Full text
PDF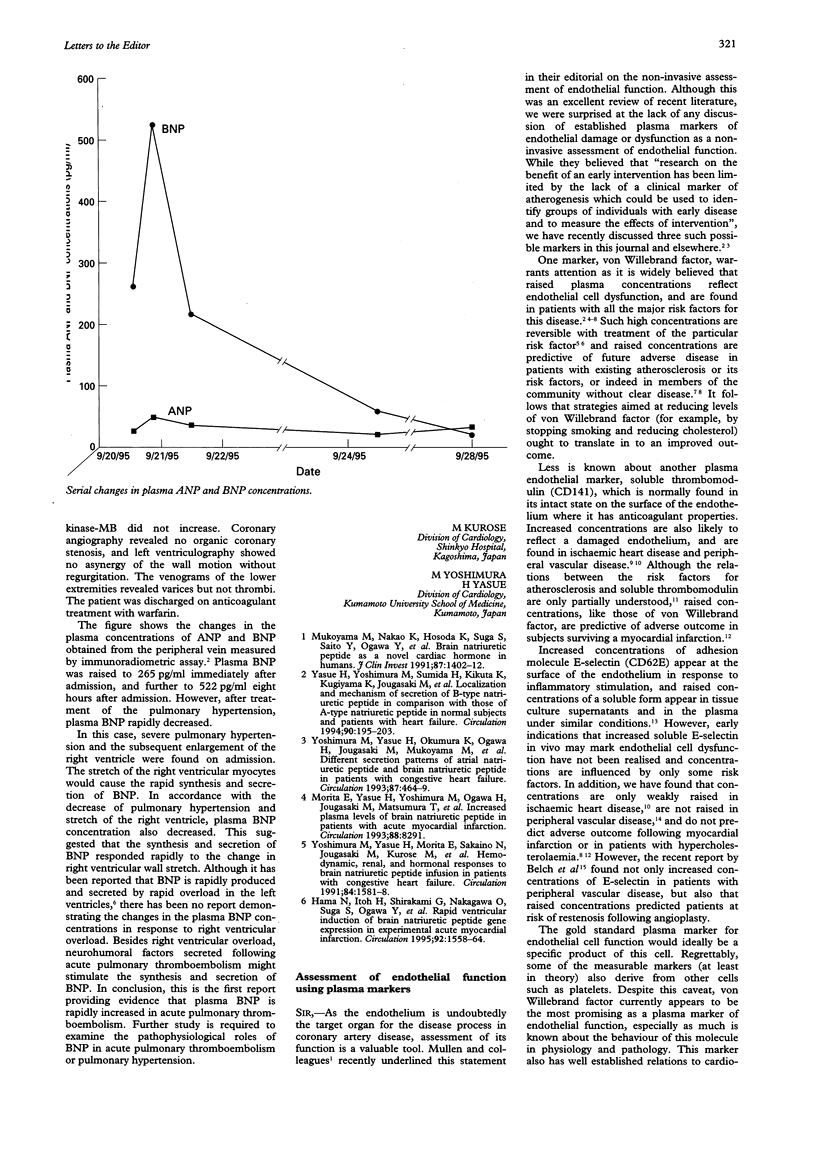

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badimon L., Badimon J. J., Chesebro J. H., Fuster V. von Willebrand factor and cardiovascular disease. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):111–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belch J. J., Shaw J. W., Kirk G., McLaren M., Robb R., Maple C., Morse P. The white blood cell adhesion molecule E-selectin predicts restenosis in patients with intermittent claudication undergoing percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Circulation. 1997 Apr 15;95(8):2027–2031. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.8.2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Amiral J., McCollum C. N. Circulating endothelial cell/leucocyte adhesion molecules in ischaemic heart disease. Br J Haematol. 1996 Nov;95(2):263–265. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.d01-1921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Miller J. P., McCollum C. N. von Willebrand factor and soluble E-selectin in the prediction of cardiovascular disease progression in hyperlipidaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1997 Jul 25;132(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(97)00081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blann A. D., Taberner D. A. A reliable marker of endothelial cell dysfunction: does it exist? Br J Haematol. 1995 Jun;90(2):244–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb05143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa M. C. Considering cellular thrombomodulin distribution and its modulating factors can facilitate the use of plasma thrombomodulin as a reliable endothelial marker? Haemostasis. 1996 Oct;26 (Suppl 4):233–243. doi: 10.1159/000217304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celermajer D. S., Sorensen K. E., Bull C., Robinson J., Deanfield J. E. Endothelium-dependent dilation in the systemic arteries of asymptomatic subjects relates to coronary risk factors and their interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Nov 15;24(6):1468–1474. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celermajer D. S., Sorensen K. E., Gooch V. M., Spiegelhalter D. J., Miller O. I., Sullivan I. D., Lloyd J. K., Deanfield J. E. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93147-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson P., Adams M. R., Powe A. J., Donald A. E., McCredie R., Robinson J., McCarthy S. N., Keech A., Celermajer D. S., Deanfield J. E. Oral L-arginine improves endothelium-dependent dilation in hypercholesterolemic young adults. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 15;97(8):1989–1994. doi: 10.1172/JCI118632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Newman W. Circulating adhesion molecules in disease. Immunol Today. 1993 Oct;14(10):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90267-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Pickering C., Knight G., Boulton A. J., Ball J., Ward J. D., Preston F. E. Changes in the factor VIII complex in diabetic ketoacidosis: evidence of endothelial cell damage? Diabetologia. 1987 Mar;30(3):160–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00274221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lip G. Y., Blann A. D. von Willebrand factor and its relevance to cardiovascular disorders. Br Heart J. 1995 Dec;74(6):580–583. doi: 10.1136/hrt.74.6.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen M. J., Thorne S. A., Deanfield J. E., Jones C. J. Non-invasive assessment of endothelial function. Heart. 1997 Apr;77(4):297–298. doi: 10.1136/hrt.77.4.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M. Inhibition of platelet-vessel wall interaction. Platelet receptors, monoclonal antibodies, and synthetic peptides. Circulation. 1990 Jan;81(1 Suppl):I35–I41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneur M., Dufourcq P., Gin H., Delafaye C., Amiral J., Pruvost A., Boisseau M. R. Plasma thrombomodulin levels increase with the severity of the diabetic retinopathy. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994 Oct;5(5):845–846. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199410000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen K. E., Celermajer D. S., Georgakopoulos D., Hatcher G., Betteridge D. J., Deanfield J. E. Impairment of endothelium-dependent dilation is an early event in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and is related to the lipoprotein(a) level. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):50–55. doi: 10.1172/JCI116983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. G., Kienast J., Pyke S. D., Haverkate F., van de Loo J. C. Hemostatic factors and the risk of myocardial infarction or sudden death in patients with angina pectoris. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilities Angina Pectoris Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 9;332(10):635–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503093321003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg M., Boers G. H., Franken D. G., Blom H. J., Van Kamp G. J., Jakobs C., Rauwerda J. A., Kluft C., Stehouwert C. D. Hyperhomocysteinaemia and endothelial dysfunction in young patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;25(3):176–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1995.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



