Abstract
Vertebrate neurogenesis requires inhibition of endogenous bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signals in the ectoderm. Blocking of BMPs in animal cap explants causes the formation of anterior neural tissues as a default fate. To identify genes involved in the anterior neural specification, we analyzed gene expression profiles using a Xenopus Affymetrix Gene Chip after BMP-4 inhibition in animal cap explants. We found that the xCyp26c gene, encoding a retinoic acid (RA) degradation enzyme, was upregulated following inhibition of BMP signaling in early neuroectodermal cells. Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis showed that xCyp26c expression started in the anterior region during the early neurula stage. Overexpression of xCyp26c weakly induced neural genes in animal cap explants. xCyp26c abolished the expression of all trans-/cis-RA-induced posterior genes, but not basic FGF-induced posterior genes. Depletion of xCyp26c by morpholino-oligonucleotides suppressed the normal formation of the axis and head, indicating that xCyp26c plays a critical role in the specification of anterior neural tissue in whole embryos. In animal cap explants, however, xCyp26c morpholinos did not alter anterior-to-posterior neural tissue formation. Together, these results suggest that xCyp26c plays a specific role in anterior-posterior (A-P) neural patterning of Xenopus embryos.
Keywords: A-P neural formation, BMP-4, xCyp26c, Xenopus laevis
INTRODUCTION
Induction of three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) and axis formation including the dorsoventral and anteroposterior posterior regions are major events during vertebrate embryo development. Signals from bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and Wnt play crucial roles during early embryo development and early patterning (Harland and Gerhart, 1997; Hemmati-Brivanlou and Thomsen, 1995; Kessler and Melton, 1994; Lee et al., 2011a; Schmidt et al., 1995).
In Xenopus, BMP-4 is expressed in the ventral mesoderm and ectoderm and acts as a ventral morphogen in a direct and long-range fashion to establish its gradient and specific cell fate (Dosch et al., 1997; Xu et al., 1999). When the BMP-4 gradient is established, responding cells activate different genes at distinct threshold levels, resulting in dorsoventral patterning of the mesoderm as well as ectoderm during early Xenopus development (Jones and Smith, 1998; Knecht and Harland, 1997). If BMP-4 mRNA is injected into Xenopus embryos, the dorsal mesoderm is converted into the ventral mesoderm (Dale et al., 1992; Hwang et al., 2002; 2003; Jones et al., 1992). On the other hand, over-expression of a dominant negative BMP-4 receptor (DNBR) into ventral territories results in the formation of a secondary body axis (Graff et al., 1994; Suzuki et al., 1994). BMP-4 is a strong candidate as an epidermal, ventral mesodermal inducer as well as a neural inhibitor (Xu et al., 1995). Previously, Wawersik et al. (2005) reported that in-vivo BMP inhibition triggered at stage 5 not only expands the neural plate but also represses the neural crest marker.
The development of the central nervous system (CNS) begins when the ectoderm gives rise to the neural plate. Early neurogenesis is initiated by inhibition of BMP signaling in the ectoderm by BMP antagonists expressed in Spemann’s organizer region, resulting in anterior neural tissue formation (Hemmati-Brivanlou and Melton, 1994). According to a generally accepted mechanism, inhibition of BMP signaling generates anterior neural tissue as a default pathway (Nieuwkoop, 1952). Wnts, FGF and retinoic acids (RA) act as modifiers of anterior to posterior neural specification (Blumberg et al., 1997; Kolm et al., 1997; Ruiz i Altaba and Jessell, 1991; Xu et al., 1997). However, it is unclear whether anterior neural tissue produced by inhibition of BMP is simply generated by a default pathway of pre-existing intracellular molecules or by the newly expressed posterior modifier inhibition molecules.
The intracellular level of active RA is determined by the balance between RA synthesis by retinaldehyde dehydrogenases (RALDHs) and its degradation by Cyp26 enzymes, the latter of which constitute a group of P450 enzymes that metabolize RA to its inactive forms (Fujii et al., 1997; Ray et al., 1997; White et al., 1996). Cyp26 enzymes are thought to play a central role in the appropriate regulation of the RA signal as a posteriorizing factor in CNS development (Abu-Abed et al., 2001; Sakai et al., 2001; Sirbu et al., 2005). Mice and humans possess three Cyp26 genes: Cyp26a1, Cyp26b1 and Cyp26c1 (MacLean et al., 2001; Nebert and Russell, 2002; Tahayato et al., 2003). Cyp26 genes have been previously characterized in various species, but their function in Xenopus leavis have not yet been fully identified. The role of Cyp26 during RA utilization and the anteriorization of the neuroectoderm during the early embryonic stages of Xenopus is also unclear.
