Abstract
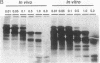
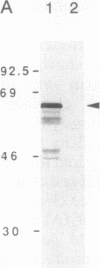
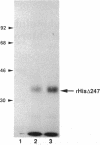
Cleavage stimulation factor is one of the multiple factors required for 3'-end cleavage of mammalian pre-mRNAs. We have shown previously that this factor is composed of three subunits with estimated molecular masses of 77, 64, and 50 kDa and that the 64-kDa subunit can be UV-crosslinked to RNA in a polyadenylylation signal (AAUAAA)-dependent manner. We have now isolated cDNAs encoding the 64-kDa subunit of human cleavage stimulation factor. The 64-kDa subunit contains a ribonucleoprotein-type RNA binding domain in the N-terminal region and a repeat structure in the C-terminal region in which a pentapeptide sequence (consensus MEARA/G) is repeated 12 times and the formation of a long alpha-helix stabilized by salt bridges is predicted. An approximately 270-amino acid segment surrounding this repeat structure is highly enriched in proline and glycine residues (approximately 20% for each). When cloned 64-kDa subunit was expressed in Escherichia coli, an N-terminal fragment containing the RNA binding domain bound to RNAs in a polyadenylylation-signal-independent manner, suggesting that the RNA binding domain is directly involved in the binding of the 64-kDa subunit to pre-mRNAs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell V. J., Zarkower D., Edmonds M., Wickens M. The enzyme that adds poly(A) to mRNAs is a classical poly(A) polymerase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):846–849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Bioassay for trans-activation using purified human immunodeficiency virus tat-encoded protein: trans-activation requires mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):821–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Molecular analyses of two poly(A) site-processing factors that determine the recognition and efficiency of cleavage of the pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2432–2438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning and structure of a yeast gene encoding a general transcription initiation factor TFIID that binds to the TATA box. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):299–303. doi: 10.1038/341299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T., Proudfoot N. J. A beginning to the biochemistry of polyadenylation. Trends Genet. 1988 Sep;4(9):243–245. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R. Hybrid selection of mRNA and hybrid arrest of translation. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:567–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. Rna synthesis in isolated nuclei processing of adenovirus serotype 2 late messenger rna precursors. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):581–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marqusee S., Baldwin R. L. Helix stabilization by Glu-...Lys+ salt bridges in short peptides of de novo design. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Chen J., Whoriskey J. Two proteins crosslinked to RNA containing the adenovirus L3 poly(A) site require the AAUAAA sequence for binding. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Analysis of RNA cleavage at the adenovirus-2 L3 polyadenylation site. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1929–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):392–392. doi: 10.1038/341392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Takagaki Y., Manley J. L. Multiple forms of poly(A) polymerases purified from HeLa cells function in specific mRNA 3'-end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4229–4238. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Stephenson P., Wickens M. P. Products of in vitro cleavage and polyadenylation of simian virus 40 late pre-mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1518–1529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A. How proteins enter the nucleus. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Drendel W., Greaser M. Stabilization of the long central helix of troponin C by intrahelical salt bridges between charged amino acid side chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7944–7947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Manley J. L., MacDonald C. C., Wilusz J., Shenk T. A multisubunit factor, CstF, is required for polyadenylation of mammalian pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2112–2120. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Four factors are required for 3'-end cleavage of pre-mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1711–1724. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terns M. P., Jacob S. T. Role of poly(A) polymerase in the cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1435–1444. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. A., Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site efficiency reflects the stability of complex formation involving the downstream element. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):215–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Characterization of a dimerization motif in AP-2 and its function in heterologous DNA-binding proteins. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1067–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.1998122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T., Takagaki Y., Manley J. L. A multicomponent complex is required for the AAUAAA-dependent cross-linking of a 64-kilodalton protein to polyadenylation substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1244–1248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]