Abstract
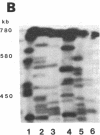
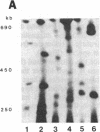
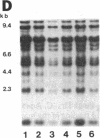
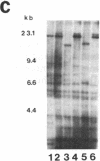
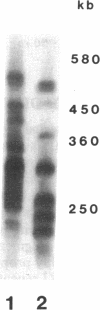
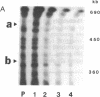
Tomato telomeres are composed of a terminal 7-base-pair tandem repeat and a closely liked 162-base-pair subtelomeric repeat (TGRI). Together, these repeats account for 2% of the total chromosomal DNA. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis has been used to examine the long-range physical structure of these arrays in closely related varieties, and we report here that these arrays are undergoing heritable changes at a frequency as great as 2% per generation. Moreover, comparisons with other known hypervariable probes (e.g., human minisatellites and M13 sequences) revealed that telomeric sites are more variable than any other known region of the plant genome and can be used to distinguish closely related plant varieties (tomato and melon) that are otherwise very similar at the DNA level. The fact that the polymorphisms are inherited in a mendelian fashion suggests applications in genetic mapping of telomeres and identification of varieties.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas J. F. Detection of DNA "fingerprints" of cultivated rice by hybridization with a human minisatellite DNA probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6831–6835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. B. Repetitive DNA and chromosome evolution in plants. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Jan 29;312(1154):227–242. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganal M. W., Lapitan N. L., Tanksley S. D. Macrostructure of the tomato telomeres. Plant Cell. 1991 Jan;3(1):87–94. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Dempster M., Dunlop M. G., Thompson A. M., Green D. K., Allshire R. C. Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):866–868. doi: 10.1038/346866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Cooke H. J. Hypervariable ultra-long telomeres in mice. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):400–402. doi: 10.1038/347400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Ausubel F. M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck-Eidens D. M., Bell R. N., Neuhausen S. L., Helentjaris T. DNA sequence variation within maize and melon: observations from polymerase chain reaction amplification and direct sequencing. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):207–217. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling J. A., Maule J., Hastie N. D., Allshire R. C. Extensive telomere repeat arrays in mouse are hypervariable. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6881–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassart G., Georges M., Monsieur R., Brocas H., Lequarre A. S., Christophe D. A sequence in M13 phage detects hypervariable minisatellites in human and animal DNA. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):683–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2880398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]