Abstract
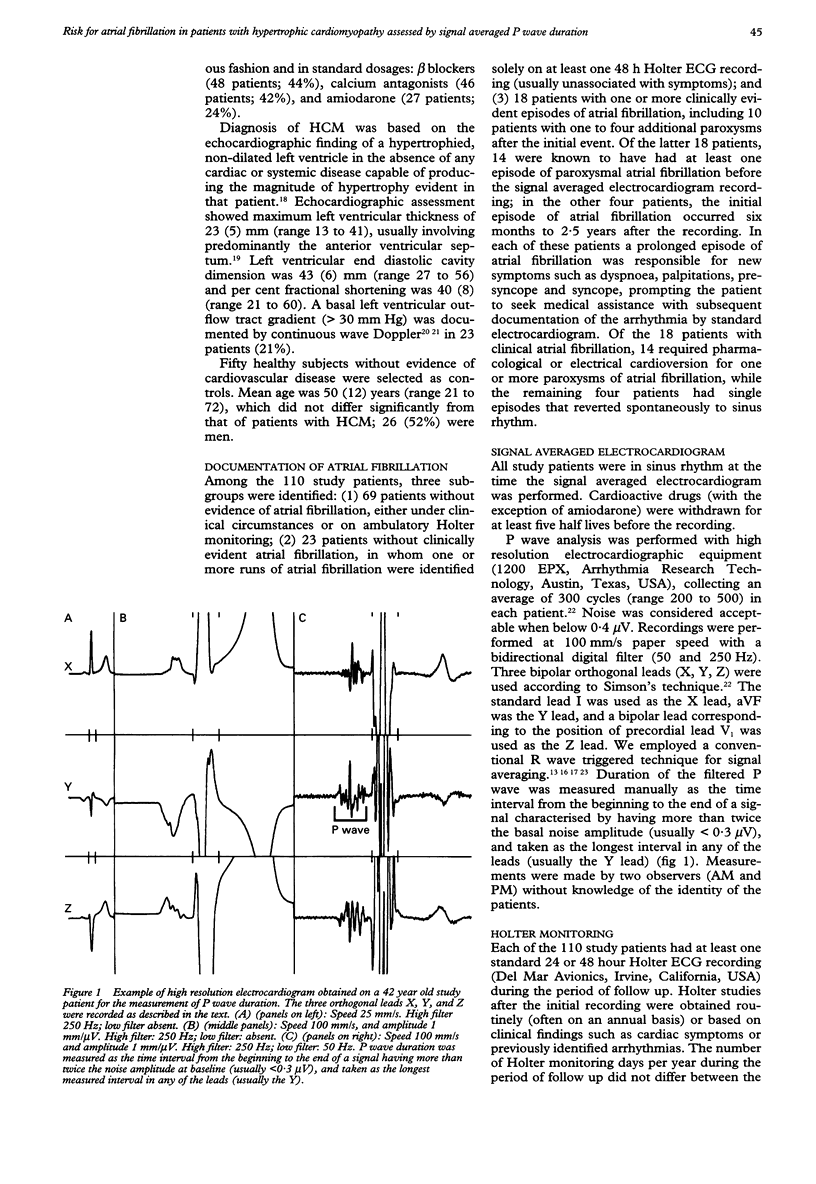
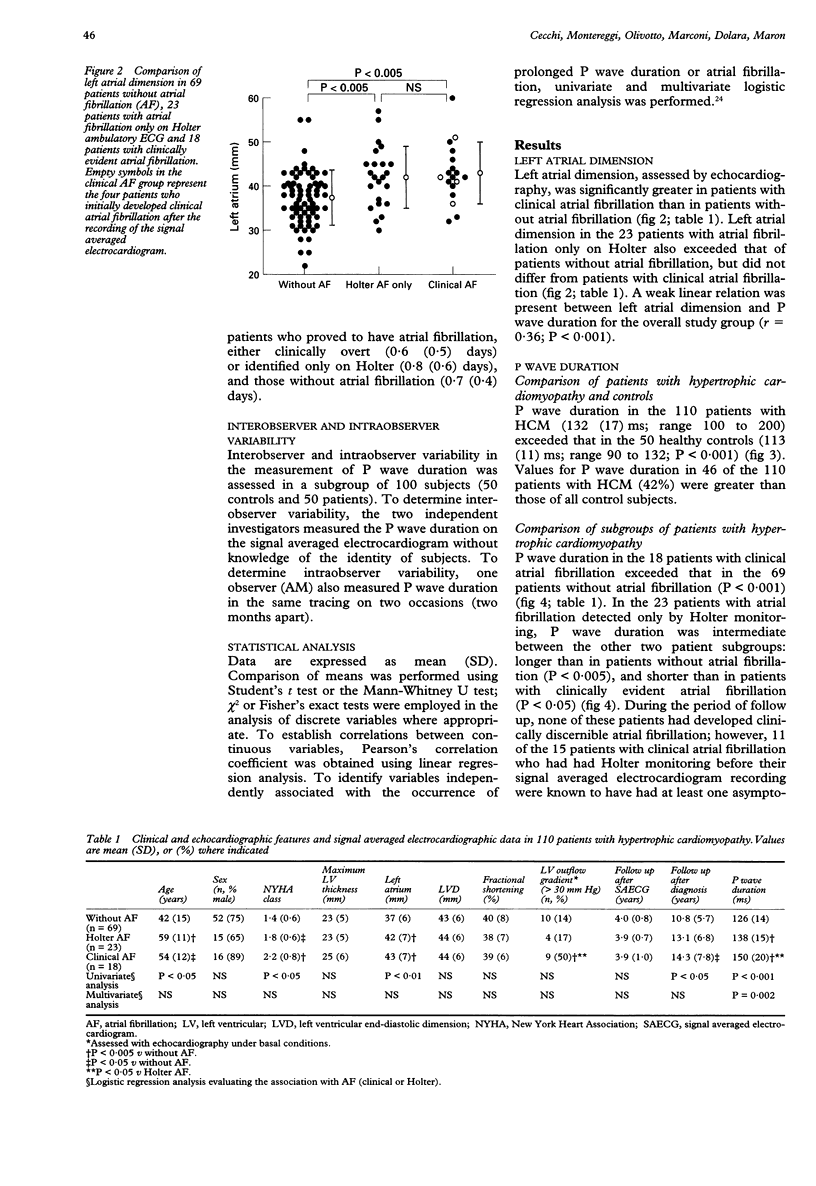
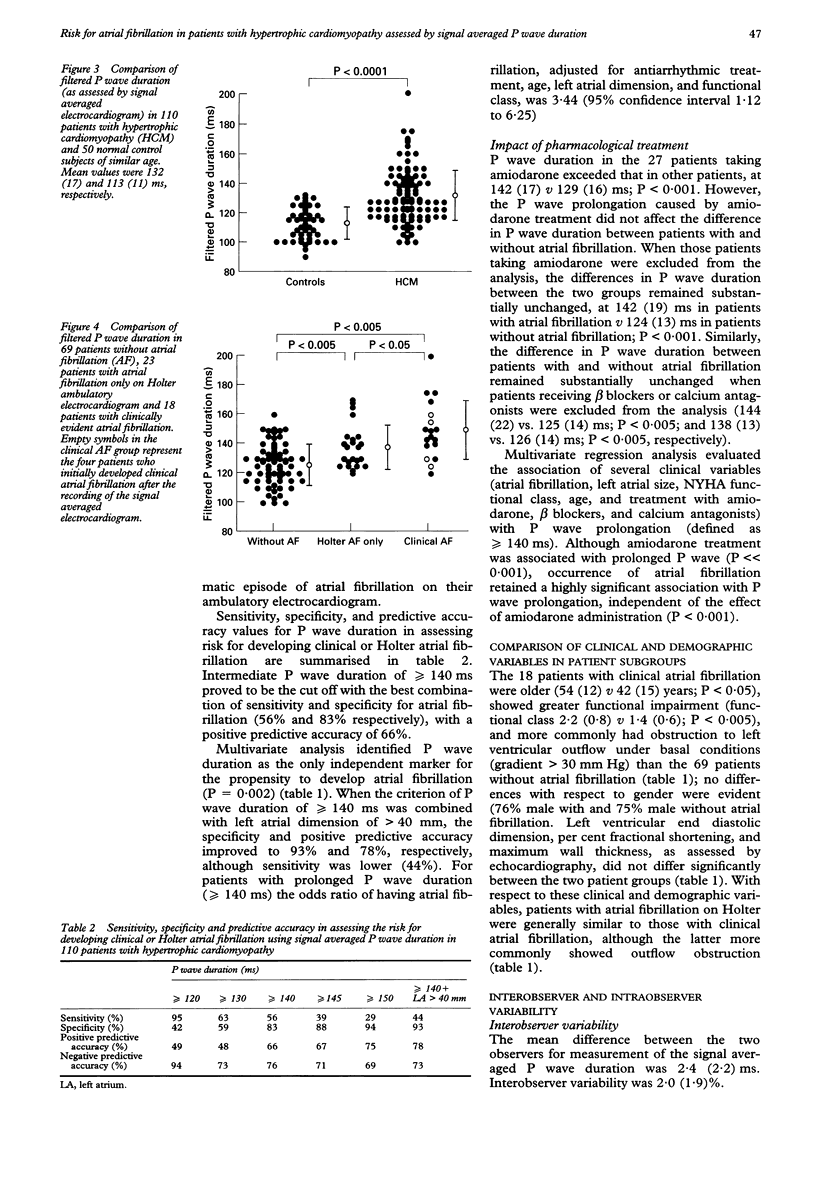
OBJECTIVE: To assess the relation between P wave duration and the occurrence of atrial fibrillation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). DESIGN: High resolution signal averaged electrocardiography was used in 110 patients with HCM to determine whether patients at risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation could be detected during sinus rhythm by measuring P wave duration. Filtered P wave duration was measured manually, over an average of 300 beats per patient. RESULTS: During follow up, 18 patients (16%) had at least one one clinical episode of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, including four patients whose initial episode followed the signal averaged electrocardiogram. The 18 patients with overt atrial fibrillation had greater P wave duration than the 69 patients who did not develop atrial fibrillation: 150 (SD 20) v 126 (14) ms; P < 0.001. Another 23 patients without clinically evident atrial fibrillation had prolonged bursts of the arrhythmia on Holter recording, and showed a P wave duration (138 (15) ms) intermediate between patients with and without clinical atrial fibrillation. In assessing risk for atrial fibrillation, P wave duration > or = 140 ms was associated with sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive accuracy values of 56%, 83%, and 66%. Multivariate analysis showed that duration of the P wave was the only independent variable associated with occurrence of atrial fibrillation; if P wave duration > or = 140 ms was combined with left atrial enlargement > 40 mm, the specificity and positive predictive accuracy for atrial fibrillation increased to 93% and 78%. CONCLUSIONS: Measurement of P wave duration in sinus rhythm by high resolution signal averaged electrocardiography may be a useful non-invasive clinical tool for identifying patients with HCM likely to develop electrical instability and atrial fibrillation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cecchi F., Olivotto I., Montereggi A., Santoro G., Dolara A., Maron B. J. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Tuscany: clinical course and outcome in an unselected regional population. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 15;26(6):1529–1536. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00353-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunami M., Yamada T., Ohmori M., Kumagai K., Umemoto K., Sakai A., Kondoh N., Minamino T., Hoki N. Detection of patients at risk for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm by P wave-triggered signal-averaged electrocardiogram. Circulation. 1991 Jan;83(1):162–169. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.1.