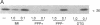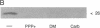Abstract
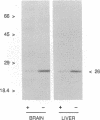
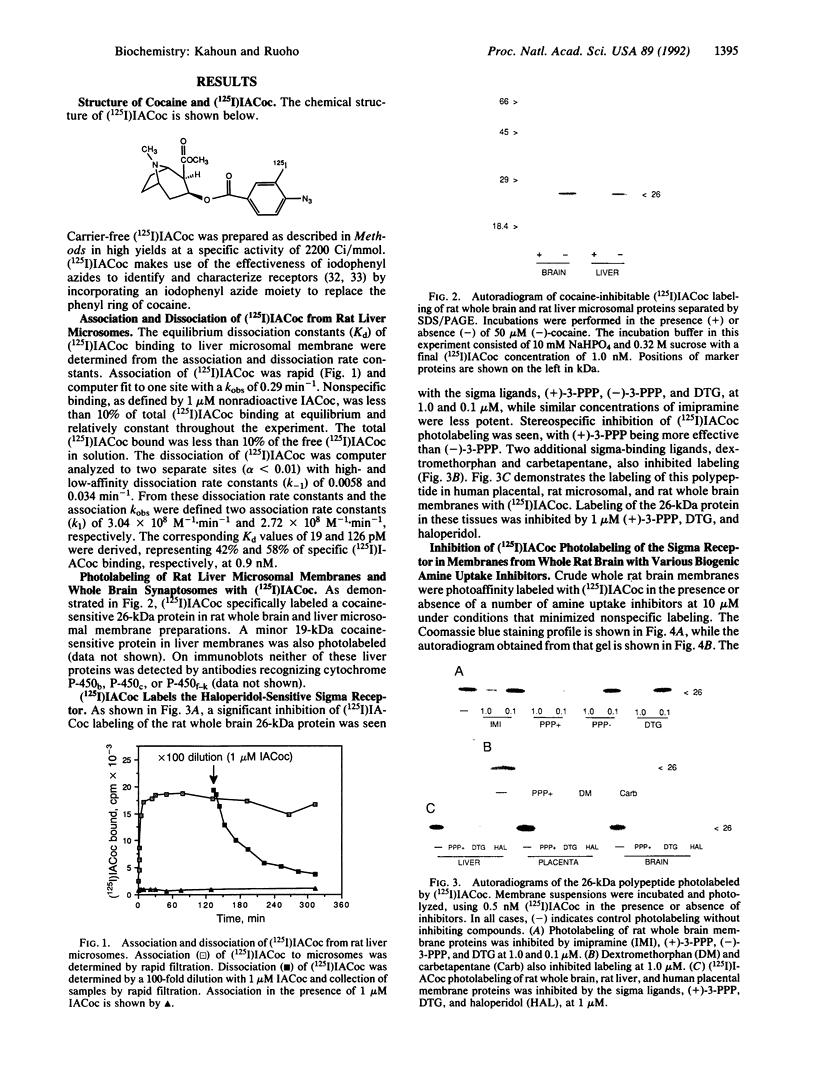
A carrier-free radioiodinated cocaine photo-affinity label, (-)-3-(125I)iodo-4-azidococaine [(125I)IACoc], has been synthesized and used as a probe for cocaine-binding proteins. Photoaffinity labeling with 0.5 nM (125I)IACoc resulted in selective derivatization of a 26-kDa polypeptide with the pharmacology of a sigma receptor in membranes derived from whole rat brain, rat liver, and human placenta. Covalent labeling of the 26-kDa polypeptide was inhibited by 1 microM haloperidol, di(2-tolyl)guanidine (DTG), 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine (3-PPP), dextromethorphan, and carbetapentane. Stereoselective protection of (125I)IACoc photolabeling by 3-PPP [(+)-3-PPP more potent than (-)-3-PPP] was observed. (125I)IACoc labeling of the 26-kDa polypeptide was also inhibited by 10 microM imipramine, amitriptyline, fluoxetine, benztropine, and tetrabenazine. The size of the (125I)I-ACoc-labeled proteins is consistent with the size of proteins photolabeled in guinea pig brain and liver membranes by using the sigma photolabel azido-[3H]DTG. Kinetic analysis of (125I)IACoc binding to rat liver microsomes revealed two sites with Kd values of 19 and 126 pM, respectively. The presence or absence of proteolytic inhibitors during membrane preparation did not alter the size of the photolabeled sigma receptor, indicating that the 26-kDa polypeptide was not derived from a larger protein. In summary, (125I)IACoc is a potent and highly specific photoaffinity label for the haloperidol-sensitive sigma receptor and will be useful for its biochemical and molecular characterization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calligaro D. O., Eldefrawi M. E. High affinity stereospecific binding of [3H] cocaine in striatum and its relationship to the dopamine transporter. Membr Biochem. 1987;7(2):87–106. doi: 10.3109/09687688709039986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craviso G. L., Musacchio J. M. High-affinity dextromethorphan binding sites in guinea pig brain. II. Competition experiments. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):629–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt S. B., Maxwell R. A., Ferris R. M. A structure-activity study of the transport sites for the hypothalamic and striatal catecholamine uptake systems. Similarities and differences. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;21(2):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonne-Pfister R., Bargetzi M. J., Meyer U. A. MPTP, the neurotoxin inducing Parkinson's disease, is a potent competitive inhibitor of human and rat cytochrome P450 isozymes (P450bufI, P450db1) catalyzing debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1144–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawin F. H. Cocaine addiction: psychology and neurophysiology. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1580–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.2011738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Matsunaga T., Nagata K., Meyer U. A., Nebert D. W., Pastewka J., Kozak C. A., Gillette J., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P. Debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase: characterization of a new P450 gene subfamily, regulation, chromosomal mapping, and molecular analysis of the DA rat polymorphism. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):149–161. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis D. E., Wilson A. A., Lew R., Sharkey J. S., Kuhar M. J. Dopamine transport sites selectively labeled by a novel photoaffinity probe: 125I-DEEP. J Neurosci. 1989 Aug;9(8):2664–2670. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-08-02664.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y., Mash D., Zhang S. H., Stein I. Characterization of N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) binding sites in C57BL/6 mouse brain: mutual effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and sigma ligands on MPTP and sigma binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;39(3):385–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh M. P., Tester B. C., Scherz M. W., Keana J. F., Weber E. Identification of the binding subunit of the sigma-type opiate receptor by photoaffinity labeling with 1-(4-azido-2-methyl[6-3H]phenyl)-3-(2-methyl[4,6-3H]phenyl)guanidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy L. T., Hanbauer I. Sodium-sensitive cocaine binding to rat striatal membrane: possible relationship to dopamine uptake sites. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Canoll P. D., Musacchio J. M. SKF 525-A and cytochrome P-450 ligands inhibit with high affinity the binding of [3H]dextromethorphan and sigma ligands to guinea pig brain. Life Sci. 1991;48(6):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90469-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koe B. K. Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Dec;199(3):649–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Wikström H., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Novel antipsychotic drugs share high affinity for sigma receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 18;155(3):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann D. J., Su T. P. Haloperidol-sensitive (+)[3H]SKF-10,047 binding sites (sigma sites) exhibit a unique distribution in rat brain subcellular fractions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;188(4-5):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90004-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann D. J., Su T. P. Solubilization and characterization of haloperidol-sensitive (+)-[3H]SKF-10,047 binding sites (sigma sites) from rat liver membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 May;257(2):547–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio J. M., Klein M., Canoll P. D. Dextromethorphan and sigma ligands: common sites but diverse effects. Life Sci. 1989;45(19):1721–1732. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90510-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata T., Yamanaka Y., Sho S., Kinemuchi H. Isoelectric analysis of 3H-pargyline-labelled monoamine oxidase in rat and carp. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1990;96(1):91–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk T., Blakely R. D., Amara S. G. Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):350–354. doi: 10.1038/350350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. S., Cler J. A., Oei E. J., Iyengar S., Wood P. L. Increased release of dopamine in vivo by BMY-14802: contrasting pattern to clozapine. Neuropharmacology. 1990 May;29(5):503–506. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(90)90173-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Iodoazidobenzylpindolol, a photoaffinity probe for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M. E., Meisler B. E., Sershen H., Lajtha A. Structural requirements for cocaine congeners to interact with dopamine and serotonin uptake sites in mouse brain and to induce stereotyped behavior. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 1;35(7):1123–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz M. C., Lamb R. J., Goldberg S. R., Kuhar M. J. Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1219–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.2820058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. B. Is the sigma opiate receptor a proadifen-sensitive subform of cytochrome P-450? Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990 Jul;67(1):93–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1990.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Reid A., Mahboubi A., Kim C. H., De Costa B. R., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C. Labeling by [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine of two high affinity binding sites in guinea pig brain: evidence for allosteric regulation by calcium channel antagonists and pseudoallosteric modulation by sigma ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallee F. R., Fogel E. L., Schwartz E., Choi S. M., Curran D. P., Niznik H. B. Photoaffinity labeling of the mammalian dopamine transporter. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81752-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey J., Glen K. A., Wolfe S., Kuhar M. J. Cocaine binding at sigma receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 27;149(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey J., Ritz M. C., Schenden J. A., Hanson R. C., Kuhar M. J. Cocaine inhibits muscarinic cholinergic receptors in heart and brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1048–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P., London E. D., Jaffe J. H. Steroid binding at sigma receptors suggests a link between endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):219–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2832949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndale R. F., Sunahara R., Inaba T., Kalow W., Gonzalez F. J., Niznik H. B. Neuronal cytochrome P450IID1 (debrisoquine/sparteine-type): potent inhibition of activity by (-)-cocaine and nucleotide sequence identity to human hepatic P450 gene CYP2D6. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;40(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski B. E., Shanahan M. F., Ruoho A. E. Derivatization of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter using a novel forskolin photoaffinity label. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17683–17689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Bowen W. D., Walker F. O., Matsumoto R. R., De Costa B., Rice K. C. Sigma receptors: biology and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Dec;42(4):355–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. K. Cocaine-induced closures of single batrachotoxin-activated Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Dec;92(6):747–765. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Sonders M., Quarum M., McLean S., Pou S., Keana J. F. 1,3-Di(2-[5-3H]tolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Ashton R. A., Schuster D. I., Murphy R. B., Meyerson L. R. 2-Nitroimipramine: a photoaffinity probe for the serotonin uptake/tricyclic binding site complex. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):971–977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Jr, Culp S. G., De Souza E. B. Sigma-receptors in endocrine organs: identification, characterization, and autoradiographic localization in rat pituitary, adrenal, testis, and ovary. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1160–1172. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Jr, Kulsakdinun C., Battaglia G., Jaffe J. H., De Souza E. B. Initial identification and characterization of sigma receptors on human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1114–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Maghrabi E. A., Calligaro D. O., Eldefrawi M. E. High affinity binding of [3H] cocaine to rat liver microsomes. Life Sci. 1988;42(17):1675–1682. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]