Wnt and FGF are also known as anterior to posterior modifiers during early neurogenesis. Cyp26 is regulated by both Wnt and FGF signaling (Kudoh et al., 2002; Lee et al., 2011b). Wnt is reportedly responsible for (A-P) neural patterning, as an injection of a truncated form of BMP receptor into the ventral side of embryos results in the formation of a secondary axis without a head. Inhibition of XWnt8 with dn-XWnt8 induces the formation of a complete axis with a head, indicating that inhibition of Wnt signaling is important for head formation (Glinka et al., 1997). xCyp26c is negatively regulated by Wnt signaling and is different from xCyp26a. Cyp26c is expressed in the anterior region, and the expression of Cyp26c is positively regulated by inhibition of canonical Wnt signaling and also by a high-dose RA treatment in the neurula (Tanibe et al., 2008).
To examine whether RA metabolism is involved in the anterior neurogenesis caused by the inhibition of BMP, we sought to identify the genes that are regulated during early neurogenesis and anterior neural patterning. The gene expression profiles were analyzed using Xenopus Affymetrix gene chips. We found that the RA-degrading enzyme xCyp26c was upregulated and the RA-synthesizing enzyme RALDH was downregulated following BMP-4 inhibition with DNBR in Xenopus animal cap explants. We found that xCyp26c played a critical role in the specification of anterior neural tissue in animal cap explants and whole embryos. In summary, we concluded that xCyp26c upregulated by DNBR is required for anterior neural development via RA degradation during early Xenopus development. We suggest that anterior neural tissue is not simply generated by a default pathway of pre-existing intracellular molecules but by the posterior modifier inhibition molecules, including xCyp26c, which is newly expressed after inhibition of BMP signaling.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Embryo injection and explant culture
Xenopus leavis embryos were obtained by artificial fertilization (Smith and Slack, 1983). Developmental stages were determined according to Nieuwkoop and Faber (Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1956). The vitelline membranes were removed by immersing the embryos in 2.5 % thioglycolic acid. Embryos at the one-cell stage or two-cell stage were injected in the animal pole with messenger RNA, as described in the figure legends. Animal caps were dissected from the injected embryos at stage 8–9 and cultured to various stages in 67% Leibovitz’s L-15 medium (GIBCO/BRL) with BSA (1 mg/ml), 7 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) and gentamicin (50 μg/ml).
In vitro transcription
All of the synthetic mRNAs used for microinjection were produced by in vitro transcription. The xCyp26c cDNA was inserted in the pCS2 vector. The cDNA was linearized and used for in synthesis of capped mRNA using an in vitro transcription kit (Ambion) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The synthetic RNA was quantified by ethidium bromide staining in comparison with a standard RNA (Yoon et al., 2014a).
RNA isolation and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from whole embryos or cultured animal explants with TRIzol reagent (Tel-Test Inc.) following the manufacturer’s instruction. RT-PCR was performed with a Superscript preamplification system (Invitrogen). PCR was performed as follows: first, a denaturation step of 94°C for 5 min; second, 94°C for 1 min; third, annealing temperature appropriate for each primer pair for 1 min; fourth, 72°C for 1 min; and fifth, repeat the second, third and fourth steps for 19–30 cycles of amplification as described by the Xenopus Molecular Marker Resource (XMMR; University of Texas).
Morpholino oligos
Morpholino oligos (Gene tools LLC) for antisense oligodeoxynucleotides were used for loss-of-function studies. The base composition of the antisense oligodeoxynucleotide was a 25-mer morpholino 5′ TAC AAG ATG TTC CTC CTT GAG ATC A 3′ (MO-xCyp26c). Morpholino oligos substitute riboside moieties with nitrogen-containing morpholine moieties and are phosphorodiamidate-linked (Summerton and Weller, 1997). Oligos were re-suspended in sterile water and injected at doses of 40 ng per embryo (Yoon et al., 2014b).
Whole-mount in situ hybridization
Whole-mount in situ hybridization was completed as described (Harland, 1991) with modifications as reported (Hollemann et al., 1998). Embryos were fixed in MEMFA and processed for the whole-mount in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labeled antisense RNA probes. To produce the xCyp26c antisense probe, the cDNA was linearized by EcoRI and transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase (Ambion).