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glancy D. L., O'Brien K. P., Gold H. K., Epstein S. E. Atrial fibrillation in patients with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. Br Heart J. 1970 Sep;32(5):652–659. doi: 10.1136/hrt.32.5.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidera S. A., Steinberg J. S. The signal-averaged P wave duration: a rapid and noninvasive marker of risk of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Jun;21(7):1645–1651. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90381-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry W. L., Morganroth J., Pearlman A. S., Clark C. E., Redwood D. R., Itscoitz S. B., Epstein S. E. Relation between echocardiographically determined left atrial size and atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1976 Feb;53(2):273–279. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.53.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madariaga I., Carmona J. R., Mateas F. R., Lezaun R., de los Arcos E. Supraventricular arrhythmia as the cause of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 1994 Jan;15(1):134–137. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maia I. G., Cruz Filho F. E., Fagundes M. L., Boghossian S. H., Vanheusden L., Sa R. M., Alves P. A. Signal-averaged P wave in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Nov 1;26(5):1310–1314. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Bonow R. O., Cannon R. O., 3rd, Leon M. B., Epstein S. E. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Interrelations of clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, and therapy (1). N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 26;316(13):780–789. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703263161305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Epstein S. E. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a discussion of nomenclature. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Jun;43(6):1242–1244. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron B. J., Gottdiener J. S., Epstein S. E. Patterns and significance of distribution of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A wide angle, two dimensional echocardiographic study of 125 patients. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Sep;48(3):418–428. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montereggi A., Marconi P., Olivotto I., Castelli G., Dolara A., Luisi M. L., Gheri R. G. Signal-averaged P-wave duration and risk of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in hyperthyroidism. Am J Cardiol. 1996 Feb 1;77(4):266–269. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)89391-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe T., Matsuhisa M., Kamakura S., Yamada J., Sato I., Nakajima K., Shimomura K. Relation between the widening of the fragmented atrial activity zone and atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Dec 1;52(10):1219–1222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson K., Frenneaux M. P., Stockins B., Karatasakis G., Poloniecki J. D., McKenna W. J. Atrial fibrillation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a longitudinal study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 May;15(6):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasson Z., Yock P. G., Hatle L. K., Alderman E. L., Popp R. L. Doppler echocardiographic determination of the pressure gradient in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Apr;11(4):752–756. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Donnerstein R. L. Alignment of P waves for signal averaging. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1990 Dec;13(12 Pt 1):1559–1562. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1990.tb06852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simson M. B. Use of signals in the terminal QRS complex to identify patients with ventricular tachycardia after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1981 Aug;64(2):235–242. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.64.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirito P., Lakatos E., Maron B. J. Degree of left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and chronic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1992 May 1;69(14):1217–1222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)90939-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford P. J., Turner I., Vincent R. Quantitative analysis of signal-averaged P waves in idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1991 Sep 15;68(8):751–755. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford W. J., Trohman R. G., Bilsker M., Zaman L., Castellanos A., Myerburg R. J. Cardiac arrest in an adolescent with atrial fibrillation and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986 Mar;7(3):701–704. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(86)80484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg J. S., Zelenkofske S., Wong S. C., Gelernt M., Sciacca R., Menchavez E. Value of the P-wave signal-averaged ECG for predicting atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. Circulation. 1993 Dec;88(6):2618–2622. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.6.2618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle E. D., Sasson Z., Henderson M. A., Ruddy T. D., Fulop J., Rakowski H., Williams W. G. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The importance of the site and the extent of hypertrophy. A review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;28(1):1–83. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(85)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



