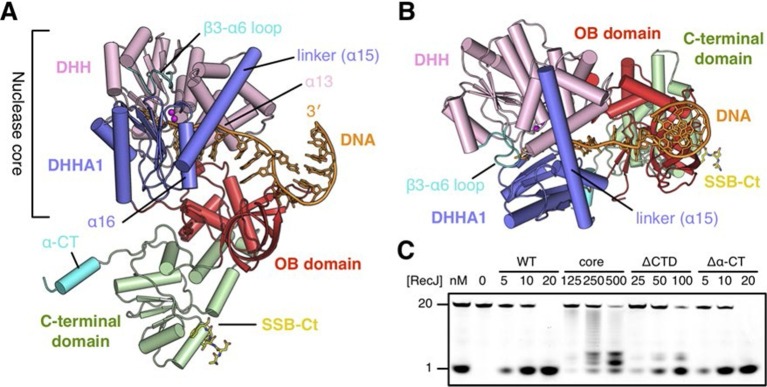
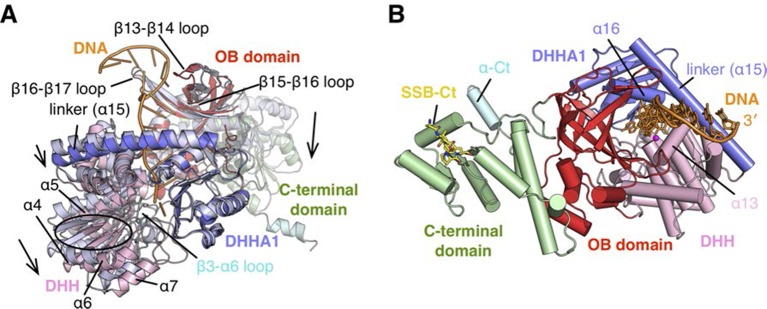
Figure 2. Structure of drRecJ complex.
(A) Overall structure of drRecJ complex viewed from the side. Protein domains of drRecJ are labeled and shown in distinct colors. The DNA and SSB-Ct are colored orange and yellow, respectively. Two Mn2+ in the active site are shown as magenta spheres. Two regions that are disordered in the ttRecJ structures (PDB code: 2ZXP) are highlighted in cyan. Three helices that form a helical gateway are also labeled. (B) Overall structure of the drRecJ complex viewed from the top of the DNA. The downstream nucleotides stack well to mimic the double-stranded DNA. (C) Denaturing PAGE gel showing the nuclease activities of different truncations of drRecJ. 3′-Fluorescence-labeled 20 nt ssDNA (100 nM) was incubated with various concentrations of different truncations of drRecJ proteins (see methods).