RESULTS
xCyp26c is induced by BMP inhibition and expressed in an anterior specific pattern in Xenopus embryos
To identify the genes involved during early neurogenesis, homogeneous animal cap explant samples were obtained from embryos with or without BMP signaling inhibition. Two nanograms of synthetic mRNA of DNBR was injected into one- or two-cell stage embryos. Animal cap explants isolated from blastula stage (stage 8–9) embryos were allowed to develop until the early gastrula stage (stage 11.5–12). The gene expression profiles were analyzed using Xenopus Affymetrix Gene chips containing 14,400 gene transcripts. Expression of various genes during early neurogenesis was induced by BMP signaling inhibition. We found ‘Xl.1946.1.A1_’ to be a newly expressed gene in early neuroectodermal cells (Fig. 1A). We isolated the full-length cDNA of this gene and identified it as a member of the Xenopus cytochrome P450 subfamily 26c (xCyp26c) through homology analysis of amino acid sequences in NCBI protein databases. Alignment of multiple sequences and phylogenetic analysis were used to determine the Cyp26 subfamilies (Fig. 1B).
Fig. 1.
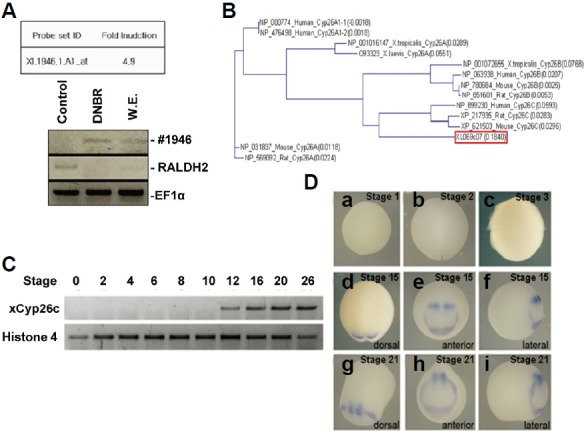
Induction of xCyp26c by blocking BMP in animal cap explants and the expression pattern of xCyp26c in whole embryos. (A) Selection of the ‘Xl.1946.1.A1_at’ gene induced by DNBR in a cDNA microarray. The expression of ‘Xl.1946.1.A1_at’ was confirmed by RT-PCR. (B) Phylogenetic relationships among the xCYP26 proteins. (C) Developmental expression of xCyp26c. RT-PCR analysis was performed at various stages, as indicated (Nieuwkoop and Faber, 1956). Histone 4 or EF1α serve as an RNA loading control. (D) Spatial expression patterns of xCyp26c. Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of xCyp26c was performed during oocyte to tail bud stages. Views of whole embryos at the stages are indicated on top of each column. xCyp26c was expressed in the presumptive anterior neural ectoderm, and the expression continued to the tail bud stage.
Using RT-PCR, we analyzed the temporal expression of xCyp26c mRNA throughout embryogenesis (Fig. 1C). Temporal-xCyp26c was not expressed maternally, but was detected in the gastrula stages (stage 12), and expression was sustained to the tail bud stage. To examine the spatial expression pattern of xCyp26c, we performed whole-mount in situ hybridization during the embryonic stages (Fig. 1D). xCyp26c shows a restricted expression pattern in the anterior region from the early neural to tail bud stage (Fig. 1D). Zygotic expression of xCyp26c was detected as a semi-circular shape during the late gastrula stage in the dorsal region (Fig. 1D) and at a tail-bud stage in the presumptive anterior neural region (Fig. 1D).
Ectopic expression of xCyp26c induces neural genes in animal cap explants
To investigate the function of xCyp26c during early Xenopus development, gain-of-function experiments were performed. For effective xCyp26c expression in Xenopus embryos, xCyp26c mRNA was injected into one- or two-cell stage embryos. Animal caps were dissected from the injected embryos at stage 8–9 and cultured to stages 12 and 24, as described in the Materials and Methods.
At stage 12, xCyp26c induced the expression of the early neural marker Zic3, Ngnr1 (Fig. 2A). However, xCyp26c had no effect on the expression of ventral (Vent1) or mesodermal markers (Xbra). At stage 24, the expression of the anterior neural marker Otx2 was slightly increased by xCyp26c (Fig. 2B). Otherwise, the posterior neural marker HoxB9 and the mesoderm marker actin were not induced by xCyp26c. These results provided evidence for a specific role for xCyp26c in anterior neural development, but not in mesoderm and posterior formation at the molecular level.
Fig. 2.
