Abstract
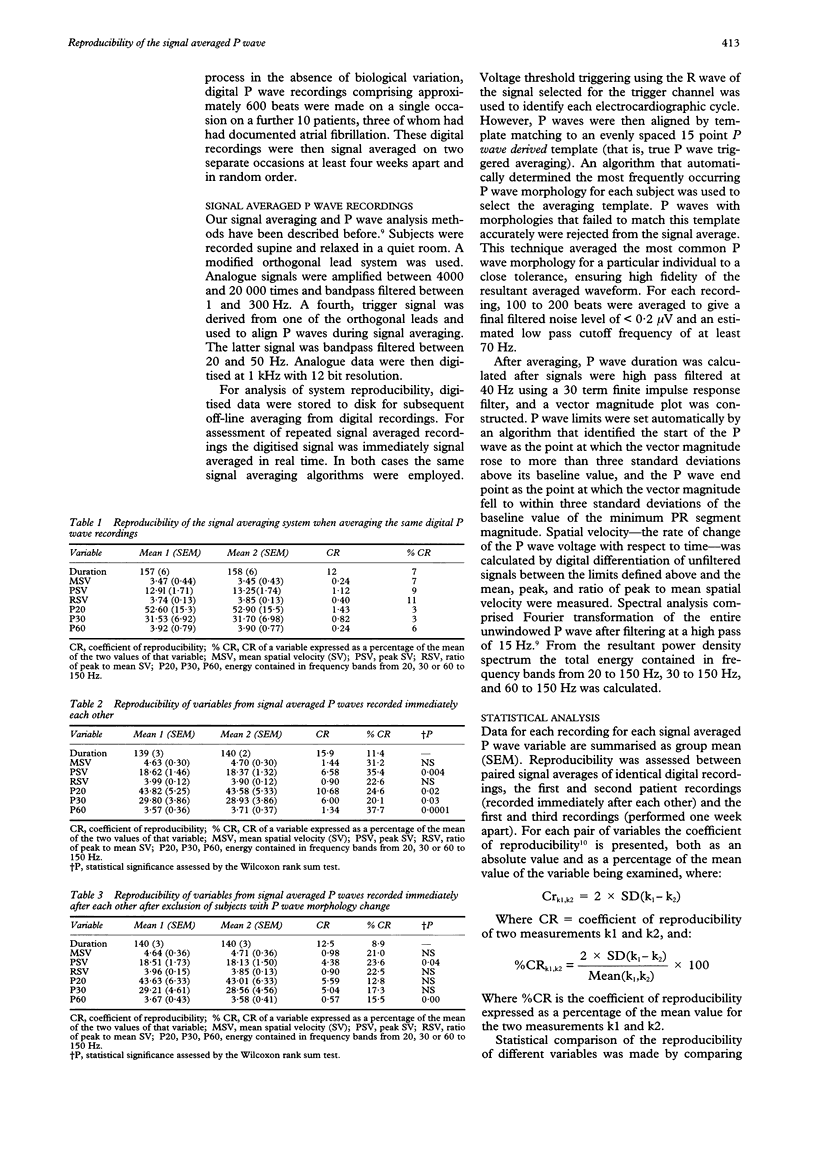
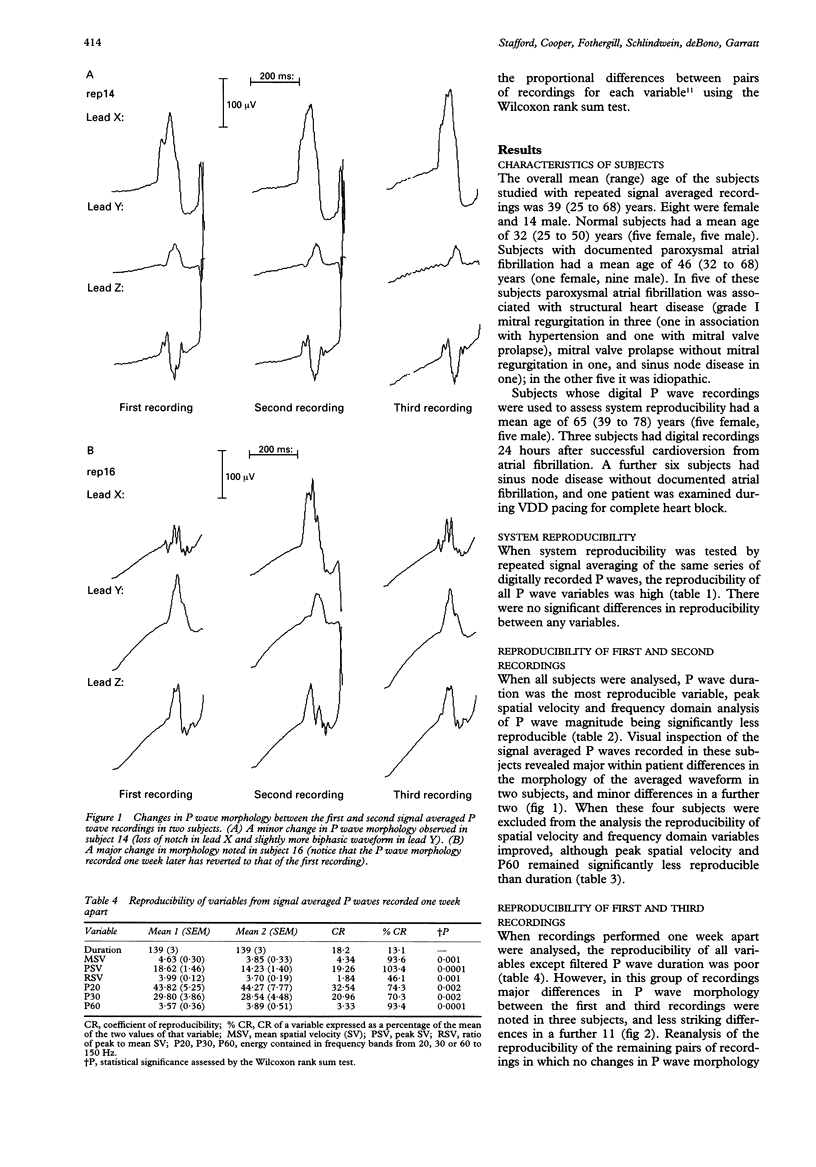
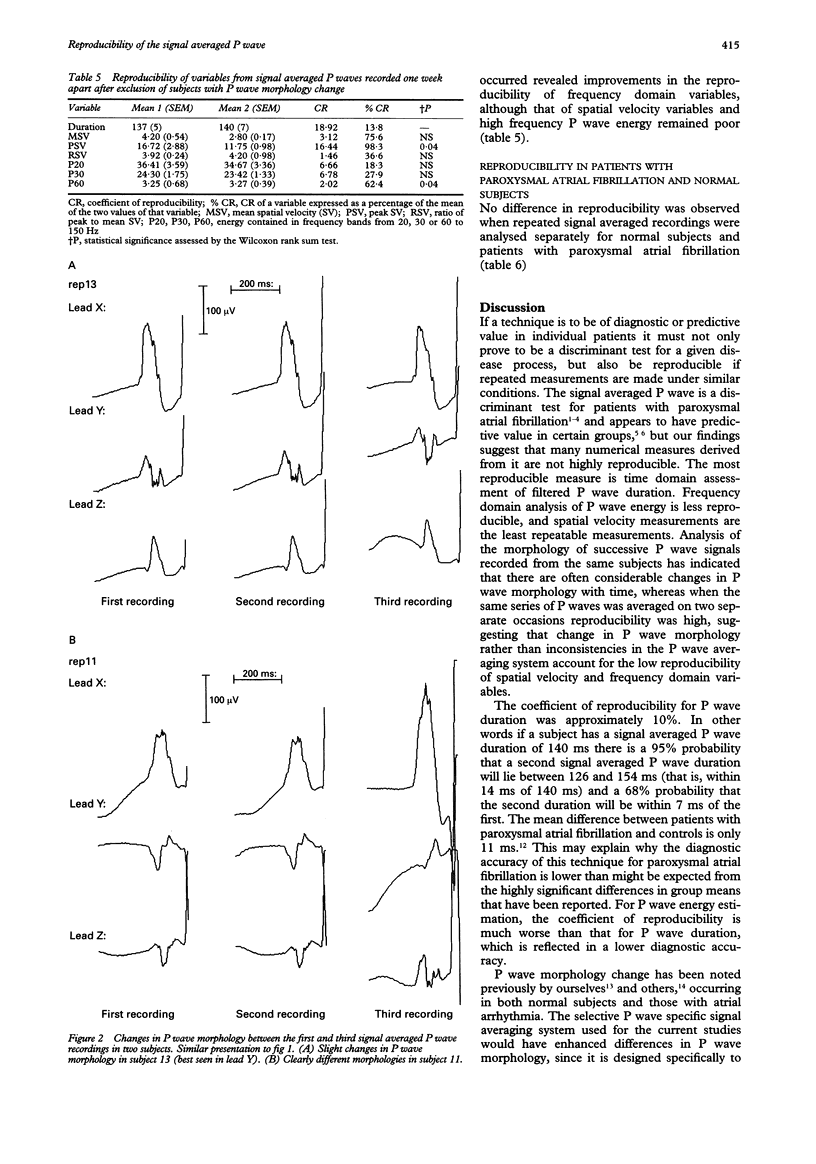
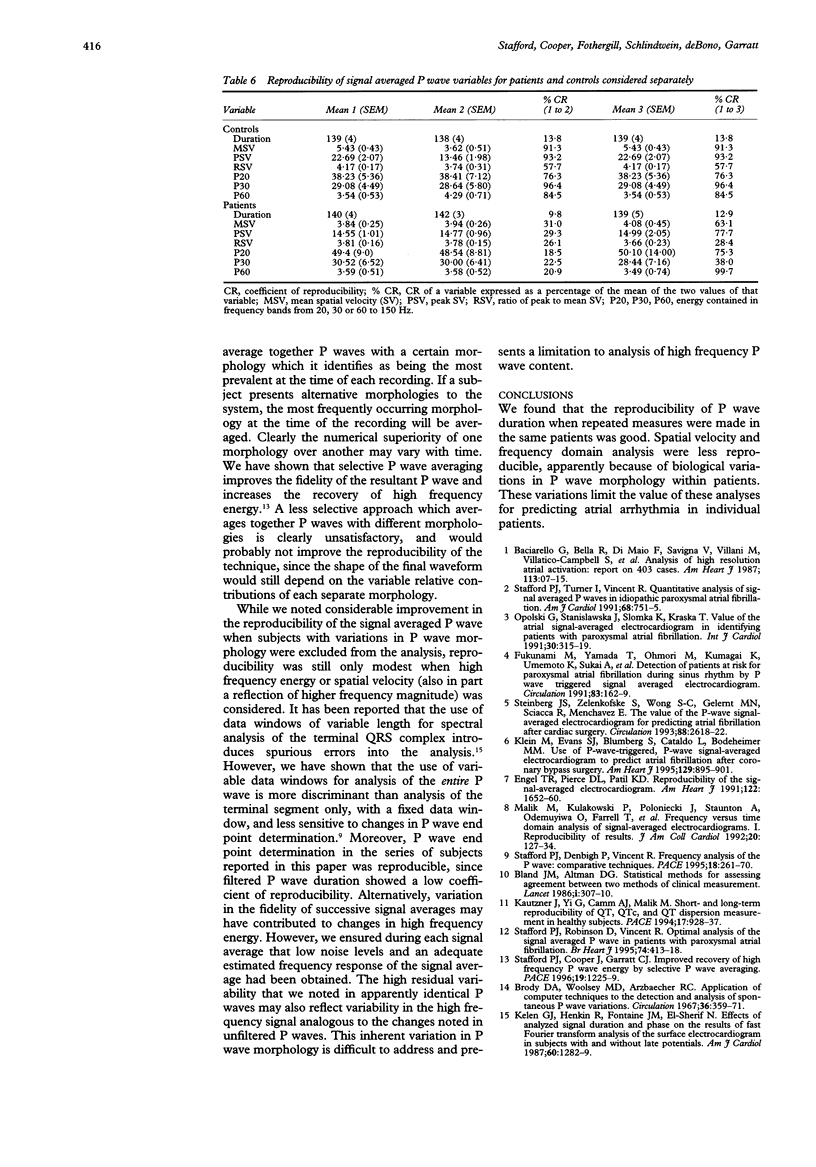
OBJECTIVE: To assess the reproducibility of time and frequency domain variables derived from the signal averaged P wave. DESIGN: Longitudinal within patient study. SETTING: Regional cardiothoracic centre. PATIENTS: 20 patients (10 with documented paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and 10 normal controls) were studied on three occasions to assess the reproducibility of repeated signal averaged P wave recordings. Digital P wave recordings were made on a further 10 patients on a single occasion and the recordings signal averaged twice in order to assess the reproducibility of the averaging system itself in the absence of biological variation. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: P wave duration, spatial velocity, and energies contained in frequency bands from 20, 30, and 60-150 Hz of the P wave spectrum were measured after P wave specific signal averaging. Coefficients of reproducibility were calculated for paired signal averaged P waves derived by signal averaging the same digital recordings on two separate occasions, for recordings performed in the same patients immediately after each other ("back to back") and those performed one week apart. RESULTS: System reproducibility when the same digital P wave recordings were signal averaged on two separate occasions was high (< 11% for all variables). For P wave duration the coefficient of reproducibility