mullen J. L., Wilson J. R. Contribution of skeletal muscle atrophy to exercise intolerance and altered muscle metabolism in heart failure. Circulation. 1992 Apr;85(4):1364–1373. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.4.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini D. M., Wilson J. R., Bolinger L., Li H., Kendrick K., Chance B., Leigh J. S. In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy measurement of deoxymyoglobin during exercise in patients with heart failure. Demonstration of abnormal muscle metabolism despite adequate oxygenation. Circulation. 1994 Jul;90(1):500–508. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie B. M., Conway M., Rajagopalan B., Yonge R., Frostick S., Ledingham J., Sleight P., Radda G. Skeletal muscle metabolism during exercise under ischemic conditions in congestive heart failure. Evidence for abnormalities unrelated to blood flow. Circulation. 1988 Aug;78(2):320–326. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.78.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie B., Conway M., Yonge R., Frostick S., Ledingham J., Sleight P., Radda G., Rajagopalan B. Skeletal muscle metabolism in patients with congestive heart failure: relation to clinical severity and blood flow. Circulation. 1987 Nov;76(5):1009–1019. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.5.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Tamura N., Hirakawa T., Kobayashi S., Takekoshi N., Murakami E. Assessment of working skeletal muscle oxygenation in patients with chronic heart failure. Am Heart J. 1995 Apr;129(4):690–695. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(95)90317-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minotti J. R., Christoph I., Oka R., Weiner M. W., Wells L., Massie B. M. Impaired skeletal muscle function in patients with congestive heart failure. Relationship to systemic exercise performance. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2077–2082. doi: 10.1172/JCI115537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minotti J. R., Johnson E. C., Hudson T. L., Zuroske G., Murata G., Fukushima E., Cagle T. G., Chick T. W., Massie B. M., Icenogle M. V. Skeletal muscle response to exercise training in congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):751–758. doi: 10.1172/JCI114771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. F., Batin P., Evans S., Hawkins M., Cowley A. J. Regional blood flow in chronic heart failure: the reason for the lack of correlation between patients' exercise tolerance and cardiac output? Br Heart J. 1992 Jun;67(6):478–481. doi: 10.1136/hrt.67.6.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch T. I., Ghaul M. R., Tranchitella V., Zelis R. Skeletal muscle glycogen depletion during submaximal exercise in rats with chronic heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol. 1990 Nov-Dec;85(6):606–618. doi: 10.1007/BF01907895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch T. I., Nguyen C. T., Pham H. V., Moore R. L. Training effects on the regional blood flow response to exercise in myocardial infarcted rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):H1846–H1852. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.6.H1846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton J. R., Dunn J. F., Adamopoulos S., Kemp G. J., Coats A. J., Rajagopalan B. Training partially reverses skeletal muscle metabolic abnormalities during exercise in heart failure. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 Apr;76(4):1575–1582. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.4.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton J. R., Kemp G. J., Daly R. C., Yacoub M., Rajagopalan B. Effects of cardiac transplantation on bioenergetic abnormalities of skeletal muscle in congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1994 Apr;89(4):1624–1631. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.4.1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. J., Green H. J., Cobb F. R. Skeletal muscle biochemistry and histology in ambulatory patients with long-term heart failure. Circulation. 1990 Feb;81(2):518–527. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.2.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. H., Kemp G. J., Rajagopalan B., Radda G. K. Abnormal ATP turnover in rat leg muscle during exercise and recovery following myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 1995 Mar;29(3):344–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. H., Kemp G. J., Rajagopalan B., Radda G. K. Metabolic abnormalities in skeletal muscle after myocardial infarction in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1994 Oct;87(4):403–406. doi: 10.1042/cs0870403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener D. H., Fink L. I., Maris J., Jones R. A., Chance B., Wilson J. R. Abnormal skeletal muscle bioenergetics during exercise in patients with heart failure: role of reduced muscle blood flow. Circulation. 1986 Jun;73(6):1127–1136. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Coyle E. F., Osbakken M. Effect of heart failure on skeletal muscle in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):H993–H998. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.4.H993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. R., Martin J. L., Schwartz D., Ferraro N. Exercise intolerance in patients with chronic heart failure: role of impaired nutritive flow to skeletal muscle. Circulation. 1984 Jun;69(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.69.6.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