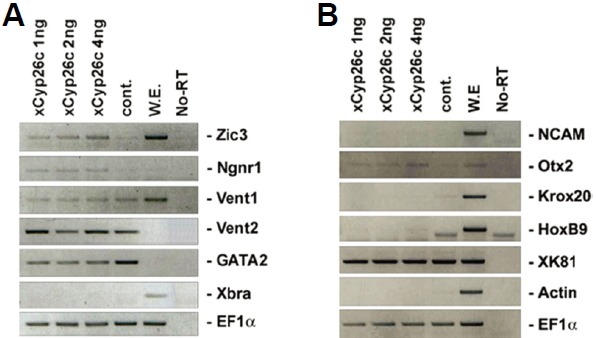
Induction of neural genes by overexpression of xCyp26c in animal cap explants. Xenopus embryos at the one cell stage or two-cell stage were injected in the animal pole with xCyp26c mRNA. Animal caps were dissected from the injected embryos at stages 8–9 and cultured to stage 12 (A) or 24 (B). RT-PCR was then performed to detect expression of the indicated genes. EF1α serves as a RNA loading control.
xCyp26c inhibits all-trans and 9-cis RA-induced posteriorization of anterior neural tissue in animal cap explants
To investigate whether xCyp26c was involved in A-P patterning, we examined the effect of xCyp26c in combination with DNBR and RA (all-trans and 9-cis RA), which induced both anterior and posterior neural tissue in animal cap explants (Tanibe et al., 2008). Animal caps were isolated from embryos injected with xCyp26c mRNA or DNBR and cultured in the presence or absence of RA (all-trans and 9-cis RA). RT-PCR analysis showed that xCyp26c enhanced anterior neural marker (Otx2, BF1) and inhibited posterior neural maker expression (HoxB9) (Figs. 3A and 3B). However, xCyp26c did not affect the expression of the anterior neural marker in A-P patterning induced by a combination of DNBR and basic FGF (bFGF), whereas it enhanced posterior neural markers (Fig. 3C). As results, we suggest that xCyp26c blocks the posteriorization caused by RA, but not by bFGF.
Fig. 3.
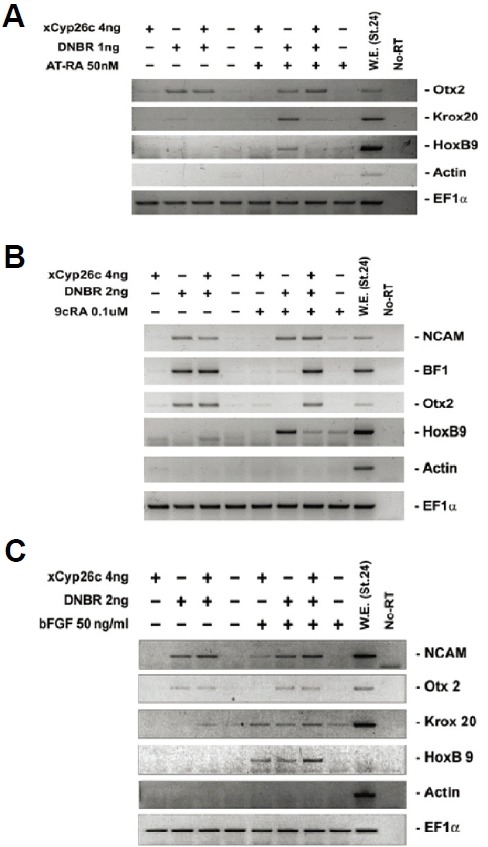
Inhibition of all-trans and 9-cis retinoic acid-induced posteriorization by overexpression of xCyp26c in animal cap explants. xCyp26c was injected with DNBR, and animal caps were treated with all-trans retinoic acid (AT-RA) (A), 9-cis retinoic acid (9cRA) (B), and basic FGF (bFGF) (C) at stage 8 and then cultured to stage 24. The expression pattern of marker genes were analyzed by RT-PCR.
Depletion of xCyp26c inhibits the formation of normal axis and head structures in whole embryos
To further verify the function of xCyp26c during normal development, we performed a loss-of-function study using the anti-sense morpholino directed against xCyp26c (MO-xCyp26c). We generated a MO-xCyp26c that targets the first 25 nucleotides of the untranslated region, including the AUG translational start site in Xenopus xCyp26c mRNA. MO-xCyp26c was effective in specifically reducing the level of the 3′-terminal end HA-or Flag-tagged xCyp26c protein (xCyp26c-HA-or xCyp26c-flag) (Fig. 4A). Injection of MO-xCyp26c into the animal region at the one- or two-cell stage caused inhibition of axis formation and the head structure of tadpole stage embryos (Fig. 4B).
Fig. 4.