was 11.4% for back to back recordings and 13.1% for those one week apart. The reproducibility of spatial velocity and P wave energy was low. Variation in P wave morphology was noted when successive P waves from the same subject were examined. If recordings with the same P wave morphology were analysed the reproducibility of spatial velocity and P wave energy improved but remained significantly poorer than that for P wave duration. CONCLUSIONS: P wave duration is reproducible within subjects in the short and medium term. Frequency domain and spatial velocity analysis are poorly reproducible, due more to spontaneous variation in P wave morphology than to instability of the signal averaging process. This may limit the utility of signal averaged P wave variables other than duration for the prediction of atrial arrhythmia.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody D. A., Woolsey M. D., Arzbaecher R. C. Application of computer techniques to the detection and analysis of spontaneous P-wave variations. Circulation. 1967 Sep;36(3):359–371. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.36.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel T. R., Pierce D. L., Patil K. D. Reproducibility of the signal-averaged electrocardiogram. Am Heart J. 1991 Dec;122(6):1652–1660. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90283-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunami M., Yamada T., Ohmori M., Kumagai K., Umemoto K., Sakai A., Kondoh N., Minamino T., Hoki N. Detection of patients at risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm by P wave-triggered signal-averaged electrocardiogram. Circulation. 1991 Jan;83(1):162–169. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.1.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kautzner J., Yi G., Camm A. J., Malik M. Short- and long-term reproducibility of QT, QTc, and QT dispersion measurement in healthy subjects. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1994 May;17(5 Pt 1):928–937. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1994.tb01435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelen G. J., Henkin R., Fontaine J. M., el-Sherif N. Effects of analyzed signal duration and phase on the results of fast fourier transform analysis of the surface electrocardiogram in subjects with and without late potentials. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Dec 1;60(16):1282–1289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90609-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Evans S. J., Blumberg S., Cataldo L., Bodenheimer M. M. Use of P-wave-triggered, P-wave signal-averaged electrocardiogram to predict atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery. Am Heart J. 1995 May;129(5):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(95)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik M., Kulakowski P., Poloniecki J., Staunton A., Odemuyiwa O., Farrell T., Camm J. Frequency versus time domain analysis of signal-averaged electrocardiograms. I. Reproducibility of the results. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Jul;20(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90148-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opolski G., Stanisławska J., Słomka K., Kraska T. Value of the atrial signal-averaged electrocardiogram in identifying patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 1991 Mar;30(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(91)90009-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford P. J., Cooper J., Garratt C. J. Improved recovery of high frequency P wave energy by selective P wave averaging. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1996 Aug;19(8):1225–1229. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1996.tb04193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford P. J., Robinson D., Vincent R. Optimal analysis of the signal averaged P wave in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Br Heart J. 1995 Oct;74(4):413–418. doi: 10.1136/hrt.74.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford P., Denbigh P., Vincent R. Frequency analysis of the P wave: comparative techniques. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1995 Feb;18(2):261–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1995.tb02516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg J. S., Zelenkofske S., Wong S. C., Gelernt M., Sciacca R., Menchavez E. Value of the P-wave signal-averaged ECG for predicting atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. Circulation. 1993 Dec;88(6):2618–2622. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.6.2618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



