Abstract
Two-thirds of sporadic colon carcinomas express elevated levels of the c-MYC protooncogene. In addition, most colon carcinoma cell lines show constitutive elevated expression (10- to 40-fold over normal) of MYC RNA and protein that is not modulated in response to a mitogenic stimulus. Indirect immunofluorescence has been used to detect c-MYC protein in such cell lines, in hybrid cells resulting from fusions of such lines with cells that regulate MYC normally, and in carcinoma cells to which a normal copy of chromosome 5 has been transferred by microcell fusion. The deregulated expression of c-MYC is suppressed by fusion with a cell that regulates MYC normally. In addition, transfer of chromosome 5 by microcell fusion results in suppression of deregulated expression. Suppressed cells are no longer tumorigenic in nude mice. Loss of the transferred chromosome results in reexpression of the tumorigenic phenotype and in constitutive elevated expression of MYC. These data indicate that function of a tumor-suppressor gene on chromosome 5 is necessary for the regulated expression of MYC in at least some colon cells. Loss of this suppressor results in deregulated MYC expression and is a necessary, but most likely not sufficient, event for the expression of the tumorigenic phenotype in a subset of colon carcinomas.
Full text
PDF


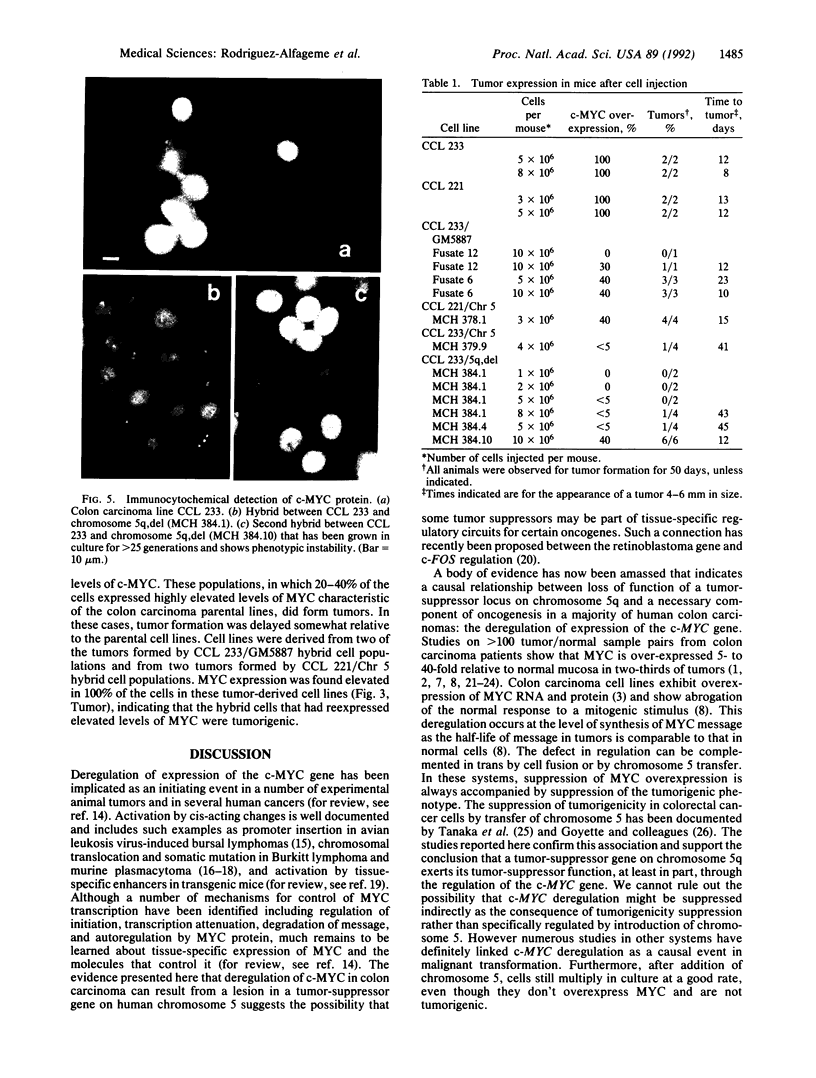

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Cory S. Transgenic models for haemopoietic malignancies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):9–31. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman E., Dalla-Favera R., Bentley D., Groudine M. Mutations in the first exon are associated with altered transcription of c-myc in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1272–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.3685977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Litwin S., Keidan R. D., Comis R. L., Astrin S. M. Noncorrelation of the expression of the c-myc oncogene in colorectal carcinoma with recurrence of disease or patient survival. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1350–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Rothberg P. G., Diehl R. E., Morse C. C., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Deregulation of c-myc gene expression in human colon carcinoma is not accompanied by amplification or rearrangement of the gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1969–1976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Scott J. K., Astrin S. M. Evidence that the familial adenomatous polyposis gene is involved in a subset of colon cancers with a complementable defect in c-myc regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4264–4268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erisman M. D., Scott J. K., Watt R. A., Astrin S. M. The c-myc protein is constitutively expressed at elevated levels in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Y. S., Davis L. M., Shows T. B. Mapping small DNA sequences by fluorescence in situ hybridization directly on banded metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6223–6227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley G. G., Schulz N. T., Hill S. A., Geiser J. R., Pipas J. M., Meisler A. I. Expression of the myc gene family in different stages of human colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 1989 Aug;4(8):963–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. J., Ghosh A. K., Moore M., Schofield P. F. A critical appraisal of the immunohistochemical detection of the c-myc oncogene product in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1987 Dec;56(6):779–783. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpfinger M., Zisser G., Ruhri C., Pütz B., Steindorfer P., Höfler H. Expression of c-myc and c-fos mRNA in colorectal carcinoma in man. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;59(3):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF02899401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., Leppert M., Dobbs M., Wasmuth J., Wolff E., Carlson M., Fujimoto E., Krapcho K., Sears T. Localization of the genetic defect in familial adenomatous polyposis within a small region of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):638–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce E. R. Some genetic aspects of familial multiple polyposis of the colon in a kindred of 1,422 members. Dis Colon Rectum. 1968 Sep-Oct;11(5):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF02616985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED T. E., NEEL J. V. A genetic study of multiple polyposis of the colon with an appendix deriving a method of estimating relative fitness. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):236–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. D., Horowitz J. M., Mulligan R. C. Negative regulation of human c-fos expression by the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):668–671. doi: 10.1038/346668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Spandorfer J. M., Erisman M. D., Staroscik R. N., Sears H. F., Petersen R. O., Astrin S. M. Evidence that c-myc expression defines two genetically distinct forms of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1985 Oct;52(4):629–632. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon P. J., Srivatsan E. S., Leipzig G. V., Sameshima J. H., Stanbridge E. J. Selective transfer of individual human chromosomes to recipient cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):140–146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon P. J., Srivatsan E. S., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of human chromosome 11 via microcell transfer controls tumorigenic expression of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3461–3466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K., Chan S., Evan G., Gabra H., Markham N., Stewart J., Watson J. c-myc oncogene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1987 Apr 1;59(7):1289–1295. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870401)59:7<1289::aid-cncr2820590710>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J., Evan G., Watson J., Sikora K. Detection of the c-myc oncogene product in colonic polyps and carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 1986 Jan;53(1):1–6. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio K., Kurata S., Sasaki M., Soejima J., Sasazuki T. Differential expression of c-myc gene and c-fos gene in premalignant and malignant tissues from patients with familial polyposis coli. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 1;48(17):4855–4861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Oshimura M., Kikuchi R., Seki M., Hayashi T., Miyaki M. Suppression of tumorigenicity in human colon carcinoma cells by introduction of normal chromosome 5 or 18. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):340–342. doi: 10.1038/349340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Battifora H., Le Fevre C., Cline M. J. Alterations of myc, myb, and rasHa proto-oncogenes in cancers are frequent and show clinical correlation. Science. 1986 Jan 17;231(4735):261–265. doi: 10.1126/science.3941898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