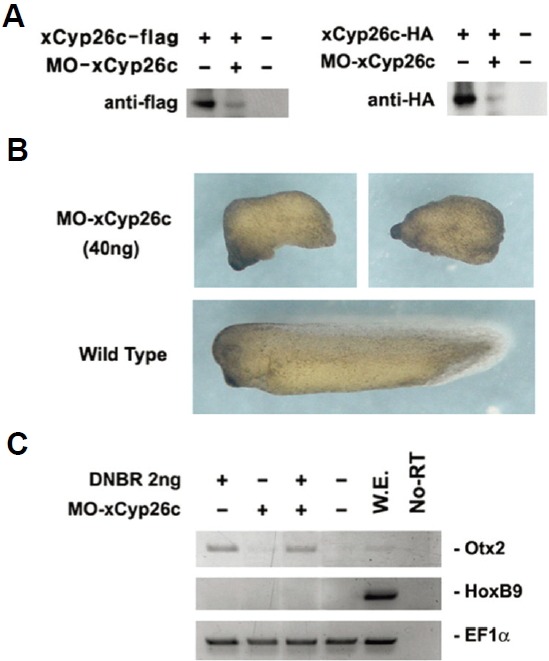
Inhibition of normal head and axis formation by depletion of endogenous xCyp26c. Morpholino activity was confirmed by Western blot. (B) Embryos injected with 40 ng of MO-xCyp26c did not have head structures and had short axis formation. (C) xCyp26c was injected with DNBR and animal caps were cultured to stage 24. Expression patterns of Otx2 and HoxB9 were analyzed by RT-PCR.
To investigate whether depletion of xCyp26c could inhibit DNBR-induced anterior neural marker expression, animal caps isolated from embryos injected with MO-xCyp26c alone or together with DNBR were incubated until stage 24. MO-xCyp26c did not suppress the expression of Otx2 induced by DNBR (Fig 4C).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we examined whether RA metabolism was involved in the anterior neurogenesis caused by the inhibition of BMP. We found that the RA-degrading enzyme xCyp26c was upregulated and that the RA-synthesizing enzyme RALDH was downregulated after BMP signaling blockade in animal cap explants from Xenopus embryos. We also observed that ectopic expression of xCyp26c induced neural gene expression and inhibited all-trans and 9-cis RA-induced posteriorization of neural tissue in animal cap explants. In addition, depletion of xCyp26c inhibited the formation of normal axis and head structures in whole embryos. Taken together, xCyp26c upregulation by DNBR is necessary for anterior neural development in Xenopus. We suggest that anterior neurogenesis may not be the default pathway for pre-existing intracellular molecules, but requires newly synthesized posterior modifier inhibitors, including xCyp26c, after inhibition of BMP signaling.
We examined whether the inhibition of BMP directly elicited anterior neurogenesis without the involvement of RA metabolism or with RA-metabolizing enzymes, which were newly up-regulated after BMP signaling blockade. To identify the genes involved in early neurogenesis, we used a Xenopus Affymetrix gene chip containing 14400 gene transcripts and obtained 107 ESTs that was upregulated after inhibition of BMP signaling. Among these ESTs, we found that X1.19461A1-at was upregulated. This was further characterized as a member the Xenopus cytochrome P450 subfamily 26, xCyp26c, which is a metabolic enzyme that converts active RA to its inactive form. In this study, we found that BMP inhibition upregulated the expression of the RA degradation enzyme xCyp26c and downregulated the RA-synthesizing enzyme RALDH during neurogenesis in animal cap explants. A-P neural patterning plays a key role in the formation of normal neural development in embryos. Antagonists of Wnt or BMPs are expressed as anteriorizing factors (Gamse and Sive, 2000), whereas Wnts induce neuroectoderm posteriorization in Xenopus (Kuhl, 2003). Other signaling molecules, such as FGFs and RA, are also involved in embryonic A-P specification as modifiers (Doniach, 1995; Gavalas and Krumlauf, 2000; Mason, 1996). Previously, it has been reported that xCyp26c is expressed in the anterior region during early neural development (Hollemann et al., 1998). Its expression is specifically restricted to the anterior neural region during the early neurula to tailbud stages. We also found that xCyp26c is not expressed maternally. Most importantly, components of RA signaling, RA receptor, and RA converting enzyme (RALDH), which are expressed in dorsolateral ectoderm and more posteriorly, lead to a reduction in anterior structures and induction of positional genes (Gamse and Sive, 2000). Alternatively, RA hydroxylase (Cyp26), which targets RA for degradation, leads to the expansion of anterior structures (de Roos et al., 1999; Hollemann et al., 1998). To examine the expression profiles of posterior modifier modulating genes in early neurogenesis (stage 11), we analyzed 98 genes that were the most upregulated by BMP inhibition in animal cap explants. At least, 3 genes were RA-related enzymes, and 4 genes were Wnt signal related molecules, including secreted frizzled protein 2, frizzled 4 and 7. In fact, xCyp26c has been reported as one of the genes that are negatively regulated by canonical Wnt signaling through the anterior neuroectoderm of early neural embryos (Tanibe et al., 2008). A more detailed study of the relationship between Wnt and RA and their mutual regulation mechanisms during anterior neurogenesis is needed. We suggest that anterior neurogenesis caused by BMP inhibition may not be the default pathway of pre-existing molecules but may require the expression of new molecules that inhibit anterior to posterior modifier molecules such as RA and Wnt.
In this study, we found that xCyp26c was expressed during the late gastrula stage, and the expression remained higher in later developmental stages. Whole-mount in situ hybridization revealed that it is anteriorly expressed, similar to previous reports that also mentioned that temporal expression of xCyp26c in the anterior embryonic region was 40-fold higher than in the posterior region. xCyp26c is expressed in only a subset of cranial nerves during late embryonic development (Tanibe et al., 2008). Because inhibition of BMP with DNBR upregulated the expression xCyp26c in animal explants, we examined the roles of xCyp26c in neurogenesis. We found that overexpression of xCyp26c upregulated the expression of neural markers zic3, otx2, and ngnr1 in animal explants. However, the expression of ventral markers vent-1, vent-2, GATA-2, xbra and actin (mesodermal marker) were not affected much. It is interesting how the overexpression of the RA degradation enzyme xCyp26c led to the upregulation of neural genes, including zic3, otx2 and ngnr1. The neurogenesis mechanism caused by xCyp26c remains unclear.
Previously, Kolm et al. (1997) reported that the Cyp26 enzyme utilizes RA as its main substrate within an expected range to a limit of RA-mediated posteriorization of embryos. Cyp26 plays a crucial role in the A-P patterning of the neural ectoderm in the late blastula stage, whereas Hoxb1 is expressed later as an earlier posterior marker (Kudoh et al., 2002). FGF signaling is also involved in posterior neural formation (Xu et al., 1997). We examined whether xCyp26c was specific for A-P patterning including RA or is also involved in FGF-mediated patterning. xCyp26c was specifically involved in A-P patterning by blocking the posteriorization caused by RA, but did not affect the posteriorization induced by FGF. The results showed that xCyp26c induced anterior neural marker (otx2 and BF1) and inhibited posterior marker expression (HoxB9), but did not affect the expression of anterior neural markers in A-P patterning in the presence of FGF and DNBR. Rather, xCyp26c upregulated the posterior neural marker expression (Fig. 3c). In a previous report in zebrafish embryos (Kudoh et al., 2002), FGF3 and Wnt signaling were reported to independently suppress Cyp26, and FGF or Wnt signals initiate posterior gene expression only in the presence of an intact RA signaling pathway. Because FGF over-activation may lead to an expansion of posterior genes more than that due to abrogation of Cyp26, FGF-mediated posteriorization may include other factors and/or different FGFs may use a different set of RA-metabolizing enzymes. Wnt facilitates the A-P patterning and requires Cyp26c mediated RA metabolism (Tanibe et al., 2008). In our study, the results indicated that bFGF mediated A-P patterning was not fully dependent on RA metabolism by xCyp26c.
We also found that the loss of function assay of xCyp26c by using Mo-xCypc26 led to anterior truncation in whole embryos. However, DNBR-induced anterior neural tissue was not suppressed by the depletion of xCyp26c in animal cap explants. These results indicate that xCyp26c is not an essential factor for anterior neurogenesis caused by BMP inhibition. Instead, we suggest that other factors, such as Wnt signal inhibitors, must contribute to the anterior neurogenesis in animal cap explants. Taken together, all of these results proved our proposed hypothesis that xCyp26c is involved in anterior neural tissue development during early embryonic stages of Xenopus leavis. However, the detailed interaction mechanism among FGF, Wnt and RA signals in neurogenesis and the mechanism for anterior neurogenesis by BMP inhibition require further study.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (NRF-2013R1A1A2008541) and Hallym University Research Fund (HRF-G-2015-3).
REFERENCES
- Abu-Abed S., Dollé P., Metzger D., Beckett B., Chambon P., Petkovich M. The retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme, Cyp26A1, is essential for normal hindbrain patterning, vertebral identity, and development of posterior structures. Genes Dev. 2001;15:226–240. doi: 10.1101/gad.855001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Bolado J., Moreno T.A., Kintner C., Evans R.M., Papalopulu N. An essential role for retinoid signaling in anteroposterior neural patterning. Development. 1997;124:373–379. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Howes G., Price B., Smith J. Bone morphogenetic protein 4: a ventralizing factor in early Xenopus development. Development. 1992;115:573–585. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Roos K., Sonneveld E., Compaan B., ten Berge D., Durston A.J., van der Saag P.T. Expression of retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase (Cyp26). during mouse and Xenopus laevis embryogenesis. Mech. Dev. 1999;82:205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach T. Basic FGF as an inducer of anteroposterior neural pattern. Cell. 1995;83:1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch R., Gawantka V., Delius H., Blumenstock C., Niehrs C. Bmp-4 acts as a morphogen in dorsoventral mesoderm patterning in Xenopus. Development. 1997;124:2325–2334. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.12.2325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Sato T., Kaneko S., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Osawa K., Kato S., Hamada H. Metabolic inactivation of retinoic acid by a novel P450 differentially expressed in developing mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1997;16:4163–4173. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.14.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse J., Sive H. Vertebrate anteroposterior patterning: the Xenopus neurectoderm as a paradigm. BioEssays. 2000;22:976–986. doi: 10.1002/1521-1878(200011)22:11<976::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalas A., Krumlauf R. Retinoid signalling and hindbrain patterning. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2000;10:380–386. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinka A., Wu W., Onichtchouk D., Blumenstock C., Niehrs C. Head induction by simultaneous repression of Bmp and Wnt signalling in Xenopus. Nature. 1997;389:517–519. doi: 10.1038/39092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J.M., Thies R.S., Song J.J., Celeste A.J., Melton D.A. Studies with a Xenopus BMP receptor suggest that ventral mesoderm-inducing signals override dorsal signals in vivo. Cell. 1994;79:169–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90409-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R.M. In situ hybridization: an improved whole-mount method for Xenopus embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:685. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Gerhart J. Formation and function of Spemann’s organizer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev .Biol. 1997;13:611–667. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Melton D.A. Inhibition of activin receptor signaling promotes neuralization in Xenopus. Cell. 1994;77:273–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Thomsen G.H. Ventral mesodermal patterning in Xenopus embryos: expression patterns and activities of BMP-2 and BMP-4. Dev. Genet. 1995;17:78–89. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020170109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollemann T., Chen Y., Grunz H., Pieler T. Regionalized metabolic activity establishes boundaries of retinoic acid signalling. EMBO J. 1998;17:7361–7372. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.24.7361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y.-S., Seo J.-J., Cha S.-W., Lee H.-S., Lee S.-Y., Roh D.-H., Kung H.-f., Kim J., Park M.J. Antimorphic PV.1 causes secondary axis by inducing ectopic organizer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;292:1081–1086. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y.-S., Lee H.-S., Roh D.-H., Cha S.-W., Lee S.-Y., Seo J.-J., Kim J., Park M.J. Active repression of organizer genes by C-terminal domain of PV.1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003;308:79–86. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)01321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C.M., Smith J. Establishment of a BMP-4 morphogen gradient by long-range inhibition. Dev. Biol. 1998;194:12–17. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C.M., Lyons K.M., Lapan P., Wright C., Hogan B. DVR-4 (bone morphogenetic protein-4). as a posterior-ventralizing factor in Xenopus mesoderm induction. Development. 1992;115:639–647. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D.S., Melton D.A. Vertebrate embryonic induction: mesodermal and neural patterning. Science. 1994;266:596–604. doi: 10.1126/science.7939714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht A.K., Harland R.M. Mechanisms of dorsal-ventral patterning in noggin-induced neural tissue. Development. 1997;124:2477–2488. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.12.2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolm P.J., Apekin V., Sive H. Xenopus hindbrain patterning requires retinoid signaling. Dev. Biol. 1997;192:1–16. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudoh T., Wilson S.W., Dawid I.B. Distinct roles for Fgf, Wnt and retinoic acid in posteriorizing the neural ectoderm. Development. 2002;129:4335–4346. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.18.4335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl M. Wnt Signaling in Development 2003 [Google Scholar]
- Lee H.-S., Lee S.-Y., Lee H., Hwang Y.-S., Cha S.-W., Park S., Lee J.-Y., Park J.-B., Kim S., Park M.J. Direct response elements of BMP within the PV.1A promoter are essential for its transcriptional regulation during early Xenopus development. PLoS One. 2011a;6:e22621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S.-Y., Yoon J., Lee H.-S., Hwang Y.-S., Cha S.-W., Jeong C.-H., Kim J.-I., Park J.-B., Lee J.-Y., Kim S. The function of heterodimeric AP-1 comprised of c-Jun and c-Fos in activin mediated Spemann organizer gene expression. PLoS One. 2011b;6:e21796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean G., Abu-Abed S., Dollé P., Tahayato A., Chambon P., Petkovich M. Cloning of a novel retinoic-acid metabolizing cytochrome P450, Cyp26B1, and comparative expression analysis with Cyp26A1 during early murine development. Mech. Dev. 2001;107:195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00463-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. Neural induction: Do fibroblast growth factors strike a cord? Curr. Biol. 1996;6:672–675. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(09)00446-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D.W., Russell D.W. Clinical importance of the cytochromes P450. The Lancet. 2002;360:1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop P. Activation and organization of the central nervous system in amphibians. Part III. Synthesis of a new working hypothesis. J. Exp. Zool. 1952;120:83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop P.D., Faber J. A systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company. Guilders; 1956. Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). [Google Scholar]
- Ray W.J., Bain G., Yao M., Gottlieb D.I. Cyp26, a novel mammalian cytochrome P450, is induced by retinoic acid and defines a new family. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:18702–18708. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.30.18702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Jessell T.M. Retinoic acid modifies the pattern of cell differentiation in the central nervous system of neurula stage Xenopus embryos. Development. 1991;112:945–958. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai Y., Meno C., Fujii H., Nishino J., Shiratori H., Saijoh Y., Rossant J., Hamada H. The retinoic acid-inactivating enzyme Cyp26 is essential for establishing an uneven distribution of retinoic acid along the anterio-posterior axis within the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 2001;15:213–225. doi: 10.1101/gad.851501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Francois V., Bier E., Kimelman D. Drosophila short gastrulation induces an ectopic axis in Xenopus: evidence for conserved mechanisms of dorsal-ventral patterning. Development. 1995;121:4319–4328. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.4319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirbu I.O., Gresh L., Barra J., Duester G. Shifting boundaries of retinoic acid activity control hindbrain segmental gene expression. Development. 2005;132:2611–2622. doi: 10.1242/dev.01845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Slack J. Dorsalization and neural induction: properties of the organizer in Xenopus laevis. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1983;78:299–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerton J., Weller D. Morpholino antisense oligomers: design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:187–195. doi: 10.1089/oli.1.1997.7.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Thies R.S., Yamaji N., Song J.J., Wozney J.M., Murakami K., Ueno N. A truncated bone morphogenetic protein receptor affects dorsal-ventral patterning in the early Xenopus embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:10255–10259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahayato A., Dollé P., Petkovich M. Cyp26C1 encodes a novel retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme expressed in the hindbrain, inner ear, first branchial arch and tooth buds during murine development. Gene Expr. Patterns. 2003;3:449–454. doi: 10.1016/s1567-133x(03)00066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanibe M., Michiue T., Yukita A., Danno H., Ikuzawa M., Ishiura S., Asashima M. Retinoic acid metabolizing factor xCyp26c is specifically expressed in neuroectoderm and regulates anterior neural patterning in Xenopus laevis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2008;52:893–901. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082683mt. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawersik S., Evola C., Whitman M. Conditional BMP inhibition in Xenopus reveals stage-specific roles for BMPs in neural and neural crest induction. Dev. Biol. 2005;277:425–442. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J.A., Guo Y.-D., Baetz K., Beckett-Jones B., Bonasoro J., Hsu K.E., Dilworth F.J., Jones G., Petkovich M. Identification of the retinoic acid-inducible all-trans-retinoic acid 4-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:29922–29927. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.47.29922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R.-H., Kim J., Taira M., Zhan S., Sredni D., Kung H. A dominant negative bone morphogenetic protein 4 receptor causes neuralization in Xenopus ectoderm. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995;212:212–219. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R.H., Kim J., Taira M., Sredni D., Kung H. Studies on the role of fibroblast growth factor signaling in neurogenesis using conjugated/aged animal caps and dorsal ectoderm-grafted embryos. J. Neurosci. 1997;17:6892–6898. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-18-06892.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R.-H., Ault K.T., Kim J., Park M.-J., Hwang Y.-S., Peng Y., Sredni D., Kung H.-f. Opposite effects of FGF and BMP-4 on embryonic blood formation: roles of PV.1 and GATA-2. Dev. Biol. 1999;208:352–361. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Kim J.H., Kim S.C., Park J.B., Lee J.Y., Kim J. PV.1 suppresses the expression of FoxD5b during neural induction in Xenopus embryos. Mol. Cells. 2014a;37:220–225. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2014.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Kim J.-H., Lee S.-Y., Kim S., Park J.-B., Lee J.-Y., Kim J. PV.1 induced by FGF-Xbra functions as a repressor of neurogenesis in Xenopus embryos. BMB Rep. 2014b;47:673. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2014.47.12.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


